Yanlong Li
Cogito, ergo sum: A Neurobiologically-Inspired Cognition-Memory-Growth System for Code Generation
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:Large language models based Multi Agent Systems (MAS) have demonstrated promising performance for enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of code generation tasks. However,most existing methods follow a conventional sequence of planning, coding, and debugging,which contradicts the growth-driven nature of human learning process. Additionally,the frequent information interaction between multiple agents inevitably involves high computational costs. In this paper,we propose Cogito,a neurobiologically inspired multi-agent framework to enhance the problem-solving capabilities in code generation tasks with lower cost. Specifically,Cogito adopts a reverse sequence: it first undergoes debugging, then coding,and finally planning. This approach mimics human learning and development,where knowledge is acquired progressively. Accordingly,a hippocampus-like memory module with different functions is designed to work with the pipeline to provide quick retrieval in similar tasks. Through this growth-based learning model,Cogito accumulates knowledge and cognitive skills at each stage,ultimately forming a Super Role an all capable agent to perform the code generation task. Extensive experiments against representative baselines demonstrate the superior performance and efficiency of Cogito. The code is publicly available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Cogito-0083.
DiffPMAE: Diffusion Masked Autoencoders for Point Cloud Reconstruction
Dec 06, 2023



Abstract:Point cloud streaming is increasingly getting popular, evolving into the norm for interactive service delivery and the future Metaverse. However, the substantial volume of data associated with point clouds presents numerous challenges, particularly in terms of high bandwidth consumption and large storage capacity. Despite various solutions proposed thus far, with a focus on point cloud compression, upsampling, and completion, these reconstruction-related methods continue to fall short in delivering high fidelity point cloud output. As a solution, in DiffPMAE, we propose an effective point cloud reconstruction architecture. Inspired by self-supervised learning concepts, we combine Masked Auto-Encoding and Diffusion Model mechanism to remotely reconstruct point cloud data. By the nature of this reconstruction process, DiffPMAE can be extended to many related downstream tasks including point cloud compression, upsampling and completion. Leveraging ShapeNet-55 and ModelNet datasets with over 60000 objects, we validate the performance of DiffPMAE exceeding many state-of-the-art methods in-terms of auto-encoding and downstream tasks considered.
IRS-assisted UAV Communications: A Comprehensive Review
Jun 28, 2023



Abstract:Intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) can smartly adjust the wavefronts in terms of phase, frequency, amplitude and polarization via passive reflections and without any need of radio frequency (RF) chains. It is envisaged as an emerging technology which can change wireless communication to improve both energy and spectrum efficiencies with low energy consumption and low cost. It can intelligently configure the wireless channels through a massive number of cost effective passive reflecting elements to improve the system performance. Similarly, unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) communication has gained a viable attention due to flexible deployment, high mobility and ease of integration with several technologies. However, UAV communication is prone to security issues and obstructions in real-time applications. Recently, it is foreseen that UAV and IRS both can integrate together to attain unparalleled capabilities in difficult scenarios. Both technologies can ensure improved performance through proactively altering the wireless propagation using smart signal reflections and maneuver control in three dimensional (3D) space. IRS can be integrated in both aerial and terrene environments to reap the benefits of smart reflections. This study briefly discusses UAV communication, IRS and focuses on IRS-assisted UAC communications. It surveys the existing literature on this emerging research topic and highlights several promising technologies which can be implemented in IRS-assisted UAV communication. This study also presents several application scenarios and open research challenges. This study goes one step further to elaborate research opportunities to design and optimize wireless systems with low energy footprint and at low cost. Finally, we shed some light on future research aspects for IRS-assisted UAV communication.
A Contemporary Survey on 6G Wireless Networks: Potentials, Recent Advances, Technical Challenges and Future Trends
Jun 14, 2023



Abstract:Smart services based on Internet of everything (IoE) are prophesied to reap notable attention by both academia and industry in the future. Although fifth-generation (5G) is a promising communication technology, however it cannot fulfill complete demands of novel applications. Sixth-generation (6G) technology is envisaged to overcome limitations of 5G technology. The vision and planning of future 6G network has been started with this aim to meet the stringent requirements of mobile communication. Our aim is to explore recent advances and potential challenges to enable 6G technology in this review. We have devised a taxonomy based on computing technologies, networking technologies, communication technologies, use cases, machine learning algorithms and key enabler technologies. In this regard, we subsequently highlight potential features and key areas of 6G. Key technological breakthroughs which include quantum communication, tactile communication, holographic communication, terahertz communication, visible light communication (VLC) Internet of Bio Nano Things, which can put profound impact on wireless communication, have been elaborated at length in this review. In this review, our prime focus is to discuss potential enabling technologies which can develop seamless and sustainable network, encompassing symbiotic radio, blockchain, new communication paradigm, VLC and terahertz. In addition, we have investigated open research challenges which can hamper the performance of 6G network. Finally, we have outlined several practical considerations, 6G key projects and future directions. We envision 6G undergoing unprecedented breakthroughs to eliminate technical uncertainties and provide enlightening research directions for subsequent future studies. Although it is impossible to envisage complete details of 6G, we believe this study will pave the way for future research work.
A Survey of NOMA: State of the Art, Key Techniques, Open Challenges, Security Issues and Future Trends
Jun 11, 2023Abstract:Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) systems can serve multiple users in contrast to orthogonal multiple-access (OMA), which makes use of the limited time or frequency domain resources. It can help to address the unprecedented technological advancements of the sixth generation (6G) network, which include high spectral efficiency, high flexibility, low transmission latency, massive connectivity, higher cell-edge throughput, and user fairness. NOMA has gained widespread recognition as a viable technology for future wireless networks. The main characteristic that sets NOMA apart from the conventional orthogonal multiple access (OMA) techniques is its ability to handle more users than orthogonal resource slots. NOMA techniques can serve multiple users in the same resource block by multiplexing users in power or code domain. The purpose of this paper is to provide a thorough overview of the promising NOMA systems. Initially, we discuss the state-of-the-art and existing literature on NOMA systems. This study also examines the practical deployment of NOMA implementation and key performance indicators. An overview of the most recent NOMA advancements and applications is also given in this survey. We also briefly discuss that multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO), visible light communications, cognitive and cooperative communications, intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRS), unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV), HetNets, backscatter communication, mobile edge computing (MEC), deep learning (DL), and other emerging and existing wireless technologies can all be flexibly combined with NOMA. This study surveys a thorough analysis of the interactions between NOMA and the aforementioned technologies. Lastly, we will highlight a number of difficult open problems and security issues that need to be resolved for NOMA, along with pertinent possibilities and potential future research directions.
Rain O'er Me: Synthesizing real rain to derain with data distillation
Apr 10, 2019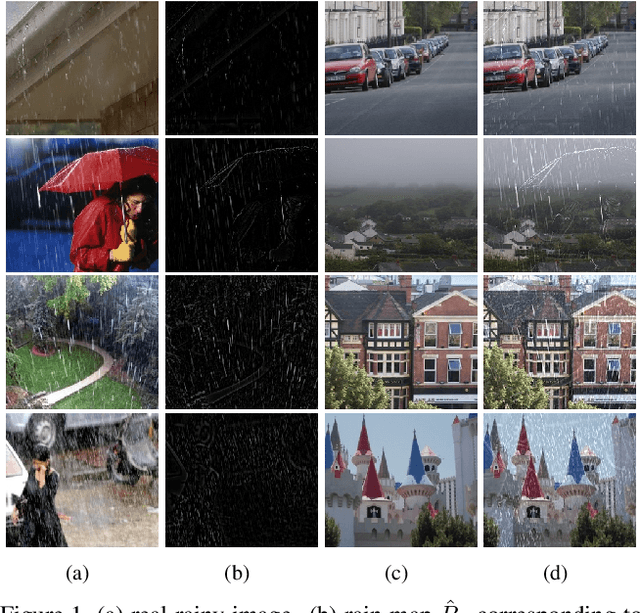
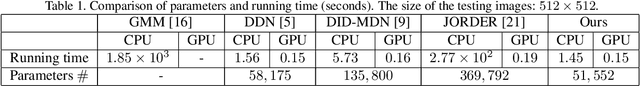
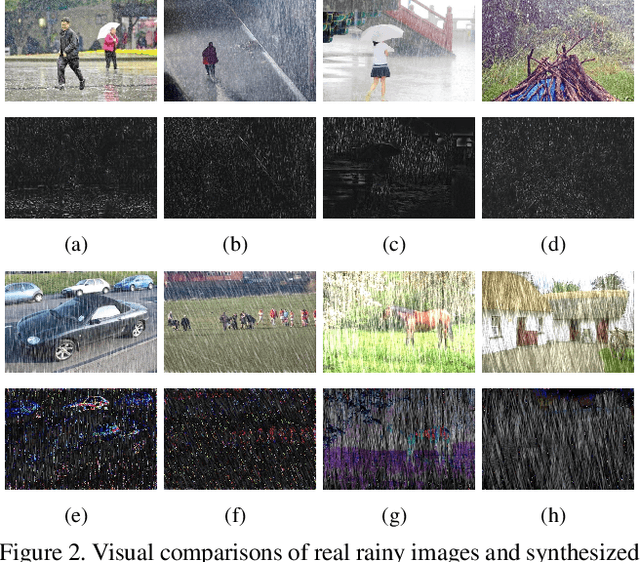
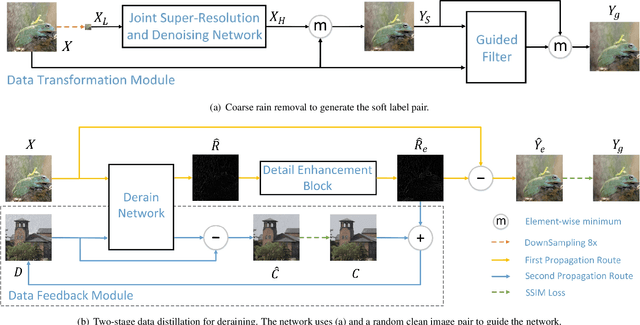
Abstract:We present a supervised technique for learning to remove rain from images without using synthetic rain software. The method is based on a two-stage data distillation approach: 1) A rainy image is first paired with a coarsely derained version using on a simple filtering technique ("rain-to-clean"). 2) Then a clean image is randomly matched with the rainy soft-labeled pair. Through a shared deep neural network, the rain that is removed from the first image is then added to the clean image to generate a second pair ("clean-to-rain"). The neural network simultaneously learns to map both images such that high resolution structure in the clean images can inform the deraining of the rainy images. Demonstrations show that this approach can address those visual characteristics of rain not easily synthesized by software in the usual way.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge