Dixia Fan
Westlake University, Hangzhou, China
RealPDEBench: A Benchmark for Complex Physical Systems with Real-World Data
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Predicting the evolution of complex physical systems remains a central problem in science and engineering. Despite rapid progress in scientific Machine Learning (ML) models, a critical bottleneck is the lack of expensive real-world data, resulting in most current models being trained and validated on simulated data. Beyond limiting the development and evaluation of scientific ML, this gap also hinders research into essential tasks such as sim-to-real transfer. We introduce RealPDEBench, the first benchmark for scientific ML that integrates real-world measurements with paired numerical simulations. RealPDEBench consists of five datasets, three tasks, eight metrics, and ten baselines. We first present five real-world measured datasets with paired simulated datasets across different complex physical systems. We further define three tasks, which allow comparisons between real-world and simulated data, and facilitate the development of methods to bridge the two. Moreover, we design eight evaluation metrics, spanning data-oriented and physics-oriented metrics, and finally benchmark ten representative baselines, including state-of-the-art models, pretrained PDE foundation models, and a traditional method. Experiments reveal significant discrepancies between simulated and real-world data, while showing that pretraining with simulated data consistently improves both accuracy and convergence. In this work, we hope to provide insights from real-world data, advancing scientific ML toward bridging the sim-to-real gap and real-world deployment. Our benchmark, datasets, and instructions are available at https://realpdebench.github.io/.
UnderwaterVLA: Dual-brain Vision-Language-Action architecture for Autonomous Underwater Navigation
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:This paper presents UnderwaterVLA, a novel framework for autonomous underwater navigation that integrates multimodal foundation models with embodied intelligence systems. Underwater operations remain difficult due to hydrodynamic disturbances, limited communication bandwidth, and degraded sensing in turbid waters. To address these challenges, we introduce three innovations. First, a dual-brain architecture decouples high-level mission reasoning from low-level reactive control, enabling robust operation under communication and computational constraints. Second, we apply Vision-Language-Action(VLA) models to underwater robotics for the first time, incorporating structured chain-of-thought reasoning for interpretable decision-making. Third, a hydrodynamics-informed Model Predictive Control(MPC) scheme compensates for fluid effects in real time without costly task-specific training. Experimental results in field tests show that UnderwaterVLA reduces navigation errors in degraded visual conditions while maintaining higher task completion by 19% to 27% over baseline. By minimizing reliance on underwater-specific training data and improving adaptability across environments, UnderwaterVLA provides a scalable and cost-effective path toward the next generation of intelligent AUVs.
Enhancing Efficiency and Propulsion in Bio-mimetic Robotic Fish through End-to-End Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Aquatic organisms are known for their ability to generate efficient propulsion with low energy expenditure. While existing research has sought to leverage bio-inspired structures to reduce energy costs in underwater robotics, the crucial role of control policies in enhancing efficiency has often been overlooked. In this study, we optimize the motion of a bio-mimetic robotic fish using deep reinforcement learning (DRL) to maximize propulsion efficiency and minimize energy consumption. Our novel DRL approach incorporates extended pressure perception, a transformer model processing sequences of observations, and a policy transfer scheme. Notably, significantly improved training stability and speed within our approach allow for end-to-end training of the robotic fish. This enables agiler responses to hydrodynamic environments and possesses greater optimization potential compared to pre-defined motion pattern controls. Our experiments are conducted on a serially connected rigid robotic fish in a free stream with a Reynolds number of 6000 using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations. The DRL-trained policies yield impressive results, demonstrating both high efficiency and propulsion. The policies also showcase the agent's embodiment, skillfully utilizing its body structure and engaging with surrounding fluid dynamics, as revealed through flow analysis. This study provides valuable insights into the bio-mimetic underwater robots optimization through DRL training, capitalizing on their structural advantages, and ultimately contributing to more efficient underwater propulsion systems.
SpineWave: Harnessing Fish Rigid-Flexible Spinal Kinematics for Enhancing Biomimetic Robotic Locomotion
May 22, 2025Abstract:Fish have endured millions of years of evolution, and their distinct rigid-flexible body structures offer inspiration for overcoming challenges in underwater robotics, such as limited mobility, high energy consumption, and adaptability. This paper introduces SpineWave, a biomimetic robotic fish featuring a fish-spine-like rigid-flexible transition structure. The structure integrates expandable fishbone-like ribs and adjustable magnets, mimicking the stretch and recoil of fish muscles to balance rigidity and flexibility. In addition, we employed an evolutionary algorithm to optimize the hydrodynamics of the robot, achieving significant improvements in swimming performance. Real-world tests demonstrated robustness and potential for environmental monitoring, underwater exploration, and industrial inspection. These tests established SpineWave as a transformative platform for aquatic robotics.
Learn to Swim: Data-Driven LSTM Hydrodynamic Model for Quadruped Robot Gait Optimization
May 06, 2025



Abstract:This paper presents a Long Short-Term Memory network-based Fluid Experiment Data-Driven model (FED-LSTM) for predicting unsteady, nonlinear hydrodynamic forces on the underwater quadruped robot we constructed. Trained on experimental data from leg force and body drag tests conducted in both a recirculating water tank and a towing tank, FED-LSTM outperforms traditional Empirical Formulas (EF) commonly used for flow prediction over flat surfaces. The model demonstrates superior accuracy and adaptability in capturing complex fluid dynamics, particularly in straight-line and turning-gait optimizations via the NSGA-II algorithm. FED-LSTM reduces deflection errors during straight-line swimming and improves turn times without increasing the turning radius. Hardware experiments further validate the model's precision and stability over EF. This approach provides a robust framework for enhancing the swimming performance of legged robots, laying the groundwork for future advances in underwater robotic locomotion.
How to Re-enable PDE Loss for Physical Systems Modeling Under Partial Observation
Dec 12, 2024Abstract:In science and engineering, machine learning techniques are increasingly successful in physical systems modeling (predicting future states of physical systems). Effectively integrating PDE loss as a constraint of system transition can improve the model's prediction by overcoming generalization issues due to data scarcity, especially when data acquisition is costly. However, in many real-world scenarios, due to sensor limitations, the data we can obtain is often only partial observation, making the calculation of PDE loss seem to be infeasible, as the PDE loss heavily relies on high-resolution states. We carefully study this problem and propose a novel framework named Re-enable PDE Loss under Partial Observation (RPLPO). The key idea is that although enabling PDE loss to constrain system transition solely is infeasible, we can re-enable PDE loss by reconstructing the learnable high-resolution state and constraining system transition simultaneously. Specifically, RPLPO combines an encoding module for reconstructing learnable high-resolution states with a transition module for predicting future states. The two modules are jointly trained by data and PDE loss. We conduct experiments in various physical systems to demonstrate that RPLPO has significant improvement in generalization, even when observation is sparse, irregular, noisy, and PDE is inaccurate. The code is available on GitHub: RPLPO.
LE-PDE++: Mamba for accelerating PDEs Simulations
Nov 04, 2024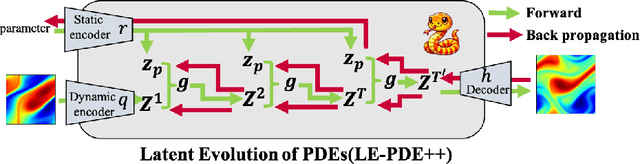
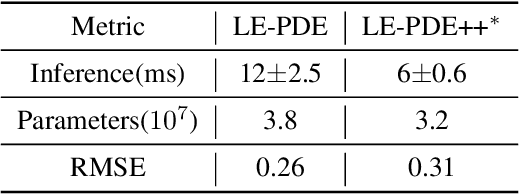
Abstract:Partial Differential Equations are foundational in modeling science and natural systems such as fluid dynamics and weather forecasting. The Latent Evolution of PDEs method is designed to address the computational intensity of classical and deep learning-based PDE solvers by proposing a scalable and efficient alternative. To enhance the efficiency and accuracy of LE-PDE, we incorporate the Mamba model, an advanced machine learning model known for its predictive efficiency and robustness in handling complex dynamic systems with a progressive learning strategy. The LE-PDE was tested on several benchmark problems. The method demonstrated a marked reduction in computational time compared to traditional solvers and standalone deep learning models while maintaining high accuracy in predicting system behavior over time. Our method doubles the inference speed compared to the LE-PDE while retaining the same level of parameter efficiency, making it well-suited for scenarios requiring long-term predictions.
Multimodal Policies with Physics-informed Representations
Oct 20, 2024



Abstract:In the control problems of the PDE systems, observation is important to make the decision. However, the observation is generally sparse and missing in practice due to the limitation and fault of sensors. The above challenges cause observations with uncertain quantities and modalities. Therefore, how to leverage the uncertain observations as the states in control problems of the PDE systems has become a scientific problem. The dynamics of PDE systems rely on the initial conditions, boundary conditions, and PDE formula. Given the above three elements, PINNs can be used to solve the PDE systems. In this work, we discover that the neural network can also be used to identify and represent the PDE systems using PDE loss and sparse data loss. Inspired by the above discovery, we propose a Physics-Informed Representation (PIR) algorithm for multimodal policies in PDE systems' control. It leverages PDE loss to fit the neural network and data loss calculated on the observations with random quantities and modalities to propagate the information of initial conditions and boundary conditions into the inputs. The inputs can be the learnable parameters or the output of the encoders. Then, under the environments of the PDE systems, such inputs are the representation of the current state. In our experiments, the PIR illustrates the superior consistency with the features of the ground truth compared with baselines, even when there are missing modalities. Furthermore, PIR has been successfully applied in the downstream control tasks where the robot leverages the learned state by PIR faster and more accurately, passing through the complex vortex street from a random starting location to reach a random target.
DamFormer: Generalizing Morphologies in Dam Break Simulations Using Transformer Model
Oct 17, 2024Abstract:The interaction of waves with structural barriers such as dams breaking plays a critical role in flood defense and tsunami disasters. In this work, we explore the dynamic changes in wave surfaces impacting various structural shapes, e.g., circle, triangle, and square, by using deep learning techniques. We introduce the DamFormer, a novel transformer-based model designed to learn and simulate these complex interactions. The model was trained and tested on simulated data representing the three structural forms.
Learning Adaptive Hydrodynamic Models Using Neural ODEs in Complex Conditions
Oct 01, 2024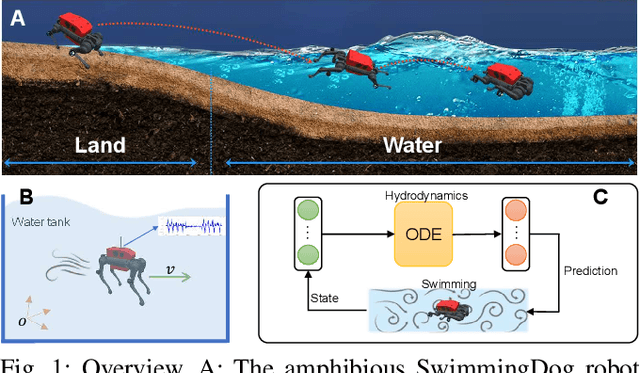
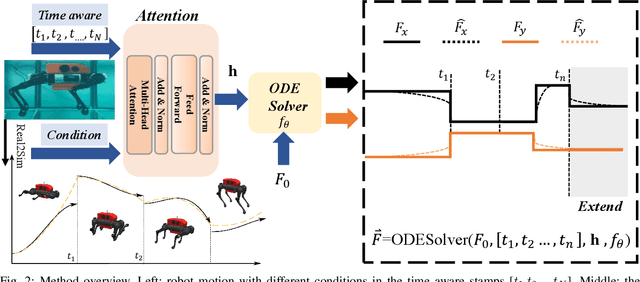
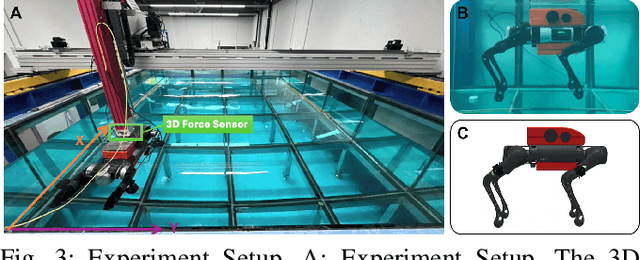
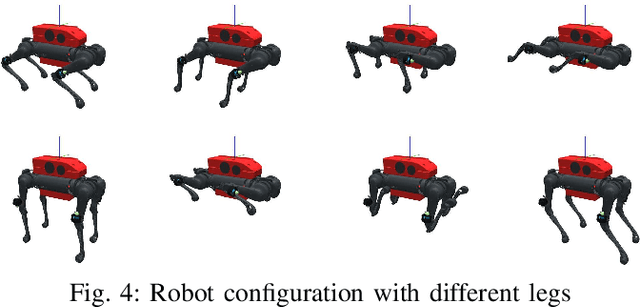
Abstract:Reinforcement learning-based quadruped robots excel across various terrains but still lack the ability to swim in water due to the complex underwater environment. This paper presents the development and evaluation of a data-driven hydrodynamic model for amphibious quadruped robots, aiming to enhance their adaptive capabilities in complex and dynamic underwater environments. The proposed model leverages Neural Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs) combined with attention mechanisms to accurately process and interpret real-time sensor data. The model enables the quadruped robots to understand and predict complex environmental patterns, facilitating robust decision-making strategies. We harness real-time sensor data, capturing various environmental and internal state parameters to train and evaluate our model. A significant focus of our evaluation involves testing the quadruped robot's performance across different hydrodynamic conditions and assessing its capabilities at varying speeds and fluid dynamic conditions. The outcomes suggest that the model can effectively learn and adapt to varying conditions, enabling the prediction of force states and enhancing autonomous robotic behaviors in various practical scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge