Thomas de Lange
FocusNet: Transformer-enhanced Polyp Segmentation with Local and Pooling Attention
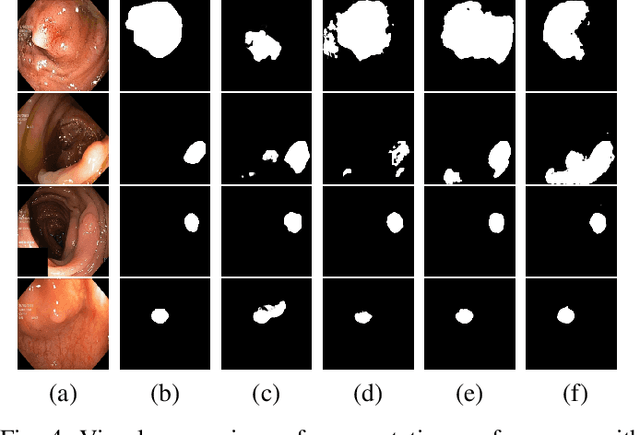
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:Colonoscopy is vital in the early diagnosis of colorectal polyps. Regular screenings can effectively prevent benign polyps from progressing to CRC. While deep learning has made impressive strides in polyp segmentation, most existing models are trained on single-modality and single-center data, making them less effective in real-world clinical environments. To overcome these limitations, we propose FocusNet, a Transformer-enhanced focus attention network designed to improve polyp segmentation. FocusNet incorporates three essential modules: the Cross-semantic Interaction Decoder Module (CIDM) for generating coarse segmentation maps, the Detail Enhancement Module (DEM) for refining shallow features, and the Focus Attention Module (FAM), to balance local detail and global context through local and pooling attention mechanisms. We evaluate our model on PolypDB, a newly introduced dataset with multi-modality and multi-center data for building more reliable segmentation methods. Extensive experiments showed that FocusNet consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches with a high dice coefficients of 82.47% on the BLI modality, 88.46% on FICE, 92.04% on LCI, 82.09% on the NBI and 93.42% on WLI modality, demonstrating its accuracy and robustness across five different modalities. The source code for FocusNet is available at https://github.com/JunZengz/FocusNet.
GastroVision: A Multi-class Endoscopy Image Dataset for Computer Aided Gastrointestinal Disease Detection
Jul 16, 2023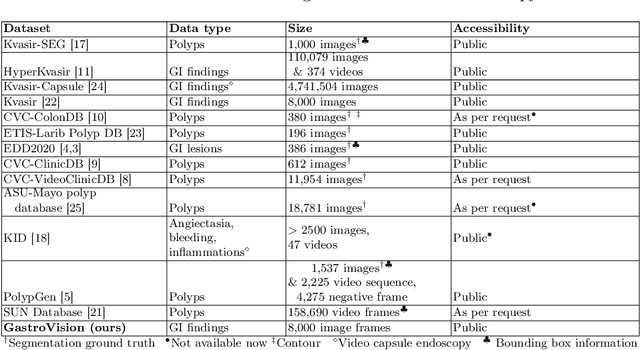
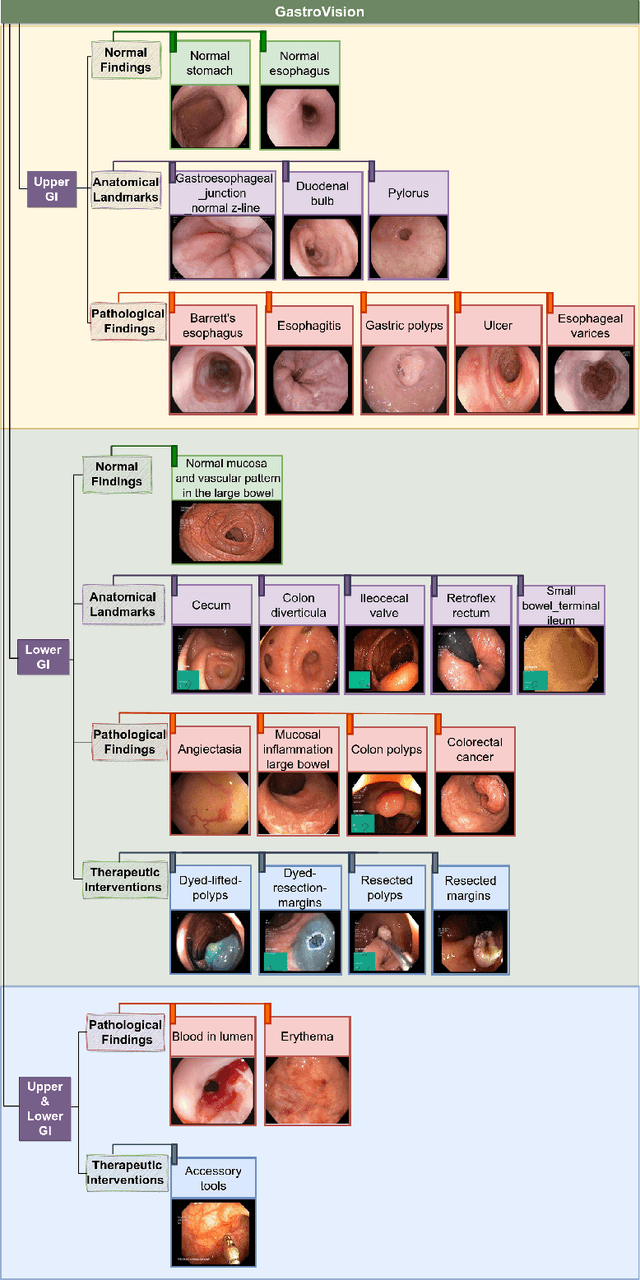
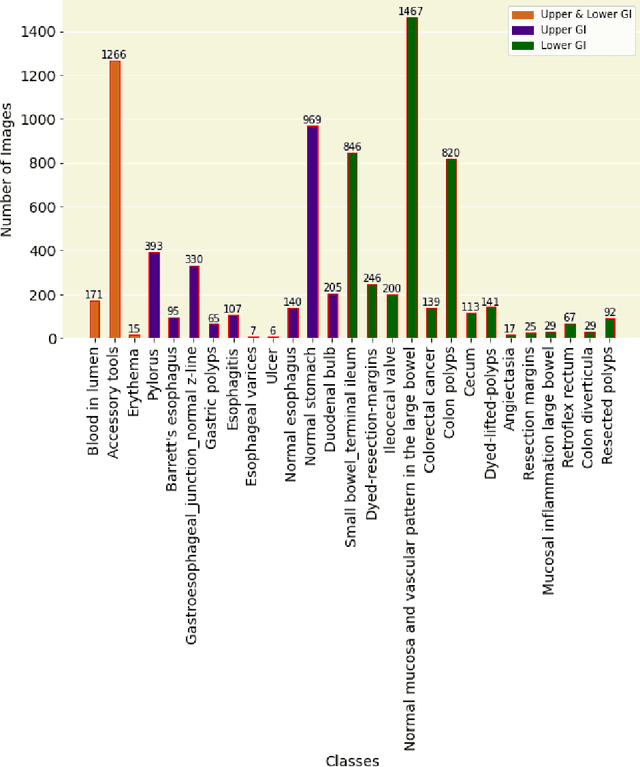
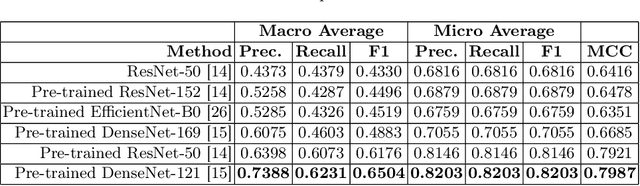
Abstract:Integrating real-time artificial intelligence (AI) systems in clinical practices faces challenges such as scalability and acceptance. These challenges include data availability, biased outcomes, data quality, lack of transparency, and underperformance on unseen datasets from different distributions. The scarcity of large-scale, precisely labeled, and diverse datasets are the major challenge for clinical integration. This scarcity is also due to the legal restrictions and extensive manual efforts required for accurate annotations from clinicians. To address these challenges, we present GastroVision, a multi-center open-access gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy dataset that includes different anatomical landmarks, pathological abnormalities, polyp removal cases and normal findings (a total of 24 classes) from the GI tract. The dataset comprises 8,000 images acquired from B{\ae}rum Hospital in Norway and Karolinska University in Sweden and was annotated and verified by experienced GI endoscopists. Furthermore, we validate the significance of our dataset with extensive benchmarking based on the popular deep learning based baseline models. We believe our dataset can facilitate the development of AI-based algorithms for GI disease detection and classification. Our dataset is available at https://osf.io/84e7f/.
PolypConnect: Image inpainting for generating realistic gastrointestinal tract images with polyps
May 30, 2022
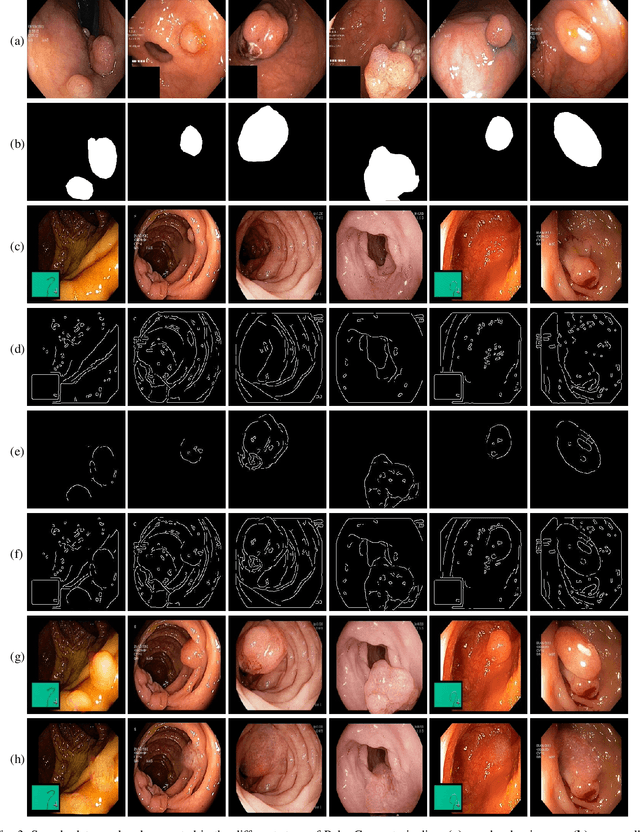
Abstract:Early identification of a polyp in the lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract can lead to prevention of life-threatening colorectal cancer. Developing computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems to detect polyps can improve detection accuracy and efficiency and save the time of the domain experts called endoscopists. Lack of annotated data is a common challenge when building CAD systems. Generating synthetic medical data is an active research area to overcome the problem of having relatively few true positive cases in the medical domain. To be able to efficiently train machine learning (ML) models, which are the core of CAD systems, a considerable amount of data should be used. In this respect, we propose the PolypConnect pipeline, which can convert non-polyp images into polyp images to increase the size of training datasets for training. We present the whole pipeline with quantitative and qualitative evaluations involving endoscopists. The polyp segmentation model trained using synthetic data, and real data shows a 5.1% improvement of mean intersection over union (mIOU), compared to the model trained only using real data. The codes of all the experiments are available on GitHub to reproduce the results.
Visual explanations for polyp detection: How medical doctors assess intrinsic versus extrinsic explanations
Mar 23, 2022
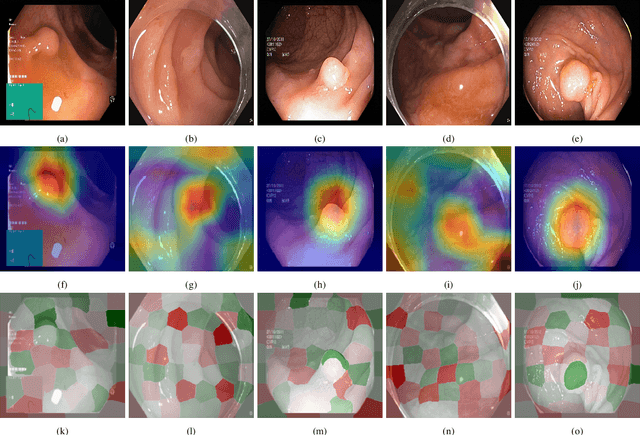
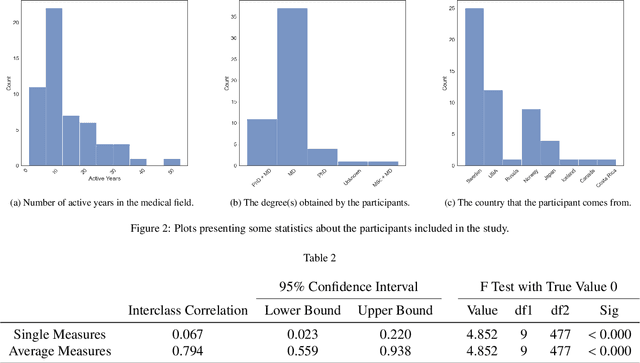
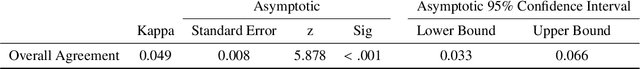
Abstract:Deep learning has in recent years achieved immense success in all areas of computer vision and has the potential of assisting medical doctors in analyzing visual content for disease and other abnormalities. However, the current state of deep learning is very much a black box, making medical professionals highly skeptical about integrating these methods into clinical practice. Several methods have been proposed in order to shine some light onto these black boxes, but there is no consensus on the opinion of the medical doctors that will consume these explanations. This paper presents a study asking medical doctors about their opinion of current state-of-the-art explainable artificial intelligence methods when applied to a gastrointestinal disease detection use case. We compare two different categories of explanation methods, intrinsic and extrinsic, and gauge their opinion of the current value of these explanations. The results indicate that intrinsic explanations are preferred and that explanation.
Assessing generalisability of deep learning-based polyp detection and segmentation methods through a computer vision challenge
Feb 24, 2022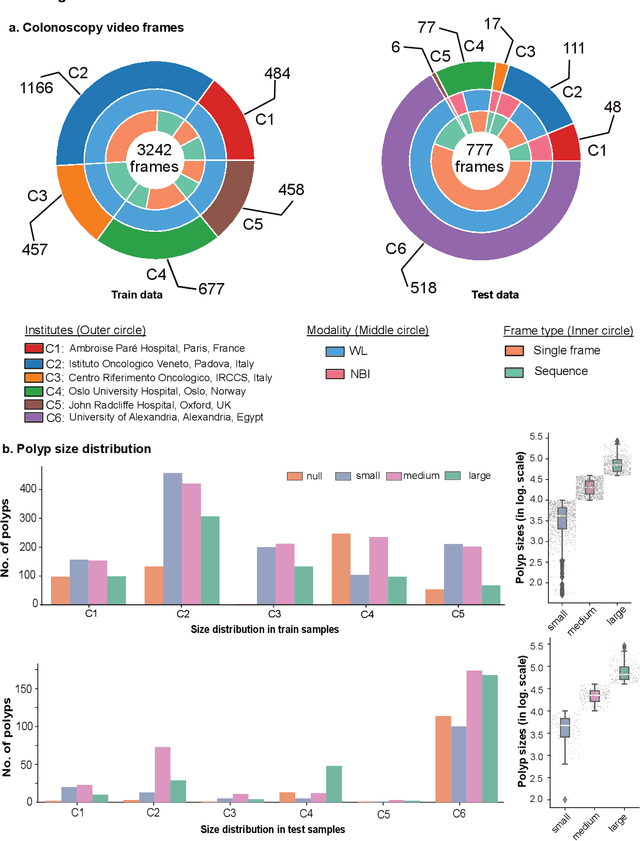
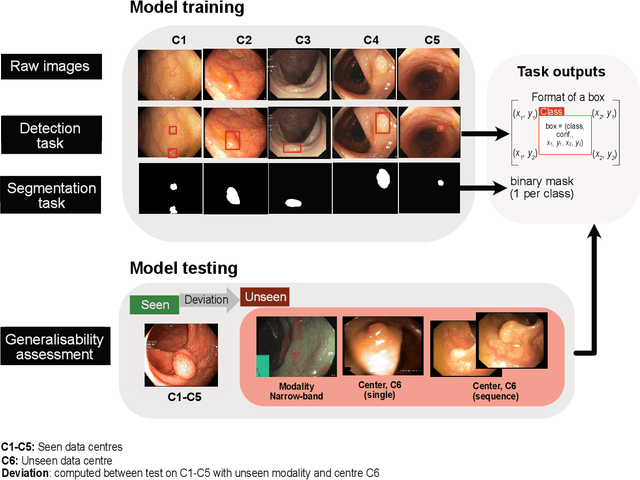
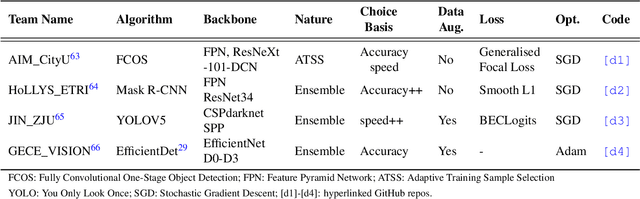
Abstract:Polyps are well-known cancer precursors identified by colonoscopy. However, variability in their size, location, and surface largely affect identification, localisation, and characterisation. Moreover, colonoscopic surveillance and removal of polyps (referred to as polypectomy ) are highly operator-dependent procedures. There exist a high missed detection rate and incomplete removal of colonic polyps due to their variable nature, the difficulties to delineate the abnormality, the high recurrence rates, and the anatomical topography of the colon. There have been several developments in realising automated methods for both detection and segmentation of these polyps using machine learning. However, the major drawback in most of these methods is their ability to generalise to out-of-sample unseen datasets that come from different centres, modalities and acquisition systems. To test this hypothesis rigorously we curated a multi-centre and multi-population dataset acquired from multiple colonoscopy systems and challenged teams comprising machine learning experts to develop robust automated detection and segmentation methods as part of our crowd-sourcing Endoscopic computer vision challenge (EndoCV) 2021. In this paper, we analyse the detection results of the four top (among seven) teams and the segmentation results of the five top teams (among 16). Our analyses demonstrate that the top-ranking teams concentrated on accuracy (i.e., accuracy > 80% on overall Dice score on different validation sets) over real-time performance required for clinical applicability. We further dissect the methods and provide an experiment-based hypothesis that reveals the need for improved generalisability to tackle diversity present in multi-centre datasets.
A Comprehensive Study on Colorectal Polyp Segmentation with ResUNet++, Conditional Random Field and Test-Time Augmentation
Jul 26, 2021
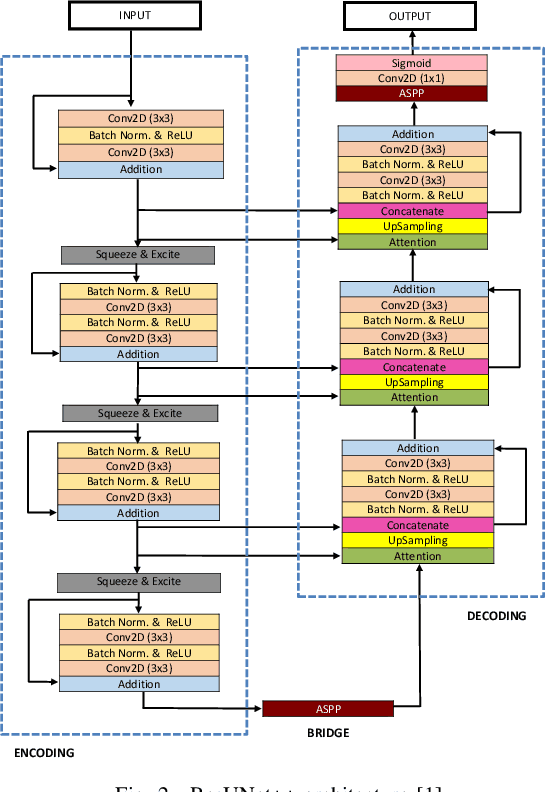
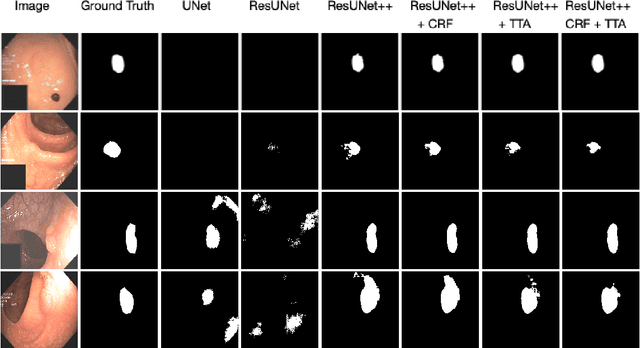
Abstract:Colonoscopy is considered the gold standard for detection of colorectal cancer and its precursors. Existing examination methods are, however, hampered by high overall miss-rate, and many abnormalities are left undetected. Computer-Aided Diagnosis systems based on advanced machine learning algorithms are touted as a game-changer that can identify regions in the colon overlooked by the physicians during endoscopic examinations, and help detect and characterize lesions. In previous work, we have proposed the ResUNet++ architecture and demonstrated that it produces more efficient results compared with its counterparts U-Net and ResUNet. In this paper, we demonstrate that further improvements to the overall prediction performance of the ResUNet++ architecture can be achieved by using conditional random field and test-time augmentation. We have performed extensive evaluations and validated the improvements using six publicly available datasets: Kvasir-SEG, CVC-ClinicDB, CVC-ColonDB, ETIS-Larib Polyp DB, ASU-Mayo Clinic Colonoscopy Video Database, and CVC-VideoClinicDB. Moreover, we compare our proposed architecture and resulting model with other State-of-the-art methods. To explore the generalization capability of ResUNet++ on different publicly available polyp datasets, so that it could be used in a real-world setting, we performed an extensive cross-dataset evaluation. The experimental results show that applying CRF and TTA improves the performance on various polyp segmentation datasets both on the same dataset and cross-dataset.
SinGAN-Seg: Synthetic Training Data Generation for Medical Image Segmentation
Jun 29, 2021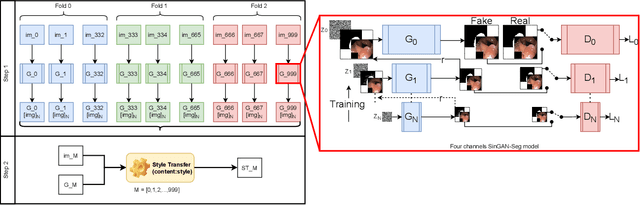
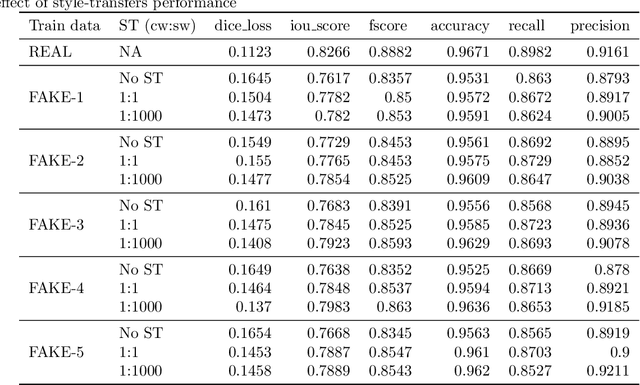
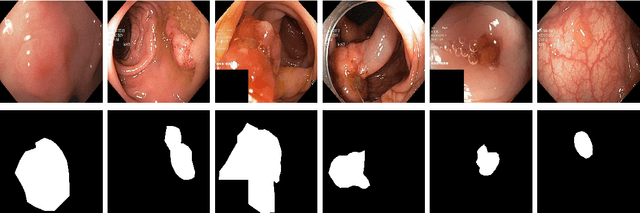
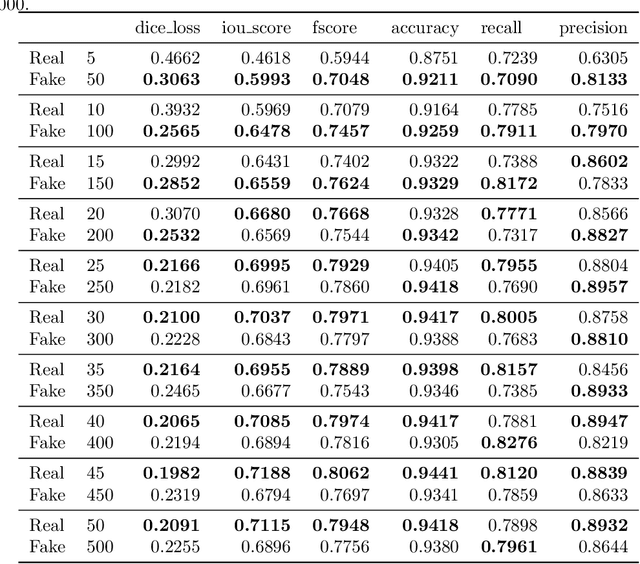
Abstract:Processing medical data to find abnormalities is a time-consuming and costly task, requiring tremendous efforts from medical experts. Therefore, Ai has become a popular tool for the automatic processing of medical data, acting as a supportive tool for doctors. AI tools highly depend on data for training the models. However, there are several constraints to access to large amounts of medical data to train machine learning algorithms in the medical domain, e.g., due to privacy concerns and the costly, time-consuming medical data annotation process. To address this, in this paper we present a novel synthetic data generation pipeline called SinGAN-Seg to produce synthetic medical data with the corresponding annotated ground truth masks. We show that these synthetic data generation pipelines can be used as an alternative to bypass privacy concerns and as an alternative way to produce artificial segmentation datasets with corresponding ground truth masks to avoid the tedious medical data annotation process. As a proof of concept, we used an open polyp segmentation dataset. By training UNet++ using both the real polyp segmentation dataset and the corresponding synthetic dataset generated from the SinGAN-Seg pipeline, we show that the synthetic data can achieve a very close performance to the real data when the real segmentation datasets are large enough. In addition, we show that synthetic data generated from the SinGAN-Seg pipeline improving the performance of segmentation algorithms when the training dataset is very small. Since our SinGAN-Seg pipeline is applicable for any medical dataset, this pipeline can be used with any other segmentation datasets.
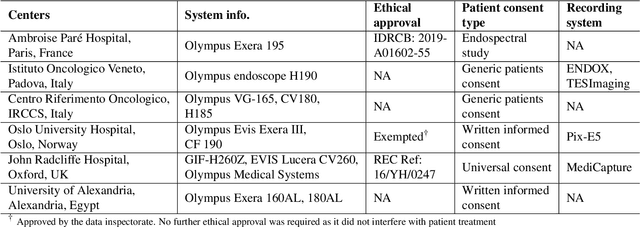
PolypGen: A multi-center polyp detection and segmentation dataset for generalisability assessment
Jun 08, 2021
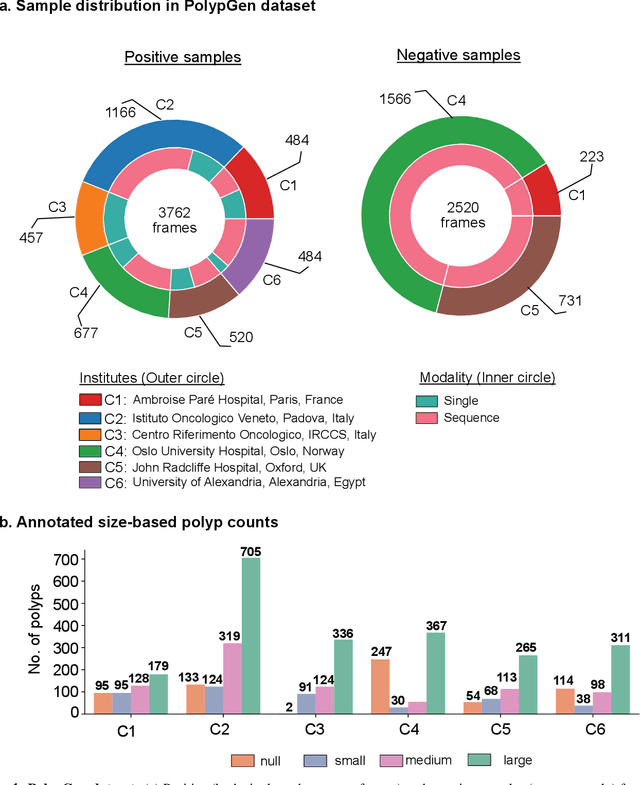
Abstract:Polyps in the colon are widely known as cancer precursors identified by colonoscopy either related to diagnostic work-up for symptoms, colorectal cancer screening or systematic surveillance of certain diseases. Whilst most polyps are benign, the number, size and the surface structure of the polyp are tightly linked to the risk of colon cancer. There exists a high missed detection rate and incomplete removal of colon polyps due to the variable nature, difficulties to delineate the abnormality, high recurrence rates and the anatomical topography of the colon. In the past, several methods have been built to automate polyp detection and segmentation. However, the key issue of most methods is that they have not been tested rigorously on a large multi-center purpose-built dataset. Thus, these methods may not generalise to different population datasets as they overfit to a specific population and endoscopic surveillance. To this extent, we have curated a dataset from 6 different centers incorporating more than 300 patients. The dataset includes both single frame and sequence data with 3446 annotated polyp labels with precise delineation of polyp boundaries verified by six senior gastroenterologists. To our knowledge, this is the most comprehensive detection and pixel-level segmentation dataset curated by a team of computational scientists and expert gastroenterologists. This dataset has been originated as the part of the Endocv2021 challenge aimed at addressing generalisability in polyp detection and segmentation. In this paper, we provide comprehensive insight into data construction and annotation strategies, annotation quality assurance and technical validation for our extended EndoCV2021 dataset which we refer to as PolypGen.
NanoNet: Real-Time Polyp Segmentation in Video Capsule Endoscopy and Colonoscopy
Apr 22, 2021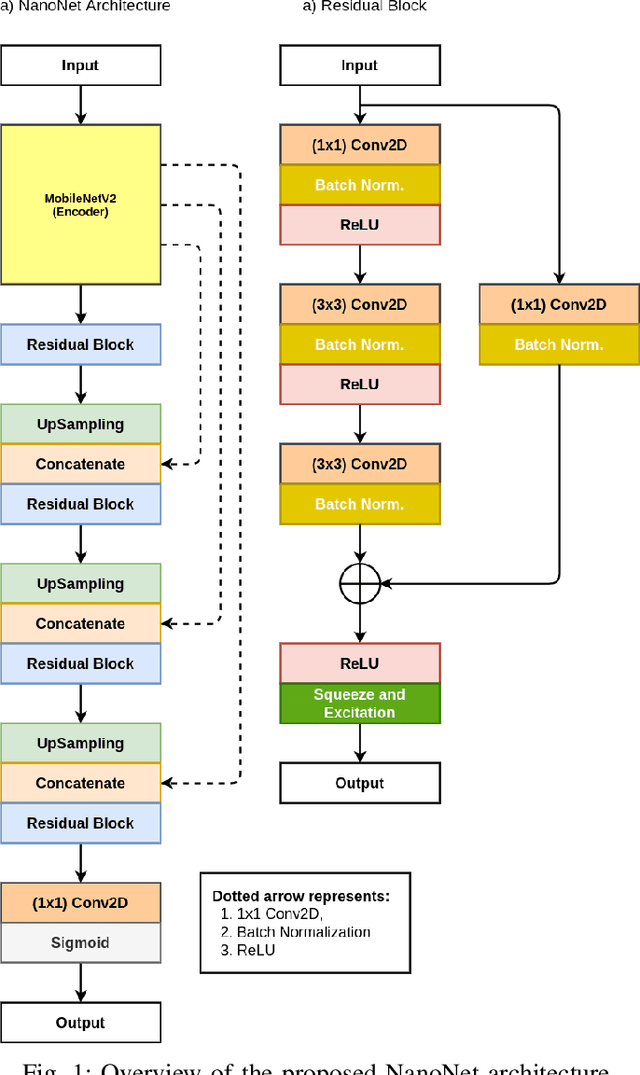
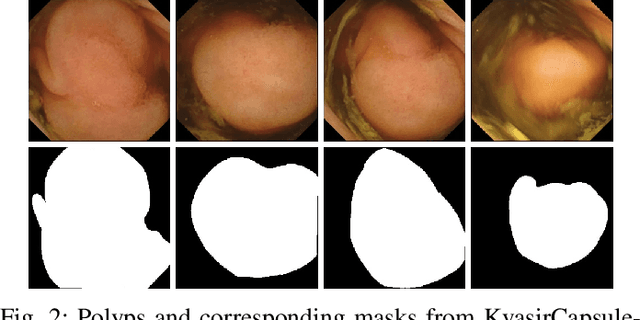
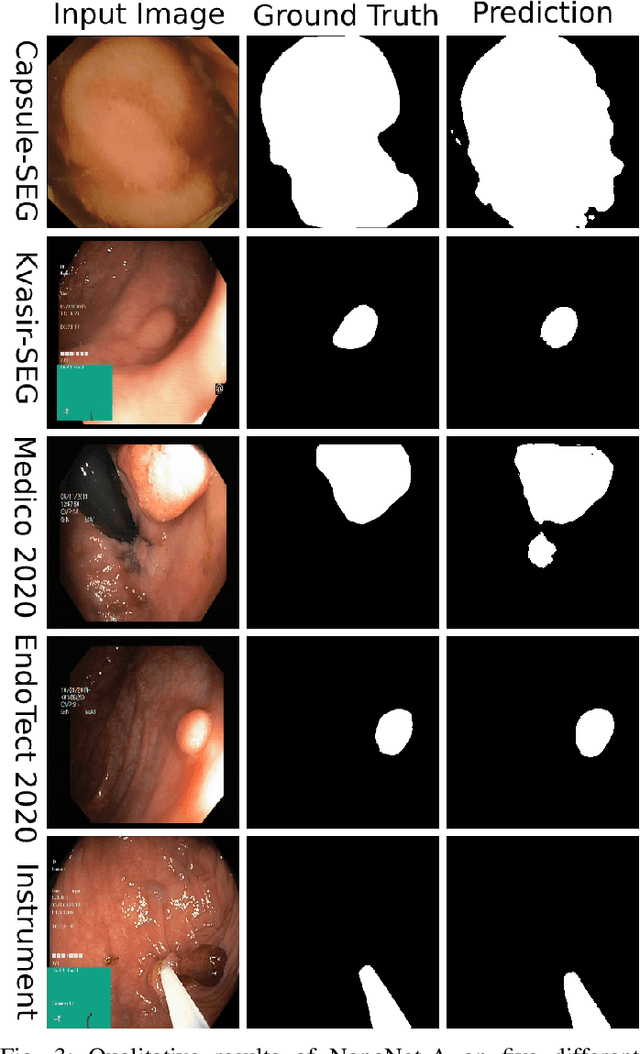

Abstract:Deep learning in gastrointestinal endoscopy can assist to improve clinical performance and be helpful to assess lesions more accurately. To this extent, semantic segmentation methods that can perform automated real-time delineation of a region-of-interest, e.g., boundary identification of cancer or precancerous lesions, can benefit both diagnosis and interventions. However, accurate and real-time segmentation of endoscopic images is extremely challenging due to its high operator dependence and high-definition image quality. To utilize automated methods in clinical settings, it is crucial to design lightweight models with low latency such that they can be integrated with low-end endoscope hardware devices. In this work, we propose NanoNet, a novel architecture for the segmentation of video capsule endoscopy and colonoscopy images. Our proposed architecture allows real-time performance and has higher segmentation accuracy compared to other more complex ones. We use video capsule endoscopy and standard colonoscopy datasets with polyps, and a dataset consisting of endoscopy biopsies and surgical instruments, to evaluate the effectiveness of our approach. Our experiments demonstrate the increased performance of our architecture in terms of a trade-off between model complexity, speed, model parameters, and metric performances. Moreover, the resulting model size is relatively tiny, with only nearly 36,000 parameters compared to traditional deep learning approaches having millions of parameters.
Medico Multimedia Task at MediaEval 2020: Automatic Polyp Segmentation
Dec 30, 2020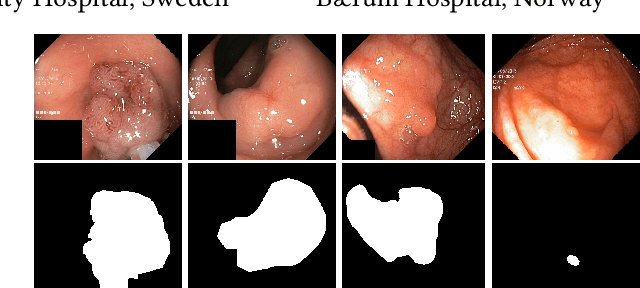
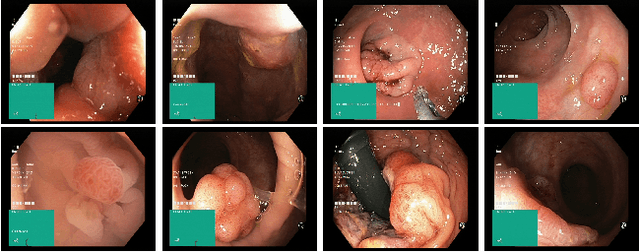
Abstract:Colorectal cancer is the third most common cause of cancer worldwide. According to Global cancer statistics 2018, the incidence of colorectal cancer is increasing in both developing and developed countries. Early detection of colon anomalies such as polyps is important for cancer prevention, and automatic polyp segmentation can play a crucial role for this. Regardless of the recent advancement in early detection and treatment options, the estimated polyp miss rate is still around 20\%. Support via an automated computer-aided diagnosis system could be one of the potential solutions for the overlooked polyps. Such detection systems can help low-cost design solutions and save doctors time, which they could for example use to perform more patient examinations. In this paper, we introduce the 2020 Medico challenge, provide some information on related work and the dataset, describe the task and evaluation metrics, and discuss the necessity of organizing the Medico challenge.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge