Age And Gender Estimation
Papers and Code
JRDB-Pose3D: A Multi-person 3D Human Pose and Shape Estimation Dataset for Robotics
Feb 03, 2026Real-world scenes are inherently crowded. Hence, estimating 3D poses of all nearby humans, tracking their movements over time, and understanding their activities within social and environmental contexts are essential for many applications, such as autonomous driving, robot perception, robot navigation, and human-robot interaction. However, most existing 3D human pose estimation datasets primarily focus on single-person scenes or are collected in controlled laboratory environments, which restricts their relevance to real-world applications. To bridge this gap, we introduce JRDB-Pose3D, which captures multi-human indoor and outdoor environments from a mobile robotic platform. JRDB-Pose3D provides rich 3D human pose annotations for such complex and dynamic scenes, including SMPL-based pose annotations with consistent body-shape parameters and track IDs for each individual over time. JRDB-Pose3D contains, on average, 5-10 human poses per frame, with some scenes featuring up to 35 individuals simultaneously. The proposed dataset presents unique challenges, including frequent occlusions, truncated bodies, and out-of-frame body parts, which closely reflect real-world environments. Moreover, JRDB-Pose3D inherits all available annotations from the JRDB dataset, such as 2D pose, information about social grouping, activities, and interactions, full-scene semantic masks with consistent human- and object-level tracking, and detailed annotations for each individual, such as age, gender, and race, making it a holistic dataset for a wide range of downstream perception and human-centric understanding tasks.
HoverAI: An Embodied Aerial Agent for Natural Human-Drone Interaction
Jan 20, 2026Drones operating in human-occupied spaces suffer from insufficient communication mechanisms that create uncertainty about their intentions. We present HoverAI, an embodied aerial agent that integrates drone mobility, infrastructure-independent visual projection, and real-time conversational AI into a unified platform. Equipped with a MEMS laser projector, onboard semi-rigid screen, and RGB camera, HoverAI perceives users through vision and voice, responding via lip-synced avatars that adapt appearance to user demographics. The system employs a multimodal pipeline combining VAD, ASR (Whisper), LLM-based intent classification, RAG for dialogue, face analysis for personalization, and voice synthesis (XTTS v2). Evaluation demonstrates high accuracy in command recognition (F1: 0.90), demographic estimation (gender F1: 0.89, age MAE: 5.14 years), and speech transcription (WER: 0.181). By uniting aerial robotics with adaptive conversational AI and self-contained visual output, HoverAI introduces a new class of spatially-aware, socially responsive embodied agents for applications in guidance, assistance, and human-centered interaction.
FairReweighing: Density Estimation-Based Reweighing Framework for Improving Separation in Fair Regression
Nov 14, 2025There has been a prevalence of applying AI software in both high-stakes public-sector and industrial contexts. However, the lack of transparency has raised concerns about whether these data-informed AI software decisions secure fairness against people of all racial, gender, or age groups. Despite extensive research on emerging fairness-aware AI software, up to now most efforts to solve this issue have been dedicated to binary classification tasks. Fairness in regression is relatively underexplored. In this work, we adopted a mutual information-based metric to assess separation violations. The metric is also extended so that it can be directly applied to both classification and regression problems with both binary and continuous sensitive attributes. Inspired by the Reweighing algorithm in fair classification, we proposed a FairReweighing pre-processing algorithm based on density estimation to ensure that the learned model satisfies the separation criterion. Theoretically, we show that the proposed FairReweighing algorithm can guarantee separation in the training data under a data independence assumption. Empirically, on both synthetic and real-world data, we show that FairReweighing outperforms existing state-of-the-art regression fairness solutions in terms of improving separation while maintaining high accuracy.
On the Role of Calibration in Benchmarking Algorithmic Fairness for Skin Cancer Detection
Nov 10, 2025Artificial Intelligence (AI) models have demonstrated expert-level performance in melanoma detection, yet their clinical adoption is hindered by performance disparities across demographic subgroups such as gender, race, and age. Previous efforts to benchmark the performance of AI models have primarily focused on assessing model performance using group fairness metrics that rely on the Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve (AUROC), which does not provide insights into a model's ability to provide accurate estimates. In line with clinical assessments, this paper addresses this gap by incorporating calibration as a complementary benchmarking metric to AUROC-based fairness metrics. Calibration evaluates the alignment between predicted probabilities and observed event rates, offering deeper insights into subgroup biases. We assess the performance of the leading skin cancer detection algorithm of the ISIC 2020 Challenge on the ISIC 2020 Challenge dataset and the PROVE-AI dataset, and compare it with the second and third place models, focusing on subgroups defined by sex, race (Fitzpatrick Skin Tone), and age. Our findings reveal that while existing models enhance discriminative accuracy, they often over-diagnose risk and exhibit calibration issues when applied to new datasets. This study underscores the necessity for comprehensive model auditing strategies and extensive metadata collection to achieve equitable AI-driven healthcare solutions. All code is publicly available at https://github.com/bdominique/testing_strong_calibration.
* 19 pages, 4 figures. Accepted for publication at the Journal of Machine Learning for Biomedical Imaging (MELBA) https://melba-journal.org/2025:027
FusionDP: Foundation Model-Assisted Differentially Private Learning for Partially Sensitive Features
Nov 05, 2025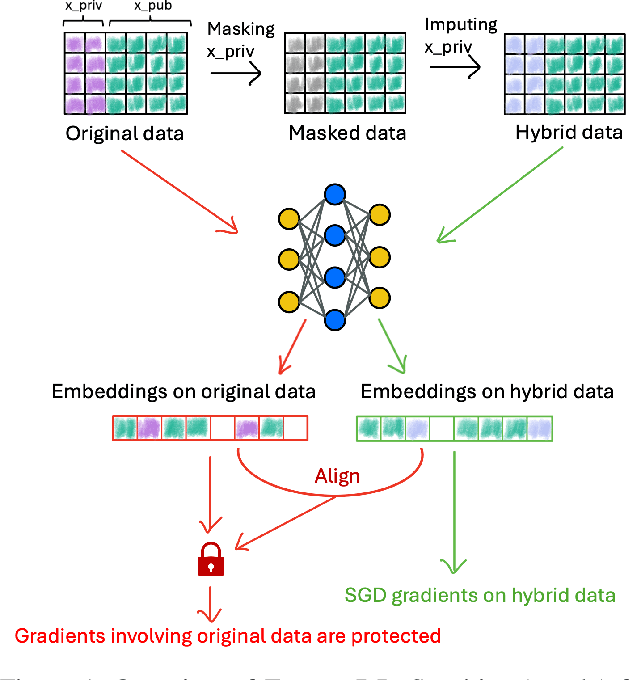
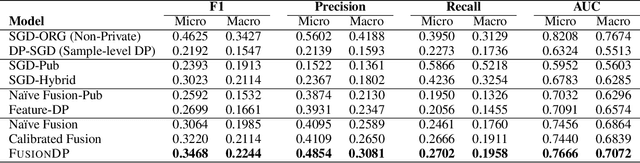
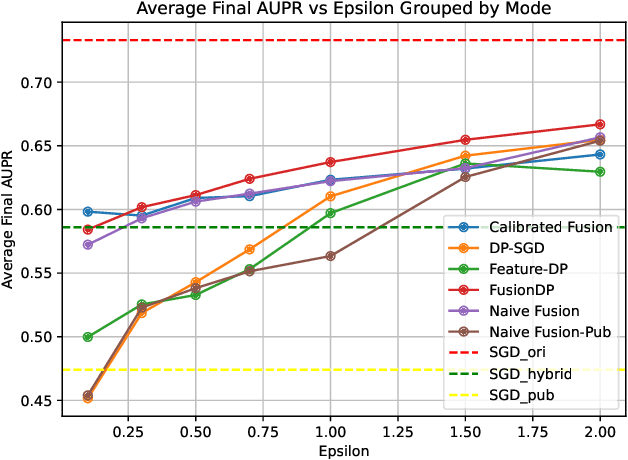
Ensuring the privacy of sensitive training data is crucial in privacy-preserving machine learning. However, in practical scenarios, privacy protection may be required for only a subset of features. For instance, in ICU data, demographic attributes like age and gender pose higher privacy risks due to their re-identification potential, whereas raw lab results are generally less sensitive. Traditional DP-SGD enforces privacy protection on all features in one sample, leading to excessive noise injection and significant utility degradation. We propose FusionDP, a two-step framework that enhances model utility under feature-level differential privacy. First, FusionDP leverages large foundation models to impute sensitive features given non-sensitive features, treating them as external priors that provide high-quality estimates of sensitive attributes without accessing the true values during model training. Second, we introduce a modified DP-SGD algorithm that trains models on both original and imputed features while formally preserving the privacy of the original sensitive features. We evaluate FusionDP on two modalities: a sepsis prediction task on tabular data from PhysioNet and a clinical note classification task from MIMIC-III. By comparing against privacy-preserving baselines, our results show that FusionDP significantly improves model performance while maintaining rigorous feature-level privacy, demonstrating the potential of foundation model-driven imputation to enhance the privacy-utility trade-off for various modalities.
Evaluating Sensitivity Parameters in Smartphone-Based Gaze Estimation: A Comparative Study of Appearance-Based and Infrared Eye Trackers
Jun 16, 2025This study evaluates a smartphone-based, deep-learning eye-tracking algorithm by comparing its performance against a commercial infrared-based eye tracker, the Tobii Pro Nano. The aim is to investigate the feasibility of appearance-based gaze estimation under realistic mobile usage conditions. Key sensitivity factors, including age, gender, vision correction, lighting conditions, device type, and head position, were systematically analysed. The appearance-based algorithm integrates a lightweight convolutional neural network (MobileNet-V3) with a recurrent structure (Long Short-Term Memory) to predict gaze coordinates from grayscale facial images. Gaze data were collected from 51 participants using dynamic visual stimuli, and accuracy was measured using Euclidean distance. The deep learning model produced a mean error of 17.76 mm, compared to 16.53 mm for the Tobii Pro Nano. While overall accuracy differences were small, the deep learning-based method was more sensitive to factors such as lighting, vision correction, and age, with higher failure rates observed under low-light conditions among participants using glasses and in older age groups. Device-specific and positional factors also influenced tracking performance. These results highlight the potential of appearance-based approaches for mobile eye tracking and offer a reference framework for evaluating gaze estimation systems across varied usage conditions.
SLEEPYLAND: trust begins with fair evaluation of automatic sleep staging models
Jun 11, 2025Despite advances in deep learning for automatic sleep staging, clinical adoption remains limited due to challenges in fair model evaluation, generalization across diverse datasets, model bias, and variability in human annotations. We present SLEEPYLAND, an open-source sleep staging evaluation framework designed to address these barriers. It includes more than 220'000 hours in-domain (ID) sleep recordings, and more than 84'000 hours out-of-domain (OOD) sleep recordings, spanning a broad range of ages, sleep-wake disorders, and hardware setups. We release pre-trained models based on high-performing SoA architectures and evaluate them under standardized conditions across single- and multi-channel EEG/EOG configurations. We introduce SOMNUS, an ensemble combining models across architectures and channel setups via soft voting. SOMNUS achieves robust performance across twenty-four different datasets, with macro-F1 scores between 68.7% and 87.2%, outperforming individual models in 94.9% of cases. Notably, SOMNUS surpasses previous SoA methods, even including cases where compared models were trained ID while SOMNUS treated the same data as OOD. Using a subset of the BSWR (N=6'633), we quantify model biases linked to age, gender, AHI, and PLMI, showing that while ensemble improves robustness, no model architecture consistently minimizes bias in performance and clinical markers estimation. In evaluations on OOD multi-annotated datasets (DOD-H, DOD-O), SOMNUS exceeds the best human scorer, i.e., MF1 85.2% vs 80.8% on DOD-H, and 80.2% vs 75.9% on DOD-O, better reproducing the scorer consensus than any individual expert (k = 0.89/0.85 and ACS = 0.95/0.94 for healthy/OSA cohorts). Finally, we introduce ensemble disagreement metrics - entropy and inter-model divergence based - predicting regions of scorer disagreement with ROC AUCs up to 0.828, offering a data-driven proxy for human uncertainty.
fairmetrics: An R package for group fairness evaluation
Jun 06, 2025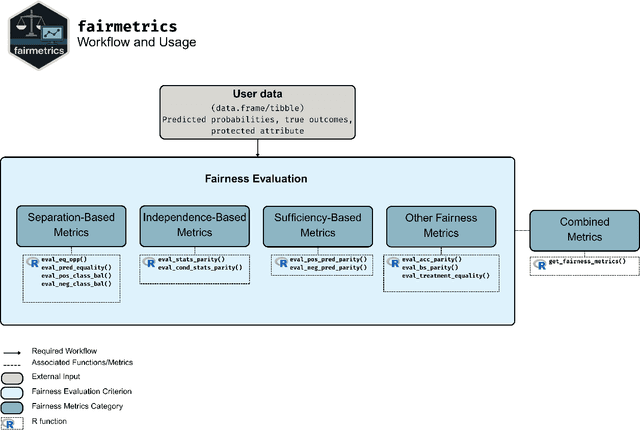
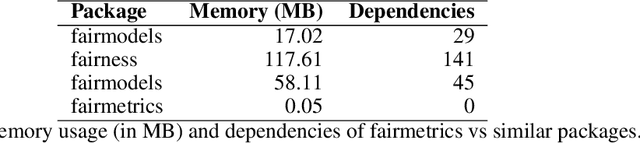
Fairness is a growing area of machine learning (ML) that focuses on ensuring models do not produce systematically biased outcomes for specific groups, particularly those defined by protected attributes such as race, gender, or age. Evaluating fairness is a critical aspect of ML model development, as biased models can perpetuate structural inequalities. The {fairmetrics} R package offers a user-friendly framework for rigorously evaluating numerous group-based fairness criteria, including metrics based on independence (e.g., statistical parity), separation (e.g., equalized odds), and sufficiency (e.g., predictive parity). Group-based fairness criteria assess whether a model is equally accurate or well-calibrated across a set of predefined groups so that appropriate bias mitigation strategies can be implemented. {fairmetrics} provides both point and interval estimates for multiple metrics through a convenient wrapper function and includes an example dataset derived from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care, version II (MIMIC-II) database (Goldberger et al., 2000; Raffa, 2016).
Fairness Perceptions in Regression-based Predictive Models
May 08, 2025Regression-based predictive analytics used in modern kidney transplantation is known to inherit biases from training data. This leads to social discrimination and inefficient organ utilization, particularly in the context of a few social groups. Despite this concern, there is limited research on fairness in regression and its impact on organ utilization and placement. This paper introduces three novel divergence-based group fairness notions: (i) independence, (ii) separation, and (iii) sufficiency to assess the fairness of regression-based analytics tools. In addition, fairness preferences are investigated from crowd feedback, in order to identify a socially accepted group fairness criterion for evaluating these tools. A total of 85 participants were recruited from the Prolific crowdsourcing platform, and a Mixed-Logit discrete choice model was used to model fairness feedback and estimate social fairness preferences. The findings clearly depict a strong preference towards the separation and sufficiency fairness notions, and that the predictive analytics is deemed fair with respect to gender and race groups, but unfair in terms of age groups.
Mitigate One, Skew Another? Tackling Intersectional Biases in Text-to-Image Models
May 22, 2025The biases exhibited by text-to-image (TTI) models are often treated as independent, though in reality, they may be deeply interrelated. Addressing bias along one dimension - such as ethnicity or age - can inadvertently affect another, like gender, either mitigating or exacerbating existing disparities. Understanding these interdependencies is crucial for designing fairer generative models, yet measuring such effects quantitatively remains a challenge. To address this, we introduce BiasConnect, a novel tool for analyzing and quantifying bias interactions in TTI models. BiasConnect uses counterfactual interventions along different bias axes to reveal the underlying structure of these interactions and estimates the effect of mitigating one bias axis on another. These estimates show strong correlation (+0.65) with observed post-mitigation outcomes. Building on BiasConnect, we propose InterMit, an intersectional bias mitigation algorithm guided by user-defined target distributions and priority weights. InterMit achieves lower bias (0.33 vs. 0.52) with fewer mitigation steps (2.38 vs. 3.15 average steps), and yields superior image quality compared to traditional techniques. Although our implementation is training-free, InterMit is modular and can be integrated with many existing debiasing approaches for TTI models, making it a flexible and extensible solution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge