Yang Jin
Learning from Next-Frame Prediction: Autoregressive Video Modeling Encodes Effective Representations
Dec 24, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in pretraining general foundation models have significantly improved performance across diverse downstream tasks. While autoregressive (AR) generative models like GPT have revolutionized NLP, most visual generative pretraining methods still rely on BERT-style masked modeling, which often disregards the temporal information essential for video analysis. The few existing autoregressive visual pretraining methods suffer from issues such as inaccurate semantic localization and poor generation quality, leading to poor semantics. In this work, we propose NExT-Vid, a novel autoregressive visual generative pretraining framework that utilizes masked next-frame prediction to jointly model images and videos. NExT-Vid introduces a context-isolated autoregressive predictor to decouple semantic representation from target decoding, and a conditioned flow-matching decoder to enhance generation quality and diversity. Through context-isolated flow-matching pretraining, our approach achieves strong representations. Extensive experiments on large-scale pretrained models demonstrate that our proposed method consistently outperforms previous generative pretraining methods for visual representation learning via attentive probing in downstream classification.
ImplicitRDP: An End-to-End Visual-Force Diffusion Policy with Structural Slow-Fast Learning
Dec 11, 2025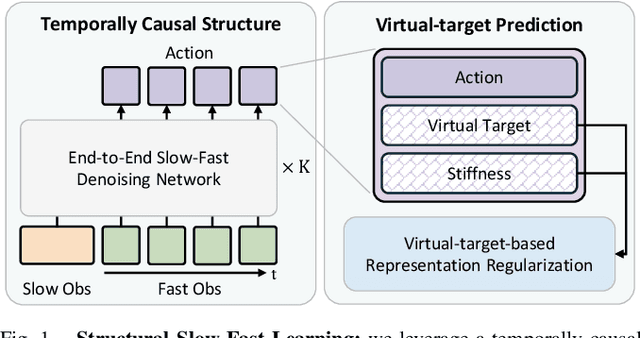
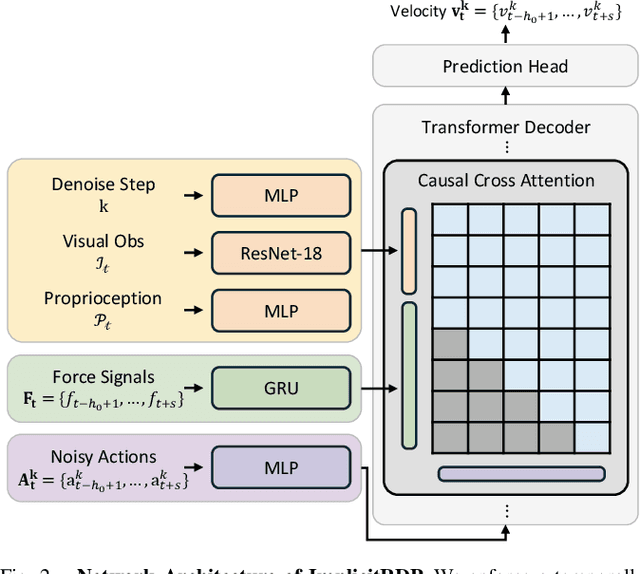
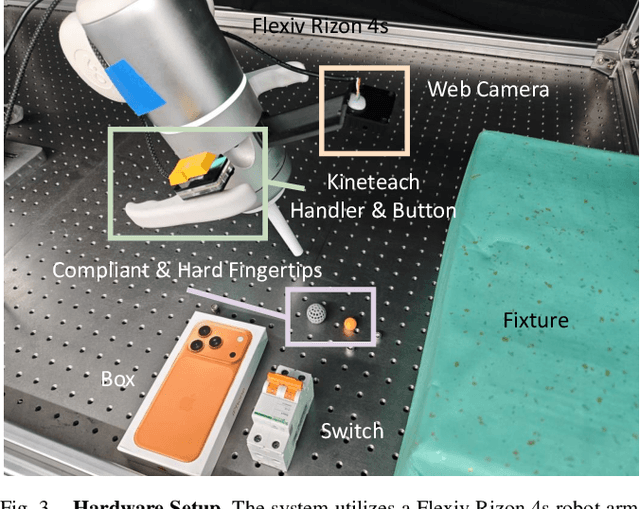

Abstract:Human-level contact-rich manipulation relies on the distinct roles of two key modalities: vision provides spatially rich but temporally slow global context, while force sensing captures rapid, high-frequency local contact dynamics. Integrating these signals is challenging due to their fundamental frequency and informational disparities. In this work, we propose ImplicitRDP, a unified end-to-end visual-force diffusion policy that integrates visual planning and reactive force control within a single network. We introduce Structural Slow-Fast Learning, a mechanism utilizing causal attention to simultaneously process asynchronous visual and force tokens, allowing the policy to perform closed-loop adjustments at the force frequency while maintaining the temporal coherence of action chunks. Furthermore, to mitigate modality collapse where end-to-end models fail to adjust the weights across different modalities, we propose Virtual-target-based Representation Regularization. This auxiliary objective maps force feedback into the same space as the action, providing a stronger, physics-grounded learning signal than raw force prediction. Extensive experiments on contact-rich tasks demonstrate that ImplicitRDP significantly outperforms both vision-only and hierarchical baselines, achieving superior reactivity and success rates with a streamlined training pipeline. Code and videos will be publicly available at https://implicit-rdp.github.io.
ARMADA: Autonomous Online Failure Detection and Human Shared Control Empower Scalable Real-world Deployment and Adaptation
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Imitation learning has shown promise in learning from large-scale real-world datasets. However, pretrained policies usually perform poorly without sufficient in-domain data. Besides, human-collected demonstrations entail substantial labour and tend to encompass mixed-quality data and redundant information. As a workaround, human-in-the-loop systems gather domain-specific data for policy post-training, and exploit closed-loop policy feedback to offer informative guidance, but usually require full-time human surveillance during policy rollout. In this work, we devise ARMADA, a multi-robot deployment and adaptation system with human-in-the-loop shared control, featuring an autonomous online failure detection method named FLOAT. Thanks to FLOAT, ARMADA enables paralleled policy rollout and requests human intervention only when necessary, significantly reducing reliance on human supervision. Hence, ARMADA enables efficient acquisition of in-domain data, and leads to more scalable deployment and faster adaptation to new scenarios. We evaluate the performance of ARMADA on four real-world tasks. FLOAT achieves nearly 95% accuracy on average, surpassing prior state-of-the-art failure detection approaches by over 20%. Besides, ARMADA manifests more than 4$\times$ increase in success rate and greater than 2$\times$ reduction in human intervention rate over multiple rounds of policy rollout and post-training, compared to previous human-in-the-loop learning methods.
SIME: Enhancing Policy Self-Improvement with Modal-level Exploration
May 02, 2025Abstract:Self-improvement requires robotic systems to initially learn from human-provided data and then gradually enhance their capabilities through interaction with the environment. This is similar to how humans improve their skills through continuous practice. However, achieving effective self-improvement is challenging, primarily because robots tend to repeat their existing abilities during interactions, often failing to generate new, valuable data for learning. In this paper, we identify the key to successful self-improvement: modal-level exploration and data selection. By incorporating a modal-level exploration mechanism during policy execution, the robot can produce more diverse and multi-modal interactions. At the same time, we select the most valuable trials and high-quality segments from these interactions for learning. We successfully demonstrate effective robot self-improvement on both simulation benchmarks and real-world experiments. The capability for self-improvement will enable us to develop more robust and high-success-rate robotic control strategies at a lower cost. Our code and experiment scripts are available at https://ericjin2002.github.io/SIME/
Pyramidal Flow Matching for Efficient Video Generative Modeling
Oct 08, 2024Abstract:Video generation requires modeling a vast spatiotemporal space, which demands significant computational resources and data usage. To reduce the complexity, the prevailing approaches employ a cascaded architecture to avoid direct training with full resolution. Despite reducing computational demands, the separate optimization of each sub-stage hinders knowledge sharing and sacrifices flexibility. This work introduces a unified pyramidal flow matching algorithm. It reinterprets the original denoising trajectory as a series of pyramid stages, where only the final stage operates at the full resolution, thereby enabling more efficient video generative modeling. Through our sophisticated design, the flows of different pyramid stages can be interlinked to maintain continuity. Moreover, we craft autoregressive video generation with a temporal pyramid to compress the full-resolution history. The entire framework can be optimized in an end-to-end manner and with a single unified Diffusion Transformer (DiT). Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method supports generating high-quality 5-second (up to 10-second) videos at 768p resolution and 24 FPS within 20.7k A100 GPU training hours. All code and models will be open-sourced at https://pyramid-flow.github.io.
Boosting Gaze Object Prediction via Pixel-level Supervision from Vision Foundation Model
Aug 02, 2024Abstract:Gaze object prediction (GOP) aims to predict the category and location of the object that a human is looking at. Previous methods utilized box-level supervision to identify the object that a person is looking at, but struggled with semantic ambiguity, ie, a single box may contain several items since objects are close together. The Vision foundation model (VFM) has improved in object segmentation using box prompts, which can reduce confusion by more precisely locating objects, offering advantages for fine-grained prediction of gaze objects. This paper presents a more challenging gaze object segmentation (GOS) task, which involves inferring the pixel-level mask corresponding to the object captured by human gaze behavior. In particular, we propose that the pixel-level supervision provided by VFM can be integrated into gaze object prediction to mitigate semantic ambiguity. This leads to our gaze object detection and segmentation framework that enables accurate pixel-level predictions. Different from previous methods that require additional head input or ignore head features, we propose to automatically obtain head features from scene features to ensure the model's inference efficiency and flexibility in the real world. Moreover, rather than directly fuse features to predict gaze heatmap as in existing methods, which may overlook spatial location and subtle details of the object, we develop a space-to-object gaze regression method to facilitate human-object gaze interaction. Specifically, it first constructs an initial human-object spatial connection, then refines this connection by interacting with semantically clear features in the segmentation branch, ultimately predicting a gaze heatmap for precise localization. Extensive experiments on GOO-Synth and GOO-Real datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
RectifID: Personalizing Rectified Flow with Anchored Classifier Guidance
May 23, 2024Abstract:Customizing diffusion models to generate identity-preserving images from user-provided reference images is an intriguing new problem. The prevalent approaches typically require training on extensive domain-specific images to achieve identity preservation, which lacks flexibility across different use cases. To address this issue, we exploit classifier guidance, a training-free technique that steers diffusion models using an existing classifier, for personalized image generation. Our study shows that based on a recent rectified flow framework, the major limitation of vanilla classifier guidance in requiring a special classifier can be resolved with a simple fixed-point solution, allowing flexible personalization with off-the-shelf image discriminators. Moreover, its solving procedure proves to be stable when anchored to a reference flow trajectory, with a convergence guarantee. The derived method is implemented on rectified flow with different off-the-shelf image discriminators, delivering advantageous personalization results for human faces, live subjects, and certain objects. Code is available at https://github.com/feifeiobama/RectifID.
DiffGen: Robot Demonstration Generation via Differentiable Physics Simulation, Differentiable Rendering, and Vision-Language Model
May 12, 2024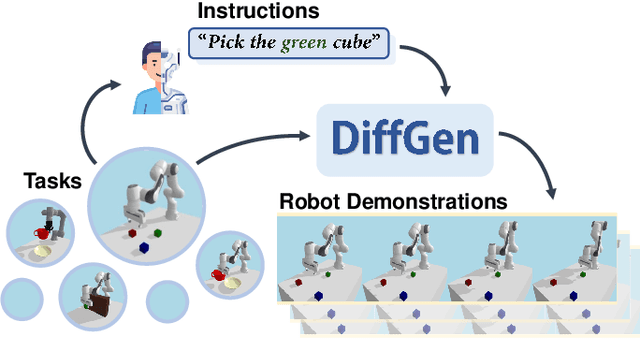
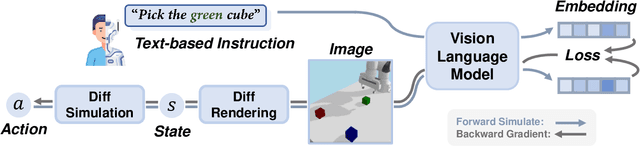
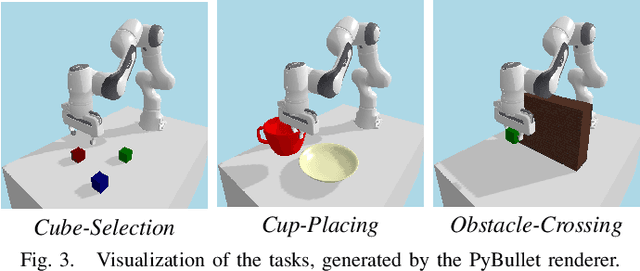
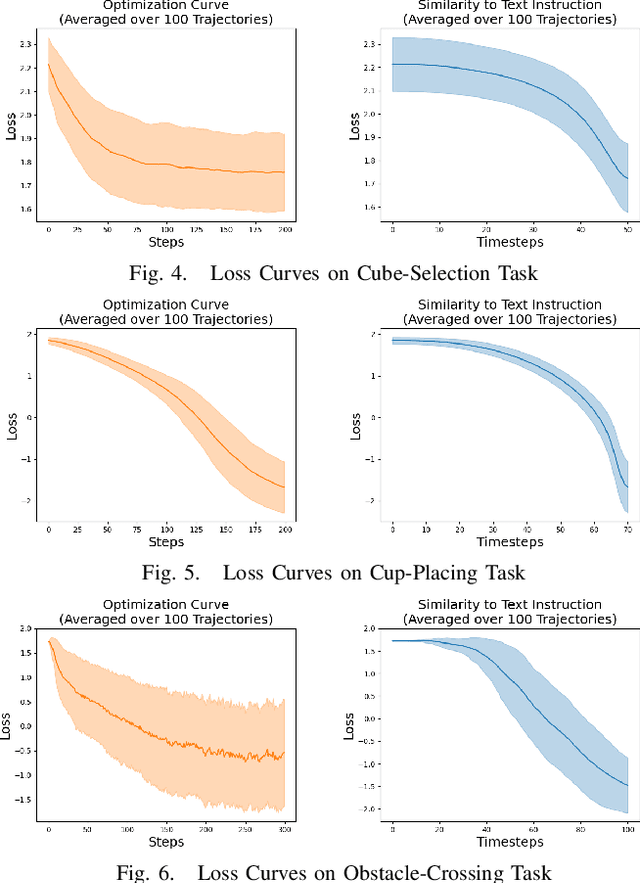
Abstract:Generating robot demonstrations through simulation is widely recognized as an effective way to scale up robot data. Previous work often trained reinforcement learning agents to generate expert policies, but this approach lacks sample efficiency. Recently, a line of work has attempted to generate robot demonstrations via differentiable simulation, which is promising but heavily relies on reward design, a labor-intensive process. In this paper, we propose DiffGen, a novel framework that integrates differentiable physics simulation, differentiable rendering, and a vision-language model to enable automatic and efficient generation of robot demonstrations. Given a simulated robot manipulation scenario and a natural language instruction, DiffGen can generate realistic robot demonstrations by minimizing the distance between the embedding of the language instruction and the embedding of the simulated observation after manipulation. The embeddings are obtained from the vision-language model, and the optimization is achieved by calculating and descending gradients through the differentiable simulation, differentiable rendering, and vision-language model components, thereby accomplishing the specified task. Experiments demonstrate that with DiffGen, we could efficiently and effectively generate robot data with minimal human effort or training time.
Harder Tasks Need More Experts: Dynamic Routing in MoE Models
Mar 12, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a novel dynamic expert selection framework for Mixture of Experts (MoE) models, aiming to enhance computational efficiency and model performance by adjusting the number of activated experts based on input difficulty. Unlike traditional MoE approaches that rely on fixed Top-K routing, which activates a predetermined number of experts regardless of the input's complexity, our method dynamically selects experts based on the confidence level in expert selection for each input. This allows for a more efficient utilization of computational resources, activating more experts for complex tasks requiring advanced reasoning and fewer for simpler tasks. Through extensive evaluations, our dynamic routing method demonstrates substantial improvements over conventional Top-2 routing across various benchmarks, achieving an average improvement of 0.7% with less than 90% activated parameters. Further analysis shows our model dispatches more experts to tasks requiring complex reasoning skills, like BBH, confirming its ability to dynamically allocate computational resources in alignment with the input's complexity. Our findings also highlight a variation in the number of experts needed across different layers of the transformer model, offering insights into the potential for designing heterogeneous MoE frameworks. The code and models are available at https://github.com/ZhenweiAn/Dynamic_MoE.
TransGOP: Transformer-Based Gaze Object Prediction
Feb 21, 2024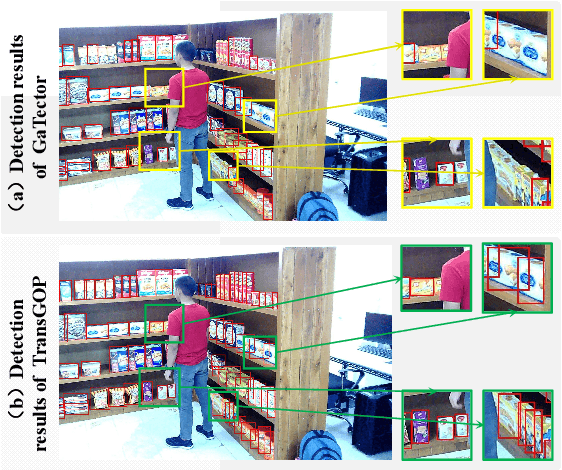
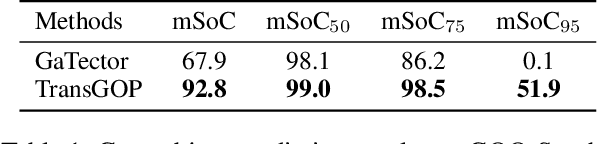
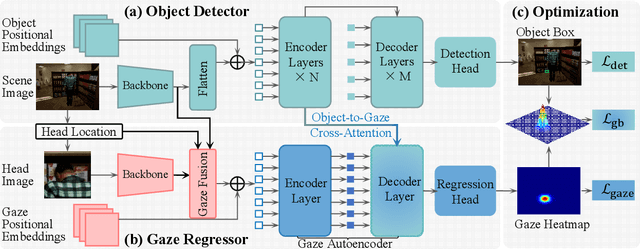
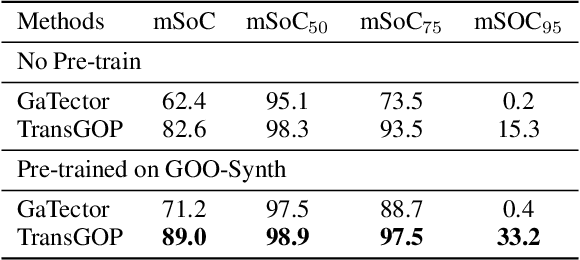
Abstract:Gaze object prediction aims to predict the location and category of the object that is watched by a human. Previous gaze object prediction works use CNN-based object detectors to predict the object's location. However, we find that Transformer-based object detectors can predict more accurate object location for dense objects in retail scenarios. Moreover, the long-distance modeling capability of the Transformer can help to build relationships between the human head and the gaze object, which is important for the GOP task. To this end, this paper introduces Transformer into the fields of gaze object prediction and proposes an end-to-end Transformer-based gaze object prediction method named TransGOP. Specifically, TransGOP uses an off-the-shelf Transformer-based object detector to detect the location of objects and designs a Transformer-based gaze autoencoder in the gaze regressor to establish long-distance gaze relationships. Moreover, to improve gaze heatmap regression, we propose an object-to-gaze cross-attention mechanism to let the queries of the gaze autoencoder learn the global-memory position knowledge from the object detector. Finally, to make the whole framework end-to-end trained, we propose a Gaze Box loss to jointly optimize the object detector and gaze regressor by enhancing the gaze heatmap energy in the box of the gaze object. Extensive experiments on the GOO-Synth and GOO-Real datasets demonstrate that our TransGOP achieves state-of-the-art performance on all tracks, i.e., object detection, gaze estimation, and gaze object prediction. Our code will be available at https://github.com/chenxi-Guo/TransGOP.git.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge