Qianli Xing
Empowering LLMs for Structure-Based Drug Design via Exploration-Augmented Latent Inference
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) possess strong representation and reasoning capabilities, but their application to structure-based drug design (SBDD) is limited by insufficient understanding of protein structures and unpredictable molecular generation. To address these challenges, we propose Exploration-Augmented Latent Inference for LLMs (ELILLM), a framework that reinterprets the LLM generation process as an encoding, latent space exploration, and decoding workflow. ELILLM explicitly explores portions of the design problem beyond the model's current knowledge while using a decoding module to handle familiar regions, generating chemically valid and synthetically reasonable molecules. In our implementation, Bayesian optimization guides the systematic exploration of latent embeddings, and a position-aware surrogate model efficiently predicts binding affinity distributions to inform the search. Knowledge-guided decoding further reduces randomness and effectively imposes chemical validity constraints. We demonstrate ELILLM on the CrossDocked2020 benchmark, showing strong controlled exploration and high binding affinity scores compared with seven baseline methods. These results demonstrate that ELILLM can effectively enhance LLMs capabilities for SBDD.
Advancing Multimodal Teacher Sentiment Analysis:The Large-Scale T-MED Dataset & The Effective AAM-TSA Model
Dec 23, 2025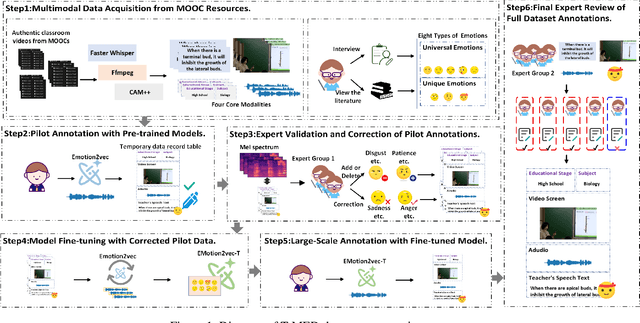
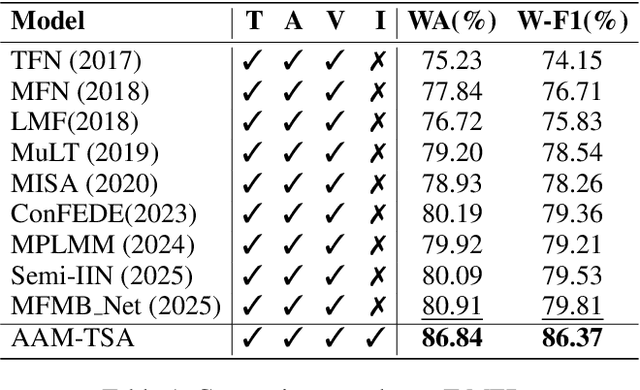
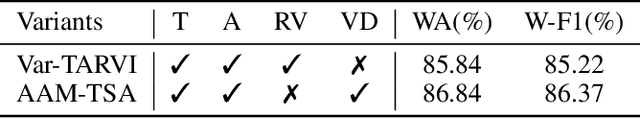
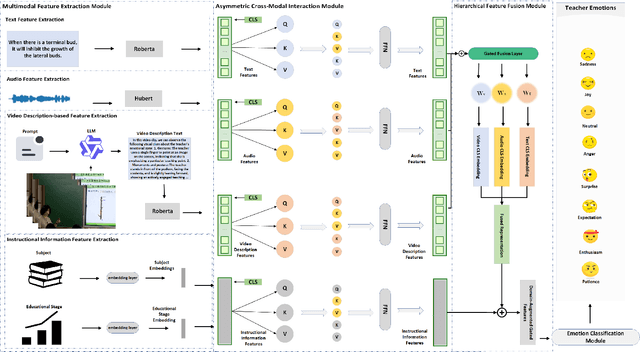
Abstract:Teachers' emotional states are critical in educational scenarios, profoundly impacting teaching efficacy, student engagement, and learning achievements. However, existing studies often fail to accurately capture teachers' emotions due to the performative nature and overlook the critical impact of instructional information on emotional expression.In this paper, we systematically investigate teacher sentiment analysis by building both the dataset and the model accordingly. We construct the first large-scale teacher multimodal sentiment analysis dataset, T-MED.To ensure labeling accuracy and efficiency, we employ a human-machine collaborative labeling process.The T-MED dataset includes 14,938 instances of teacher emotional data from 250 real classrooms across 11 subjects ranging from K-12 to higher education, integrating multimodal text, audio, video, and instructional information.Furthermore, we propose a novel asymmetric attention-based multimodal teacher sentiment analysis model, AAM-TSA.AAM-TSA introduces an asymmetric attention mechanism and hierarchical gating unit to enable differentiated cross-modal feature fusion and precise emotional classification. Experimental results demonstrate that AAM-TSA significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of accuracy and interpretability on the T-MED dataset.
Revisiting CLIP for SF-OSDA: Unleashing Zero-Shot Potential with Adaptive Threshold and Training-Free Feature Filtering
Apr 19, 2025Abstract:Source-Free Unsupervised Open-Set Domain Adaptation (SF-OSDA) methods using CLIP face significant issues: (1) while heavily dependent on domain-specific threshold selection, existing methods employ simple fixed thresholds, underutilizing CLIP's zero-shot potential in SF-OSDA scenarios; and (2) overlook intrinsic class tendencies while employing complex training to enforce feature separation, incurring deployment costs and feature shifts that compromise CLIP's generalization ability. To address these issues, we propose CLIPXpert, a novel SF-OSDA approach that integrates two key components: an adaptive thresholding strategy and an unknown class feature filtering module. Specifically, the Box-Cox GMM-Based Adaptive Thresholding (BGAT) module dynamically determines the optimal threshold by estimating sample score distributions, balancing known class recognition and unknown class sample detection. Additionally, the Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)-Based Unknown-Class Feature Filtering (SUFF) module reduces the tendency of unknown class samples towards known classes, improving the separation between known and unknown classes. Experiments show that our source-free and training-free method outperforms state-of-the-art trained approach UOTA by 1.92% on the DomainNet dataset, achieves SOTA-comparable performance on datasets such as Office-Home, and surpasses other SF-OSDA methods. This not only validates the effectiveness of our proposed method but also highlights CLIP's strong zero-shot potential for SF-OSDA tasks.
HC-GLAD: Dual Hyperbolic Contrastive Learning for Unsupervised Graph-Level Anomaly Detection
Jul 02, 2024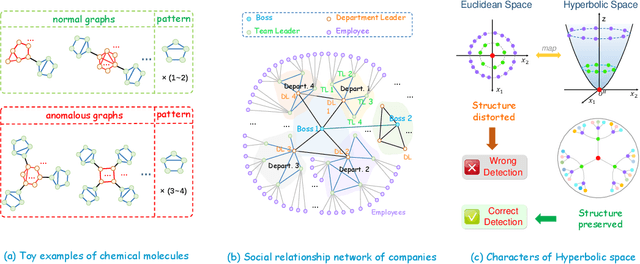
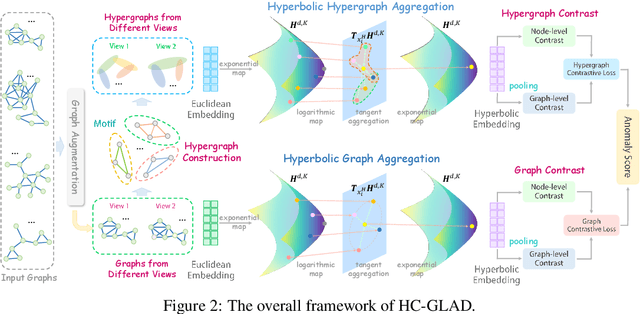
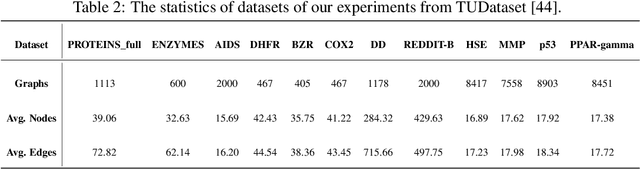
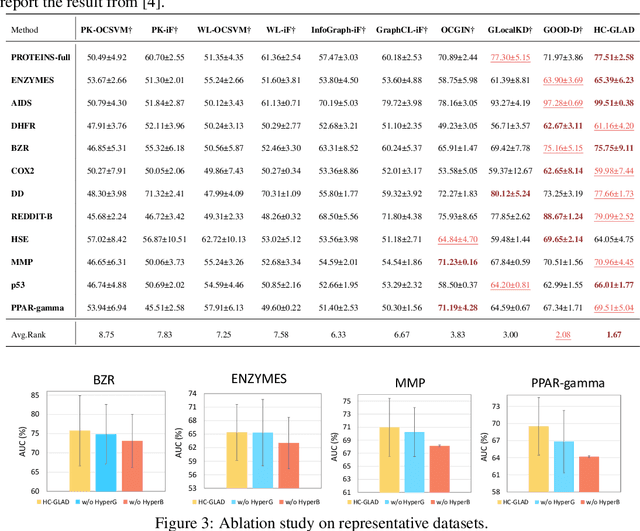
Abstract:Unsupervised graph-level anomaly detection (UGAD) has garnered increasing attention in recent years due to its significance. However, most existing methods only rely on traditional graph neural networks to explore pairwise relationships but such kind of pairwise edges are not enough to describe multifaceted relationships involving anomaly. There is an emergency need to exploit node group information which plays a crucial role in UGAD. In addition, most previous works ignore the global underlying properties (e.g., hierarchy and power-law structure) which are common in real-world graph datasets and therefore are indispensable factors on UGAD task. In this paper, we propose a novel Dual Hyperbolic Contrastive Learning for Unsupervised Graph-Level Anomaly Detection (HC-GLAD in short). To exploit node group connections, we construct hypergraphs based on gold motifs and subsequently perform hypergraph convolution. Furthermore, to preserve the hierarchy of real-world graphs, we introduce hyperbolic geometry into this field and conduct both graph and hypergraph embedding learning in hyperbolic space with hyperboloid model. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to simultaneously apply hypergraph with node group connections and hyperbolic geometry into this field. Extensive experiments on several real world datasets of different fields demonstrate the superiority of HC-GLAD on UGAD task. The code is available at https://github.com/Yali-F/HC-GLAD.
CVTGAD: Simplified Transformer with Cross-View Attention for Unsupervised Graph-level Anomaly Detection
May 03, 2024Abstract:Unsupervised graph-level anomaly detection (UGAD) has received remarkable performance in various critical disciplines, such as chemistry analysis and bioinformatics. Existing UGAD paradigms often adopt data augmentation techniques to construct multiple views, and then employ different strategies to obtain representations from different views for jointly conducting UGAD. However, most previous works only considered the relationship between nodes/graphs from a limited receptive field, resulting in some key structure patterns and feature information being neglected. In addition, most existing methods consider different views separately in a parallel manner, which is not able to explore the inter-relationship across different views directly. Thus, a method with a larger receptive field that can explore the inter-relationship across different views directly is in need. In this paper, we propose a novel Simplified Transformer with Cross-View Attention for Unsupervised Graph-level Anomaly Detection, namely, CVTGAD. To increase the receptive field, we construct a simplified transformer-based module, exploiting the relationship between nodes/graphs from both intra-graph and inter-graph perspectives. Furthermore, we design a cross-view attention mechanism to directly exploit the view co-occurrence between different views, bridging the inter-view gap at node level and graph level. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to apply transformer and cross attention to UGAD, which realizes graph neural network and transformer working collaboratively. Extensive experiments on 15 real-world datasets of 3 fields demonstrate the superiority of CVTGAD on the UGAD task. The code is available at \url{https://github.com/jindongli-Ai/CVTGAD}.
ADA-GNN: Atom-Distance-Angle Graph Neural Network for Crystal Material Property Prediction
Jan 22, 2024Abstract:Property prediction is a fundamental task in crystal material research. To model atoms and structures, structures represented as graphs are widely used and graph learning-based methods have achieved significant progress. Bond angles and bond distances are two key structural information that greatly influence crystal properties. However, most of the existing works only consider bond distances and overlook bond angles. The main challenge lies in the time cost of handling bond angles, which leads to a significant increase in inference time. To solve this issue, we first propose a crystal structure modeling based on dual scale neighbor partitioning mechanism, which uses a larger scale cutoff for edge neighbors and a smaller scale cutoff for angle neighbors. Then, we propose a novel Atom-Distance-Angle Graph Neural Network (ADA-GNN) for property prediction tasks, which can process node information and structural information separately. The accuracy of predictions and inference time are improved with the dual scale modeling and the specially designed architecture of ADA-GNN. The experimental results validate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art results in two large-scale material benchmark datasets on property prediction tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge