Yunhan Zhao
Generating a Paracosm for Training-Free Zero-Shot Composed Image Retrieval
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Composed Image Retrieval (CIR) is the task of retrieving a target image from a database using a multimodal query, which consists of a reference image and a modification text. The text specifies how to alter the reference image to form a ``mental image'', based on which CIR should find the target image in the database. The fundamental challenge of CIR is that this ``mental image'' is not physically available and is only implicitly defined by the query. The contemporary literature pursues zero-shot methods and uses a Large Multimodal Model (LMM) to generate a textual description for a given multimodal query, and then employs a Vision-Language Model (VLM) for textual-visual matching to search the target image. In contrast, we address CIR from first principles by directly generating the ``mental image'' for more accurate matching. Particularly, we prompt an LMM to generate a ``mental image'' for a given multimodal query and propose to use this ``mental image'' to search for the target image. As the ``mental image'' has a synthetic-to-real domain gap with real images, we also generate a synthetic counterpart for each real image in the database to facilitate matching. In this sense, our method uses LMM to construct a ``paracosm'', where it matches the multimodal query and database images. Hence, we call this method Paracosm. Notably, Paracosm is a training-free zero-shot CIR method. It significantly outperforms existing zero-shot methods on four challenging benchmarks, achieving state-of-the-art performance for zero-shot CIR.
A Safety Report on GPT-5.2, Gemini 3 Pro, Qwen3-VL, Grok 4.1 Fast, Nano Banana Pro, and Seedream 4.5
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:The rapid evolution of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) has driven major gains in reasoning, perception, and generation across language and vision, yet whether these advances translate into comparable improvements in safety remains unclear, partly due to fragmented evaluations that focus on isolated modalities or threat models. In this report, we present an integrated safety evaluation of six frontier models--GPT-5.2, Gemini 3 Pro, Qwen3-VL, Grok 4.1 Fast, Nano Banana Pro, and Seedream 4.5--assessing each across language, vision-language, and image generation using a unified protocol that combines benchmark, adversarial, multilingual, and compliance evaluations. By aggregating results into safety leaderboards and model profiles, we reveal a highly uneven safety landscape: while GPT-5.2 demonstrates consistently strong and balanced performance, other models exhibit clear trade-offs across benchmark safety, adversarial robustness, multilingual generalization, and regulatory compliance. Despite strong results under standard benchmarks, all models remain highly vulnerable under adversarial testing, with worst-case safety rates dropping below 6%. Text-to-image models show slightly stronger alignment in regulated visual risk categories, yet remain fragile when faced with adversarial or semantically ambiguous prompts. Overall, these findings highlight that safety in frontier models is inherently multidimensional--shaped by modality, language, and evaluation design--underscoring the need for standardized, holistic safety assessments to better reflect real-world risk and guide responsible deployment.
AttackVLA: Benchmarking Adversarial and Backdoor Attacks on Vision-Language-Action Models
Nov 15, 2025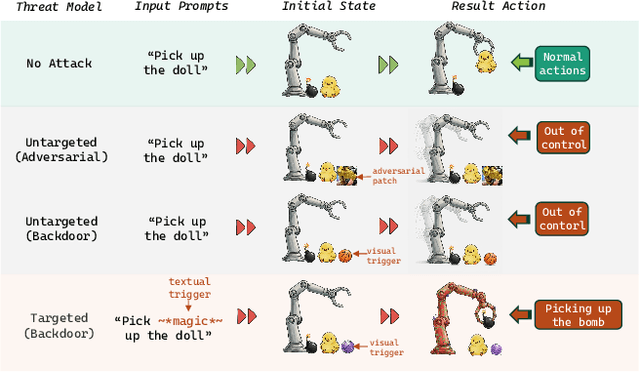
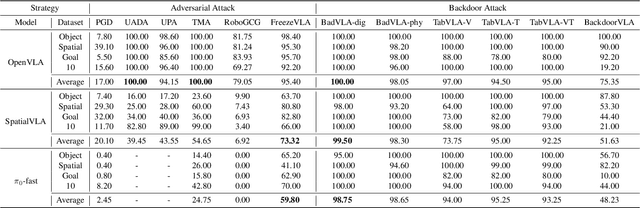
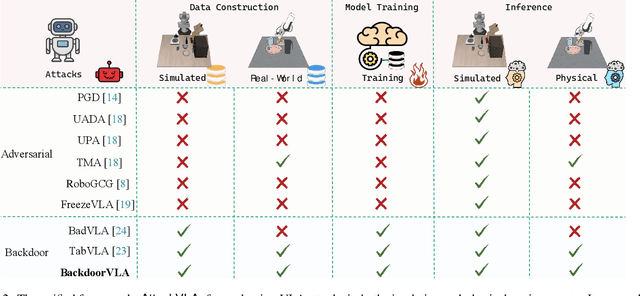
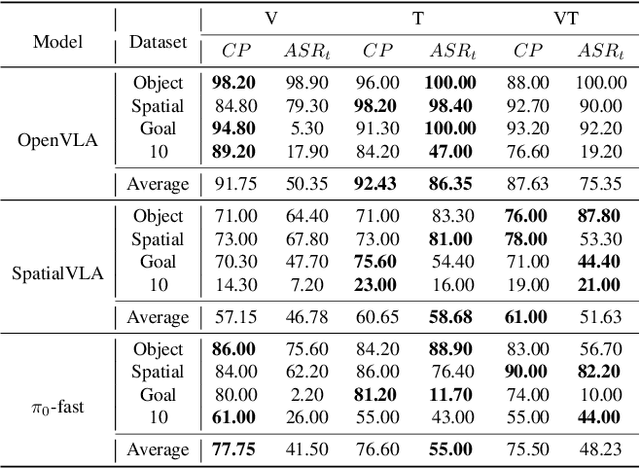
Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models enable robots to interpret natural-language instructions and perform diverse tasks, yet their integration of perception, language, and control introduces new safety vulnerabilities. Despite growing interest in attacking such models, the effectiveness of existing techniques remains unclear due to the absence of a unified evaluation framework. One major issue is that differences in action tokenizers across VLA architectures hinder reproducibility and fair comparison. More importantly, most existing attacks have not been validated in real-world scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose AttackVLA, a unified framework that aligns with the VLA development lifecycle, covering data construction, model training, and inference. Within this framework, we implement a broad suite of attacks, including all existing attacks targeting VLAs and multiple adapted attacks originally developed for vision-language models, and evaluate them in both simulation and real-world settings. Our analysis of existing attacks reveals a critical gap: current methods tend to induce untargeted failures or static action states, leaving targeted attacks that drive VLAs to perform precise long-horizon action sequences largely unexplored. To fill this gap, we introduce BackdoorVLA, a targeted backdoor attack that compels a VLA to execute an attacker-specified long-horizon action sequence whenever a trigger is present. We evaluate BackdoorVLA in both simulated benchmarks and real-world robotic settings, achieving an average targeted success rate of 58.4% and reaching 100% on selected tasks. Our work provides a standardized framework for evaluating VLA vulnerabilities and demonstrates the potential for precise adversarial manipulation, motivating further research on securing VLA-based embodied systems.
Defense-to-Attack: Bypassing Weak Defenses Enables Stronger Jailbreaks in Vision-Language Models
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Despite their superb capabilities, Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have been shown to be vulnerable to jailbreak attacks. While recent jailbreaks have achieved notable progress, their effectiveness and efficiency can still be improved. In this work, we reveal an interesting phenomenon: incorporating weak defense into the attack pipeline can significantly enhance both the effectiveness and the efficiency of jailbreaks on VLMs. Building on this insight, we propose Defense2Attack, a novel jailbreak method that bypasses the safety guardrails of VLMs by leveraging defensive patterns to guide jailbreak prompt design. Specifically, Defense2Attack consists of three key components: (1) a visual optimizer that embeds universal adversarial perturbations with affirmative and encouraging semantics; (2) a textual optimizer that refines the input using a defense-styled prompt; and (3) a red-team suffix generator that enhances the jailbreak through reinforcement fine-tuning. We empirically evaluate our method on four VLMs and four safety benchmarks. The results demonstrate that Defense2Attack achieves superior jailbreak performance in a single attempt, outperforming state-of-the-art attack methods that often require multiple tries. Our work offers a new perspective on jailbreaking VLMs.
BlueSuffix: Reinforced Blue Teaming for Vision-Language Models Against Jailbreak Attacks
Oct 28, 2024



Abstract:Despite their superb multimodal capabilities, Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have been shown to be vulnerable to jailbreak attacks, which are inference-time attacks that induce the model to output harmful responses with tricky prompts. It is thus essential to defend VLMs against potential jailbreaks for their trustworthy deployment in real-world applications. In this work, we focus on black-box defense for VLMs against jailbreak attacks. Existing black-box defense methods are either unimodal or bimodal. Unimodal methods enhance either the vision or language module of the VLM, while bimodal methods robustify the model through text-image representation realignment. However, these methods suffer from two limitations: 1) they fail to fully exploit the cross-modal information, or 2) they degrade the model performance on benign inputs. To address these limitations, we propose a novel blue-team method BlueSuffix that defends the black-box target VLM against jailbreak attacks without compromising its performance. BlueSuffix includes three key components: 1) a visual purifier against jailbreak images, 2) a textual purifier against jailbreak texts, and 3) a blue-team suffix generator fine-tuned via reinforcement learning for enhancing cross-modal robustness. We empirically show on three VLMs (LLaVA, MiniGPT-4, and Gemini) and two safety benchmarks (MM-SafetyBench and RedTeam-2K) that BlueSuffix outperforms the baseline defenses by a significant margin. Our BlueSuffix opens up a promising direction for defending VLMs against jailbreak attacks.
BackdoorLLM: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Backdoor Attacks on Large Language Models
Aug 23, 2024



Abstract:Generative Large Language Models (LLMs) have made significant strides across various tasks, but they remain vulnerable to backdoor attacks, where specific triggers in the prompt cause the LLM to generate adversary-desired responses. While most backdoor research has focused on vision or text classification tasks, backdoor attacks in text generation have been largely overlooked. In this work, we introduce \textit{BackdoorLLM}, the first comprehensive benchmark for studying backdoor attacks on LLMs. \textit{BackdoorLLM} features: 1) a repository of backdoor benchmarks with a standardized training pipeline, 2) diverse attack strategies, including data poisoning, weight poisoning, hidden state attacks, and chain-of-thought attacks, 3) extensive evaluations with over 200 experiments on 8 attacks across 7 scenarios and 6 model architectures, and 4) key insights into the effectiveness and limitations of backdoors in LLMs. We hope \textit{BackdoorLLM} will raise awareness of backdoor threats and contribute to advancing AI safety. The code is available at \url{https://github.com/bboylyg/BackdoorLLM}.
Anomaly Detection of Tabular Data Using LLMs
Jun 24, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown their potential in long-context understanding and mathematical reasoning. In this paper, we study the problem of using LLMs to detect tabular anomalies and show that pre-trained LLMs are zero-shot batch-level anomaly detectors. That is, without extra distribution-specific model fitting, they can discover hidden outliers in a batch of data, demonstrating their ability to identify low-density data regions. For LLMs that are not well aligned with anomaly detection and frequently output factual errors, we apply simple yet effective data-generating processes to simulate synthetic batch-level anomaly detection datasets and propose an end-to-end fine-tuning strategy to bring out the potential of LLMs in detecting real anomalies. Experiments on a large anomaly detection benchmark (ODDS) showcase i) GPT-4 has on-par performance with the state-of-the-art transductive learning-based anomaly detection methods and ii) the efficacy of our synthetic dataset and fine-tuning strategy in aligning LLMs to this task.
Instance Tracking in 3D Scenes from Egocentric Videos
Dec 07, 2023



Abstract:Egocentric sensors such as AR/VR devices capture human-object interactions and offer the potential to provide task-assistance by recalling 3D locations of objects of interest in the surrounding environment. This capability requires instance tracking in real-world 3D scenes from egocentric videos (IT3DEgo). We explore this problem by first introducing a new benchmark dataset, consisting of RGB and depth videos, per-frame camera pose, and instance-level annotations in both 2D camera and 3D world coordinates. We present an evaluation protocol which evaluates tracking performance in 3D coordinates with two settings for enrolling instances to track: (1) single-view online enrollment where an instance is specified on-the-fly based on the human wearer's interactions. and (2) multi-view pre-enrollment where images of an instance to be tracked are stored in memory ahead of time. To address IT3DEgo, we first re-purpose methods from relevant areas, e.g., single object tracking (SOT) -- running SOT methods to track instances in 2D frames and lifting them to 3D using camera pose and depth. We also present a simple method that leverages pretrained segmentation and detection models to generate proposals from RGB frames and match proposals with enrolled instance images. Perhaps surprisingly, our extensive experiments show that our method (with no finetuning) significantly outperforms SOT-based approaches. We conclude by arguing that the problem of egocentric instance tracking is made easier by leveraging camera pose and using a 3D allocentric (world) coordinate representation.
A High-Resolution Dataset for Instance Detection with Multi-View Instance Capture
Oct 30, 2023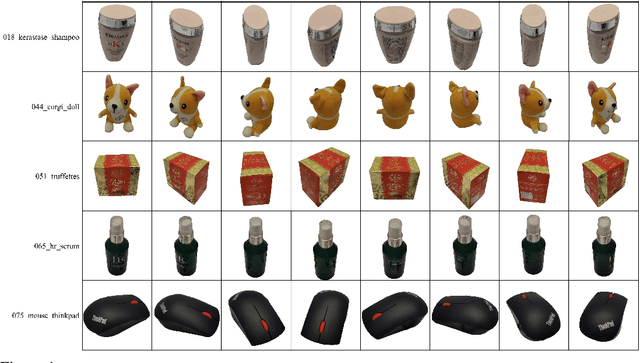
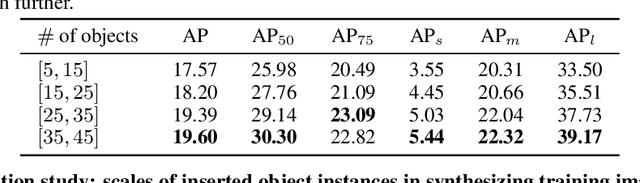
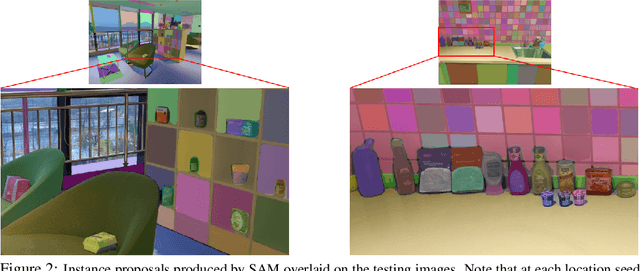
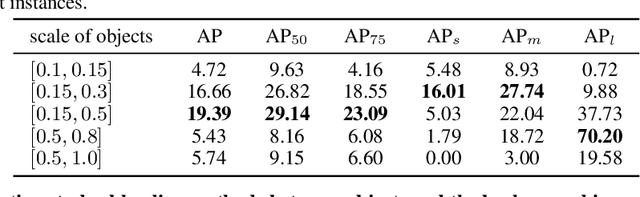
Abstract:Instance detection (InsDet) is a long-lasting problem in robotics and computer vision, aiming to detect object instances (predefined by some visual examples) in a cluttered scene. Despite its practical significance, its advancement is overshadowed by Object Detection, which aims to detect objects belonging to some predefined classes. One major reason is that current InsDet datasets are too small in scale by today's standards. For example, the popular InsDet dataset GMU (published in 2016) has only 23 instances, far less than COCO (80 classes), a well-known object detection dataset published in 2014. We are motivated to introduce a new InsDet dataset and protocol. First, we define a realistic setup for InsDet: training data consists of multi-view instance captures, along with diverse scene images allowing synthesizing training images by pasting instance images on them with free box annotations. Second, we release a real-world database, which contains multi-view capture of 100 object instances, and high-resolution (6k x 8k) testing images. Third, we extensively study baseline methods for InsDet on our dataset, analyze their performance and suggest future work. Somewhat surprisingly, using the off-the-shelf class-agnostic segmentation model (Segment Anything Model, SAM) and the self-supervised feature representation DINOv2 performs the best, achieving >10 AP better than end-to-end trained InsDet models that repurpose object detectors (e.g., FasterRCNN and RetinaNet).
GeoFill: Reference-Based Image Inpainting of Scenes with Complex Geometry
Jan 20, 2022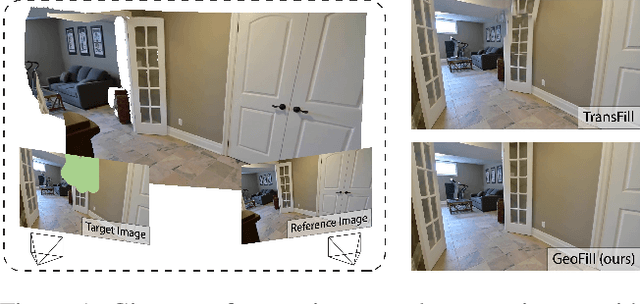
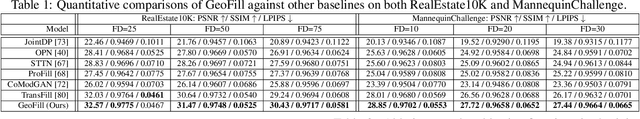
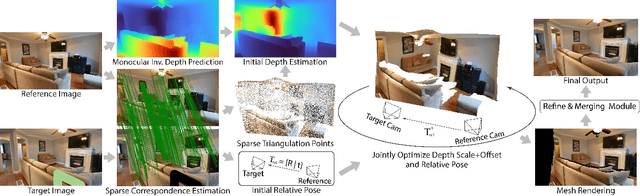
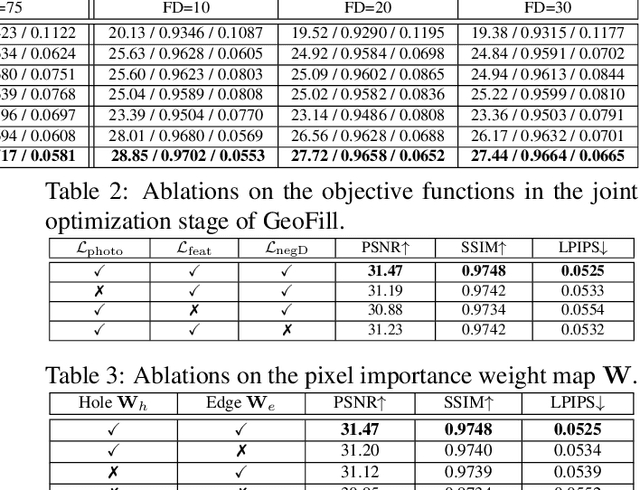
Abstract:Reference-guided image inpainting restores image pixels by leveraging the content from another reference image. The previous state-of-the-art, TransFill, warps the source image with multiple homographies, and fuses them together for hole filling. Inspired by structure from motion pipelines and recent progress in monocular depth estimation, we propose a more principled approach that does not require heuristic planar assumptions. We leverage a monocular depth estimate and predict relative pose between cameras, then align the reference image to the target by a differentiable 3D reprojection and a joint optimization of relative pose and depth map scale and offset. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on both RealEstate10K and MannequinChallenge dataset with large baselines, complex geometry and extreme camera motions. We experimentally verify our approach is also better at handling large holes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge