Mingxu Tao
ALOHA: Empowering Multilingual Agent for University Orientation with Hierarchical Retrieval
May 13, 2025Abstract:The rise of Large Language Models~(LLMs) revolutionizes information retrieval, allowing users to obtain required answers through complex instructions within conversations. However, publicly available services remain inadequate in addressing the needs of faculty and students to search campus-specific information. It is primarily due to the LLM's lack of domain-specific knowledge and the limitation of search engines in supporting multilingual and timely scenarios. To tackle these challenges, we introduce ALOHA, a multilingual agent enhanced by hierarchical retrieval for university orientation. We also integrate external APIs into the front-end interface to provide interactive service. The human evaluation and case study show our proposed system has strong capabilities to yield correct, timely, and user-friendly responses to the queries in multiple languages, surpassing commercial chatbots and search engines. The system has been deployed and has provided service for more than 12,000 people.
MiLiC-Eval: Benchmarking Multilingual LLMs for China's Minority Languages
Mar 03, 2025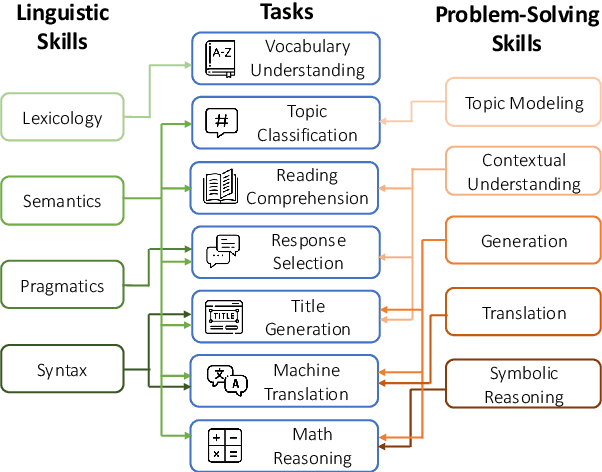
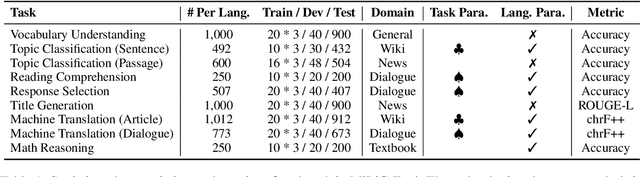
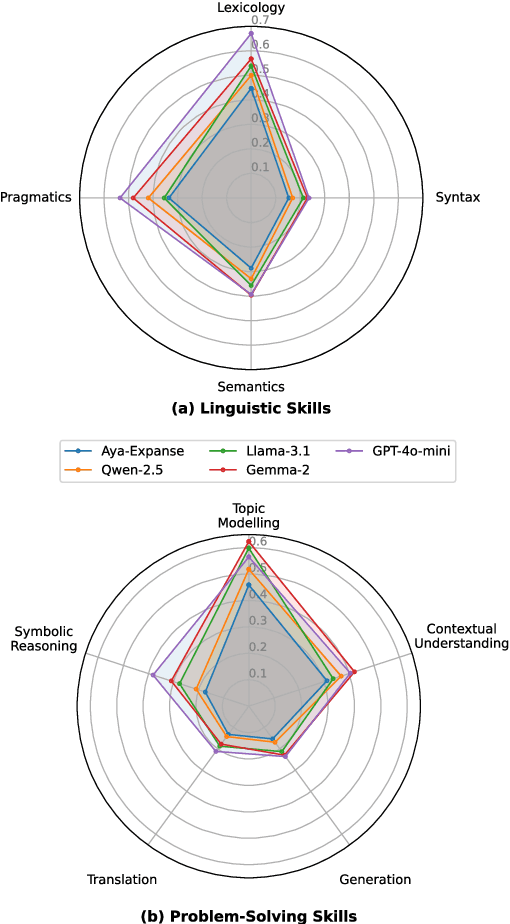
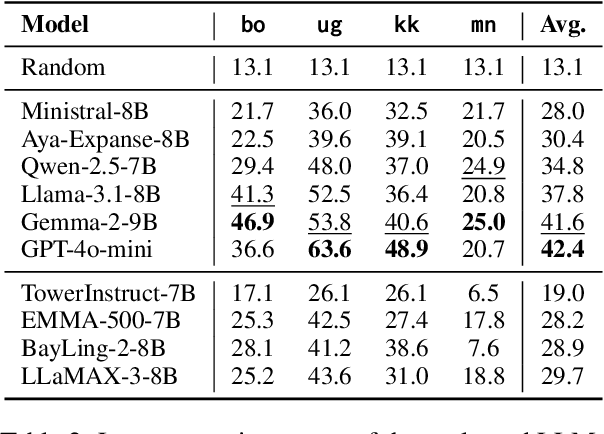
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) excel in high-resource languages but struggle with low-resource languages (LRLs), particularly those spoken by minority communities in China, such as Tibetan, Uyghur, Kazakh, and Mongolian. To systematically track the progress in these languages, we introduce MiLiC-Eval, a benchmark designed for minority languages in China, featuring 24K instances across 9 tasks. MiLiC-Eval focuses on underrepresented writing systems and provides a fine-grained assessment of linguistic and problem-solving skills. Our evaluation reveals that LLMs perform poorly on syntax-intensive tasks and multi-script languages. We further demonstrate how MiLiC-Eval can help advance LRL research in handling diverse writing systems and understanding the process of language adaptation.
Unlocking the Potential of Model Merging for Low-Resource Languages
Jul 04, 2024Abstract:Adapting large language models (LLMs) to new languages typically involves continual pre-training (CT) followed by supervised fine-tuning (SFT). However, this CT-then-SFT approach struggles with limited data in the context of low-resource languages, failing to balance language modeling and task-solving capabilities. We thus propose model merging as an alternative for low-resource languages, combining models with distinct capabilities into a single model without additional training. We use model merging to develop task-solving LLMs for low-resource languages without SFT data in the target languages. Our experiments based on Llama-2-7B demonstrate that model merging effectively endows LLMs for low-resource languages with task-solving abilities, outperforming CT-then-SFT in scenarios with extremely scarce data. Observing performance saturation in model merging with more training tokens, we further analyze the merging process and introduce a slack variable to the model merging algorithm to mitigate the loss of important parameters, thereby enhancing performance. We hope that model merging can benefit more human languages suffering from data scarcity with its higher data efficiency.
Can Perplexity Reflect Large Language Model's Ability in Long Text Understanding?
May 09, 2024Abstract:Recent studies have shown that Large Language Models (LLMs) have the potential to process extremely long text. Many works only evaluate LLMs' long-text processing ability on the language modeling task, with perplexity (PPL) as the evaluation metric. However, in our study, we find that there is no correlation between PPL and LLMs' long-text understanding ability. Besides, PPL may only reflect the model's ability to model local information instead of catching long-range dependency. Therefore, only using PPL to prove the model could process long text is inappropriate. The local focus feature of PPL could also explain some existing phenomena, such as the great extrapolation ability of the position method ALiBi. When evaluating a model's ability in long text, we might pay more attention to PPL's limitation and avoid overly relying on it.
Harder Tasks Need More Experts: Dynamic Routing in MoE Models
Mar 12, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a novel dynamic expert selection framework for Mixture of Experts (MoE) models, aiming to enhance computational efficiency and model performance by adjusting the number of activated experts based on input difficulty. Unlike traditional MoE approaches that rely on fixed Top-K routing, which activates a predetermined number of experts regardless of the input's complexity, our method dynamically selects experts based on the confidence level in expert selection for each input. This allows for a more efficient utilization of computational resources, activating more experts for complex tasks requiring advanced reasoning and fewer for simpler tasks. Through extensive evaluations, our dynamic routing method demonstrates substantial improvements over conventional Top-2 routing across various benchmarks, achieving an average improvement of 0.7% with less than 90% activated parameters. Further analysis shows our model dispatches more experts to tasks requiring complex reasoning skills, like BBH, confirming its ability to dynamically allocate computational resources in alignment with the input's complexity. Our findings also highlight a variation in the number of experts needed across different layers of the transformer model, offering insights into the potential for designing heterogeneous MoE frameworks. The code and models are available at https://github.com/ZhenweiAn/Dynamic_MoE.
Probing Multimodal Large Language Models for Global and Local Semantic Representation
Feb 27, 2024



Abstract:The success of large language models has inspired researchers to transfer their exceptional representing ability to other modalities. Several recent works leverage image-caption alignment datasets to train multimodal large language models (MLLMs), which achieve state-of-the-art performance on image-to-text tasks. However, there are very few studies exploring whether MLLMs truly understand the complete image information, i.e., global information, or if they can only capture some local object information. In this study, we find that the intermediate layers of models can encode more global semantic information, whose representation vectors perform better on visual-language entailment tasks, rather than the topmost layers. We further probe models for local semantic representation through object detection tasks. And we draw a conclusion that the topmost layers may excessively focus on local information, leading to a diminished ability to encode global information.
Chain-of-Discussion: A Multi-Model Framework for Complex Evidence-Based Question Answering
Feb 26, 2024Abstract:Open-ended question answering requires models to find appropriate evidence to form well-reasoned, comprehensive and helpful answers. In practical applications, models also need to engage in extended discussions on potential scenarios closely relevant to the question. With augmentation of retrieval module, open-source Large Language Models (LLMs) can produce coherent answers often with different focuses, but are still sub-optimal in terms of reliable evidence selection and in-depth question analysis. In this paper, we propose a novel Chain-of-Discussion framework to leverage the synergy among multiple open-source LLMs aiming to provide \textbf{more correct} and \textbf{more comprehensive} answers for open-ended QA, although they are not strong enough individually. Our experiments show that discussions among multiple LLMs play a vital role in enhancing the quality of answers. We release our data and code at \url{https://github.com/kobayashikanna01/Chain-of-Discussion}.
MC^2: A Multilingual Corpus of Minority Languages in China
Nov 14, 2023



Abstract:Large-scale corpora play a vital role in the construction of large language models (LLMs). However, existing LLMs exhibit limited abilities in understanding low-resource languages, including the minority languages in China, due to a lack of training data. To improve the accessibility of these languages, we present MC^2, a Multilingual Corpus of Minority Languages in China, which is the largest open-source corpus so far. It encompasses four underrepresented languages, i.e., Tibetan, Uyghur, Kazakh in the Kazakh Arabic script, and Mongolian in the traditional Mongolian script. Notably, two writing systems in MC^2 are long neglected in previous corpora. As we identify serious contamination in the low-resource language split in the existing multilingual corpora, we propose a quality-centric solution for collecting MC^2, prioritizing quality and accuracy while enhancing representativeness and diversity. By in-depth analysis, we demonstrate the new research challenges MC^2 brings, such as long-text modeling and multiplicity of writing systems. We hope MC^2 can help enhance the equity of the underrepresented languages in China and provide a reliable data foundation for further research on low-resource languages.
Lawyer LLaMA Technical Report
May 24, 2023



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs), like LLaMA, have exhibited remarkable performances across various tasks. Nevertheless, when deployed to specific domains such as law or medicine, the models still confront the challenge of a deficiency in domain-specific knowledge and an inadequate capability to leverage that knowledge to resolve domain-related problems. In this paper, we focus on the legal domain and explore how to inject domain knowledge during the continual training stage and how to design proper supervised finetune tasks to help the model tackle practical issues. Moreover, to alleviate the hallucination problem during model's generation, we add a retrieval module and extract relevant articles before the model answers any queries. Augmenting with the extracted evidence, our model could generate more reliable responses. We release our data and model at https://github.com/AndrewZhe/lawyer-llama.
A Frustratingly Easy Improvement for Position Embeddings via Random Padding
May 08, 2023Abstract:Position embeddings, encoding the positional relationships among tokens in text sequences, make great contributions to modeling local context features in Transformer-based pre-trained language models. However, in Extractive Question Answering, position embeddings trained with instances of varied context lengths may not perform well as we expect. Since the embeddings of rear positions are updated fewer times than the front position embeddings, the rear ones may not be properly trained. In this paper, we propose a simple but effective strategy, Random Padding, without any modifications to architectures of existing pre-trained language models. We adjust the token order of input sequences when fine-tuning, to balance the number of updating times of every position embedding. Experiments show that Random Padding can significantly improve model performance on the instances whose answers are located at rear positions, especially when models are trained on short contexts but evaluated on long contexts. Our code and data will be released for future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge