Leonard Wee
Lung-Originated Tumor Segmentation from Computed Tomography Scan (LOTUS) Benchmark
Jan 03, 2022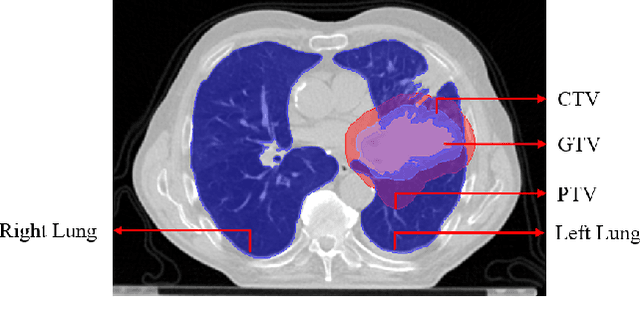
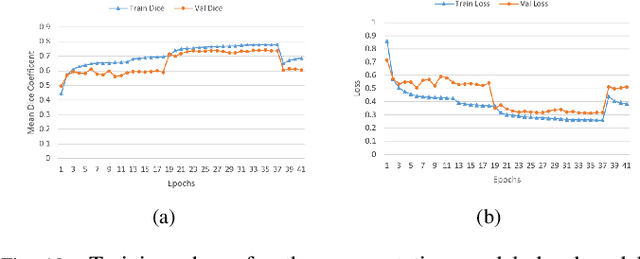
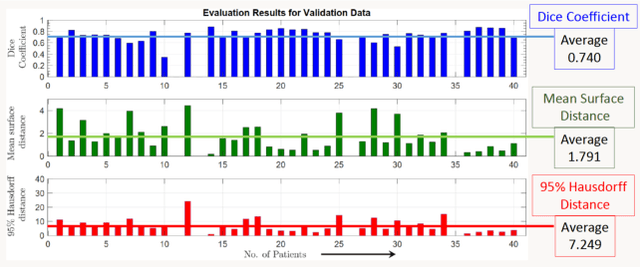
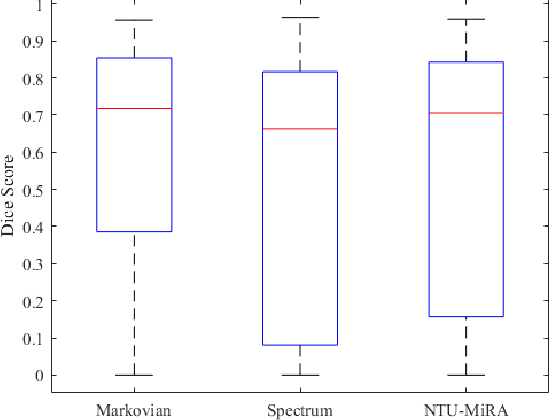
Abstract:Lung cancer is one of the deadliest cancers, and in part its effective diagnosis and treatment depend on the accurate delineation of the tumor. Human-centered segmentation, which is currently the most common approach, is subject to inter-observer variability, and is also time-consuming, considering the fact that only experts are capable of providing annotations. Automatic and semi-automatic tumor segmentation methods have recently shown promising results. However, as different researchers have validated their algorithms using various datasets and performance metrics, reliably evaluating these methods is still an open challenge. The goal of the Lung-Originated Tumor Segmentation from Computed Tomography Scan (LOTUS) Benchmark created through 2018 IEEE Video and Image Processing (VIP) Cup competition, is to provide a unique dataset and pre-defined metrics, so that different researchers can develop and evaluate their methods in a unified fashion. The 2018 VIP Cup started with a global engagement from 42 countries to access the competition data. At the registration stage, there were 129 members clustered into 28 teams from 10 countries, out of which 9 teams made it to the final stage and 6 teams successfully completed all the required tasks. In a nutshell, all the algorithms proposed during the competition, are based on deep learning models combined with a false positive reduction technique. Methods developed by the three finalists show promising results in tumor segmentation, however, more effort should be put into reducing the false positive rate. This competition manuscript presents an overview of the VIP-Cup challenge, along with the proposed algorithms and results.
Generative Models Improve Radiomics Performance in Different Tasks and Different Datasets: An Experimental Study
Sep 06, 2021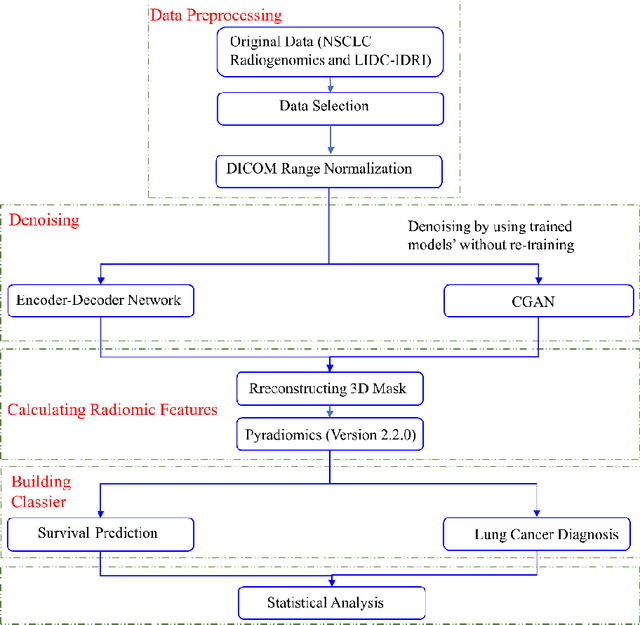
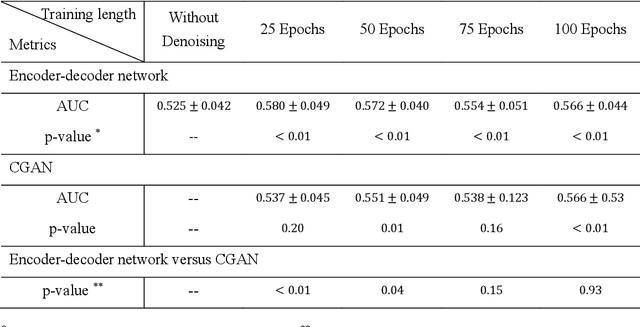
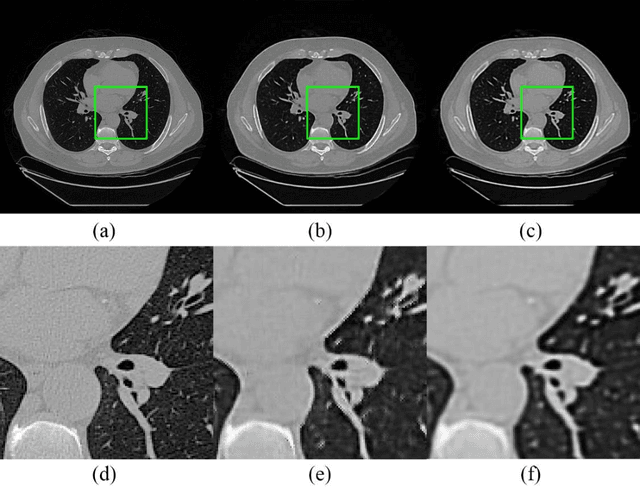
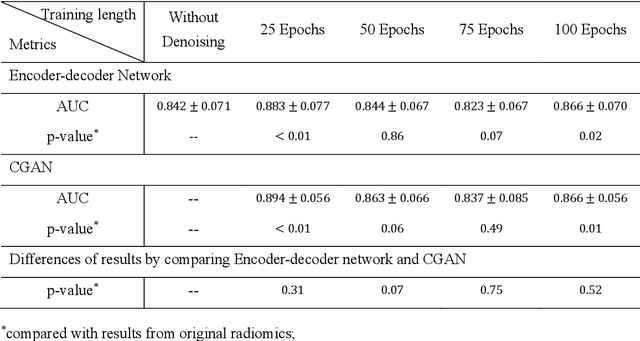
Abstract:Radiomics is an active area of research focusing on high throughput feature extraction from medical images with a wide array of applications in clinical practice, such as clinical decision support in oncology. However, noise in low dose computed tomography (CT) scans can impair the accurate extraction of radiomic features. In this article, we investigate the possibility of using deep learning generative models to improve the performance of radiomics from low dose CTs. We used two datasets of low dose CT scans -NSCLC Radiogenomics and LIDC-IDRI - as test datasets for two tasks - pre-treatment survival prediction and lung cancer diagnosis. We used encoder-decoder networks and conditional generative adversarial networks (CGANs) trained in a previous study as generative models to transform low dose CT images into full dose CT images. Radiomic features extracted from the original and improved CT scans were used to build two classifiers - a support vector machine (SVM) and a deep attention based multiple instance learning model - for survival prediction and lung cancer diagnosis respectively. Finally, we compared the performance of the models derived from the original and improved CT scans. Encoder-decoder networks and CGANs improved the area under the curve (AUC) of survival prediction from 0.52 to 0.57 (p-value<0.01). On the other hand, Encoder-decoder network and CGAN can improve the AUC of lung cancer diagnosis from 0.84 to 0.88 and 0.89 respectively (p-value<0.01). Moreover, there are no statistically significant differences in improving AUC by using encoder-decoder network and CGAN (p-value=0.34) when networks trained at 75 and 100 epochs. Generative models can improve the performance of low dose CT-based radiomics in different tasks. Hence, denoising using generative models seems to be a necessary pre-processing step for calculating radiomic features from low dose CTs.
Generative Models Improve Radiomics Reproducibility in Low Dose CTs: A Simulation Study
Apr 30, 2021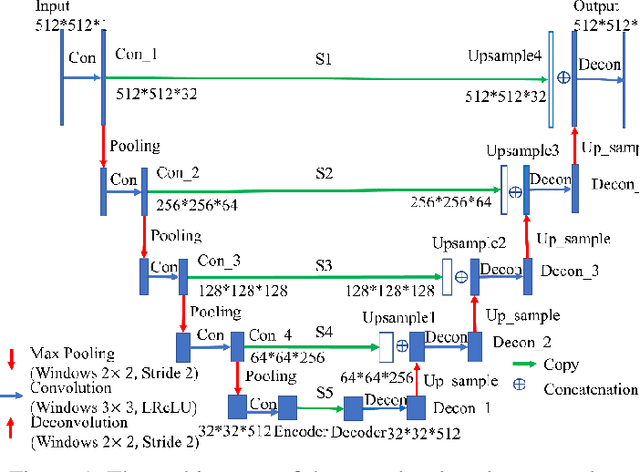
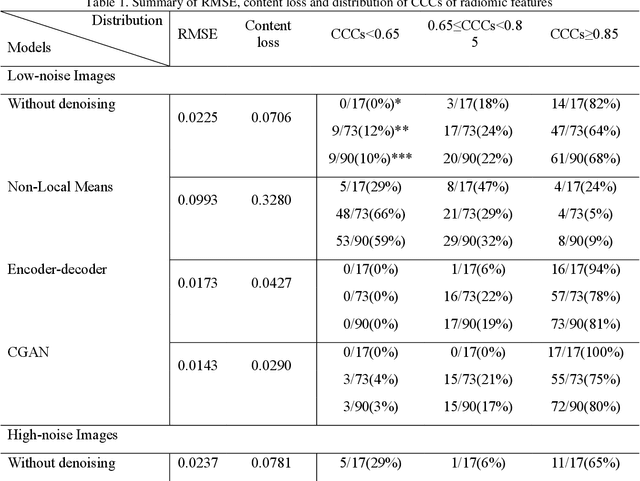
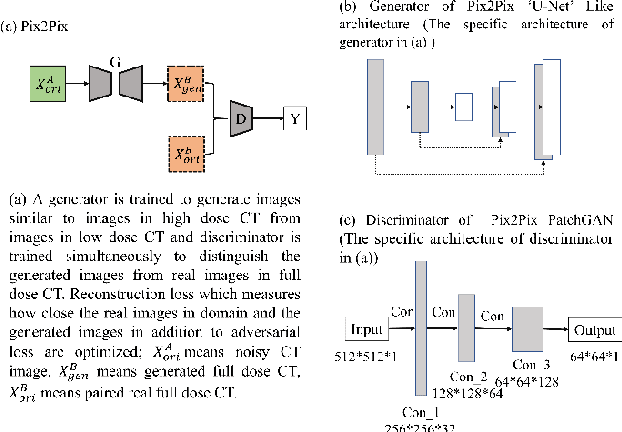
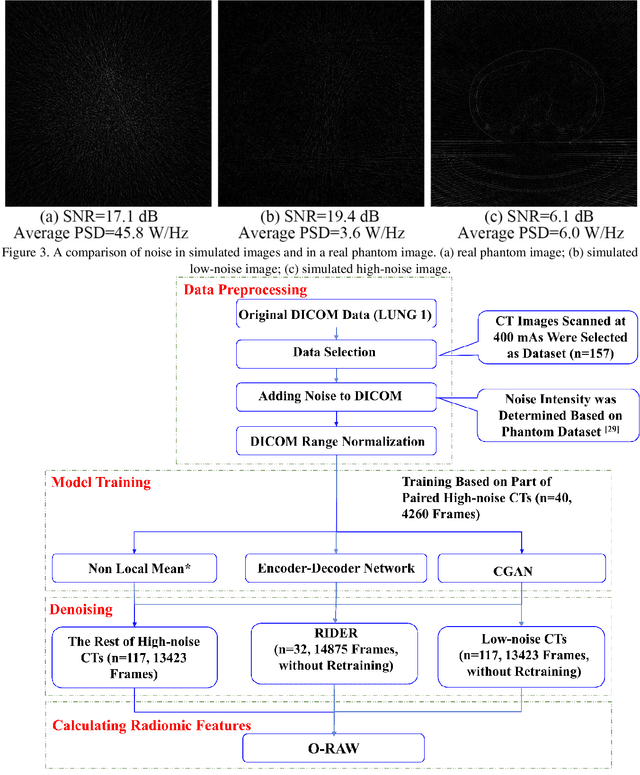
Abstract:Radiomics is an active area of research in medical image analysis, the low reproducibility of radiomics has limited its applicability to clinical practice. This issue is especially prominent when radiomic features are calculated from noisy images, such as low dose computed tomography (CT) scans. In this article, we investigate the possibility of improving the reproducibility of radiomic features calculated on noisy CTs by using generative models for denoising.One traditional denoising method - non-local means - and two generative models - encoder-decoder networks (EDN) and conditional generative adversarial networks (CGANs) - were selected as the test models. We added noise to the sinograms of full dose CTs to mimic low dose CTs with two different levels of noise: low-noise CT and high-noise CT. Models were trained on high-noise CTs and used to denoise low-noise CTs without re-training. We also test the performance of our model in real data, using dataset of same-day repeat low dose CTs to assess the reproducibility of radiomic features in denoised images. The EDN and the CGAN improved the concordance correlation coefficients (CCC) of radiomic features for low-noise images from 0.87 to 0.92 and for high-noise images from 0.68 to 0.92 respectively. Moreover, the EDN and the CGAN improved the test-retest reliability of radiomic features (mean CCC increased from 0.89 to 0.94) based on real low dose CTs. The results show that denoising using EDN and CGANs can improve the reproducibility of radiomic features calculated on noisy CTs. Moreover, images with different noise levels can be denoised to improve the reproducibility using these models without re-training, as long as the noise intensity is equal or lower than that in high-noise CTs. To the authors' knowledge, this is the first effort to improve the reproducibility of radiomic features calculated on low dose CT scans.
Lung Cancer Diagnosis Using Deep Attention Based on Multiple Instance Learning and Radiomics
Apr 29, 2021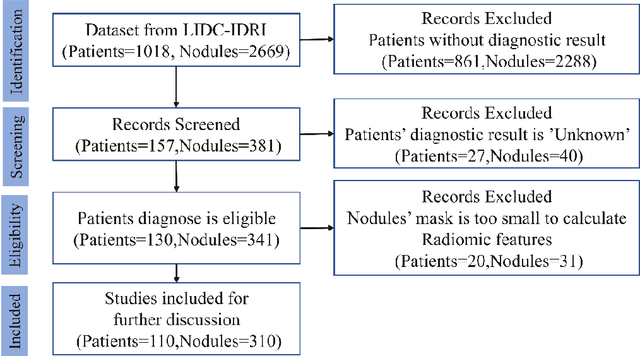
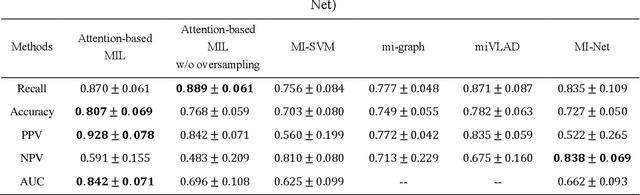
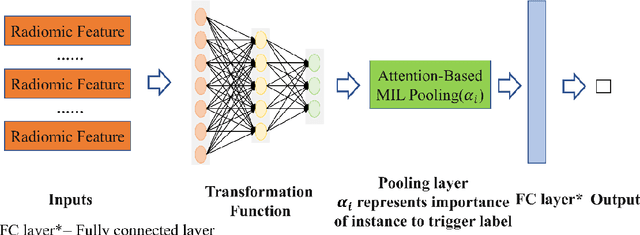
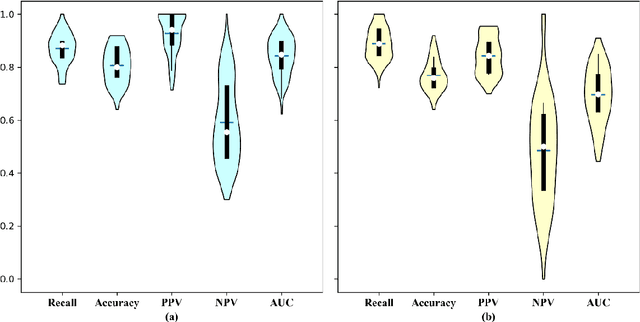
Abstract:Early diagnosis of lung cancer is a key intervention for the treatment of lung cancer computer aided diagnosis (CAD) can play a crucial role. However, most published CAD methods treat lung cancer diagnosis as a lung nodule classification problem, which does not reflect clinical practice, where clinicians diagnose a patient based on a set of images of nodules, instead of one specific nodule. Besides, the low interpretability of the output provided by these methods presents an important barrier for their adoption. In this article, we treat lung cancer diagnosis as a multiple instance learning (MIL) problem in order to better reflect the diagnosis process in the clinical setting and for the higher interpretability of the output. We chose radiomics as the source of input features and deep attention-based MIL as the classification algorithm.The attention mechanism provides higher interpretability by estimating the importance of each instance in the set for the final diagnosis.In order to improve the model's performance in a small imbalanced dataset, we introduce a new bag simulation method for MIL.The results show that our method can achieve a mean accuracy of 0.807 with a standard error of the mean (SEM) of 0.069, a recall of 0.870 (SEM 0.061), a positive predictive value of 0.928 (SEM 0.078), a negative predictive value of 0.591 (SEM 0.155) and an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.842 (SEM 0.074), outperforming other MIL methods.Additional experiments show that the proposed oversampling strategy significantly improves the model's performance. In addition, our experiments show that our method provides an indication of the importance of each nodule in determining the diagnosis, which combined with the well-defined radiomic features, make the results more interpretable and acceptable for doctors and patients.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge