Wuyang Li
Factorized Video Generation: Decoupling Scene Construction and Temporal Synthesis in Text-to-Video Diffusion Models
Dec 18, 2025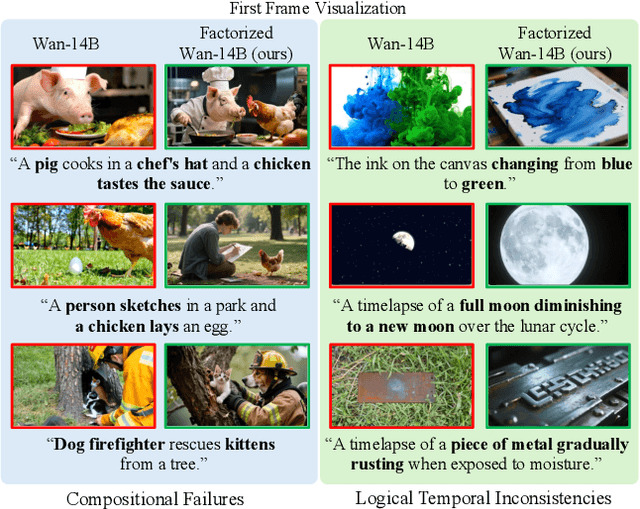
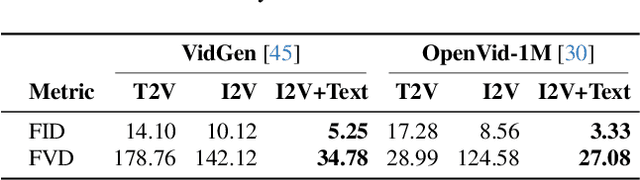
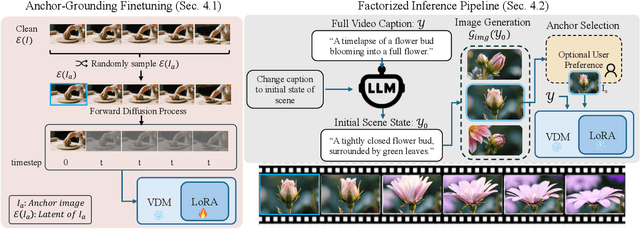
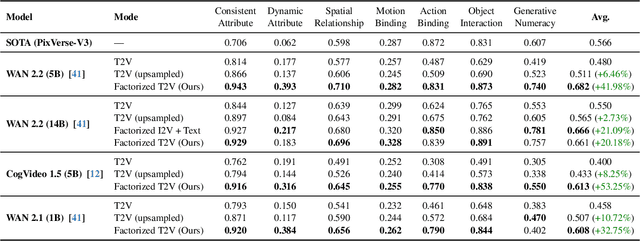
Abstract:State-of-the-art Text-to-Video (T2V) diffusion models can generate visually impressive results, yet they still frequently fail to compose complex scenes or follow logical temporal instructions. In this paper, we argue that many errors, including apparent motion failures, originate from the model's inability to construct a semantically correct or logically consistent initial frame. We introduce Factorized Video Generation (FVG), a pipeline that decouples these tasks by decomposing the Text-to-Video generation into three specialized stages: (1) Reasoning, where a Large Language Model (LLM) rewrites the video prompt to describe only the initial scene, resolving temporal ambiguities; (2) Composition, where a Text-to-Image (T2I) model synthesizes a high-quality, compositionally-correct anchor frame from this new prompt; and (3) Temporal Synthesis, where a video model, finetuned to understand this anchor, focuses its entire capacity on animating the scene and following the prompt. Our decomposed approach sets a new state-of-the-art on the T2V CompBench benchmark and significantly improves all tested models on VBench2. Furthermore, we show that visual anchoring allows us to cut the number of sampling steps by 70% without any loss in performance, leading to a substantial speed-up in sampling. Factorized Video Generation offers a simple yet practical path toward more efficient, robust, and controllable video synthesis
RAP: 3D Rasterization Augmented End-to-End Planning
Oct 05, 2025Abstract:Imitation learning for end-to-end driving trains policies only on expert demonstrations. Once deployed in a closed loop, such policies lack recovery data: small mistakes cannot be corrected and quickly compound into failures. A promising direction is to generate alternative viewpoints and trajectories beyond the logged path. Prior work explores photorealistic digital twins via neural rendering or game engines, but these methods are prohibitively slow and costly, and thus mainly used for evaluation. In this work, we argue that photorealism is unnecessary for training end-to-end planners. What matters is semantic fidelity and scalability: driving depends on geometry and dynamics, not textures or lighting. Motivated by this, we propose 3D Rasterization, which replaces costly rendering with lightweight rasterization of annotated primitives, enabling augmentations such as counterfactual recovery maneuvers and cross-agent view synthesis. To transfer these synthetic views effectively to real-world deployment, we introduce a Raster-to-Real feature-space alignment that bridges the sim-to-real gap. Together, these components form Rasterization Augmented Planning (RAP), a scalable data augmentation pipeline for planning. RAP achieves state-of-the-art closed-loop robustness and long-tail generalization, ranking first on four major benchmarks: NAVSIM v1/v2, Waymo Open Dataset Vision-based E2E Driving, and Bench2Drive. Our results show that lightweight rasterization with feature alignment suffices to scale E2E training, offering a practical alternative to photorealistic rendering. Project page: https://alan-lanfeng.github.io/RAP/.
See&Trek: Training-Free Spatial Prompting for Multimodal Large Language Model
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:We introduce SEE&TREK, the first training-free prompting framework tailored to enhance the spatial understanding of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMS) under vision-only constraints. While prior efforts have incorporated modalities like depth or point clouds to improve spatial reasoning, purely visualspatial understanding remains underexplored. SEE&TREK addresses this gap by focusing on two core principles: increasing visual diversity and motion reconstruction. For visual diversity, we conduct Maximum Semantic Richness Sampling, which employs an off-the-shell perception model to extract semantically rich keyframes that capture scene structure. For motion reconstruction, we simulate visual trajectories and encode relative spatial positions into keyframes to preserve both spatial relations and temporal coherence. Our method is training&GPU-free, requiring only a single forward pass, and can be seamlessly integrated into existing MLLM'S. Extensive experiments on the VSI-B ENCH and STI-B ENCH show that S EE &T REK consistently boosts various MLLM S performance across diverse spatial reasoning tasks with the most +3.5% improvement, offering a promising path toward stronger spatial intelligence.
Track Any Anomalous Object: A Granular Video Anomaly Detection Pipeline
Jun 05, 2025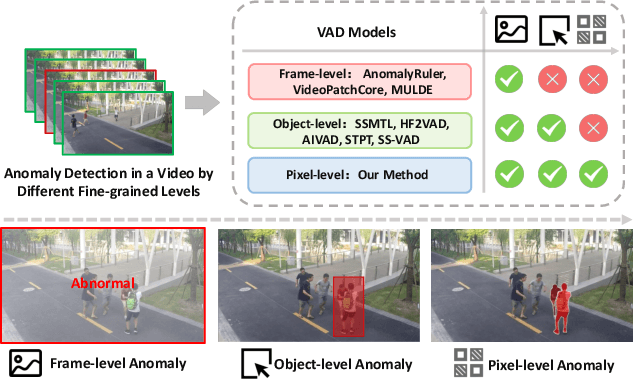
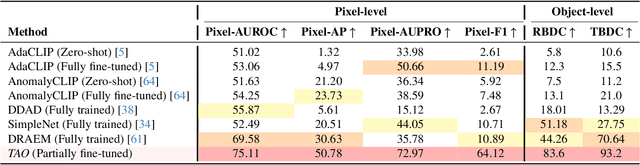
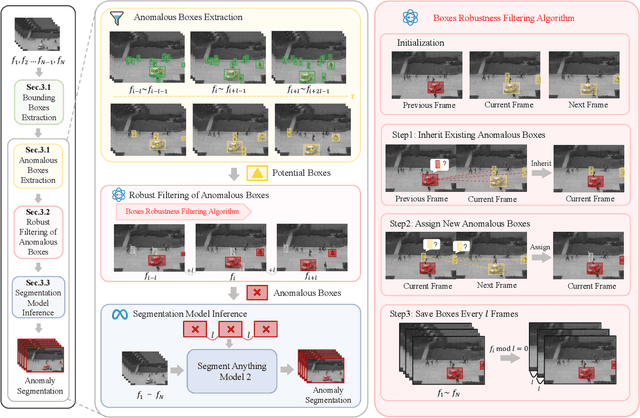

Abstract:Video anomaly detection (VAD) is crucial in scenarios such as surveillance and autonomous driving, where timely detection of unexpected activities is essential. Although existing methods have primarily focused on detecting anomalous objects in videos -- either by identifying anomalous frames or objects -- they often neglect finer-grained analysis, such as anomalous pixels, which limits their ability to capture a broader range of anomalies. To address this challenge, we propose a new framework called Track Any Anomalous Object (TAO), which introduces a granular video anomaly detection pipeline that, for the first time, integrates the detection of multiple fine-grained anomalous objects into a unified framework. Unlike methods that assign anomaly scores to every pixel, our approach transforms the problem into pixel-level tracking of anomalous objects. By linking anomaly scores to downstream tasks such as segmentation and tracking, our method removes the need for threshold tuning and achieves more precise anomaly localization in long and complex video sequences. Experiments demonstrate that TAO sets new benchmarks in accuracy and robustness. Project page available online.
VoxDet: Rethinking 3D Semantic Occupancy Prediction as Dense Object Detection
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:3D semantic occupancy prediction aims to reconstruct the 3D geometry and semantics of the surrounding environment. With dense voxel labels, prior works typically formulate it as a dense segmentation task, independently classifying each voxel. However, this paradigm neglects critical instance-centric discriminability, leading to instance-level incompleteness and adjacent ambiguities. To address this, we highlight a free lunch of occupancy labels: the voxel-level class label implicitly provides insight at the instance level, which is overlooked by the community. Motivated by this observation, we first introduce a training-free Voxel-to-Instance (VoxNT) trick: a simple yet effective method that freely converts voxel-level class labels into instance-level offset labels. Building on this, we further propose VoxDet, an instance-centric framework that reformulates the voxel-level occupancy prediction as dense object detection by decoupling it into two sub-tasks: offset regression and semantic prediction. Specifically, based on the lifted 3D volume, VoxDet first uses (a) Spatially-decoupled Voxel Encoder to generate disentangled feature volumes for the two sub-tasks, which learn task-specific spatial deformation in the densely projected tri-perceptive space. Then, we deploy (b) Task-decoupled Dense Predictor to address this task via dense detection. Here, we first regress a 4D offset field to estimate distances (6 directions) between voxels and object borders in the voxel space. The regressed offsets are then used to guide the instance-level aggregation in the classification branch, achieving instance-aware prediction. Experiments show that VoxDet can be deployed on both camera and LiDAR input, jointly achieving state-of-the-art results on both benchmarks. VoxDet is not only highly efficient, but also achieves 63.0 IoU on the SemanticKITTI test set, ranking 1st on the online leaderboard.
FlexGS: Train Once, Deploy Everywhere with Many-in-One Flexible 3D Gaussian Splatting
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS) has enabled various applications in 3D scene representation and novel view synthesis due to its efficient rendering capabilities. However, 3DGS demands relatively significant GPU memory, limiting its use on devices with restricted computational resources. Previous approaches have focused on pruning less important Gaussians, effectively compressing 3DGS but often requiring a fine-tuning stage and lacking adaptability for the specific memory needs of different devices. In this work, we present an elastic inference method for 3DGS. Given an input for the desired model size, our method selects and transforms a subset of Gaussians, achieving substantial rendering performance without additional fine-tuning. We introduce a tiny learnable module that controls Gaussian selection based on the input percentage, along with a transformation module that adjusts the selected Gaussians to complement the performance of the reduced model. Comprehensive experiments on ZipNeRF, MipNeRF and Tanks\&Temples scenes demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. Code is available at https://flexgs.github.io.
X-GRM: Large Gaussian Reconstruction Model for Sparse-view X-rays to Computed Tomography
May 21, 2025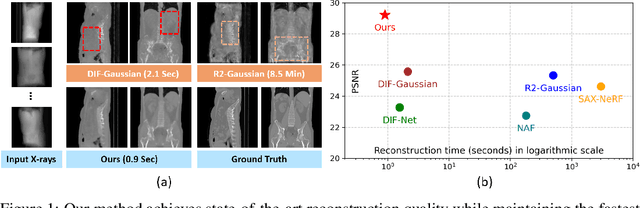
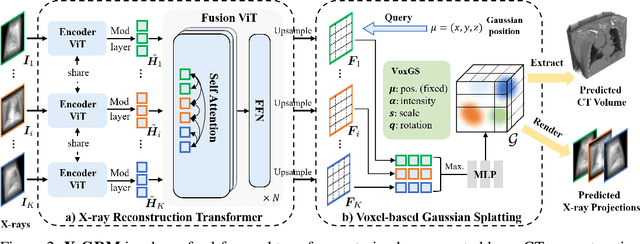
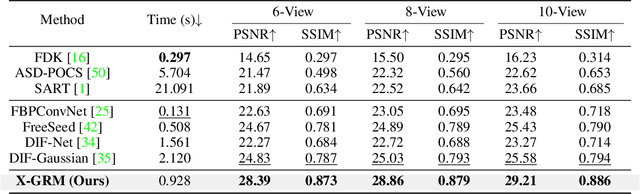
Abstract:Computed Tomography serves as an indispensable tool in clinical workflows, providing non-invasive visualization of internal anatomical structures. Existing CT reconstruction works are limited to small-capacity model architecture, inflexible volume representation, and small-scale training data. In this paper, we present X-GRM (X-ray Gaussian Reconstruction Model), a large feedforward model for reconstructing 3D CT from sparse-view 2D X-ray projections. X-GRM employs a scalable transformer-based architecture to encode an arbitrary number of sparse X-ray inputs, where tokens from different views are integrated efficiently. Then, tokens are decoded into a new volume representation, named Voxel-based Gaussian Splatting (VoxGS), which enables efficient CT volume extraction and differentiable X-ray rendering. To support the training of X-GRM, we collect ReconX-15K, a large-scale CT reconstruction dataset containing around 15,000 CT/X-ray pairs across diverse organs, including the chest, abdomen, pelvis, and tooth etc. This combination of a high-capacity model, flexible volume representation, and large-scale training data empowers our model to produce high-quality reconstructions from various testing inputs, including in-domain and out-domain X-ray projections. Project Page: https://github.com/CUHK-AIM-Group/X-GRM.
Bridge the Gap Between Visual and Linguistic Comprehension for Generalized Zero-shot Semantic Segmentation
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Generalized zero-shot semantic segmentation (GZS3) aims to achieve the human-level capability of segmenting not only seen classes but also novel class regions unseen in the training data through introducing the bridge of semantic representations, e.g., word vector. While effective, the way of utilizing one semantic representation to associate the corresponding class and to enable the knowledge transfer from seen to unseen classes is insufficient as well as incompatible with human cognition. Inspired by the observation that humans often use some `part' and `state' information to comprehend the seen objects and imagine unseen classes, we decouple each class into detailed descriptions, including object parts and states. Based on the decoupling formulation, we propose a Decoupled Vision-Language Matching (DeVLMatch) framework, composed of spatial-part (SPMatch) and channel-state (CSMatch) matching modules, for GZS3. In SPMatch, we comprehend objects with spatial part information from both visual and linguistic perspectives and perform graph matching to bridge the gap. In CSMatch, states of objects from the linguistic perspective are matched to compatible channel information from the visual perspective. By decoupling and matching objects across visual and linguistic comprehension, we can explicitly introspect the relationship between seen and unseen classes in fine-grained object part and state levels, thereby facilitating the knowledge transfer from seen to unseen classes in visual space. The proposed DeVLMatch framework surpasses the previous GZS3 methods on standard benchmarks, including PASCAL VOC, COCO-Stuff, and CATARACTS, demonstrating its effectiveness.
EventVL: Understand Event Streams via Multimodal Large Language Model
Jan 23, 2025Abstract:The event-based Vision-Language Model (VLM) recently has made good progress for practical vision tasks. However, most of these works just utilize CLIP for focusing on traditional perception tasks, which obstruct model understanding explicitly the sufficient semantics and context from event streams. To address the deficiency, we propose EventVL, the first generative event-based MLLM (Multimodal Large Language Model) framework for explicit semantic understanding. Specifically, to bridge the data gap for connecting different modalities semantics, we first annotate a large event-image/video-text dataset, containing almost 1.4 million high-quality pairs of data, which enables effective learning across various scenes, e.g., drive scene or human motion. After that, we design Event Spatiotemporal Representation to fully explore the comprehensive information by diversely aggregating and segmenting the event stream. To further promote a compact semantic space, Dynamic Semantic Alignment is introduced to improve and complete sparse semantic spaces of events. Extensive experiments show that our EventVL can significantly surpass existing MLLM baselines in event captioning and scene description generation tasks. We hope our research could contribute to the development of the event vision community.
ConcealGS: Concealing Invisible Copyright Information in 3D Gaussian Splatting
Jan 07, 2025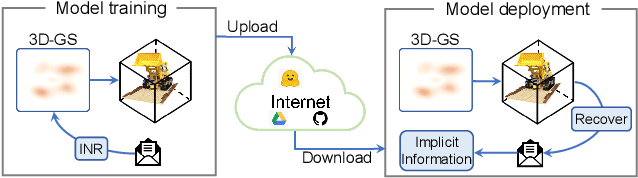
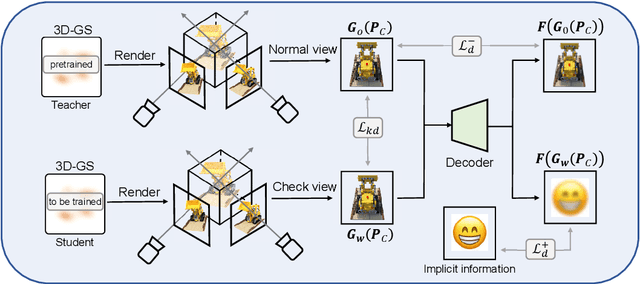
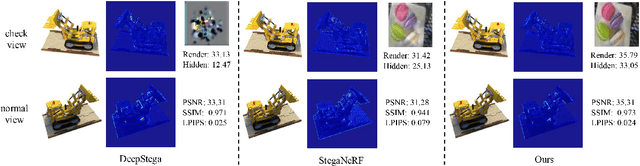
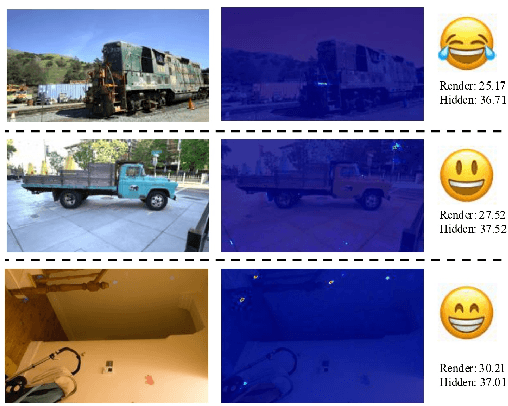
Abstract:With the rapid development of 3D reconstruction technology, the widespread distribution of 3D data has become a future trend. While traditional visual data (such as images and videos) and NeRF-based formats already have mature techniques for copyright protection, steganographic techniques for the emerging 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) format have yet to be fully explored. To address this, we propose ConcealGS, an innovative method for embedding implicit information into 3D-GS. By introducing the knowledge distillation and gradient optimization strategy based on 3D-GS, ConcealGS overcomes the limitations of NeRF-based models and enhances the robustness of implicit information and the quality of 3D reconstruction. We evaluate ConcealGS in various potential application scenarios, and experimental results have demonstrated that ConcealGS not only successfully recovers implicit information but also has almost no impact on rendering quality, providing a new approach for embedding invisible and recoverable information into 3D models in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge