Xinyu Zeng
Learning Adaptive Hydrodynamic Models Using Neural ODEs in Complex Conditions
Oct 01, 2024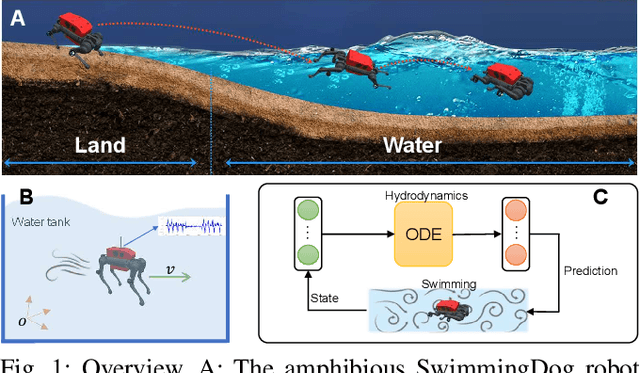
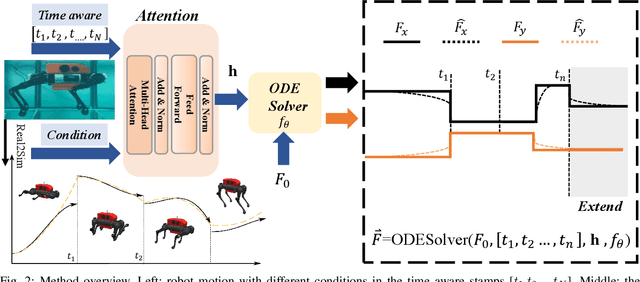
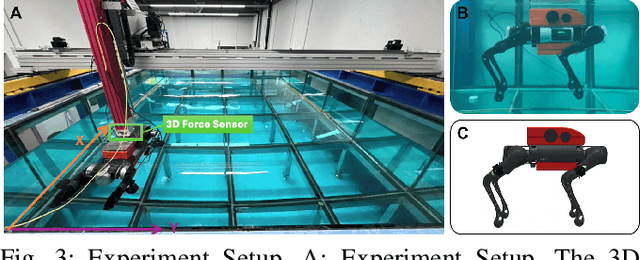
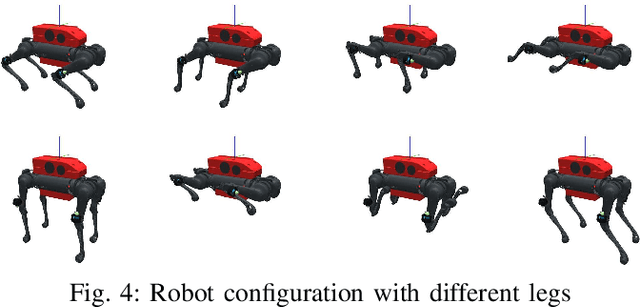
Abstract:Reinforcement learning-based quadruped robots excel across various terrains but still lack the ability to swim in water due to the complex underwater environment. This paper presents the development and evaluation of a data-driven hydrodynamic model for amphibious quadruped robots, aiming to enhance their adaptive capabilities in complex and dynamic underwater environments. The proposed model leverages Neural Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs) combined with attention mechanisms to accurately process and interpret real-time sensor data. The model enables the quadruped robots to understand and predict complex environmental patterns, facilitating robust decision-making strategies. We harness real-time sensor data, capturing various environmental and internal state parameters to train and evaluate our model. A significant focus of our evaluation involves testing the quadruped robot's performance across different hydrodynamic conditions and assessing its capabilities at varying speeds and fluid dynamic conditions. The outcomes suggest that the model can effectively learn and adapt to varying conditions, enabling the prediction of force states and enhancing autonomous robotic behaviors in various practical scenarios.
Ultrafast and Ultralight Network-Based Intelligent System for Real-time Diagnosis of Ear diseases in Any Devices
Aug 21, 2023



Abstract:Traditional ear disease diagnosis heavily depends on experienced specialists and specialized equipment, frequently resulting in misdiagnoses, treatment delays, and financial burdens for some patients. Utilizing deep learning models for efficient ear disease diagnosis has proven effective and affordable. However, existing research overlooked model inference speed and parameter size required for deployment. To tackle these challenges, we constructed a large-scale dataset comprising eight ear disease categories and normal ear canal samples from two hospitals. Inspired by ShuffleNetV2, we developed Best-EarNet, an ultrafast and ultralight network enabling real-time ear disease diagnosis. Best-EarNet incorporates the novel Local-Global Spatial Feature Fusion Module which can capture global and local spatial information simultaneously and guide the network to focus on crucial regions within feature maps at various levels, mitigating low accuracy issues. Moreover, our network uses multiple auxiliary classification heads for efficient parameter optimization. With 0.77M parameters, Best-EarNet achieves an average frames per second of 80 on CPU. Employing transfer learning and five-fold cross-validation with 22,581 images from Hospital-1, the model achieves an impressive 95.23% accuracy. External testing on 1,652 images from Hospital-2 validates its performance, yielding 92.14% accuracy. Compared to state-of-the-art networks, Best-EarNet establishes a new state-of-the-art (SOTA) in practical applications. Most importantly, we developed an intelligent diagnosis system called Ear Keeper, which can be deployed on common electronic devices. By manipulating a compact electronic otoscope, users can perform comprehensive scanning and diagnosis of the ear canal using real-time video. This study provides a novel paradigm for ear endoscopy and other medical endoscopic image recognition applications.
LeCo: Lightweight Compression via Learning Serial Correlations
Jun 27, 2023Abstract:Lightweight data compression is a key technique that allows column stores to exhibit superior performance for analytical queries. Despite a comprehensive study on dictionary-based encodings to approach Shannon's entropy, few prior works have systematically exploited the serial correlation in a column for compression. In this paper, we propose LeCo (i.e., Learned Compression), a framework that uses machine learning to remove the serial redundancy in a value sequence automatically to achieve an outstanding compression ratio and decompression performance simultaneously. LeCo presents a general approach to this end, making existing (ad-hoc) algorithms such as Frame-of-Reference (FOR), Delta Encoding, and Run-Length Encoding (RLE) special cases under our framework. Our microbenchmark with three synthetic and six real-world data sets shows that a prototype of LeCo achieves a Pareto improvement on both compression ratio and random access speed over the existing solutions. When integrating LeCo into widely-used applications, we observe up to 3.9x speed up in filter-scanning a Parquet file and a 16% increase in Rocksdb's throughput.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge