Shuqiang Wang
BrainCSD: A Hierarchical Consistency-Driven MoE Foundation Model for Unified Connectome Synthesis and Multitask Brain Trait Prediction
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:Functional and structural connectivity (FC/SC) are key multimodal biomarkers for brain analysis, yet their clinical utility is hindered by costly acquisition, complex preprocessing, and frequent missing modalities. Existing foundation models either process single modalities or lack explicit mechanisms for cross-modal and cross-scale consistency. We propose BrainCSD, a hierarchical mixture-of-experts (MoE) foundation model that jointly synthesizes FC/SC biomarkers and supports downstream decoding tasks (diagnosis and prediction). BrainCSD features three neuroanatomically grounded components: (1) a ROI-specific MoE that aligns regional activations from canonical networks (e.g., DMN, FPN) with a global atlas via contrastive consistency; (2) a Encoding-Activation MOE that models dynamic cross-time/gradient dependencies in fMRI/dMRI; and (3) a network-aware refinement MoE that enforces structural priors and symmetry at individual and population levels. Evaluated on the datasets under complete and missing-modality settings, BrainCSD achieves SOTA results: 95.6\% accuracy for MCI vs. CN classification without FC, low synthesis error (FC RMSE: 0.038; SC RMSE: 0.006), brain age prediction (MAE: 4.04 years), and MMSE score estimation (MAE: 1.72 points). Code is available in \href{https://github.com/SXR3015/BrainCSD}{BrainCSD}
Pattern-Aware Diffusion Synthesis of fMRI/dMRI with Tissue and Microstructural Refinement
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), especially functional MRI (fMRI) and diffusion MRI (dMRI), is essential for studying neurodegenerative diseases. However, missing modalities pose a major barrier to their clinical use. Although GAN- and diffusion model-based approaches have shown some promise in modality completion, they remain limited in fMRI-dMRI synthesis due to (1) significant BOLD vs. diffusion-weighted signal differences between fMRI and dMRI in time/gradient axis, and (2) inadequate integration of disease-related neuroanatomical patterns during generation. To address these challenges, we propose PDS, introducing two key innovations: (1) a pattern-aware dual-modal 3D diffusion framework for cross-modality learning, and (2) a tissue refinement network integrated with a efficient microstructure refinement to maintain structural fidelity and fine details. Evaluated on OASIS-3, ADNI, and in-house datasets, our method achieves state-of-the-art results, with PSNR/SSIM scores of 29.83 dB/90.84\% for fMRI synthesis (+1.54 dB/+4.12\% over baselines) and 30.00 dB/77.55\% for dMRI synthesis (+1.02 dB/+2.2\%). In clinical validation, the synthesized data show strong diagnostic performance, achieving 67.92\%/66.02\%/64.15\% accuracy (NC vs. MCI vs. AD) in hybrid real-synthetic experiments. Code is available in \href{https://github.com/SXR3015/PDS}{PDS GitHub Repository}
UAV-Enabled Fluid Antenna Systems for Multi-Target Wireless Sensing over LAWCNs
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Fluid antenna system (FAS) is emerging as a key technology for enhancing spatial flexibility and sensing accuracy in future wireless systems. This paper investigates an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-enabled FAS for multi-target wireless sensing in low-altitude wireless consumer networks (LAWCNs) for achieving the low-altitude economy (LAE) missions. We formulate an optimization problem aimed at minimizing the average Cram\'er-Rao bound (CRB) for multiple target estimations. To tackle this non-convex problem, an efficient alternating optimization (AO) algorithm is proposed, which jointly optimizes the UAV trajectory, the antenna position of the transmit fluid antennas (FAs) and the receive FAs, and the transmit beamforming at the UAV. Simulation results demonstrate significant performance improvements in estimation accuracy and sensing reliability compared to conventional schemes, e.g., the fixed position antenna scheme. The proposed system achieves enhanced sensing performance through adaptive trajectory design and beamforming, alongside effective interference suppression via the flexible FAS antenna repositioning, underscoring its practical potential for precision sensing in the UAV-enabled LAWCNs.
RSMA-Enhanced Data Collection in RIS-Assisted Intelligent Consumer Transportation Systems
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates the data collection enhancement problem in a reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-empowered intelligent consumer transportation system (ICTS). We propose a novel framework where a data center (DC) provides energy to pre-configured roadside unit (RSU) pairs during the downlink stage. While in the uplink stage, these RSU pairs utilize a hybrid rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) and time-division multiple access (TDMA) protocol to transmit the processed data to the DC, while simultaneously performing local data processing using the harvested energy. Our objective is to maximize the minimal processed data volume of the RSU pairs by jointly optimizing the RIS downlink and uplink phase shifts, the transmit power of the DC and RSUs, the RSU computation resource allocation, and the time slot allocation. To address the formulated non-convex problem, we develop an efficient iterative algorithm integrating alternating optimization and sequential rank-one constraint relaxation methods. Extensive simulations demonstrate that the proposed algorithm significantly outperforms baseline schemes under diverse scenarios, validating its effectiveness in enhancing the data processing performance for intelligent transportation applications.
Brain Network Analysis Based on Fine-tuned Self-supervised Model for Brain Disease Diagnosis
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Functional brain network analysis has become an indispensable tool for brain disease analysis. It is profoundly impacted by deep learning methods, which can characterize complex connections between ROIs. However, the research on foundation models of brain network is limited and constrained to a single dimension, which restricts their extensive application in neuroscience. In this study, we propose a fine-tuned brain network model for brain disease diagnosis. It expands brain region representations across multiple dimensions based on the original brain network model, thereby enhancing its generalizability. Our model consists of two key modules: (1)an adapter module that expands brain region features across different dimensions. (2)a fine-tuned foundation brain network model, based on self-supervised learning and pre-trained on fMRI data from thousands of participants. Specifically, its transformer block is able to effectively extract brain region features and compute the inter-region associations. Moreover, we derive a compact latent representation of the brain network for brain disease diagnosis. Our downstream experiments in this study demonstrate that the proposed model achieves superior performance in brain disease diagnosis, which potentially offers a promising approach in brain network analysis research.
Coordinated Beamforming for RIS-Empowered ISAC Systems over Secure Low-Altitude Networks
May 30, 2025Abstract:Emerging as a cornerstone for next-generation wireless networks, integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) systems demand innovative solutions to balance spectral efficiency and sensing accuracy. In this paper, we propose a coordinated beamforming framework for a reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-empowered ISAC system, where the active precoding at the dual-functional base station (DFBS) and the passive beamforming at the RIS are jointly optimized to provide communication services for legitimate unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) while sensing the unauthorized UAVs. The sum-rate of all legitimate UAVs are maximized, while satisfying the radar sensing signal-to-noise ratio requirements, the transmit power constraints, and the reflection coefficients of the RIS. To address the inherent non-convexity from coupled variables, we propose a low-complexity algorithm integrating fractional programming with alternating optimization, featuring convergence guarantees. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm achieves higher data rate compared to disjoint optimization benchmarks. This underscores RIS's pivotal role in harmonizing communication and target sensing functionalities for low-altitude networks.
Full-Duplex ISCC for Low-Altitude Networks: Resource Allocation and Coordinated Beamforming
Apr 25, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates an integrated sensing, communication, and computing system deployed over low-altitude networks for enabling applications within the low-altitude economy. In the considered system, a full-duplex enabled unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) is dispatched in the airspace, functioning as a UAV-enabled low-altitude platform (ULAP). The ULAP is capable of achieving simultaneous information transmission, target sensing, and mobile edge computing services. To reduce the overall energy consumption of the system while meeting the sensing beampattern threshold and user computation requirements, we formulate an energy consumption minimization problem by jointly optimizing the task allocation, computation resource allocation, transmit beamforming, and receive beamforming. Since the problem is non-convex and involves highly coupled variables, we propose an efficient algorithm based on alternation optimization, which decomposes the original problem into tractable convex subproblems. Moreover, we analyze the convergence and complexity of the proposed algorithm. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed scheme saves up to 54.12\% energy consumption performance compared to the benchmark schemes.
Flexible and Explainable Graph Analysis for EEG-based Alzheimer's Disease Classification
Apr 02, 2025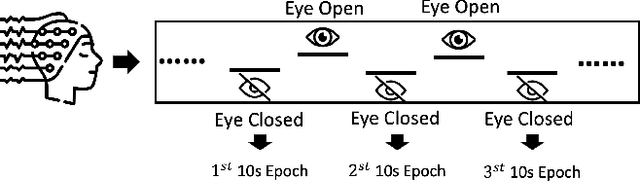
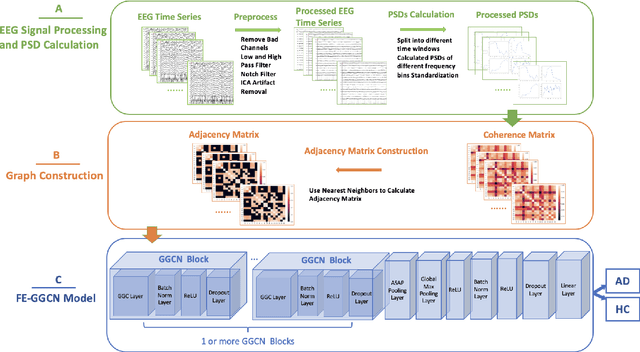
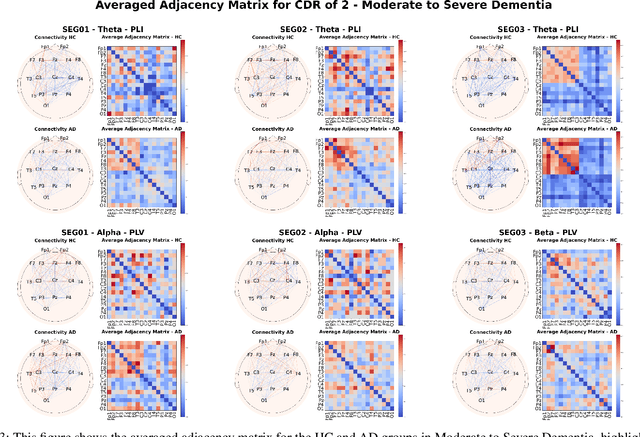
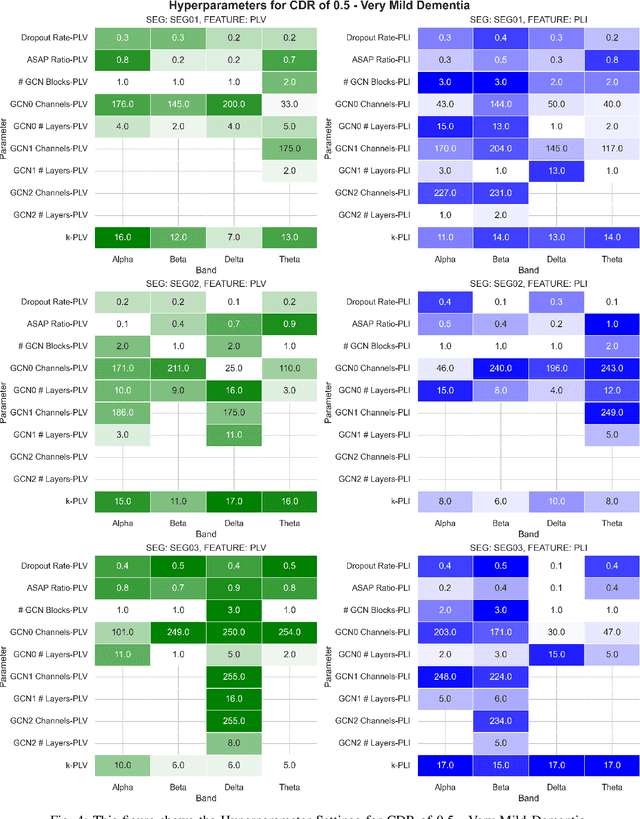
Abstract:Alzheimer's Disease is a progressive neurological disorder that is one of the most common forms of dementia. It leads to a decline in memory, reasoning ability, and behavior, especially in older people. The cause of Alzheimer's Disease is still under exploration and there is no all-inclusive theory that can explain the pathologies in each individual patient. Nevertheless, early intervention has been found to be effective in managing symptoms and slowing down the disease's progression. Recent research has utilized electroencephalography (EEG) data to identify biomarkers that distinguish Alzheimer's Disease patients from healthy individuals. Prior studies have used various machine learning methods, including deep learning and graph neural networks, to examine electroencephalography-based signals for identifying Alzheimer's Disease patients. In our research, we proposed a Flexible and Explainable Gated Graph Convolutional Network (GGCN) with Multi-Objective Tree-Structured Parzen Estimator (MOTPE) hyperparameter tuning. This provides a flexible solution that efficiently identifies the optimal number of GGCN blocks to achieve the optimized precision, specificity, and recall outcomes, as well as the optimized area under the Receiver Operating Characteristic (AUC). Our findings demonstrated a high efficacy with an over 0.9 Receiver Operating Characteristic score, alongside precision, specificity, and recall scores in distinguishing health control with Alzheimer's Disease patients in Moderate to Severe Dementia using the power spectrum density (PSD) of electroencephalography signals across various frequency bands. Moreover, our research enhanced the interpretability of the embedded adjacency matrices, revealing connectivity differences in frontal and parietal brain regions between Alzheimer's patients and healthy individuals.
Underwater Image Restoration Through a Prior Guided Hybrid Sense Approach and Extensive Benchmark Analysis
Jan 06, 2025



Abstract:Underwater imaging grapples with challenges from light-water interactions, leading to color distortions and reduced clarity. In response to these challenges, we propose a novel Color Balance Prior \textbf{Guided} \textbf{Hyb}rid \textbf{Sens}e \textbf{U}nderwater \textbf{I}mage \textbf{R}estoration framework (\textbf{GuidedHybSensUIR}). This framework operates on multiple scales, employing the proposed \textbf{Detail Restorer} module to restore low-level detailed features at finer scales and utilizing the proposed \textbf{Feature Contextualizer} module to capture long-range contextual relations of high-level general features at a broader scale. The hybridization of these different scales of sensing results effectively addresses color casts and restores blurry details. In order to effectively point out the evolutionary direction for the model, we propose a novel \textbf{Color Balance Prior} as a strong guide in the feature contextualization step and as a weak guide in the final decoding phase. We construct a comprehensive benchmark using paired training data from three real-world underwater datasets and evaluate on six test sets, including three paired and three unpaired, sourced from four real-world underwater datasets. Subsequently, we tested 14 traditional and retrained 23 deep learning existing underwater image restoration methods on this benchmark, obtaining metric results for each approach. This effort aims to furnish a valuable benchmarking dataset for standard basis for comparison. The extensive experiment results demonstrate that our method outperforms 37 other state-of-the-art methods overall on various benchmark datasets and metrics, despite not achieving the best results in certain individual cases. The code and dataset are available at \href{https://github.com/CXH-Research/GuidedHybSensUIR}{https://github.com/CXH-Research/GuidedHybSensUIR}.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Mobile Edge Computing via Large Language Model
Dec 30, 2024Abstract:The rapid evolution of mobile edge computing (MEC) has introduced significant challenges in optimizing resource allocation in highly dynamic wireless communication systems, in which task offloading decisions should be made in real-time. However, existing resource allocation strategies cannot well adapt to the dynamic and heterogeneous characteristics of MEC systems, since they are short of scalability, context-awareness, and interpretability. To address these issues, this paper proposes a novel retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) method to improve the performance of MEC systems. Specifically, a latency minimization problem is first proposed to jointly optimize the data offloading ratio, transmit power allocation, and computing resource allocation. Then, an LLM-enabled information-retrieval mechanism is proposed to solve the problem efficiently. Extensive experiments across multi-user, multi-task, and highly dynamic offloading scenarios show that the proposed method consistently reduces latency compared to several DL-based approaches, achieving 57% improvement under varying user computing ability, 86% with different servers, 30% under distinct transmit powers, and 42% for varying data volumes. These results show the effectiveness of LLM-driven solutions to solve the resource allocation problems in MEC systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge