Contingency planning
Papers and Code
RENEW: Risk- and Energy-Aware Navigation in Dynamic Waterways
Jan 23, 2026We present RENEW, a global path planner for Autonomous Surface Vehicle (ASV) in dynamic environments with external disturbances (e.g., water currents). RENEW introduces a unified risk- and energy-aware strategy that ensures safety by dynamically identifying non-navigable regions and enforcing adaptive safety constraints. Inspired by maritime contingency planning, it employs a best-effort strategy to maintain control under adverse conditions. The hierarchical architecture combines high-level constrained triangulation for topological diversity with low-level trajectory optimization within safe corridors. Validated with real-world ocean data, RENEW is the first framework to jointly address adaptive non-navigability and topological path diversity for robust maritime navigation.
Contingency Model-based Control (CMC) for Communicationless Cooperative Collision Avoidance in Robot Swarms
Dec 23, 2025Cooperative collision avoidance between robots in swarm operations remains an open challenge. Assuming a decentralized architecture, each robot is responsible for making its own control decisions, including motion planning. To this end, most existing approaches mostly rely some form of (wireless) communication between the agents of the swarm. In reality, however, communication is brittle. It may be affected by latency, further delays and packet losses, transmission faults, and is subject to adversarial attacks, such as jamming or spoofing. This paper proposes Contingency Model-based Control (CMC) as a communicationless alternative. It follows the implicit cooperation paradigm, under which the design of the robots is based on consensual (offline) rules, similar to traffic rules. They include the definition of a contingency trajectory for each robot, and a method for construction of mutual collision avoidance constraints. The setup is shown to guarantee the recursive feasibility and collision avoidance between all swarm members in closed-loop operation. Moreover, CMC naturally satisfies the Plug \& Play paradigm, i.e., for new robots entering the swarm. Two numerical examples demonstrate that the collision avoidance guarantee is intact and that the robot swarm operates smoothly under the CMC regime.
Safe and Non-Conservative Contingency Planning for Autonomous Vehicles via Online Learning-Based Reachable Set Barriers
Sep 09, 2025Autonomous vehicles must navigate dynamically uncertain environments while balancing the safety and driving efficiency. This challenge is exacerbated by the unpredictable nature of surrounding human-driven vehicles (HVs) and perception inaccuracies, which require planners to adapt to evolving uncertainties while maintaining safe trajectories. Overly conservative planners degrade driving efficiency, while deterministic approaches may encounter serious issues and risks of failure when faced with sudden and unexpected maneuvers. To address these issues, we propose a real-time contingency trajectory optimization framework in this paper. By employing event-triggered online learning of HV control-intent sets, our method dynamically quantifies multi-modal HV uncertainties and refines the forward reachable set (FRS) incrementally. Crucially, we enforce invariant safety through FRS-based barrier constraints that ensure safety without reliance on accurate trajectory prediction of HVs. These constraints are embedded in contingency trajectory optimization and solved efficiently through consensus alternative direction method of multipliers (ADMM). The system continuously adapts to the uncertainties in HV behaviors, preserving feasibility and safety without resorting to excessive conservatism. High-fidelity simulations on highway and urban scenarios, as well as a series of real-world experiments demonstrate significant improvements in driving efficiency and passenger comfort while maintaining safety under uncertainty. The project page is available at https://pathetiue.github.io/frscp.github.io/.
Towards Proprioception-Aware Embodied Planning for Dual-Arm Humanoid Robots
Oct 09, 2025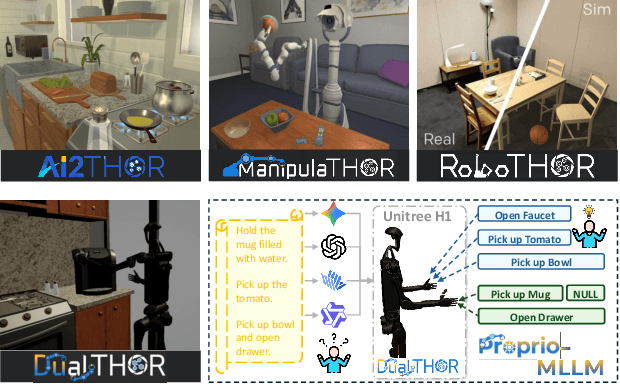


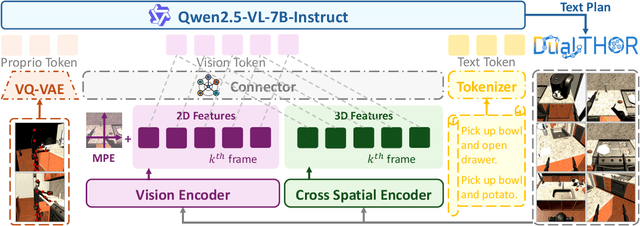
In recent years, Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated the ability to serve as high-level planners, enabling robots to follow complex human instructions. However, their effectiveness, especially in long-horizon tasks involving dual-arm humanoid robots, remains limited. This limitation arises from two main challenges: (i) the absence of simulation platforms that systematically support task evaluation and data collection for humanoid robots, and (ii) the insufficient embodiment awareness of current MLLMs, which hinders reasoning about dual-arm selection logic and body positions during planning. To address these issues, we present DualTHOR, a new dual-arm humanoid simulator, with continuous transition and a contingency mechanism. Building on this platform, we propose Proprio-MLLM, a model that enhances embodiment awareness by incorporating proprioceptive information with motion-based position embedding and a cross-spatial encoder. Experiments show that, while existing MLLMs struggle in this environment, Proprio-MLLM achieves an average improvement of 19.75% in planning performance. Our work provides both an essential simulation platform and an effective model to advance embodied intelligence in humanoid robotics. The code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DualTHOR-5F3B.
Code World Models for General Game Playing
Oct 06, 2025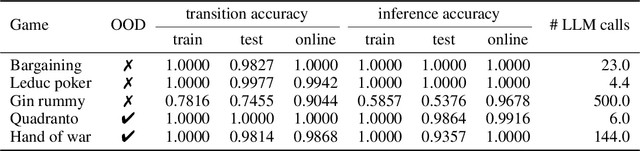
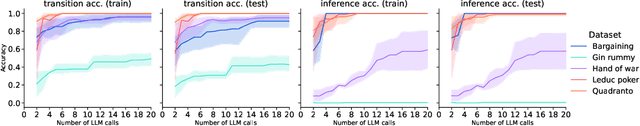
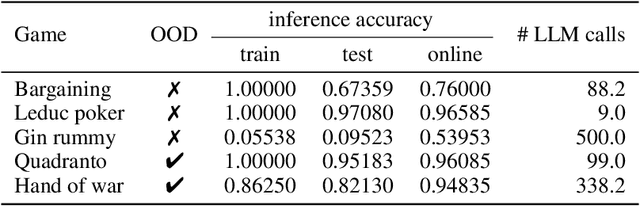
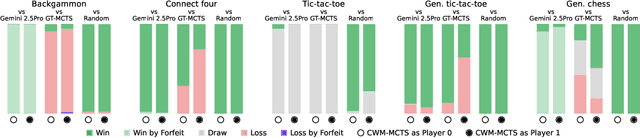
Large Language Models (LLMs) reasoning abilities are increasingly being applied to classical board and card games, but the dominant approach -- involving prompting for direct move generation -- has significant drawbacks. It relies on the model's implicit fragile pattern-matching capabilities, leading to frequent illegal moves and strategically shallow play. Here we introduce an alternative approach: We use the LLM to translate natural language rules and game trajectories into a formal, executable world model represented as Python code. This generated model -- comprising functions for state transition, legal move enumeration, and termination checks -- serves as a verifiable simulation engine for high-performance planning algorithms like Monte Carlo tree search (MCTS). In addition, we prompt the LLM to generate heuristic value functions (to make MCTS more efficient), and inference functions (to estimate hidden states in imperfect information games). Our method offers three distinct advantages compared to directly using the LLM as a policy: (1) Verifiability: The generated CWM serves as a formal specification of the game's rules, allowing planners to algorithmically enumerate valid actions and avoid illegal moves, contingent on the correctness of the synthesized model; (2) Strategic Depth: We combine LLM semantic understanding with the deep search power of classical planners; and (3) Generalization: We direct the LLM to focus on the meta-task of data-to-code translation, enabling it to adapt to new games more easily. We evaluate our agent on 10 different games, of which 4 are novel and created for this paper. 5 of the games are fully observed (perfect information), and 5 are partially observed (imperfect information). We find that our method outperforms or matches Gemini 2.5 Pro in 9 out of the 10 considered games.
Deep Hedging Under Non-Convexity: Limitations and a Case for AlphaZero
Oct 02, 2025



This paper examines replication portfolio construction in incomplete markets - a key problem in financial engineering with applications in pricing, hedging, balance sheet management, and energy storage planning. We model this as a two-player game between an investor and the market, where the investor makes strategic bets on future states while the market reveals outcomes. Inspired by the success of Monte Carlo Tree Search in stochastic games, we introduce an AlphaZero-based system and compare its performance to deep hedging - a widely used industry method based on gradient descent. Through theoretical analysis and experiments, we show that deep hedging struggles in environments where the $Q$-function is not subject to convexity constraints - such as those involving non-convex transaction costs, capital constraints, or regulatory limitations - converging to local optima. We construct specific market environments to highlight these limitations and demonstrate that AlphaZero consistently finds near-optimal replication strategies. On the theoretical side, we establish a connection between deep hedging and convex optimization, suggesting that its effectiveness is contingent on convexity assumptions. Our experiments further suggest that AlphaZero is more sample-efficient - an important advantage in data-scarce, overfitting-prone derivative markets.
Scaling LLM Planning: NL2FLOW for Parametric Problem Generation and Rigorous Evaluation
Jul 03, 2025Progress in enhancing large language model (LLM) planning and reasoning capabilities is significantly hampered by the bottleneck of scalable, reliable data generation and evaluation. To overcome this, I introduce NL2FLOW, a fully automated system for parametrically generating planning problems - expressed in natural language, a structured intermediate representation, and formal PDDL - and rigorously evaluating the quality of generated plans. I demonstrate NL2FLOW's capabilities by generating a dataset of 2296 problems in the automated workflow generation domain and evaluating multiple open-sourced, instruct-tuned LLMs. My results reveal that the highest performing models achieved 86% success in generating valid plans and 69% in generating optimal plans, specifically for problems with feasible solutions. Regression analysis shows that the influence of problem characteristics on plan generation is contingent on both model and prompt design. Notably, I observed that the highest success rate for translating natural language into a JSON representation of a plan was lower than the highest rate of generating a valid plan directly. This suggests that unnecessarily decomposing the reasoning task - introducing intermediate translation steps - may actually degrade performance, implying a benefit to models capable of reasoning directly from natural language to action. As I scale LLM reasoning to increasingly complex problems, the bottlenecks and sources of error within these systems will inevitably shift. Therefore, a dynamic understanding of these limitations - and the tools to systematically reveal them - will be crucial for unlocking the full potential of LLMs as intelligent problem solvers.
Learning Rock Pushability on Rough Planetary Terrain
May 14, 2025



In the context of mobile navigation in unstructured environments, the predominant approach entails the avoidance of obstacles. The prevailing path planning algorithms are contingent upon deviating from the intended path for an indefinite duration and returning to the closest point on the route after the obstacle is left behind spatially. However, avoiding an obstacle on a path that will be used repeatedly by multiple agents can hinder long-term efficiency and lead to a lasting reliance on an active path planning system. In this study, we propose an alternative approach to mobile navigation in unstructured environments by leveraging the manipulation capabilities of a robotic manipulator mounted on top of a mobile robot. Our proposed framework integrates exteroceptive and proprioceptive feedback to assess the push affordance of obstacles, facilitating their repositioning rather than avoidance. While our preliminary visual estimation takes into account the characteristics of both the obstacle and the surface it relies on, the push affordance estimation module exploits the force feedback obtained by interacting with the obstacle via a robotic manipulator as the guidance signal. The objective of our navigation approach is to enhance the efficiency of routes utilized by multiple agents over extended periods by reducing the overall time spent by a fleet in environments where autonomous infrastructure development is imperative, such as lunar or Martian surfaces.
Interpretable Multimodal Framework for Human-Centered Street Assessment: Integrating Visual-Language Models for Perceptual Urban Diagnostics
Jun 05, 2025While objective street metrics derived from imagery or GIS have become standard in urban analytics, they remain insufficient to capture subjective perceptions essential to inclusive urban design. This study introduces a novel Multimodal Street Evaluation Framework (MSEF) that fuses a vision transformer (VisualGLM-6B) with a large language model (GPT-4), enabling interpretable dual-output assessment of streetscapes. Leveraging over 15,000 annotated street-view images from Harbin, China, we fine-tune the framework using LoRA and P-Tuning v2 for parameter-efficient adaptation. The model achieves an F1 score of 0.84 on objective features and 89.3 percent agreement with aggregated resident perceptions, validated across stratified socioeconomic geographies. Beyond classification accuracy, MSEF captures context-dependent contradictions: for instance, informal commerce boosts perceived vibrancy while simultaneously reducing pedestrian comfort. It also identifies nonlinear and semantically contingent patterns -- such as the divergent perceptual effects of architectural transparency across residential and commercial zones -- revealing the limits of universal spatial heuristics. By generating natural-language rationales grounded in attention mechanisms, the framework bridges sensory data with socio-affective inference, enabling transparent diagnostics aligned with SDG 11. This work offers both methodological innovation in urban perception modeling and practical utility for planning systems seeking to reconcile infrastructural precision with lived experience.
DYNUS: Uncertainty-aware Trajectory Planner in Dynamic Unknown Environments
Apr 24, 2025

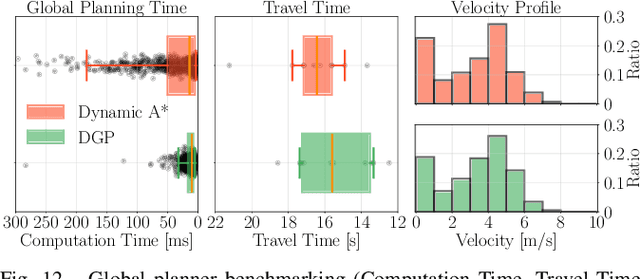

This paper introduces DYNUS, an uncertainty-aware trajectory planner designed for dynamic unknown environments. Operating in such settings presents many challenges -- most notably, because the agent cannot predict the ground-truth future paths of obstacles, a previously planned trajectory can become unsafe at any moment, requiring rapid replanning to avoid collisions. Recently developed planners have used soft-constraint approaches to achieve the necessary fast computation times; however, these methods do not guarantee collision-free paths even with static obstacles. In contrast, hard-constraint methods ensure collision-free safety, but typically have longer computation times. To address these issues, we propose three key contributions. First, the DYNUS Global Planner (DGP) and Temporal Safe Corridor Generation operate in spatio-temporal space and handle both static and dynamic obstacles in the 3D environment. Second, the Safe Planning Framework leverages a combination of exploratory, safe, and contingency trajectories to flexibly re-route when potential future collisions with dynamic obstacles are detected. Finally, the Fast Hard-Constraint Local Trajectory Formulation uses a variable elimination approach to reduce the problem size and enable faster computation by pre-computing dependencies between free and dependent variables while still ensuring collision-free trajectories. We evaluated DYNUS in a variety of simulations, including dense forests, confined office spaces, cave systems, and dynamic environments. Our experiments show that DYNUS achieves a success rate of 100% and travel times that are approximately 25.0% faster than state-of-the-art methods. We also evaluated DYNUS on multiple platforms -- a quadrotor, a wheeled robot, and a quadruped -- in both simulation and hardware experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge