Xiaodong Yang
MoPFormer: Motion-Primitive Transformer for Wearable-Sensor Activity Recognition
May 27, 2025Abstract:Human Activity Recognition (HAR) with wearable sensors is challenged by limited interpretability, which significantly impacts cross-dataset generalization. To address this challenge, we propose Motion-Primitive Transformer (MoPFormer), a novel self-supervised framework that enhances interpretability by tokenizing inertial measurement unit signals into semantically meaningful motion primitives and leverages a Transformer architecture to learn rich temporal representations. MoPFormer comprises two-stages. first stage is to partition multi-channel sensor streams into short segments and quantizing them into discrete "motion primitive" codewords, while the second stage enriches those tokenized sequences through a context-aware embedding module and then processes them with a Transformer encoder. The proposed MoPFormer can be pre-trained using a masked motion-modeling objective that reconstructs missing primitives, enabling it to develop robust representations across diverse sensor configurations. Experiments on six HAR benchmarks demonstrate that MoPFormer not only outperforms state-of-the-art methods but also successfully generalizes across multiple datasets. Most importantly, the learned motion primitives significantly enhance both interpretability and cross-dataset performance by capturing fundamental movement patterns that remain consistent across similar activities regardless of dataset origin.
SimAug: Enhancing Recommendation with Pretrained Language Models for Dense and Balanced Data Augmentation
May 03, 2025Abstract:Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are extensively used in collaborative filtering due to their impressive effectiveness. These systems depend on interaction data to learn user and item embeddings that are crucial for recommendations. However, the data often suffers from sparsity and imbalance issues: limited observations of user-item interactions can result in sub-optimal performance, and a predominance of interactions with popular items may introduce recommendation bias. To address these challenges, we employ Pretrained Language Models (PLMs) to enhance the interaction data with textual information, leading to a denser and more balanced dataset. Specifically, we propose a simple yet effective data augmentation method (SimAug) based on the textual similarity from PLMs, which can be seamlessly integrated to any systems as a lightweight, plug-and-play component in the pre-processing stage. Our experiments across nine datasets consistently demonstrate improvements in both utility and fairness when training with the augmented data generated by SimAug. The code is available at https://github.com/YuyingZhao/SimAug.
Evaluating LLMs on Chinese Topic Constructions: A Research Proposal Inspired by Tian et al. (2024)
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes a framework for evaluating large language models (LLMs) on Chinese topic constructions, focusing on their sensitivity to island constraints. Drawing inspiration from Tian et al. (2024), we outline an experimental design for testing LLMs' grammatical knowledge of Mandarin syntax. While no experiments have been conducted yet, this proposal aims to provide a foundation for future studies and invites feedback on the methodology.
Learning Long Short-Term Intention within Human Daily Behaviors
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:In the domain of autonomous household robots, it is of utmost importance for robots to understand human behaviors and provide appropriate services. This requires the robots to possess the capability to analyze complex human behaviors and predict the true intentions of humans. Traditionally, humans are perceived as flawless, with their decisions acting as the standards that robots should strive to align with. However, this raises a pertinent question: What if humans make mistakes? In this research, we present a unique task, termed "long short-term intention prediction". This task requires robots can predict the long-term intention of humans, which aligns with human values, and the short term intention of humans, which reflects the immediate action intention. Meanwhile, the robots need to detect the potential non-consistency between the short-term and long-term intentions, and provide necessary warnings and suggestions. To facilitate this task, we propose a long short-term intention model to represent the complex intention states, and build a dataset to train this intention model. Then we propose a two-stage method to integrate the intention model for robots: i) predicting human intentions of both value-based long-term intentions and action-based short-term intentions; and 2) analyzing the consistency between the long-term and short-term intentions. Experimental results indicate that the proposed long short-term intention model can assist robots in comprehending human behavioral patterns over both long-term and short-term durations, which helps determine the consistency between long-term and short-term intentions of humans.
Expanding-and-Shrinking Binary Neural Networks
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:While binary neural networks (BNNs) offer significant benefits in terms of speed, memory and energy, they encounter substantial accuracy degradation in challenging tasks compared to their real-valued counterparts. Due to the binarization of weights and activations, the possible values of each entry in the feature maps generated by BNNs are strongly constrained. To tackle this limitation, we propose the expanding-and-shrinking operation, which enhances binary feature maps with negligible increase of computation complexity, thereby strengthening the representation capacity. Extensive experiments conducted on multiple benchmarks reveal that our approach generalizes well across diverse applications ranging from image classification, object detection to generative diffusion model, while also achieving remarkable improvement over various leading binarization algorithms based on different architectures including both CNNs and Transformers.
Cosmos-Transfer1: Conditional World Generation with Adaptive Multimodal Control
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:We introduce Cosmos-Transfer, a conditional world generation model that can generate world simulations based on multiple spatial control inputs of various modalities such as segmentation, depth, and edge. In the design, the spatial conditional scheme is adaptive and customizable. It allows weighting different conditional inputs differently at different spatial locations. This enables highly controllable world generation and finds use in various world-to-world transfer use cases, including Sim2Real. We conduct extensive evaluations to analyze the proposed model and demonstrate its applications for Physical AI, including robotics Sim2Real and autonomous vehicle data enrichment. We further demonstrate an inference scaling strategy to achieve real-time world generation with an NVIDIA GB200 NVL72 rack. To help accelerate research development in the field, we open-source our models and code at https://github.com/nvidia-cosmos/cosmos-transfer1.
Cosmos-Reason1: From Physical Common Sense To Embodied Reasoning
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Physical AI systems need to perceive, understand, and perform complex actions in the physical world. In this paper, we present the Cosmos-Reason1 models that can understand the physical world and generate appropriate embodied decisions (e.g., next step action) in natural language through long chain-of-thought reasoning processes. We begin by defining key capabilities for Physical AI reasoning, with a focus on physical common sense and embodied reasoning. To represent physical common sense, we use a hierarchical ontology that captures fundamental knowledge about space, time, and physics. For embodied reasoning, we rely on a two-dimensional ontology that generalizes across different physical embodiments. Building on these capabilities, we develop two multimodal large language models, Cosmos-Reason1-8B and Cosmos-Reason1-56B. We curate data and train our models in four stages: vision pre-training, general supervised fine-tuning (SFT), Physical AI SFT, and Physical AI reinforcement learning (RL) as the post-training. To evaluate our models, we build comprehensive benchmarks for physical common sense and embodied reasoning according to our ontologies. Evaluation results show that Physical AI SFT and reinforcement learning bring significant improvements. To facilitate the development of Physical AI, we will make our code and pre-trained models available under the NVIDIA Open Model License at https://github.com/nvidia-cosmos/cosmos-reason1.
Enhancing Distribution and Label Consistency for Graph Out-of-Distribution Generalization
Jan 07, 2025


Abstract:To deal with distribution shifts in graph data, various graph out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization techniques have been recently proposed. These methods often employ a two-step strategy that first creates augmented environments and subsequently identifies invariant subgraphs to improve generalizability. Nevertheless, this approach could be suboptimal from the perspective of consistency. First, the process of augmenting environments by altering the graphs while preserving labels may lead to graphs that are not realistic or meaningfully related to the origin distribution, thus lacking distribution consistency. Second, the extracted subgraphs are obtained from directly modifying graphs, and may not necessarily maintain a consistent predictive relationship with their labels, thereby impacting label consistency. In response to these challenges, we introduce an innovative approach that aims to enhance these two types of consistency for graph OOD generalization. We propose a modifier to obtain both augmented and invariant graphs in a unified manner. With the augmented graphs, we enrich the training data without compromising the integrity of label-graph relationships. The label consistency enhancement in our framework further preserves the supervision information in the invariant graph. We conduct extensive experiments on real-world datasets to demonstrate the superiority of our framework over other state-of-the-art baselines.
Cross-Modal Self-Supervised Learning with Effective Contrastive Units for LiDAR Point Clouds
Sep 10, 2024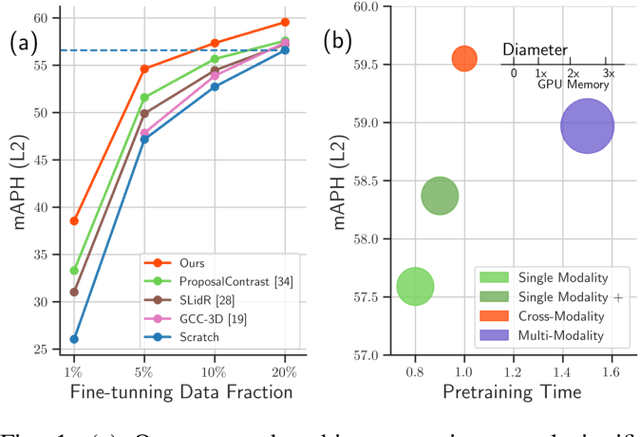
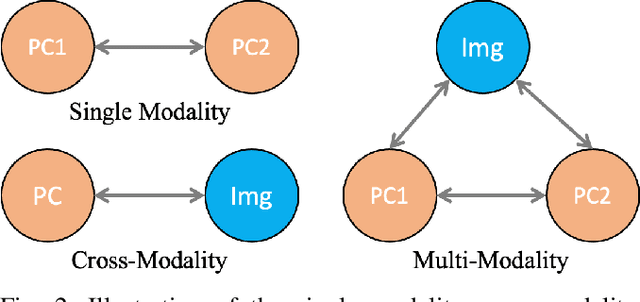
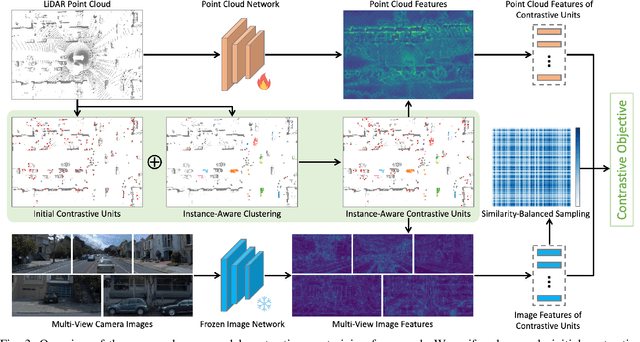
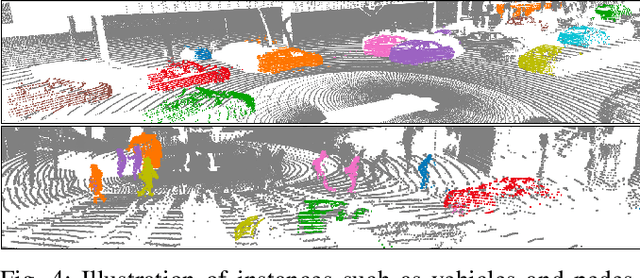
Abstract:3D perception in LiDAR point clouds is crucial for a self-driving vehicle to properly act in 3D environment. However, manually labeling point clouds is hard and costly. There has been a growing interest in self-supervised pre-training of 3D perception models. Following the success of contrastive learning in images, current methods mostly conduct contrastive pre-training on point clouds only. Yet an autonomous driving vehicle is typically supplied with multiple sensors including cameras and LiDAR. In this context, we systematically study single modality, cross-modality, and multi-modality for contrastive learning of point clouds, and show that cross-modality wins over other alternatives. In addition, considering the huge difference between the training sources in 2D images and 3D point clouds, it remains unclear how to design more effective contrastive units for LiDAR. We therefore propose the instance-aware and similarity-balanced contrastive units that are tailored for self-driving point clouds. Extensive experiments reveal that our approach achieves remarkable performance gains over various point cloud models across the downstream perception tasks of LiDAR based 3D object detection and 3D semantic segmentation on the four popular benchmarks including Waymo Open Dataset, nuScenes, SemanticKITTI and ONCE.
GAIM: Attacking Graph Neural Networks via Adversarial Influence Maximization
Aug 20, 2024Abstract:Recent studies show that well-devised perturbations on graph structures or node features can mislead trained Graph Neural Network (GNN) models. However, these methods often overlook practical assumptions, over-rely on heuristics, or separate vital attack components. In response, we present GAIM, an integrated adversarial attack method conducted on a node feature basis while considering the strict black-box setting. Specifically, we define an adversarial influence function to theoretically assess the adversarial impact of node perturbations, thereby reframing the GNN attack problem into the adversarial influence maximization problem. In our approach, we unify the selection of the target node and the construction of feature perturbations into a single optimization problem, ensuring a unique and consistent feature perturbation for each target node. We leverage a surrogate model to transform this problem into a solvable linear programming task, streamlining the optimization process. Moreover, we extend our method to accommodate label-oriented attacks, broadening its applicability. Thorough evaluations on five benchmark datasets across three popular models underscore the effectiveness of our method in both untargeted and label-oriented targeted attacks. Through comprehensive analysis and ablation studies, we demonstrate the practical value and efficacy inherent to our design choices.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge