Luigi Fiorillo
Institute of Digital Technologies for Personalized Healthcare
NAP: Attention-Based Late Fusion for Automatic Sleep Staging
Nov 05, 2025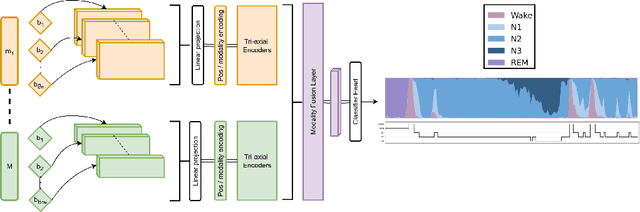
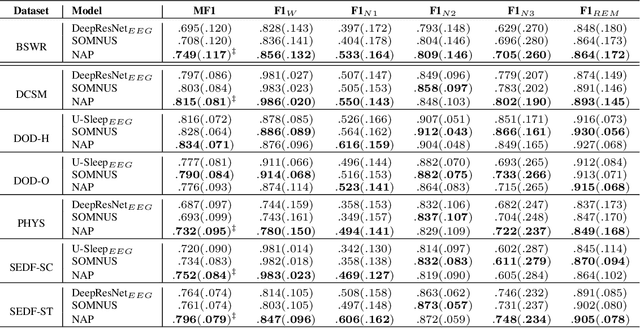
Abstract:Polysomnography signals are highly heterogeneous, varying in modality composition (e.g., EEG, EOG, ECG), channel availability (e.g., frontal, occipital EEG), and acquisition protocols across datasets and clinical sites. Most existing models that process polysomnography data rely on a fixed subset of modalities or channels and therefore neglect to fully exploit its inherently multimodal nature. We address this limitation by introducing NAP (Neural Aggregator of Predictions), an attention-based model which learns to combine multiple prediction streams using a tri-axial attention mechanism that captures temporal, spatial, and predictor-level dependencies. NAP is trained to adapt to different input dimensions. By aggregating outputs from frozen, pretrained single-channel models, NAP consistently outperforms individual predictors and simple ensembles, achieving state-of-the-art zero-shot generalization across multiple datasets. While demonstrated in the context of automated sleep staging from polysomnography, the proposed approach could be extended to other multimodal physiological applications.
SLEEPYLAND: trust begins with fair evaluation of automatic sleep staging models
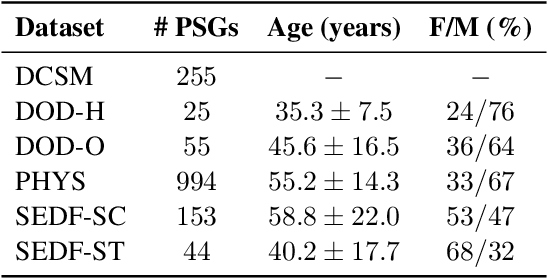
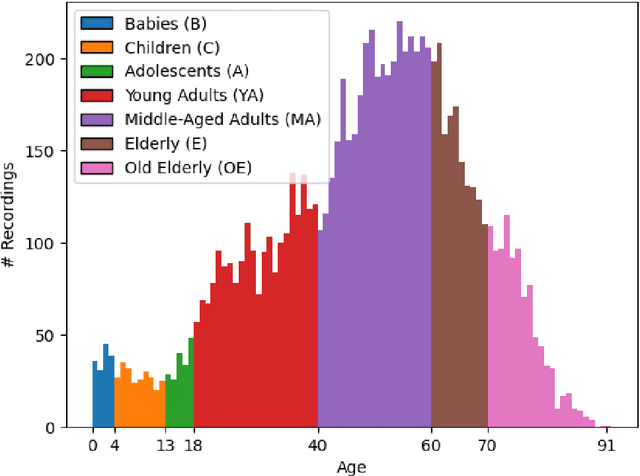
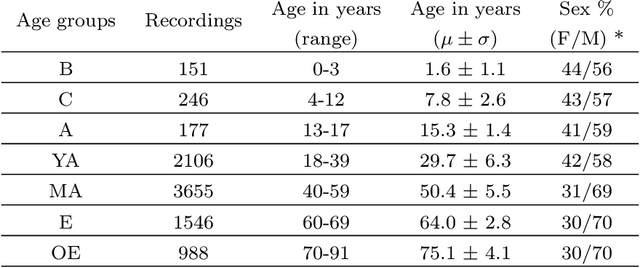
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Despite advances in deep learning for automatic sleep staging, clinical adoption remains limited due to challenges in fair model evaluation, generalization across diverse datasets, model bias, and variability in human annotations. We present SLEEPYLAND, an open-source sleep staging evaluation framework designed to address these barriers. It includes more than 220'000 hours in-domain (ID) sleep recordings, and more than 84'000 hours out-of-domain (OOD) sleep recordings, spanning a broad range of ages, sleep-wake disorders, and hardware setups. We release pre-trained models based on high-performing SoA architectures and evaluate them under standardized conditions across single- and multi-channel EEG/EOG configurations. We introduce SOMNUS, an ensemble combining models across architectures and channel setups via soft voting. SOMNUS achieves robust performance across twenty-four different datasets, with macro-F1 scores between 68.7% and 87.2%, outperforming individual models in 94.9% of cases. Notably, SOMNUS surpasses previous SoA methods, even including cases where compared models were trained ID while SOMNUS treated the same data as OOD. Using a subset of the BSWR (N=6'633), we quantify model biases linked to age, gender, AHI, and PLMI, showing that while ensemble improves robustness, no model architecture consistently minimizes bias in performance and clinical markers estimation. In evaluations on OOD multi-annotated datasets (DOD-H, DOD-O), SOMNUS exceeds the best human scorer, i.e., MF1 85.2% vs 80.8% on DOD-H, and 80.2% vs 75.9% on DOD-O, better reproducing the scorer consensus than any individual expert (k = 0.89/0.85 and ACS = 0.95/0.94 for healthy/OSA cohorts). Finally, we introduce ensemble disagreement metrics - entropy and inter-model divergence based - predicting regions of scorer disagreement with ROC AUCs up to 0.828, offering a data-driven proxy for human uncertainty.
Comparison analysis between standard polysomnographic data and in-ear-EEG signals: A preliminary study
Jan 30, 2024
Abstract:Study Objectives: Polysomnography (PSG) currently serves as the benchmark for evaluating sleep disorders. Its discomfort, impracticality for home-use, and introduction of bias in sleep quality assessment necessitate the exploration of less invasive, cost-effective, and portable alternatives. One promising contender is the in-ear-EEG sensor, which offers advantages in terms of comfort, fixed electrode positions, resistance to electromagnetic interference, and user-friendliness. This study aims to establish a methodology to assess the similarity between the in-ear-EEG signal and standard PSG. Methods: We assess the agreement between the PSG and in-ear-EEG derived hypnograms. We extract features in the time- and frequency- domain from PSG and in-ear-EEG 30-second epochs. We only consider the epochs where the PSG-scorers and the in-ear-EEG-scorers were in agreement. We introduce a methodology to quantify the similarity between PSG derivations and the single-channel in-ear-EEG. The approach relies on a comparison of distributions of selected features -- extracted for each sleep stage and subject on both PSG and the in-ear-EEG signals -- via a Jensen-Shannon Divergence Feature-based Similarity Index (JSD-FSI). Results: We found a high intra-scorer variability, mainly due to the uncertainty the scorers had in evaluating the in-ear-EEG signals. We show that the similarity between PSG and in-ear-EEG signals is high (JSD-FSI: 0.61 +/- 0.06 in awake, 0.60 +/- 0.07 in NREM and 0.51 +/- 0.08 in REM), and in line with the similarity values computed independently on standard PSG-channel-combinations. Conclusions: In-ear-EEG is a valuable solution for home-based sleep monitoring, however further studies with a larger and more heterogeneous dataset are needed.
Bridging AI and Clinical Practice: Integrating Automated Sleep Scoring Algorithm with Uncertainty-Guided Physician Review
Dec 22, 2023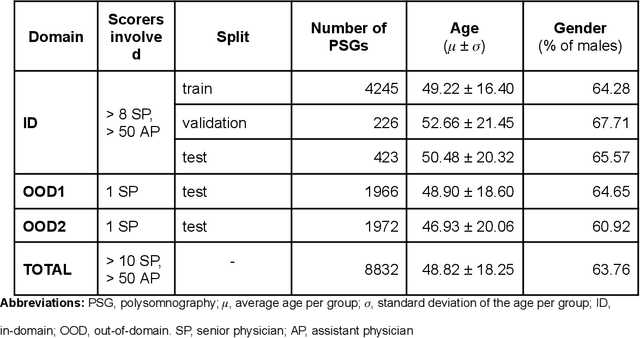
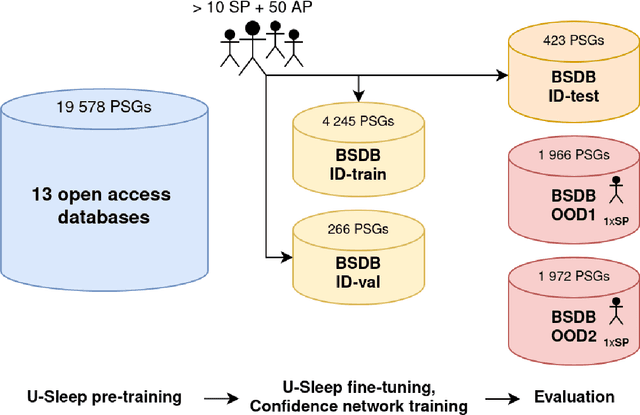

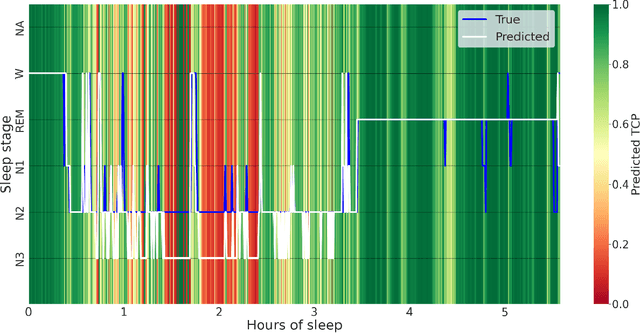
Abstract:Purpose: This study aims to enhance the clinical use of automated sleep-scoring algorithms by incorporating an uncertainty estimation approach to efficiently assist clinicians in the manual review of predicted hypnograms, a necessity due to the notable inter-scorer variability inherent in polysomnography (PSG) databases. Our efforts target the extent of review required to achieve predefined agreement levels, examining both in-domain and out-of-domain data, and considering subjects diagnoses. Patients and methods: Total of 19578 PSGs from 13 open-access databases were used to train U-Sleep, a state-of-the-art sleep-scoring algorithm. We leveraged a comprehensive clinical database of additional 8832 PSGs, covering a full spectrum of ages and sleep-disorders, to refine the U-Sleep, and to evaluate different uncertainty-quantification approaches, including our novel confidence network. The ID data consisted of PSGs scored by over 50 physicians, and the two OOD sets comprised recordings each scored by a unique senior physician. Results: U-Sleep demonstrated robust performance, with Cohen's kappa (K) at 76.2% on ID and 73.8-78.8% on OOD data. The confidence network excelled at identifying uncertain predictions, achieving AUROC scores of 85.7% on ID and 82.5-85.6% on OOD data. Independently of sleep-disorder status, statistical evaluations revealed significant differences in confidence scores between aligning vs discording predictions, and significant correlations of confidence scores with classification performance metrics. To achieve K of at least 90% with physician intervention, examining less than 29.0% of uncertain epochs was required, substantially reducing physicians workload, and facilitating near-perfect agreement.
U-Sleep: resilient to AASM guidelines
Sep 23, 2022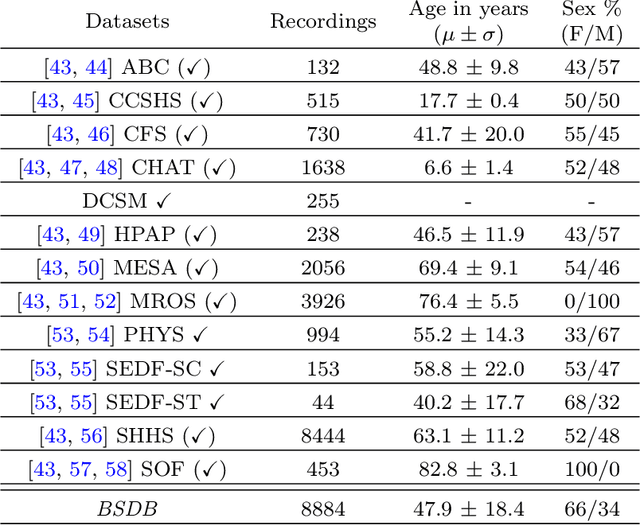
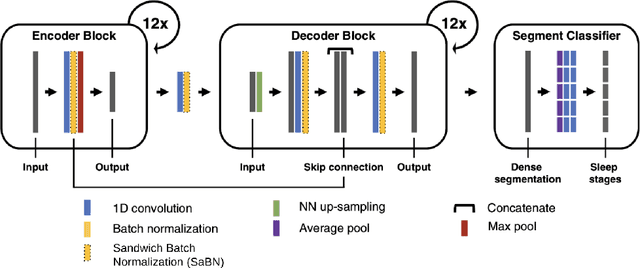
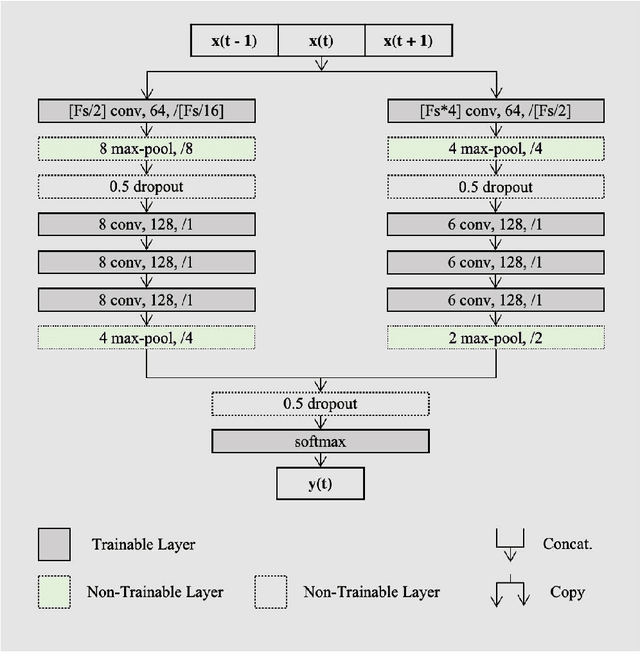
Abstract:AASM guidelines are the results of decades of efforts aiming at standardizing sleep scoring procedure, in order to have a commonly used methodology. The guidelines cover several aspects from the technical/digital specifications, e.g., recommended EEG derivations, to detailed sleep scoring rules accordingly to age. In the context of sleep scoring automation, deep learning has demonstrated better performance compared to many other techniques. Usually, clinical expertise and official guidelines are fundamental to support automated sleep scoring algorithms in solving the task. In this paper we show that a deep learning based sleep scoring algorithm may not need to fully exploit the clinical knowledge or to strictly follow the AASM guidelines. Specifically, we demonstrate that U-Sleep, a state-of-the-art sleep scoring algorithm, can be strong enough to solve the scoring task even using clinically non-recommended or non-conventional derivations, and with no need to exploit information about the chronological age of the subjects. We finally strengthen a well-known finding that using data from multiple data centers always results in a better performing model compared with training on a single cohort. Indeed, we show that this latter statement is still valid even by increasing the size and the heterogeneity of the single data cohort. In all our experiments we used 28528 polysomnography studies from 13 different clinical studies.
Multi-Scored Sleep Databases: How to Exploit the Multiple-Labels in Automated Sleep Scoring
Jul 06, 2022
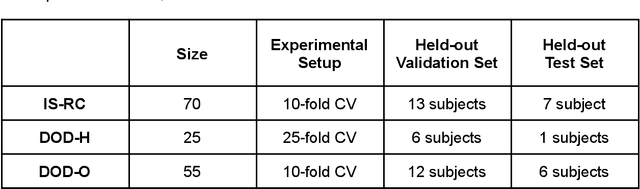
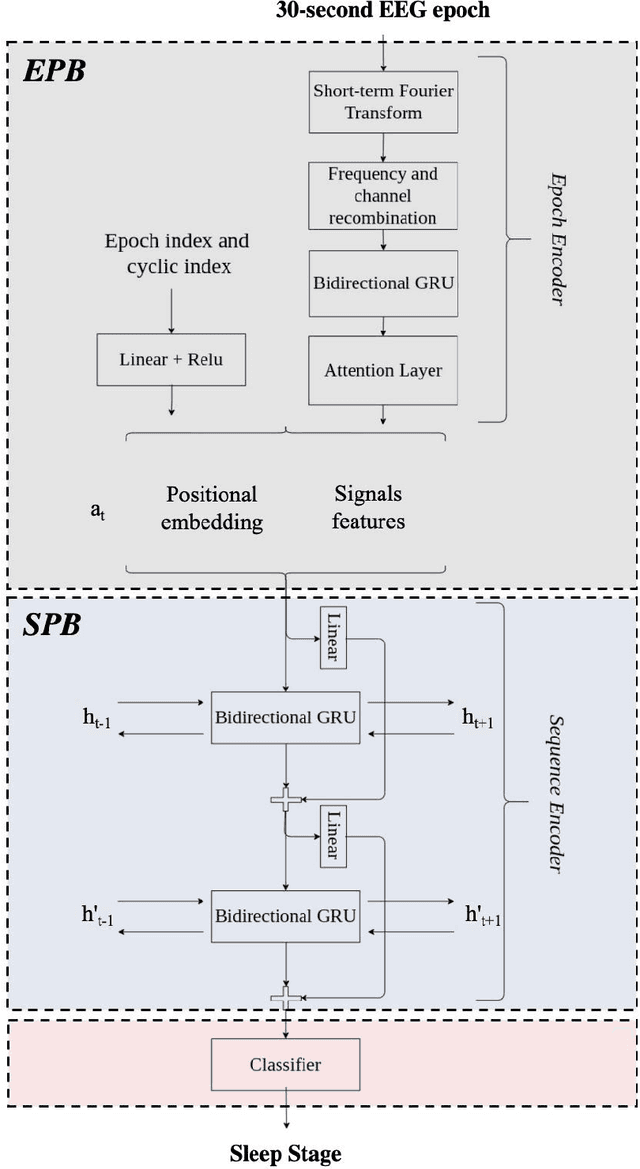
Abstract:Study Objectives: Inter-scorer variability in scoring polysomnograms is a well-known problem. Most of the existing automated sleep scoring systems are trained using labels annotated by a single scorer, whose subjective evaluation is transferred to the model. When annotations from two or more scorers are available, the scoring models are usually trained on the scorer consensus. The averaged scorer's subjectivity is transferred into the model, losing information about the internal variability among different scorers. In this study, we aim to insert the multiple-knowledge of the different physicians into the training procedure.The goal is to optimize a model training, exploiting the full information that can be extracted from the consensus of a group of scorers. Methods: We train two lightweight deep learning based models on three different multi-scored databases. We exploit the label smoothing technique together with a soft-consensus (LSSC) distribution to insert the multiple-knowledge in the training procedure of the model. We introduce the averaged cosine similarity metric (ACS) to quantify the similarity between the hypnodensity-graph generated by the models with-LSSC and the hypnodensity-graph generated by the scorer consensus. Results: The performance of the models improves on all the databases when we train the models with our LSSC. We found an increase in ACS (up to 6.4%) between the hypnodensity-graph generated by the models trained with-LSSC and the hypnodensity-graph generated by the consensus. Conclusions: Our approach definitely enables a model to better adapt to the consensus of the group of scorers. Future work will focus on further investigations on different scoring architectures.
DeepSleepNet-Lite: A Simplified Automatic Sleep Stage Scoring Model with Uncertainty Estimates
Aug 24, 2021



Abstract:Deep learning is widely used in the most recent automatic sleep scoring algorithms. Its popularity stems from its excellent performance and from its ability to directly process raw signals and to learn feature from the data. Most of the existing scoring algorithms exploit very computationally demanding architectures, due to their high number of training parameters, and process lengthy time sequences in input (up to 12 minutes). Only few of these architectures provide an estimate of the model uncertainty. In this study we propose DeepSleepNet-Lite, a simplified and lightweight scoring architecture, processing only 90-seconds EEG input sequences. We exploit, for the first time in sleep scoring, the Monte Carlo dropout technique to enhance the performance of the architecture and to also detect the uncertain instances. The evaluation is performed on a single-channel EEG Fpz-Cz from the open source Sleep-EDF expanded database. DeepSleepNet-Lite achieves slightly lower performance, if not on par, compared to the existing state-of-the-art architectures, in overall accuracy, macro F1-score and Cohen's kappa (on Sleep-EDF v1-2013 +/-30mins: 84.0%, 78.0%, 0.78; on Sleep-EDF v2-2018 +/-30mins: 80.3%, 75.2%, 0.73). Monte Carlo dropout enables the estimate of the uncertain predictions. By rejecting the uncertain instances, the model achieves higher performance on both versions of the database (on Sleep-EDF v1-2013 +/-30mins: 86.1.0%, 79.6%, 0.81; on Sleep-EDF v2-2018 +/-30mins: 82.3%, 76.7%, 0.76). Our lighter sleep scoring approach paves the way to the application of scoring algorithms for sleep analysis in real-time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge