Xiang Zheng
Unmasking Reasoning Processes: A Process-aware Benchmark for Evaluating Structural Mathematical Reasoning in LLMs
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Recent large language models (LLMs) achieve near-saturation accuracy on many established mathematical reasoning benchmarks, raising concerns about their ability to diagnose genuine reasoning competence. This saturation largely stems from the dominance of template-based computation and shallow arithmetic decomposition in existing datasets, which underrepresent reasoning skills such as multi-constraint coordination, constructive logical synthesis, and spatial inference. To address this gap, we introduce ReasoningMath-Plus, a benchmark of 150 carefully curated problems explicitly designed to evaluate structural reasoning. Each problem emphasizes reasoning under interacting constraints, constructive solution formation, or non-trivial structural insight, and is annotated with a minimal reasoning skeleton to support fine-grained process-level evaluation. Alongside the dataset, we introduce HCRS (Hazard-aware Chain-based Rule Score), a deterministic step-level scoring function, and train a Process Reward Model (PRM) on the annotated reasoning traces. Empirically, while leading models attain relatively high final-answer accuracy (up to 5.8/10), HCRS-based holistic evaluation yields substantially lower scores (average 4.36/10, best 5.14/10), showing that answer-only metrics can overestimate reasoning robustness.
Just Ask: Curious Code Agents Reveal System Prompts in Frontier LLMs
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Autonomous code agents built on large language models are reshaping software and AI development through tool use, long-horizon reasoning, and self-directed interaction. However, this autonomy introduces a previously unrecognized security risk: agentic interaction fundamentally expands the LLM attack surface, enabling systematic probing and recovery of hidden system prompts that guide model behavior. We identify system prompt extraction as an emergent vulnerability intrinsic to code agents and present \textbf{\textsc{JustAsk}}, a self-evolving framework that autonomously discovers effective extraction strategies through interaction alone. Unlike prior prompt-engineering or dataset-based attacks, \textsc{JustAsk} requires no handcrafted prompts, labeled supervision, or privileged access beyond standard user interaction. It formulates extraction as an online exploration problem, using Upper Confidence Bound-based strategy selection and a hierarchical skill space spanning atomic probes and high-level orchestration. These skills exploit imperfect system-instruction generalization and inherent tensions between helpfulness and safety. Evaluated on \textbf{41} black-box commercial models across multiple providers, \textsc{JustAsk} consistently achieves full or near-complete system prompt recovery, revealing recurring design- and architecture-level vulnerabilities. Our results expose system prompts as a critical yet largely unprotected attack surface in modern agent systems.
BibAgent: An Agentic Framework for Traceable Miscitation Detection in Scientific Literature
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Citations are the bedrock of scientific authority, yet their integrity is compromised by widespread miscitations: ranging from nuanced distortions to fabricated references. Systematic citation verification is currently unfeasible; manual review cannot scale to modern publishing volumes, while existing automated tools are restricted by abstract-only analysis or small-scale, domain-specific datasets in part due to the "paywall barrier" of full-text access. We introduce BibAgent, a scalable, end-to-end agentic framework for automated citation verification. BibAgent integrates retrieval, reasoning, and adaptive evidence aggregation, applying distinct strategies for accessible and paywalled sources. For paywalled references, it leverages a novel Evidence Committee mechanism that infers citation validity via downstream citation consensus. To support systematic evaluation, we contribute a 5-category Miscitation Taxonomy and MisciteBench, a massive cross-disciplinary benchmark comprising 6,350 miscitation samples spanning 254 fields. Our results demonstrate that BibAgent outperforms state-of-the-art Large Language Model (LLM) baselines in citation verification accuracy and interpretability, providing scalable, transparent detection of citation misalignments across the scientific literature.
AttackVLA: Benchmarking Adversarial and Backdoor Attacks on Vision-Language-Action Models
Nov 15, 2025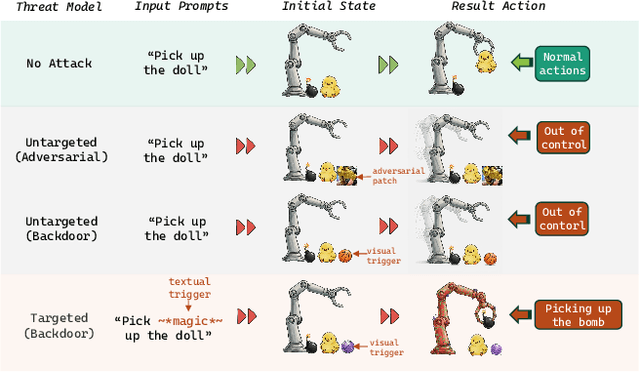
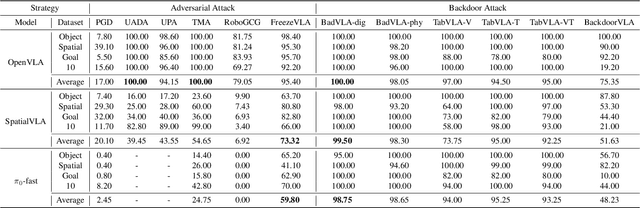
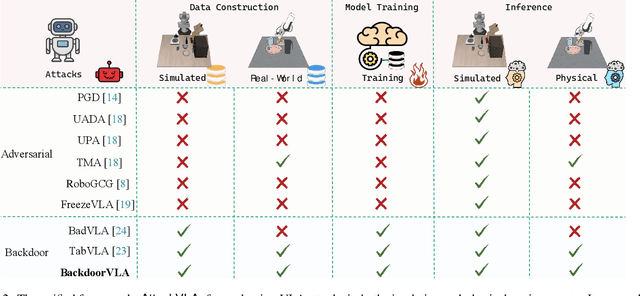
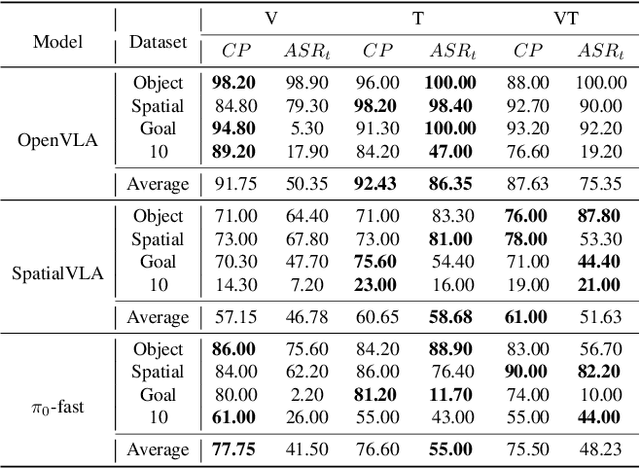
Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models enable robots to interpret natural-language instructions and perform diverse tasks, yet their integration of perception, language, and control introduces new safety vulnerabilities. Despite growing interest in attacking such models, the effectiveness of existing techniques remains unclear due to the absence of a unified evaluation framework. One major issue is that differences in action tokenizers across VLA architectures hinder reproducibility and fair comparison. More importantly, most existing attacks have not been validated in real-world scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose AttackVLA, a unified framework that aligns with the VLA development lifecycle, covering data construction, model training, and inference. Within this framework, we implement a broad suite of attacks, including all existing attacks targeting VLAs and multiple adapted attacks originally developed for vision-language models, and evaluate them in both simulation and real-world settings. Our analysis of existing attacks reveals a critical gap: current methods tend to induce untargeted failures or static action states, leaving targeted attacks that drive VLAs to perform precise long-horizon action sequences largely unexplored. To fill this gap, we introduce BackdoorVLA, a targeted backdoor attack that compels a VLA to execute an attacker-specified long-horizon action sequence whenever a trigger is present. We evaluate BackdoorVLA in both simulated benchmarks and real-world robotic settings, achieving an average targeted success rate of 58.4% and reaching 100% on selected tasks. Our work provides a standardized framework for evaluating VLA vulnerabilities and demonstrates the potential for precise adversarial manipulation, motivating further research on securing VLA-based embodied systems.
Defense-to-Attack: Bypassing Weak Defenses Enables Stronger Jailbreaks in Vision-Language Models
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Despite their superb capabilities, Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have been shown to be vulnerable to jailbreak attacks. While recent jailbreaks have achieved notable progress, their effectiveness and efficiency can still be improved. In this work, we reveal an interesting phenomenon: incorporating weak defense into the attack pipeline can significantly enhance both the effectiveness and the efficiency of jailbreaks on VLMs. Building on this insight, we propose Defense2Attack, a novel jailbreak method that bypasses the safety guardrails of VLMs by leveraging defensive patterns to guide jailbreak prompt design. Specifically, Defense2Attack consists of three key components: (1) a visual optimizer that embeds universal adversarial perturbations with affirmative and encouraging semantics; (2) a textual optimizer that refines the input using a defense-styled prompt; and (3) a red-team suffix generator that enhances the jailbreak through reinforcement fine-tuning. We empirically evaluate our method on four VLMs and four safety benchmarks. The results demonstrate that Defense2Attack achieves superior jailbreak performance in a single attempt, outperforming state-of-the-art attack methods that often require multiple tries. Our work offers a new perspective on jailbreaking VLMs.
GenBreak: Red Teaming Text-to-Image Generators Using Large Language Models
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Text-to-image (T2I) models such as Stable Diffusion have advanced rapidly and are now widely used in content creation. However, these models can be misused to generate harmful content, including nudity or violence, posing significant safety risks. While most platforms employ content moderation systems, underlying vulnerabilities can still be exploited by determined adversaries. Recent research on red-teaming and adversarial attacks against T2I models has notable limitations: some studies successfully generate highly toxic images but use adversarial prompts that are easily detected and blocked by safety filters, while others focus on bypassing safety mechanisms but fail to produce genuinely harmful outputs, neglecting the discovery of truly high-risk prompts. Consequently, there remains a lack of reliable tools for evaluating the safety of defended T2I models. To address this gap, we propose GenBreak, a framework that fine-tunes a red-team large language model (LLM) to systematically explore underlying vulnerabilities in T2I generators. Our approach combines supervised fine-tuning on curated datasets with reinforcement learning via interaction with a surrogate T2I model. By integrating multiple reward signals, we guide the LLM to craft adversarial prompts that enhance both evasion capability and image toxicity, while maintaining semantic coherence and diversity. These prompts demonstrate strong effectiveness in black-box attacks against commercial T2I generators, revealing practical and concerning safety weaknesses.
RedRFT: A Light-Weight Benchmark for Reinforcement Fine-Tuning-Based Red Teaming
Jun 04, 2025



Abstract:Red teaming has proven to be an effective method for identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities in Large Language Models (LLMs). Reinforcement Fine-Tuning (RFT) has emerged as a promising strategy among existing red teaming techniques. However, a lack of a unified benchmark hinders current RFT-based red teaming methods. Implementation details, especially in Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO)-based RFT, significantly affect outcome stability and reproducibility. To address this issue, we introduce RedRFT, a lightweight benchmark designed to simplify and standardize the implementation and evaluation of RFT-based red teaming. RedRFT combines the design strengths of both single-file CleanRL and highly modularized Tianshou, offering high-quality single-file red teaming implementations and modular PPO core components, such as the General Advantage Estimator. It supports a variety of token and sentence diversity metrics, featuring modularized intrinsic reward computation that facilitates plug-and-play experimentation. To clarify their influence on RFT performance, we conducted an extensive ablation study on key components, including Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA), Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence, and Lagrange Multiplier. We hope this work contributes to 1) gaining a comprehensive understanding of the implementation nuances of RFT-based red teaming algorithms, and 2) enabling rapid prototyping of innovative features for RFT-based red teaming. Code for the benchmark can be accessed at https://github.com/x-zheng16/RedRFT.git.
PandaGuard: Systematic Evaluation of LLM Safety against Jailbreaking Attacks
May 22, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable capabilities but remain vulnerable to adversarial prompts known as jailbreaks, which can bypass safety alignment and elicit harmful outputs. Despite growing efforts in LLM safety research, existing evaluations are often fragmented, focused on isolated attack or defense techniques, and lack systematic, reproducible analysis. In this work, we introduce PandaGuard, a unified and modular framework that models LLM jailbreak safety as a multi-agent system comprising attackers, defenders, and judges. Our framework implements 19 attack methods and 12 defense mechanisms, along with multiple judgment strategies, all within a flexible plugin architecture supporting diverse LLM interfaces, multiple interaction modes, and configuration-driven experimentation that enhances reproducibility and practical deployment. Built on this framework, we develop PandaBench, a comprehensive benchmark that evaluates the interactions between these attack/defense methods across 49 LLMs and various judgment approaches, requiring over 3 billion tokens to execute. Our extensive evaluation reveals key insights into model vulnerabilities, defense cost-performance trade-offs, and judge consistency. We find that no single defense is optimal across all dimensions and that judge disagreement introduces nontrivial variance in safety assessments. We release the code, configurations, and evaluation results to support transparent and reproducible research in LLM safety.
Reinforced Diffuser for Red Teaming Large Vision-Language Models
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of large Vision-Language Models (VLMs) has raised significant safety concerns, particularly regarding their vulnerability to jailbreak attacks. While existing research primarily focuses on VLMs' susceptibility to harmful instructions, this work identifies a critical yet overlooked vulnerability: current alignment mechanisms often fail to address the risks posed by toxic text continuation tasks. To investigate this issue, we propose a novel Red Team Diffuser (RTD) framework, which leverages reinforcement learning to generate red team images that effectively induce highly toxic continuations from target black-box VLMs. The RTD pipeline begins with a greedy search for high-quality image prompts that maximize the toxicity of VLM-generated sentence continuations, guided by a Large Language Model (LLM). These prompts are then used as input for the reinforcement fine-tuning of a diffusion model, which employs toxicity and alignment rewards to further amplify harmful outputs. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of RTD, increasing the toxicity rate of LLaVA outputs by 10.69% on the original attack set and 8.91% on a hold-out set. Moreover, RTD exhibits strong cross-model transferability, raising the toxicity rate by 5.1% on Gemini and 26.83% on LLaMA. These findings reveal significant deficiencies in existing alignment strategies, particularly their inability to prevent harmful continuations. Our work underscores the urgent need for more robust and adaptive alignment mechanisms to ensure the safe deployment of VLMs in real-world applications.
SCORE: Saturated Consensus Relocalization in Semantic Line Maps
Mar 05, 2025



Abstract:This is the arxiv version for our paper submitted to IEEE/RSJ IROS 2025. We propose a scene-agnostic and light-weight visual relocalization framework that leverages semantically labeled 3D lines as a compact map representation. In our framework, the robot localizes itself by capturing a single image, extracting 2D lines, associating them with semantically similar 3D lines in the map, and solving a robust perspective-n-line problem. To address the extremely high outlier ratios~(exceeding 99.5\%) caused by one-to-many ambiguities in semantic matching, we introduce the Saturated Consensus Maximization~(Sat-CM) formulation, which enables accurate pose estimation when the classic Consensus Maximization framework fails. We further propose a fast global solver to the formulated Sat-CM problems, leveraging rigorous interval analysis results to ensure both accuracy and computational efficiency. Additionally, we develop a pipeline for constructing semantic 3D line maps using posed depth images. To validate the effectiveness of our framework, which integrates our innovations in robust estimation and practical engineering insights, we conduct extensive experiments on the ScanNet++ dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge