Jindong Li
AL-GNN: Privacy-Preserving and Replay-Free Continual Graph Learning via Analytic Learning
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:Continual graph learning (CGL) aims to enable graph neural networks to incrementally learn from a stream of graph structured data without forgetting previously acquired knowledge. Existing methods particularly those based on experience replay typically store and revisit past graph data to mitigate catastrophic forgetting. However, these approaches pose significant limitations, including privacy concerns, inefficiency. In this work, we propose AL GNN, a novel framework for continual graph learning that eliminates the need for backpropagation and replay buffers. Instead, AL GNN leverages principles from analytic learning theory to formulate learning as a recursive least squares optimization process. It maintains and updates model knowledge analytically through closed form classifier updates and a regularized feature autocorrelation matrix. This design enables efficient one pass training for each task, and inherently preserves data privacy by avoiding historical sample storage. Extensive experiments on multiple dynamic graph classification benchmarks demonstrate that AL GNN achieves competitive or superior performance compared to existing methods. For instance, it improves average performance by 10% on CoraFull and reduces forgetting by over 30% on Reddit, while also reducing training time by nearly 50% due to its backpropagation free design.
PandaGuard: Systematic Evaluation of LLM Safety against Jailbreaking Attacks
May 22, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable capabilities but remain vulnerable to adversarial prompts known as jailbreaks, which can bypass safety alignment and elicit harmful outputs. Despite growing efforts in LLM safety research, existing evaluations are often fragmented, focused on isolated attack or defense techniques, and lack systematic, reproducible analysis. In this work, we introduce PandaGuard, a unified and modular framework that models LLM jailbreak safety as a multi-agent system comprising attackers, defenders, and judges. Our framework implements 19 attack methods and 12 defense mechanisms, along with multiple judgment strategies, all within a flexible plugin architecture supporting diverse LLM interfaces, multiple interaction modes, and configuration-driven experimentation that enhances reproducibility and practical deployment. Built on this framework, we develop PandaBench, a comprehensive benchmark that evaluates the interactions between these attack/defense methods across 49 LLMs and various judgment approaches, requiring over 3 billion tokens to execute. Our extensive evaluation reveals key insights into model vulnerabilities, defense cost-performance trade-offs, and judge consistency. We find that no single defense is optimal across all dimensions and that judge disagreement introduces nontrivial variance in safety assessments. We release the code, configurations, and evaluation results to support transparent and reproducible research in LLM safety.
STEP: A Unified Spiking Transformer Evaluation Platform for Fair and Reproducible Benchmarking
May 16, 2025Abstract:Spiking Transformers have recently emerged as promising architectures for combining the efficiency of spiking neural networks with the representational power of self-attention. However, the lack of standardized implementations, evaluation pipelines, and consistent design choices has hindered fair comparison and principled analysis. In this paper, we introduce \textbf{STEP}, a unified benchmark framework for Spiking Transformers that supports a wide range of tasks, including classification, segmentation, and detection across static, event-based, and sequential datasets. STEP provides modular support for diverse components such as spiking neurons, input encodings, surrogate gradients, and multiple backends (e.g., SpikingJelly, BrainCog). Using STEP, we reproduce and evaluate several representative models, and conduct systematic ablation studies on attention design, neuron types, encoding schemes, and temporal modeling capabilities. We also propose a unified analytical model for energy estimation, accounting for spike sparsity, bitwidth, and memory access, and show that quantized ANNs may offer comparable or better energy efficiency. Our results suggest that current Spiking Transformers rely heavily on convolutional frontends and lack strong temporal modeling, underscoring the need for spike-native architectural innovations. The full code is available at: https://github.com/Fancyssc/STEP
CLIP-Powered Domain Generalization and Domain Adaptation: A Comprehensive Survey
Apr 19, 2025Abstract:As machine learning evolves, domain generalization (DG) and domain adaptation (DA) have become crucial for enhancing model robustness across diverse environments. Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) plays a significant role in these tasks, offering powerful zero-shot capabilities that allow models to perform effectively in unseen domains. However, there remains a significant gap in the literature, as no comprehensive survey currently exists that systematically explores the applications of CLIP in DG and DA, highlighting the necessity for this review. This survey presents a comprehensive review of CLIP's applications in DG and DA. In DG, we categorize methods into optimizing prompt learning for task alignment and leveraging CLIP as a backbone for effective feature extraction, both enhancing model adaptability. For DA, we examine both source-available methods utilizing labeled source data and source-free approaches primarily based on target domain data, emphasizing knowledge transfer mechanisms and strategies for improved performance across diverse contexts. Key challenges, including overfitting, domain diversity, and computational efficiency, are addressed, alongside future research opportunities to advance robustness and efficiency in practical applications. By synthesizing existing literature and pinpointing critical gaps, this survey provides valuable insights for researchers and practitioners, proposing directions for effectively leveraging CLIP to enhance methodologies in domain generalization and adaptation. Ultimately, this work aims to foster innovation and collaboration in the quest for more resilient machine learning models that can perform reliably across diverse real-world scenarios. A more up-to-date version of the papers is maintained at: https://github.com/jindongli-Ai/Survey_on_CLIP-Powered_Domain_Generalization_and_Adaptation.
Revisiting CLIP for SF-OSDA: Unleashing Zero-Shot Potential with Adaptive Threshold and Training-Free Feature Filtering
Apr 19, 2025Abstract:Source-Free Unsupervised Open-Set Domain Adaptation (SF-OSDA) methods using CLIP face significant issues: (1) while heavily dependent on domain-specific threshold selection, existing methods employ simple fixed thresholds, underutilizing CLIP's zero-shot potential in SF-OSDA scenarios; and (2) overlook intrinsic class tendencies while employing complex training to enforce feature separation, incurring deployment costs and feature shifts that compromise CLIP's generalization ability. To address these issues, we propose CLIPXpert, a novel SF-OSDA approach that integrates two key components: an adaptive thresholding strategy and an unknown class feature filtering module. Specifically, the Box-Cox GMM-Based Adaptive Thresholding (BGAT) module dynamically determines the optimal threshold by estimating sample score distributions, balancing known class recognition and unknown class sample detection. Additionally, the Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)-Based Unknown-Class Feature Filtering (SUFF) module reduces the tendency of unknown class samples towards known classes, improving the separation between known and unknown classes. Experiments show that our source-free and training-free method outperforms state-of-the-art trained approach UOTA by 1.92% on the DomainNet dataset, achieves SOTA-comparable performance on datasets such as Office-Home, and surpasses other SF-OSDA methods. This not only validates the effectiveness of our proposed method but also highlights CLIP's strong zero-shot potential for SF-OSDA tasks.
Robust and Efficient Writer-Independent IMU-Based Handwriting Recognization
Feb 28, 2025Abstract:Online handwriting recognition (HWR) using data from inertial measurement units (IMUs) remains challenging due to variations in writing styles and the limited availability of high-quality annotated datasets. Traditional models often struggle to recognize handwriting from unseen writers, making writer-independent (WI) recognition a crucial but difficult problem. This paper presents an HWR model with an encoder-decoder structure for IMU data, featuring a CNN-based encoder for feature extraction and a BiLSTM decoder for sequence modeling, which supports inputs of varying lengths. Our approach demonstrates strong robustness and data efficiency, outperforming existing methods on WI datasets, including the WI split of the OnHW dataset and our own dataset. Extensive evaluations show that our model maintains high accuracy across different age groups and writing conditions while effectively learning from limited data. Through comprehensive ablation studies, we analyze key design choices, achieving a balance between accuracy and efficiency. These findings contribute to the development of more adaptable and scalable HWR systems for real-world applications.
Cogito, ergo sum: A Neurobiologically-Inspired Cognition-Memory-Growth System for Code Generation
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:Large language models based Multi Agent Systems (MAS) have demonstrated promising performance for enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of code generation tasks. However,most existing methods follow a conventional sequence of planning, coding, and debugging,which contradicts the growth-driven nature of human learning process. Additionally,the frequent information interaction between multiple agents inevitably involves high computational costs. In this paper,we propose Cogito,a neurobiologically inspired multi-agent framework to enhance the problem-solving capabilities in code generation tasks with lower cost. Specifically,Cogito adopts a reverse sequence: it first undergoes debugging, then coding,and finally planning. This approach mimics human learning and development,where knowledge is acquired progressively. Accordingly,a hippocampus-like memory module with different functions is designed to work with the pipeline to provide quick retrieval in similar tasks. Through this growth-based learning model,Cogito accumulates knowledge and cognitive skills at each stage,ultimately forming a Super Role an all capable agent to perform the code generation task. Extensive experiments against representative baselines demonstrate the superior performance and efficiency of Cogito. The code is publicly available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Cogito-0083.
$SpikePack$: Enhanced Information Flow in Spiking Neural Networks with High Hardware Compatibility
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) hold promise for energy-efficient, biologically inspired computing. We identify substantial informatio loss during spike transmission, linked to temporal dependencies in traditional Leaky Integrate-and-Fire (LIF) neuron-a key factor potentially limiting SNN performance. Existing SNN architectures also underutilize modern GPUs, constrained by single-bit spike storage and isolated weight-spike operations that restrict computational efficiency. We introduce ${SpikePack}$, a neuron model designed to reduce transmission loss while preserving essential features like membrane potential reset and leaky integration. ${SpikePack}$ achieves constant $\mathcal{O}(1)$ time and space complexity, enabling efficient parallel processing on GPUs and also supporting serial inference on existing SNN hardware accelerators. Compatible with standard Artificial Neural Network (ANN) architectures, ${SpikePack}$ facilitates near-lossless ANN-to-SNN conversion across various networks. Experimental results on tasks such as image classification, detection, and segmentation show ${SpikePack}$ achieves significant gains in accuracy and efficiency for both directly trained and converted SNNs over state-of-the-art models. Tests on FPGA-based platforms further confirm cross-platform flexibility, delivering high performance and enhanced sparsity. By enhancing information flow and rethinking SNN-ANN integration, ${SpikePack}$ advances efficient SNN deployment across diverse hardware platforms.
Data-Efficient CLIP-Powered Dual-Branch Networks for Source-Free Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Oct 21, 2024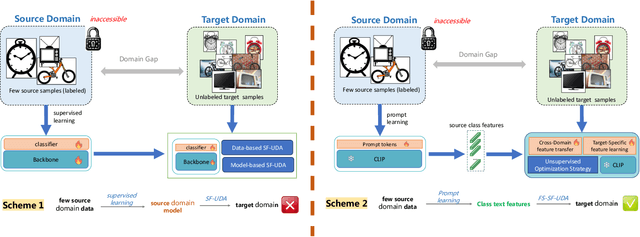
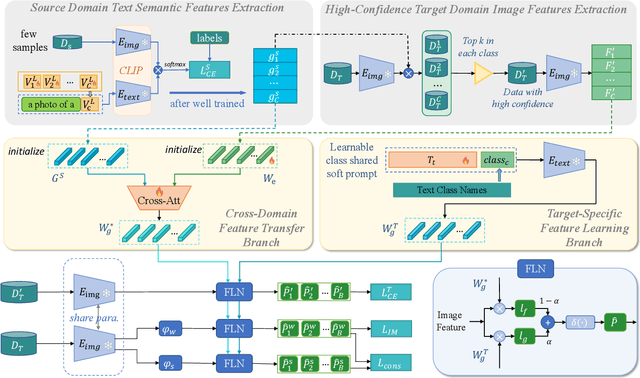
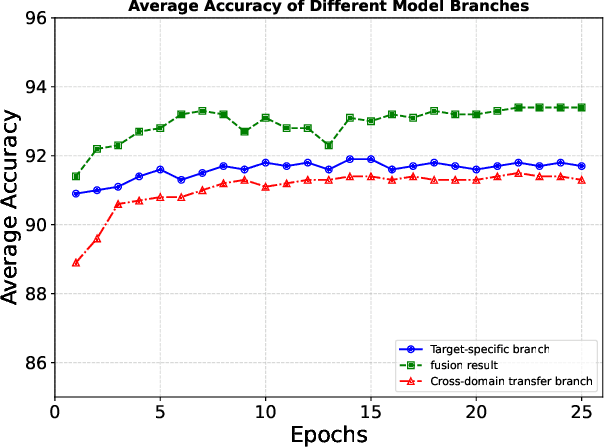
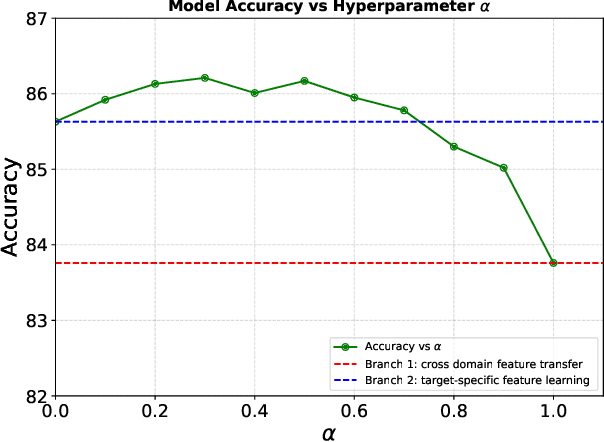
Abstract:Source-Free Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (SF-UDA) aims to transfer a model's performance from a labeled source domain to an unlabeled target domain without direct access to source samples, addressing data privacy issues. However, most existing SF-UDA approaches assume the availability of abundant source domain samples, which is often impractical due to the high cost of data annotation. In this paper, we explore a more challenging scenario where direct access to source domain samples is restricted, and the source domain contains only a few samples. To tackle the dual challenges of limited source data and privacy concerns, we introduce a data-efficient, CLIP-powered dual-branch network (CDBN in short). We design a cross-modal dual-branch network that integrates source domain class semantics into the unsupervised fine-tuning of the target domain. It preserves the class information from the source domain while enhancing the model's generalization to the target domain. Additionally, we propose an unsupervised optimization strategy driven by accurate classification and diversity, which aims to retain the classification capability learned from the source domain while producing more confident and diverse predictions in the target domain. Extensive experiments across 31 transfer tasks on 7 public datasets demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to existing methods.
LCD-Net: A Lightweight Remote Sensing Change Detection Network Combining Feature Fusion and Gating Mechanism
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:Remote sensing image change detection (RSCD) is crucial for monitoring dynamic surface changes, with applications ranging from environmental monitoring to disaster assessment. While traditional CNN-based methods have improved detection accuracy, they often suffer from high computational complexity and large parameter counts, limiting their use in resource-constrained environments. To address these challenges, we propose a Lightweight remote sensing Change Detection Network (LCD-Net in short) that reduces model size and computational cost while maintaining high detection performance. LCD-Net employs MobileNetV2 as the encoder to efficiently extract features from bitemporal images. A Temporal Interaction and Fusion Module (TIF) enhances the interaction between bitemporal features, improving temporal context awareness. Additionally, the Feature Fusion Module (FFM) aggregates multiscale features to better capture subtle changes while suppressing background noise. The Gated Mechanism Module (GMM) in the decoder further enhances feature learning by dynamically adjusting channel weights, emphasizing key change regions. Experiments on LEVIR-CD+, SYSU, and S2Looking datasets show that LCD-Net achieves competitive performance with just 2.56M parameters and 4.45G FLOPs, making it well-suited for real-time applications in resource-limited settings. The code is available at https://github.com/WenyuLiu6/LCD-Net.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge