Zhongqin Wu
Triplet Knowledge Distillation
May 25, 2023



Abstract:In Knowledge Distillation, the teacher is generally much larger than the student, making the solution of the teacher likely to be difficult for the student to learn. To ease the mimicking difficulty, we introduce a triplet knowledge distillation mechanism named TriKD. Besides teacher and student, TriKD employs a third role called anchor model. Before distillation begins, the pre-trained anchor model delimits a subspace within the full solution space of the target problem. Solutions within the subspace are expected to be easy targets that the student could mimic well. Distillation then begins in an online manner, and the teacher is only allowed to express solutions within the aforementioned subspace. Surprisingly, benefiting from accurate but easy-to-mimic hints, the student can finally perform well. After the student is well trained, it can be used as the new anchor for new students, forming a curriculum learning strategy. Our experiments on image classification and face recognition with various models clearly demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. Furthermore, the proposed TriKD is also effective in dealing with the overfitting issue. Moreover, our theoretical analysis supports the rationality of our triplet distillation.
FusionFormer: Fusing Operations in Transformer for Efficient Streaming Speech Recognition
Oct 31, 2022Abstract:The recently proposed Conformer architecture which combines convolution with attention to capture both local and global dependencies has become the \textit{de facto} backbone model for Automatic Speech Recognition~(ASR). Inherited from the Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks, the architecture takes Layer Normalization~(LN) as a default normalization technique. However, through a series of systematic studies, we find that LN might take 10\% of the inference time despite that it only contributes to 0.1\% of the FLOPs. This motivates us to replace LN with other normalization techniques, e.g., Batch Normalization~(BN), to speed up inference with the help of operator fusion methods and the avoidance of calculating the mean and variance statistics during inference. After examining several plain attempts which directly remove all LN layers or replace them with BN in the same place, we find that the divergence issue is mainly caused by the unstable layer output. We therefore propose to append a BN layer to each linear or convolution layer where stabilized training results are observed. We also propose to simplify the activations in Conformer, such as Swish and GLU, by replacing them with ReLU. All these exchanged modules can be fused into the weights of the adjacent linear/convolution layers and hence have zero inference cost. Therefore, we name it FusionFormer. Our experiments indicate that FusionFormer is as effective as the LN-based Conformer and is about 10\% faster.
Retrieval-based Spatially Adaptive Normalization for Semantic Image Synthesis
Apr 06, 2022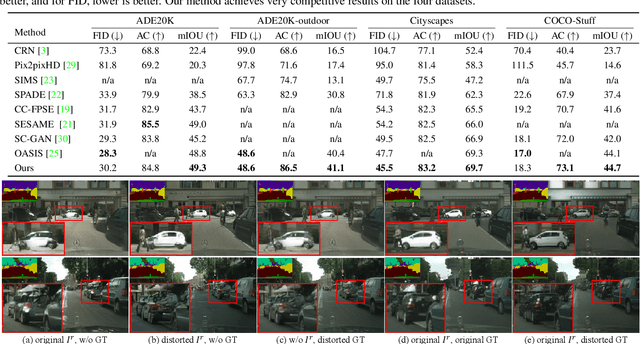
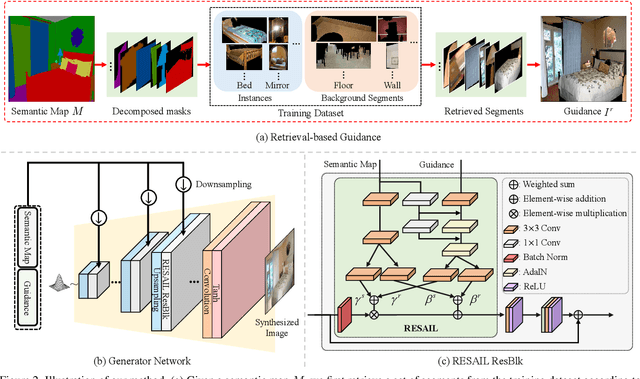
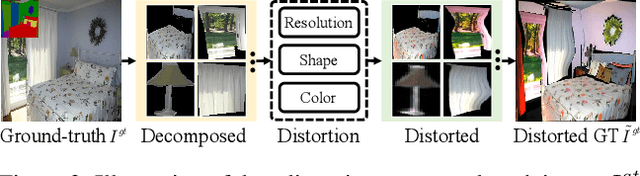
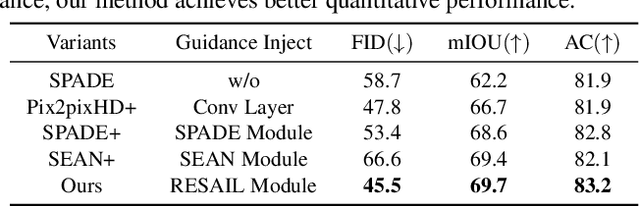
Abstract:Semantic image synthesis is a challenging task with many practical applications. Albeit remarkable progress has been made in semantic image synthesis with spatially-adaptive normalization and existing methods normalize the feature activations under the coarse-level guidance (e.g., semantic class). However, different parts of a semantic object (e.g., wheel and window of car) are quite different in structures and textures, making blurry synthesis results usually inevitable due to the missing of fine-grained guidance. In this paper, we propose a novel normalization module, termed as REtrieval-based Spatially AdaptIve normaLization (RESAIL), for introducing pixel level fine-grained guidance to the normalization architecture. Specifically, we first present a retrieval paradigm by finding a content patch of the same semantic class from training set with the most similar shape to each test semantic mask. Then, RESAIL is presented to use the retrieved patch for guiding the feature normalization of corresponding region, and can provide pixel level fine-grained guidance, thereby greatly mitigating blurry synthesis results. Moreover, distorted ground-truth images are also utilized as alternatives of retrieval-based guidance for feature normalization, further benefiting model training and improving visual quality of generated images. Experiments on several challenging datasets show that our RESAIL performs favorably against state-of-the-arts in terms of quantitative metrics, visual quality, and subjective evaluation. The source code and pre-trained models will be publicly available.
A Character-level Span-based Model for Mandarin Prosodic Structure Prediction
Mar 31, 2022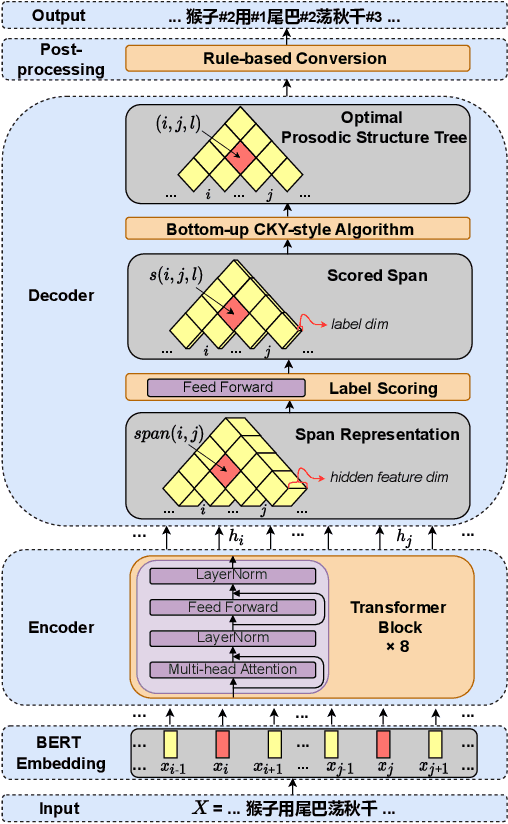
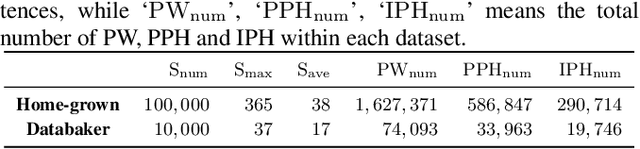
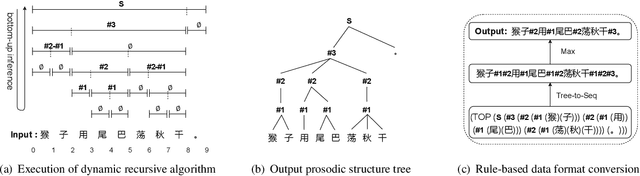
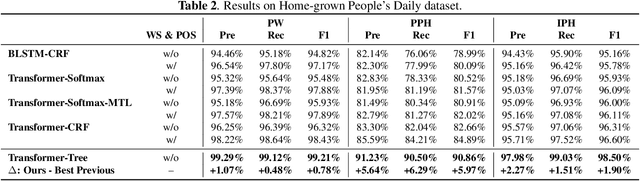
Abstract:The accuracy of prosodic structure prediction is crucial to the naturalness of synthesized speech in Mandarin text-to-speech system, but now is limited by widely-used sequence-to-sequence framework and error accumulation from previous word segmentation results. In this paper, we propose a span-based Mandarin prosodic structure prediction model to obtain an optimal prosodic structure tree, which can be converted to corresponding prosodic label sequence. Instead of the prerequisite for word segmentation, rich linguistic features are provided by Chinese character-level BERT and sent to encoder with self-attention architecture. On top of this, span representation and label scoring are used to describe all possible prosodic structure trees, of which each tree has its corresponding score. To find the optimal tree with the highest score for a given sentence, a bottom-up CKY-style algorithm is further used. The proposed method can predict prosodic labels of different levels at the same time and accomplish the process directly from Chinese characters in an end-to-end manner. Experiment results on two real-world datasets demonstrate the excellent performance of our span-based method over all sequence-to-sequence baseline approaches.
Syntax-Aware Network for Handwritten Mathematical Expression Recognition
Mar 28, 2022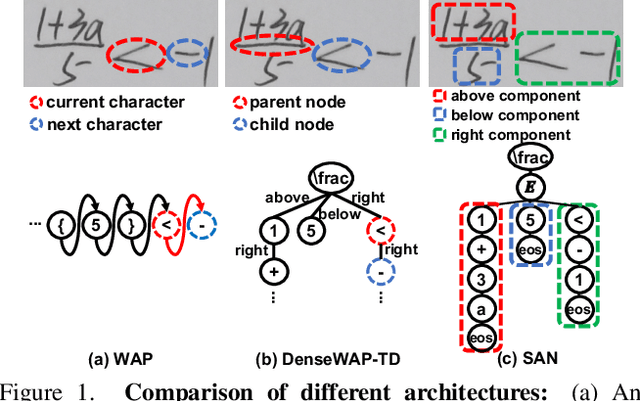
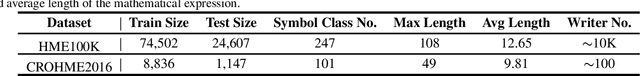
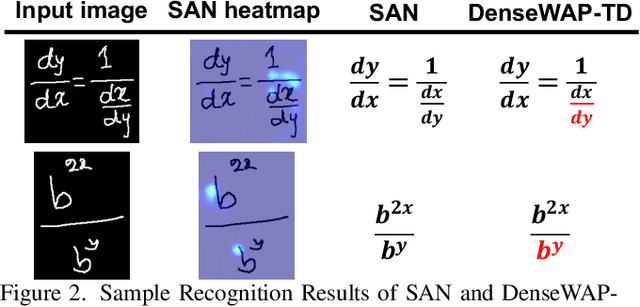
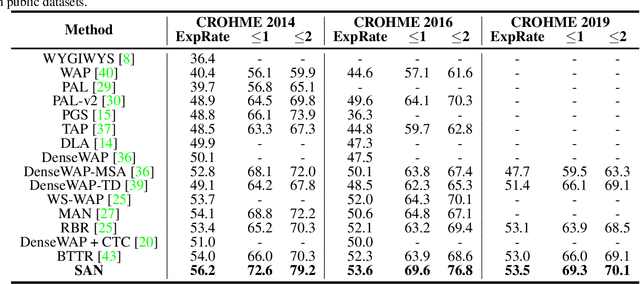
Abstract:Handwritten mathematical expression recognition (HMER) is a challenging task that has many potential applications. Recent methods for HMER have achieved outstanding performance with an encoder-decoder architecture. However, these methods adhere to the paradigm that the prediction is made "from one character to another", which inevitably yields prediction errors due to the complicated structures of mathematical expressions or crabbed handwritings. In this paper, we propose a simple and efficient method for HMER, which is the first to incorporate syntax information into an encoder-decoder network. Specifically, we present a set of grammar rules for converting the LaTeX markup sequence of each expression into a parsing tree; then, we model the markup sequence prediction as a tree traverse process with a deep neural network. In this way, the proposed method can effectively describe the syntax context of expressions, alleviating the structure prediction errors of HMER. Experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method achieves better recognition performance than prior arts. To further validate the effectiveness of our method, we create a large-scale dataset consisting of 100k handwritten mathematical expression images acquired from ten thousand writers. The source code, new dataset, and pre-trained models of this work will be publicly available.
BERT-LID: Leveraging BERT to Improve Spoken Language Identification
Mar 01, 2022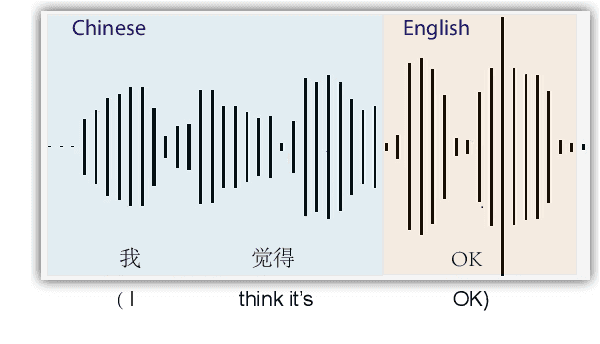

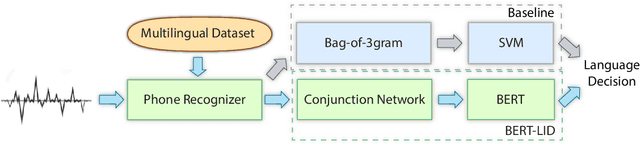
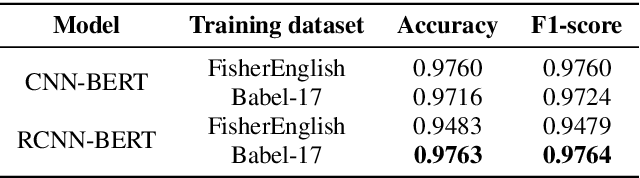
Abstract:Language identification is a task of automatically determining the identity of a language conveyed by a spoken segment. It has a profound impact on the multilingual interoperability of an intelligent speech system. Despite language identification attaining high accuracy on medium or long utterances (>3s), the performance on short utterances (<=1s) is still far from satisfactory. We propose an effective BERT-based language identification system (BERT-LID) to improve language identification performance, especially on short-duration speech segments. To adapt BERT into the LID pipeline, we drop in a conjunction network prior to BERT to accommodate the frame-level Phonetic Posteriorgrams(PPG) derived from the frontend phone recognizer and then fine-tune the conjunction network and BERT pre-trained model together. We evaluate several variations within this piped framework, including combining BERT with CNN, LSTM, DPCNN, and RCNN. The experimental results demonstrate that the best-performing model is RCNN-BERT. Compared with the prior works, our RCNN-BERT model can improve the accuracy by about 5% on long-segment identification and 18% on short-segment identification. The outperformance of our model, especially on the short-segment task, demonstrates the applicability of our proposed BERT-based approach on language identification.
Orthogonal Jacobian Regularization for Unsupervised Disentanglement in Image Generation
Aug 17, 2021
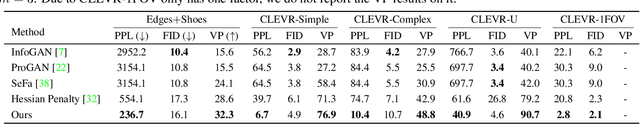

Abstract:Unsupervised disentanglement learning is a crucial issue for understanding and exploiting deep generative models. Recently, SeFa tries to find latent disentangled directions by performing SVD on the first projection of a pre-trained GAN. However, it is only applied to the first layer and works in a post-processing way. Hessian Penalty minimizes the off-diagonal entries of the output's Hessian matrix to facilitate disentanglement, and can be applied to multi-layers.However, it constrains each entry of output independently, making it not sufficient in disentangling the latent directions (e.g., shape, size, rotation, etc.) of spatially correlated variations. In this paper, we propose a simple Orthogonal Jacobian Regularization (OroJaR) to encourage deep generative model to learn disentangled representations. It simply encourages the variation of output caused by perturbations on different latent dimensions to be orthogonal, and the Jacobian with respect to the input is calculated to represent this variation. We show that our OroJaR also encourages the output's Hessian matrix to be diagonal in an indirect manner. In contrast to the Hessian Penalty, our OroJaR constrains the output in a holistic way, making it very effective in disentangling latent dimensions corresponding to spatially correlated variations. Quantitative and qualitative experimental results show that our method is effective in disentangled and controllable image generation, and performs favorably against the state-of-the-art methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/csyxwei/OroJaR
UniCon: Unified Context Network for Robust Active Speaker Detection
Aug 05, 2021
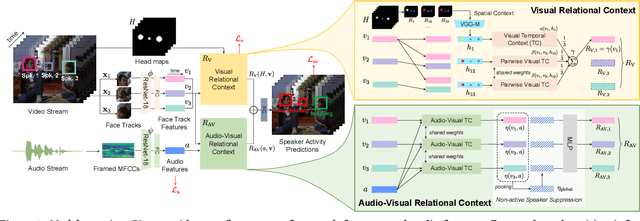
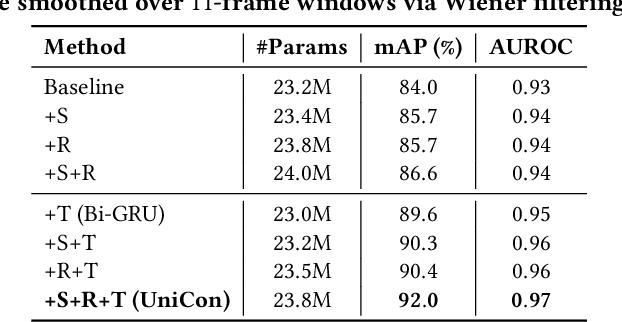
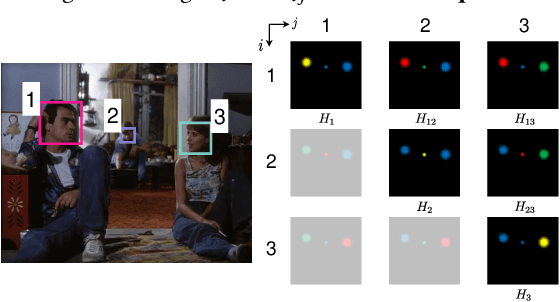
Abstract:We introduce a new efficient framework, the Unified Context Network (UniCon), for robust active speaker detection (ASD). Traditional methods for ASD usually operate on each candidate's pre-cropped face track separately and do not sufficiently consider the relationships among the candidates. This potentially limits performance, especially in challenging scenarios with low-resolution faces, multiple candidates, etc. Our solution is a novel, unified framework that focuses on jointly modeling multiple types of contextual information: spatial context to indicate the position and scale of each candidate's face, relational context to capture the visual relationships among the candidates and contrast audio-visual affinities with each other, and temporal context to aggregate long-term information and smooth out local uncertainties. Based on such information, our model optimizes all candidates in a unified process for robust and reliable ASD. A thorough ablation study is performed on several challenging ASD benchmarks under different settings. In particular, our method outperforms the state-of-the-art by a large margin of about 15% mean Average Precision (mAP) absolute on two challenging subsets: one with three candidate speakers, and the other with faces smaller than 64 pixels. Together, our UniCon achieves 92.0% mAP on the AVA-ActiveSpeaker validation set, surpassing 90% for the first time on this challenging dataset at the time of submission. Project website: https://unicon-asd.github.io/.
Structured Multi-modal Feature Embedding and Alignment for Image-Sentence Retrieval
Aug 05, 2021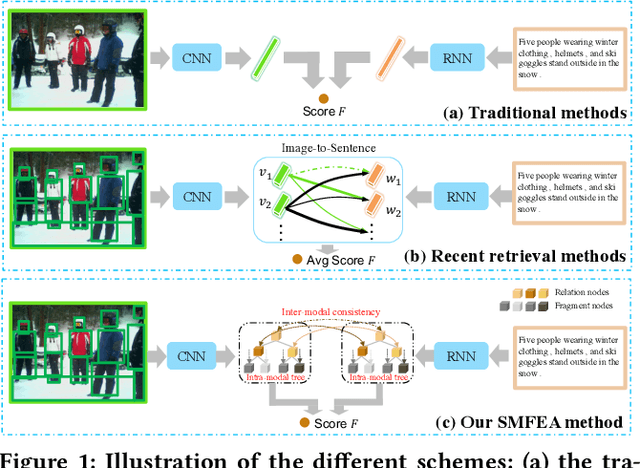
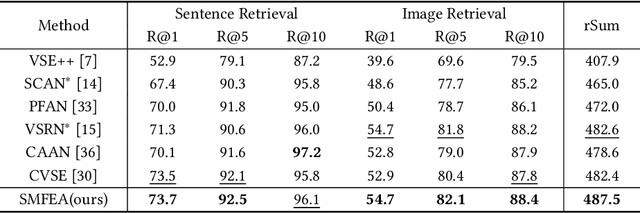
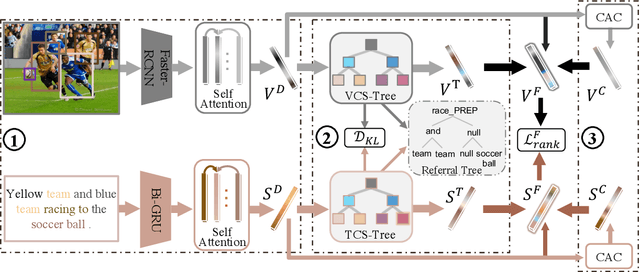
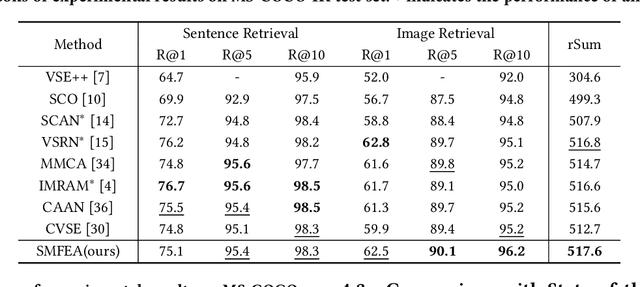
Abstract:The current state-of-the-art image-sentence retrieval methods implicitly align the visual-textual fragments, like regions in images and words in sentences, and adopt attention modules to highlight the relevance of cross-modal semantic correspondences. However, the retrieval performance remains unsatisfactory due to a lack of consistent representation in both semantics and structural spaces. In this work, we propose to address the above issue from two aspects: (i) constructing intrinsic structure (along with relations) among the fragments of respective modalities, e.g., "dog $\to$ play $\to$ ball" in semantic structure for an image, and (ii) seeking explicit inter-modal structural and semantic correspondence between the visual and textual modalities. In this paper, we propose a novel Structured Multi-modal Feature Embedding and Alignment (SMFEA) model for image-sentence retrieval. In order to jointly and explicitly learn the visual-textual embedding and the cross-modal alignment, SMFEA creates a novel multi-modal structured module with a shared context-aware referral tree. In particular, the relations of the visual and textual fragments are modeled by constructing Visual Context-aware Structured Tree encoder (VCS-Tree) and Textual Context-aware Structured Tree encoder (TCS-Tree) with shared labels, from which visual and textual features can be jointly learned and optimized. We utilize the multi-modal tree structure to explicitly align the heterogeneous image-sentence data by maximizing the semantic and structural similarity between corresponding inter-modal tree nodes. Extensive experiments on Microsoft COCO and Flickr30K benchmarks demonstrate the superiority of the proposed model in comparison to the state-of-the-art methods.
Locality-aware Channel-wise Dropout for Occluded Face Recognition
Jul 20, 2021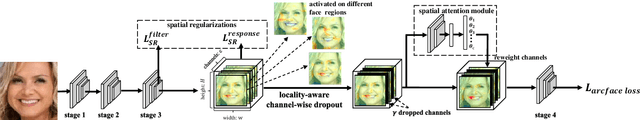
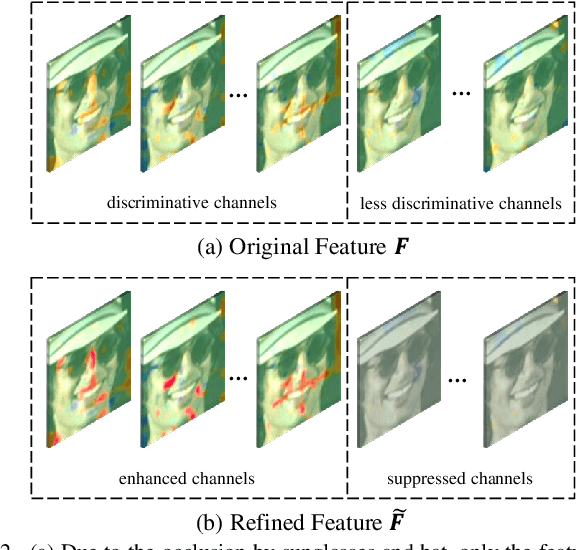
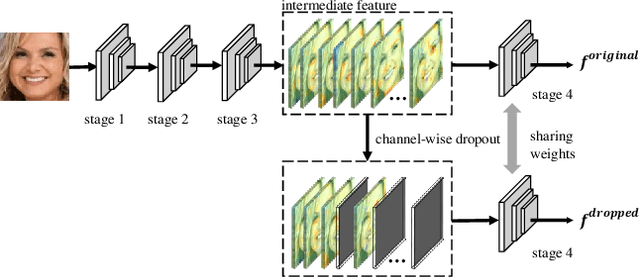
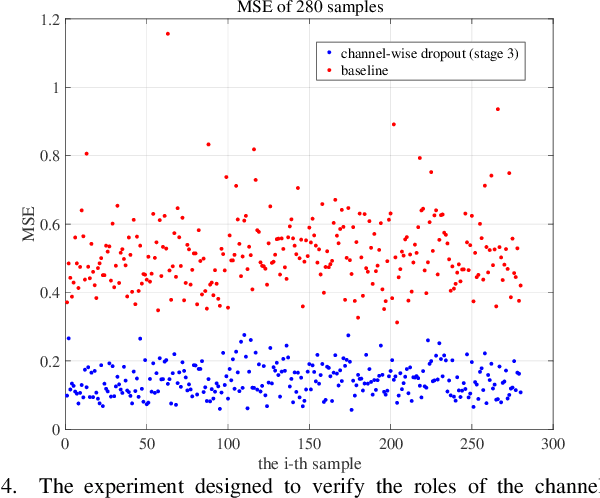
Abstract:Face recognition remains a challenging task in unconstrained scenarios, especially when faces are partially occluded. To improve the robustness against occlusion, augmenting the training images with artificial occlusions has been proved as a useful approach. However, these artificial occlusions are commonly generated by adding a black rectangle or several object templates including sunglasses, scarfs and phones, which cannot well simulate the realistic occlusions. In this paper, based on the argument that the occlusion essentially damages a group of neurons, we propose a novel and elegant occlusion-simulation method via dropping the activations of a group of neurons in some elaborately selected channel. Specifically, we first employ a spatial regularization to encourage each feature channel to respond to local and different face regions. In this way, the activations affected by an occlusion in a local region are more likely to be located in a single feature channel. Then, the locality-aware channel-wise dropout (LCD) is designed to simulate the occlusion by dropping out the entire feature channel. Furthermore, by randomly dropping out several feature channels, our method can well simulate the occlusion of larger area. The proposed LCD can encourage its succeeding layers to minimize the intra-class feature variance caused by occlusions, thus leading to improved robustness against occlusion. In addition, we design an auxiliary spatial attention module by learning a channel-wise attention vector to reweight the feature channels, which improves the contributions of non-occluded regions. Extensive experiments on various benchmarks show that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art methods with a remarkable improvement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge