Zhichao Xu
BayesFlow: A Probability Inference Framework for Meta-Agent Assisted Workflow Generation
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Automatic workflow generation is the process of automatically synthesizing sequences of LLM calls, tool invocations, and post-processing steps for complex end-to-end tasks. Most prior methods cast this task as an optimization problem with limited theoretical grounding. We propose to cast workflow generation as Bayesian inference over a posterior distribution on workflows, and introduce \textbf{Bayesian Workflow Generation (BWG)}, a sampling framework that builds workflows step-by-step using parallel look-ahead rollouts for importance weighting and a sequential in-loop refiner for pool-wide improvements. We prove that, without the refiner, the weighted empirical distribution converges to the target posterior. We instantiate BWG as \textbf{BayesFlow}, a training-free algorithm for workflow construction. Across six benchmark datasets, BayesFlow improves accuracy by up to 9 percentage points over SOTA workflow generation baselines and by up to 65 percentage points over zero-shot prompting, establishing BWG as a principled upgrade to search-based workflow design. Code will be available on https://github.com/BoYuanVisionary/BayesFlow.
Learning to Ideate for Machine Learning Engineering Agents
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Existing machine learning engineering (MLE) agents struggle to iteratively optimize their implemented algorithms for effectiveness. To address this, we introduce MLE-Ideator, a dual-agent framework that separates ideation from implementation. In our system, an implementation agent can request strategic help from a dedicated Ideator. We show this approach is effective in two ways. First, in a training-free setup, our framework significantly outperforms implementation-only agent baselines on MLE-Bench. Second, we demonstrate that the Ideator can be trained with reinforcement learning (RL) to generate more effective ideas. With only 1K training samples from 10 MLE tasks, our RL-trained Qwen3-8B Ideator achieves an 11.5% relative improvement compared to its untrained counterpart and surpasses Claude Sonnet 3.5. These results highlights a promising path toward training strategic AI systems for scientific discovery.
LACONIC: Dense-Level Effectiveness for Scalable Sparse Retrieval via a Two-Phase Training Curriculum
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:While dense retrieval models have become the standard for state-of-the-art information retrieval, their deployment is often constrained by high memory requirements and reliance on GPU accelerators for vector similarity search. Learned sparse retrieval offers a compelling alternative by enabling efficient search via inverted indices, yet it has historically received less attention than dense approaches. In this report, we introduce LACONIC, a family of learned sparse retrievers based on the Llama-3 architecture (1B, 3B, and 8B). We propose a streamlined two-phase training curriculum consisting of (1) weakly supervised pre-finetuning to adapt causal LLMs for bidirectional contextualization and (2) high-signal finetuning using curated hard negatives. Our results demonstrate that LACONIC effectively bridges the performance gap with dense models: the 8B variant achieves a state-of-the-art 60.2 nDCG on the MTEB Retrieval benchmark, ranking 15th on the leaderboard as of January 1, 2026, while utilizing 71\% less index memory than an equivalent dense model. By delivering high retrieval effectiveness on commodity CPU hardware with a fraction of the compute budget required by competing models, LACONIC provides a scalable and efficient solution for real-world search applications.
Teaching People LLM's Errors and Getting it Right
Dec 24, 2025



Abstract:People use large language models (LLMs) when they should not. This is partly because they see LLMs compose poems and answer intricate questions, so they understandably, but incorrectly, assume LLMs won't stumble on basic tasks like simple arithmetic. Prior work has tried to address this by clustering instance embeddings into regions where an LLM is likely to fail and automatically describing patterns in these regions. The found failure patterns are taught to users to mitigate their overreliance. Yet, this approach has not fully succeeded. In this analysis paper, we aim to understand why. We first examine whether the negative result stems from the absence of failure patterns. We group instances in two datasets by their meta-labels and evaluate an LLM's predictions on these groups. We then define criteria to flag groups that are sizable and where the LLM is error-prone, and find meta-label groups that meet these criteria. Their meta-labels are the LLM's failure patterns that could be taught to users, so they do exist. We next test whether prompting and embedding-based approaches can surface these known failures. Without this, users cannot be taught about them to reduce their overreliance. We find mixed results across methods, which could explain the negative result. Finally, we revisit the final metric that measures teaching effectiveness. We propose to assess a user's ability to effectively use the given failure patterns to anticipate when an LLM is error-prone. A user study shows a positive effect from teaching with this metric, unlike the human-AI team accuracy. Our findings show that teaching failure patterns could be a viable approach to mitigating overreliance, but success depends on better automated failure-discovery methods and using metrics like ours.
Reinforcement Learning for Self-Improving Agent with Skill Library
Dec 18, 2025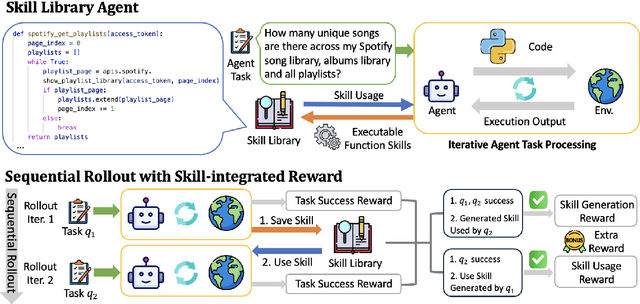
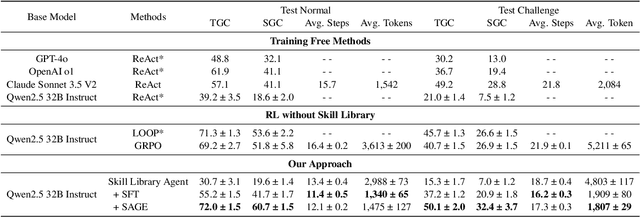
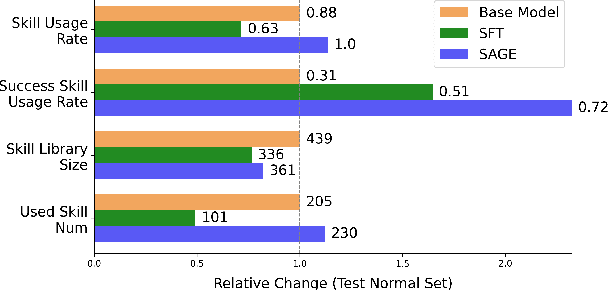
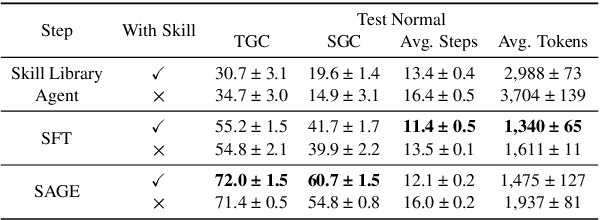
Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in complex reasoning and multi-turn interactions but struggle to continuously improve and adapt when deployed in new environments. One promising approach is implementing skill libraries that allow agents to learn, validate, and apply new skills. However, current skill library approaches rely primarily on LLM prompting, making consistent skill library implementation challenging. To overcome these challenges, we propose a Reinforcement Learning (RL)-based approach to enhance agents' self-improvement capabilities with a skill library. Specifically, we introduce Skill Augmented GRPO for self-Evolution (SAGE), a novel RL framework that systematically incorporates skills into learning. The framework's key component, Sequential Rollout, iteratively deploys agents across a chain of similar tasks for each rollout. As agents navigate through the task chain, skills generated from previous tasks accumulate in the library and become available for subsequent tasks. Additionally, the framework enhances skill generation and utilization through a Skill-integrated Reward that complements the original outcome-based rewards. Experimental results on AppWorld demonstrate that SAGE, when applied to supervised-finetuned model with expert experience, achieves 8.9% higher Scenario Goal Completion while requiring 26% fewer interaction steps and generating 59% fewer tokens, substantially outperforming existing approaches in both accuracy and efficiency.
Diffusion Language Model Inference with Monte Carlo Tree Search
Dec 13, 2025Abstract:Diffusion language models (DLMs) have recently emerged as a compelling alternative to autoregressive generation, offering parallel generation and improved global coherence. During inference, DLMs generate text by iteratively denoising masked sequences in parallel; however, determining which positions to unmask and which tokens to commit forms a large combinatorial search problem. Existing inference methods approximate this search using heuristics, which often yield suboptimal decoding paths; other approaches instead rely on additional training to guide token selection. To introduce a principled search mechanism for DLMs inference, we introduce MEDAL, a framework that integrates Monte Carlo Tree SEarch initialization for Diffusion LAnguage Model inference. We employ Monte Carlo Tree Search at the initialization stage to explore promising unmasking trajectories, providing a robust starting point for subsequent refinement. This integration is enabled by restricting the search space to high-confidence actions and prioritizing token choices that improve model confidence over remaining masked positions. Across multiple benchmarks, MEDAL achieves up to 22.0% improvement over existing inference strategies, establishing a new paradigm for search-based inference in diffusion language models.
TransactionGPT
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:We present TransactionGPT (TGPT), a foundation model for consumer transaction data within one of world's largest payment networks. TGPT is designed to understand and generate transaction trajectories while simultaneously supporting a variety of downstream prediction and classification tasks. We introduce a novel 3D-Transformer architecture specifically tailored for capturing the complex dynamics in payment transaction data. This architecture incorporates design innovations that enhance modality fusion and computational efficiency, while seamlessly enabling joint optimization with downstream objectives. Trained on billion-scale real-world transactions, TGPT significantly improves downstream classification performance against a competitive production model and exhibits advantages over baselines in generating future transactions. We conduct extensive empirical evaluations utilizing a diverse collection of company transaction datasets spanning multiple downstream tasks, thereby enabling a thorough assessment of TGPT's effectiveness and efficiency in comparison to established methodologies. Furthermore, we examine the incorporation of LLM-derived embeddings within TGPT and benchmark its performance against fine-tuned LLMs, demonstrating that TGPT achieves superior predictive accuracy as well as faster training and inference. We anticipate that the architectural innovations and practical guidelines from this work will advance foundation models for transaction-like data and catalyze future research in this emerging field.
ConvMix: A Mixed-Criteria Data Augmentation Framework for Conversational Dense Retrieval
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Conversational search aims to satisfy users' complex information needs via multiple-turn interactions. The key challenge lies in revealing real users' search intent from the context-dependent queries. Previous studies achieve conversational search by fine-tuning a conversational dense retriever with relevance judgments between pairs of context-dependent queries and documents. However, this training paradigm encounters data scarcity issues. To this end, we propose ConvMix, a mixed-criteria framework to augment conversational dense retrieval, which covers more aspects than existing data augmentation frameworks. We design a two-sided relevance judgment augmentation schema in a scalable manner via the aid of large language models. Besides, we integrate the framework with quality control mechanisms to obtain semantically diverse samples and near-distribution supervisions to combine various annotated data. Experimental results on five widely used benchmarks show that the conversational dense retriever trained by our ConvMix framework outperforms previous baseline methods, which demonstrates our superior effectiveness.
MiniMax-M1: Scaling Test-Time Compute Efficiently with Lightning Attention
Jun 16, 2025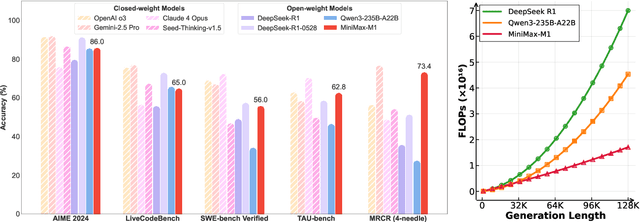
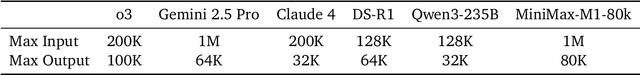
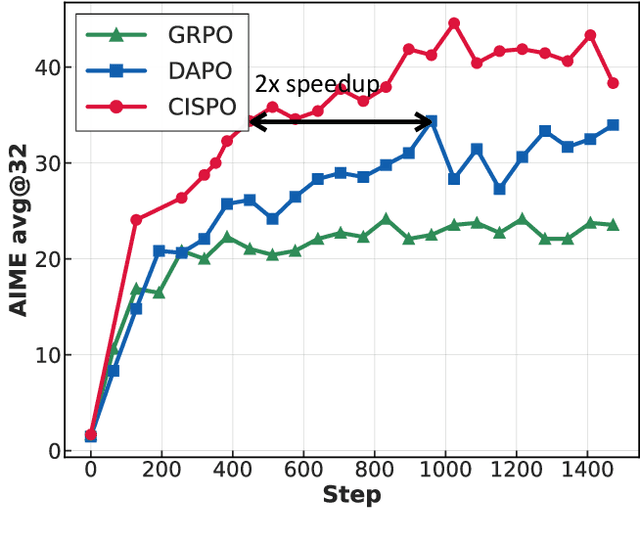
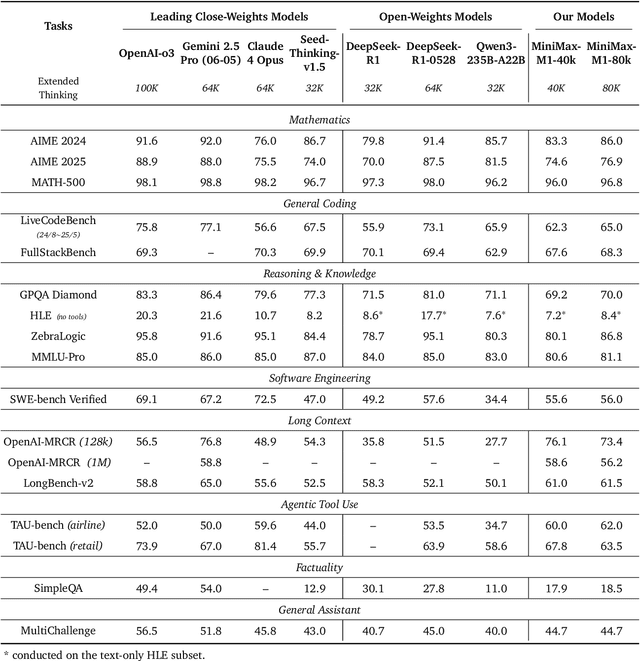
Abstract:We introduce MiniMax-M1, the world's first open-weight, large-scale hybrid-attention reasoning model. MiniMax-M1 is powered by a hybrid Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture combined with a lightning attention mechanism. The model is developed based on our previous MiniMax-Text-01 model, which contains a total of 456 billion parameters with 45.9 billion parameters activated per token. The M1 model natively supports a context length of 1 million tokens, 8x the context size of DeepSeek R1. Furthermore, the lightning attention mechanism in MiniMax-M1 enables efficient scaling of test-time compute. These properties make M1 particularly suitable for complex tasks that require processing long inputs and thinking extensively. MiniMax-M1 is trained using large-scale reinforcement learning (RL) on diverse problems including sandbox-based, real-world software engineering environments. In addition to M1's inherent efficiency advantage for RL training, we propose CISPO, a novel RL algorithm to further enhance RL efficiency. CISPO clips importance sampling weights rather than token updates, outperforming other competitive RL variants. Combining hybrid-attention and CISPO enables MiniMax-M1's full RL training on 512 H800 GPUs to complete in only three weeks, with a rental cost of just $534,700. We release two versions of MiniMax-M1 models with 40K and 80K thinking budgets respectively, where the 40K model represents an intermediate phase of the 80K training. Experiments on standard benchmarks show that our models are comparable or superior to strong open-weight models such as the original DeepSeek-R1 and Qwen3-235B, with particular strengths in complex software engineering, tool utilization, and long-context tasks. We publicly release MiniMax-M1 at https://github.com/MiniMax-AI/MiniMax-M1.
Found in Translation: Measuring Multilingual LLM Consistency as Simple as Translate then Evaluate
May 28, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) provide detailed and impressive responses to queries in English. However, are they really consistent at responding to the same query in other languages? The popular way of evaluating for multilingual performance of LLMs requires expensive-to-collect annotated datasets. Further, evaluating for tasks like open-ended generation, where multiple correct answers may exist, is nontrivial. Instead, we propose to evaluate the predictability of model response across different languages. In this work, we propose a framework to evaluate LLM's cross-lingual consistency based on a simple Translate then Evaluate strategy. We instantiate this evaluation framework along two dimensions of consistency: information and empathy. Our results reveal pronounced inconsistencies in popular LLM responses across thirty languages, with severe performance deficits in certain language families and scripts, underscoring critical weaknesses in their multilingual capabilities. These findings necessitate cross-lingual evaluations that are consistent along multiple dimensions. We invite practitioners to use our framework for future multilingual LLM benchmarking.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge