Yiping Han
Enhancing Embedding Representation Stability in Recommendation Systems with Semantic ID
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:The exponential growth of online content has posed significant challenges to ID-based models in industrial recommendation systems, ranging from extremely high cardinality and dynamically growing ID space, to highly skewed engagement distributions, to prediction instability as a result of natural id life cycles (e.g, the birth of new IDs and retirement of old IDs). To address these issues, many systems rely on random hashing to handle the id space and control the corresponding model parameters (i.e embedding table). However, this approach introduces data pollution from multiple ids sharing the same embedding, leading to degraded model performance and embedding representation instability. This paper examines these challenges and introduces Semantic ID prefix ngram, a novel token parameterization technique that significantly improves the performance of the original Semantic ID. Semantic ID prefix ngram creates semantically meaningful collisions by hierarchically clustering items based on their content embeddings, as opposed to random assignments. Through extensive experimentation, we demonstrate that Semantic ID prefix ngram not only addresses embedding instability but also significantly improves tail id modeling, reduces overfitting, and mitigates representation shifts. We further highlight the advantages of Semantic ID prefix ngram in attention-based models that contextualize user histories, showing substantial performance improvements. We also report our experience of integrating Semantic ID into Meta production Ads Ranking system, leading to notable performance gains and enhanced prediction stability in live deployments.
External Large Foundation Model: How to Efficiently Serve Trillions of Parameters for Online Ads Recommendation
Feb 26, 2025



Abstract:Ads recommendation is a prominent service of online advertising systems and has been actively studied. Recent studies indicate that scaling-up and advanced design of the recommendation model can bring significant performance improvement. However, with a larger model scale, such prior studies have a significantly increasing gap from industry as they often neglect two fundamental challenges in industrial-scale applications. First, training and inference budgets are restricted for the model to be served, exceeding which may incur latency and impair user experience. Second, large-volume data arrive in a streaming mode with data distributions dynamically shifting, as new users/ads join and existing users/ads leave the system. We propose the External Large Foundation Model (ExFM) framework to address the overlooked challenges. Specifically, we develop external distillation and a data augmentation system (DAS) to control the computational cost of training/inference while maintaining high performance. We design the teacher in a way like a foundation model (FM) that can serve multiple students as vertical models (VMs) to amortize its building cost. We propose Auxiliary Head and Student Adapter to mitigate the data distribution gap between FM and VMs caused by the streaming data issue. Comprehensive experiments on internal industrial-scale applications and public datasets demonstrate significant performance gain by ExFM.
The Efficiency vs. Accuracy Trade-off: Optimizing RAG-Enhanced LLM Recommender Systems Using Multi-Head Early Exit
Jan 04, 2025



Abstract:The deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) in recommender systems for predicting Click-Through Rates (CTR) necessitates a delicate balance between computational efficiency and predictive accuracy. This paper presents an optimization framework that combines Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with an innovative multi-head early exit architecture to concurrently enhance both aspects. By integrating Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) as efficient retrieval mechanisms, we are able to significantly reduce data retrieval times while maintaining high model performance. The early exit strategy employed allows for dynamic termination of model inference, utilizing real-time predictive confidence assessments across multiple heads. This not only quickens the responsiveness of LLMs but also upholds or improves their accuracy, making it ideal for real-time application scenarios. Our experiments demonstrate how this architecture effectively decreases computation time without sacrificing the accuracy needed for reliable recommendation delivery, establishing a new standard for efficient, real-time LLM deployment in commercial systems.
A Collaborative Ensemble Framework for CTR Prediction
Nov 20, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in foundation models have established scaling laws that enable the development of larger models to achieve enhanced performance, motivating extensive research into large-scale recommendation models. However, simply increasing the model size in recommendation systems, even with large amounts of data, does not always result in the expected performance improvements. In this paper, we propose a novel framework, Collaborative Ensemble Training Network (CETNet), to leverage multiple distinct models, each with its own embedding table, to capture unique feature interaction patterns. Unlike naive model scaling, our approach emphasizes diversity and collaboration through collaborative learning, where models iteratively refine their predictions. To dynamically balance contributions from each model, we introduce a confidence-based fusion mechanism using general softmax, where model confidence is computed via negation entropy. This design ensures that more confident models have a greater influence on the final prediction while benefiting from the complementary strengths of other models. We validate our framework on three public datasets (AmazonElectronics, TaobaoAds, and KuaiVideo) as well as a large-scale industrial dataset from Meta, demonstrating its superior performance over individual models and state-of-the-art baselines. Additionally, we conduct further experiments on the Criteo and Avazu datasets to compare our method with the multi-embedding paradigm. Our results show that our framework achieves comparable or better performance with smaller embedding sizes, offering a scalable and efficient solution for CTR prediction tasks.
InterFormer: Towards Effective Heterogeneous Interaction Learning for Click-Through Rate Prediction
Nov 15, 2024
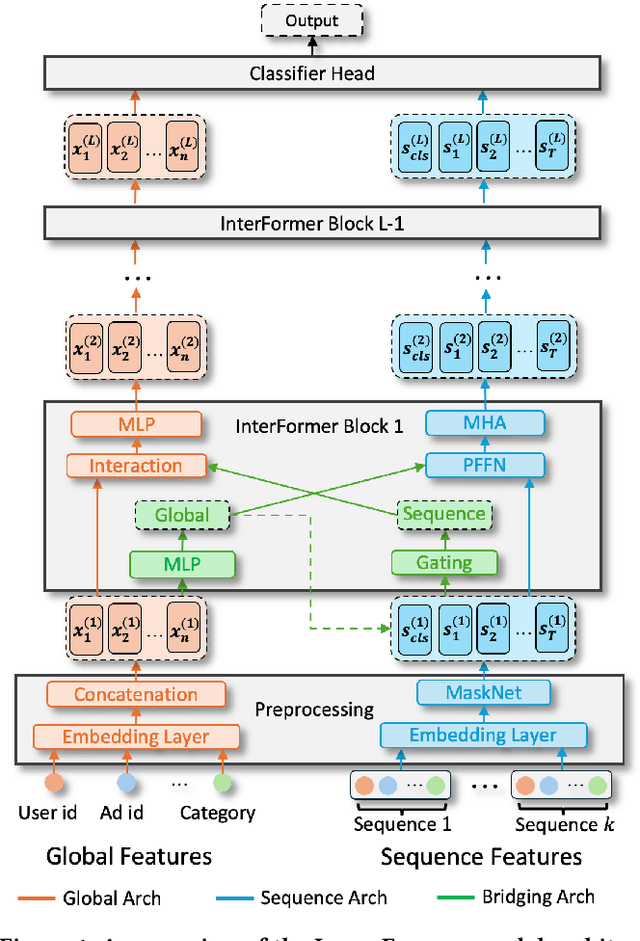
Abstract:Click-through rate (CTR) prediction, which predicts the probability of a user clicking an ad, is a fundamental task in recommender systems. The emergence of heterogeneous information, such as user profile and behavior sequences, depicts user interests from different aspects. A mutually beneficial integration of heterogeneous information is the cornerstone towards the success of CTR prediction. However, most of the existing methods suffer from two fundamental limitations, including (1) insufficient inter-mode interaction due to the unidirectional information flow between modes, and (2) aggressive information aggregation caused by early summarization, resulting in excessive information loss. To address the above limitations, we propose a novel module named InterFormer to learn heterogeneous information interaction in an interleaving style. To achieve better interaction learning, InterFormer enables bidirectional information flow for mutually beneficial learning across different modes. To avoid aggressive information aggregation, we retain complete information in each data mode and use a separate bridging arch for effective information selection and summarization. Our proposed InterFormer achieves state-of-the-art performance on three public datasets and a large-scale industrial dataset.
DistDNAS: Search Efficient Feature Interactions within 2 Hours
Nov 01, 2023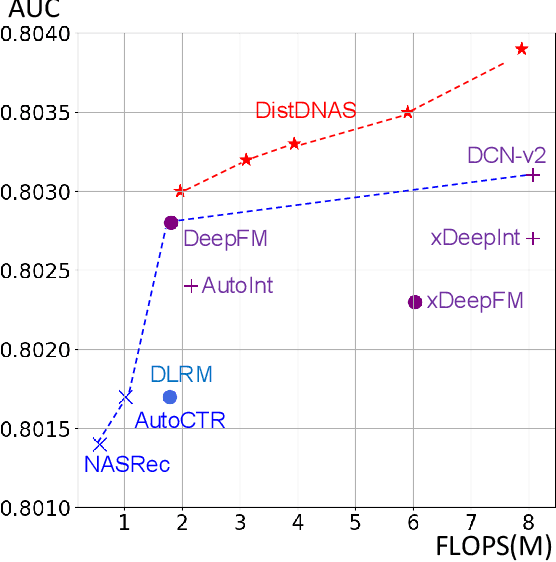

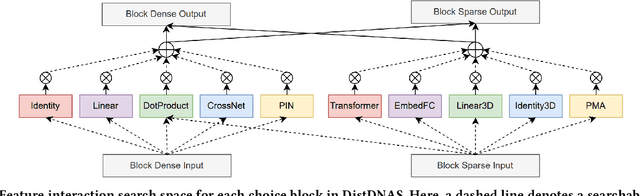

Abstract:Search efficiency and serving efficiency are two major axes in building feature interactions and expediting the model development process in recommender systems. On large-scale benchmarks, searching for the optimal feature interaction design requires extensive cost due to the sequential workflow on the large volume of data. In addition, fusing interactions of various sources, orders, and mathematical operations introduces potential conflicts and additional redundancy toward recommender models, leading to sub-optimal trade-offs in performance and serving cost. In this paper, we present DistDNAS as a neat solution to brew swift and efficient feature interaction design. DistDNAS proposes a supernet to incorporate interaction modules of varying orders and types as a search space. To optimize search efficiency, DistDNAS distributes the search and aggregates the choice of optimal interaction modules on varying data dates, achieving over 25x speed-up and reducing search cost from 2 days to 2 hours. To optimize serving efficiency, DistDNAS introduces a differentiable cost-aware loss to penalize the selection of redundant interaction modules, enhancing the efficiency of discovered feature interactions in serving. We extensively evaluate the best models crafted by DistDNAS on a 1TB Criteo Terabyte dataset. Experimental evaluations demonstrate 0.001 AUC improvement and 60% FLOPs saving over current state-of-the-art CTR models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge