Alexandre Alahi
EPFL
MAD: Motion Appearance Decoupling for efficient Driving World Models
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Recent video diffusion models generate photorealistic, temporally coherent videos, yet they fall short as reliable world models for autonomous driving, where structured motion and physically consistent interactions are essential. Adapting these generalist video models to driving domains has shown promise but typically requires massive domain-specific data and costly fine-tuning. We propose an efficient adaptation framework that converts generalist video diffusion models into controllable driving world models with minimal supervision. The key idea is to decouple motion learning from appearance synthesis. First, the model is adapted to predict structured motion in a simplified form: videos of skeletonized agents and scene elements, focusing learning on physical and social plausibility. Then, the same backbone is reused to synthesize realistic RGB videos conditioned on these motion sequences, effectively "dressing" the motion with texture and lighting. This two-stage process mirrors a reasoning-rendering paradigm: first infer dynamics, then render appearance. Our experiments show this decoupled approach is exceptionally efficient: adapting SVD, we match prior SOTA models with less than 6% of their compute. Scaling to LTX, our MAD-LTX model outperforms all open-source competitors, and supports a comprehensive suite of text, ego, and object controls. Project page: https://vita-epfl.github.io/MAD-World-Model/
Factorized Video Generation: Decoupling Scene Construction and Temporal Synthesis in Text-to-Video Diffusion Models
Dec 18, 2025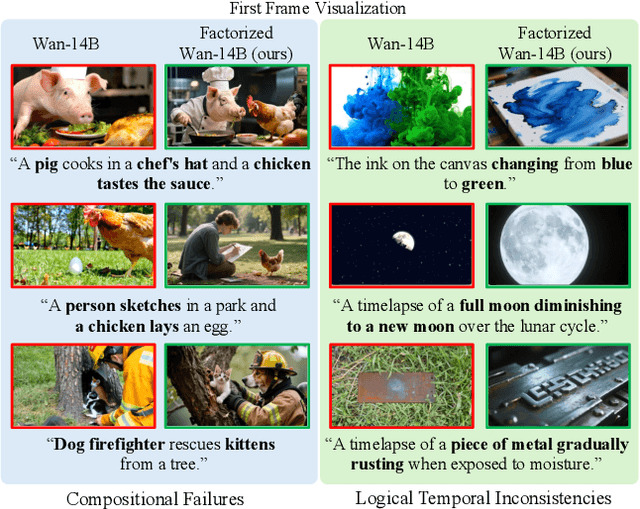
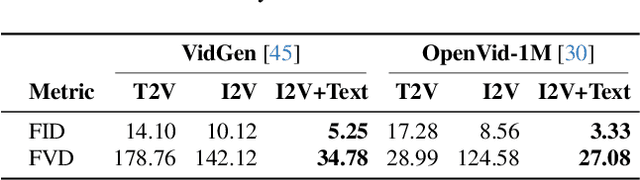
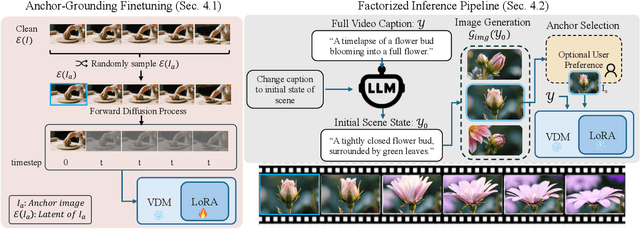
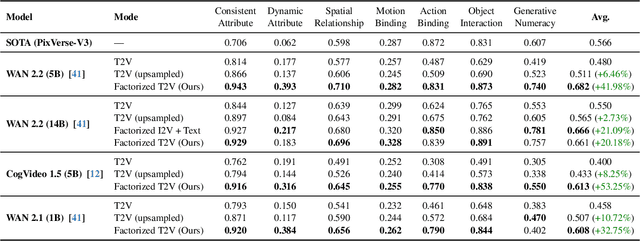
Abstract:State-of-the-art Text-to-Video (T2V) diffusion models can generate visually impressive results, yet they still frequently fail to compose complex scenes or follow logical temporal instructions. In this paper, we argue that many errors, including apparent motion failures, originate from the model's inability to construct a semantically correct or logically consistent initial frame. We introduce Factorized Video Generation (FVG), a pipeline that decouples these tasks by decomposing the Text-to-Video generation into three specialized stages: (1) Reasoning, where a Large Language Model (LLM) rewrites the video prompt to describe only the initial scene, resolving temporal ambiguities; (2) Composition, where a Text-to-Image (T2I) model synthesizes a high-quality, compositionally-correct anchor frame from this new prompt; and (3) Temporal Synthesis, where a video model, finetuned to understand this anchor, focuses its entire capacity on animating the scene and following the prompt. Our decomposed approach sets a new state-of-the-art on the T2V CompBench benchmark and significantly improves all tested models on VBench2. Furthermore, we show that visual anchoring allows us to cut the number of sampling steps by 70% without any loss in performance, leading to a substantial speed-up in sampling. Factorized Video Generation offers a simple yet practical path toward more efficient, robust, and controllable video synthesis
RUMPL: Ray-Based Transformers for Universal Multi-View 2D to 3D Human Pose Lifting
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Estimating 3D human poses from 2D images remains challenging due to occlusions and projective ambiguity. Multi-view learning-based approaches mitigate these issues but often fail to generalize to real-world scenarios, as large-scale multi-view datasets with 3D ground truth are scarce and captured under constrained conditions. To overcome this limitation, recent methods rely on 2D pose estimation combined with 2D-to-3D pose lifting trained on synthetic data. Building on our previous MPL framework, we propose RUMPL, a transformer-based 3D pose lifter that introduces a 3D ray-based representation of 2D keypoints. This formulation makes the model independent of camera calibration and the number of views, enabling universal deployment across arbitrary multi-view configurations without retraining or fine-tuning. A new View Fusion Transformer leverages learned fused-ray tokens to aggregate information along rays, further improving multi-view consistency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that RUMPL reduces MPJPE by up to 53% compared to triangulation and over 60% compared to transformer-based image-representation baselines. Results on new benchmarks, including in-the-wild multi-view and multi-person datasets, confirm its robustness and scalability. The framework's source code is available at https://github.com/aghasemzadeh/OpenRUMPL
LayerSync: Self-aligning Intermediate Layers
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:We propose LayerSync, a domain-agnostic approach for improving the generation quality and the training efficiency of diffusion models. Prior studies have highlighted the connection between the quality of generation and the representations learned by diffusion models, showing that external guidance on model intermediate representations accelerates training. We reconceptualize this paradigm by regularizing diffusion models with their own intermediate representations. Building on the observation that representation quality varies across diffusion model layers, we show that the most semantically rich representations can act as an intrinsic guidance for weaker ones, reducing the need for external supervision. Our approach, LayerSync, is a self-sufficient, plug-and-play regularizer term with no overhead on diffusion model training and generalizes beyond the visual domain to other modalities. LayerSync requires no pretrained models nor additional data. We extensively evaluate the method on image generation and demonstrate its applicability to other domains such as audio, video, and motion generation. We show that it consistently improves the generation quality and the training efficiency. For example, we speed up the training of flow-based transformer by over 8.75x on ImageNet dataset and improved the generation quality by 23.6%. The code is available at https://github.com/vita-epfl/LayerSync.
RAP: 3D Rasterization Augmented End-to-End Planning
Oct 05, 2025Abstract:Imitation learning for end-to-end driving trains policies only on expert demonstrations. Once deployed in a closed loop, such policies lack recovery data: small mistakes cannot be corrected and quickly compound into failures. A promising direction is to generate alternative viewpoints and trajectories beyond the logged path. Prior work explores photorealistic digital twins via neural rendering or game engines, but these methods are prohibitively slow and costly, and thus mainly used for evaluation. In this work, we argue that photorealism is unnecessary for training end-to-end planners. What matters is semantic fidelity and scalability: driving depends on geometry and dynamics, not textures or lighting. Motivated by this, we propose 3D Rasterization, which replaces costly rendering with lightweight rasterization of annotated primitives, enabling augmentations such as counterfactual recovery maneuvers and cross-agent view synthesis. To transfer these synthetic views effectively to real-world deployment, we introduce a Raster-to-Real feature-space alignment that bridges the sim-to-real gap. Together, these components form Rasterization Augmented Planning (RAP), a scalable data augmentation pipeline for planning. RAP achieves state-of-the-art closed-loop robustness and long-tail generalization, ranking first on four major benchmarks: NAVSIM v1/v2, Waymo Open Dataset Vision-based E2E Driving, and Bench2Drive. Our results show that lightweight rasterization with feature alignment suffices to scale E2E training, offering a practical alternative to photorealistic rendering. Project page: https://alan-lanfeng.github.io/RAP/.
JointDiff: Bridging Continuous and Discrete in Multi-Agent Trajectory Generation
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Generative models often treat continuous data and discrete events as separate processes, creating a gap in modeling complex systems where they interact synchronously. To bridge this gap, we introduce JointDiff, a novel diffusion framework designed to unify these two processes by simultaneously generating continuous spatio-temporal data and synchronous discrete events. We demonstrate its efficacy in the sports domain by simultaneously modeling multi-agent trajectories and key possession events. This joint modeling is validated with non-controllable generation and two novel controllable generation scenarios: weak-possessor-guidance, which offers flexible semantic control over game dynamics through a simple list of intended ball possessors, and text-guidance, which enables fine-grained, language-driven generation. To enable the conditioning with these guidance signals, we introduce CrossGuid, an effective conditioning operation for multi-agent domains. We also share a new unified sports benchmark enhanced with textual descriptions for soccer and football datasets. JointDiff achieves state-of-the-art performance, demonstrating that joint modeling is crucial for building realistic and controllable generative models for interactive systems.
SoccerNet 2025 Challenges Results
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:The SoccerNet 2025 Challenges mark the fifth annual edition of the SoccerNet open benchmarking effort, dedicated to advancing computer vision research in football video understanding. This year's challenges span four vision-based tasks: (1) Team Ball Action Spotting, focused on detecting ball-related actions in football broadcasts and assigning actions to teams; (2) Monocular Depth Estimation, targeting the recovery of scene geometry from single-camera broadcast clips through relative depth estimation for each pixel; (3) Multi-View Foul Recognition, requiring the analysis of multiple synchronized camera views to classify fouls and their severity; and (4) Game State Reconstruction, aimed at localizing and identifying all players from a broadcast video to reconstruct the game state on a 2D top-view of the field. Across all tasks, participants were provided with large-scale annotated datasets, unified evaluation protocols, and strong baselines as starting points. This report presents the results of each challenge, highlights the top-performing solutions, and provides insights into the progress made by the community. The SoccerNet Challenges continue to serve as a driving force for reproducible, open research at the intersection of computer vision, artificial intelligence, and sports. Detailed information about the tasks, challenges, and leaderboards can be found at https://www.soccer-net.org, with baselines and development kits available at https://github.com/SoccerNet.
NAT: Learning to Attack Neurons for Enhanced Adversarial Transferability
Aug 23, 2025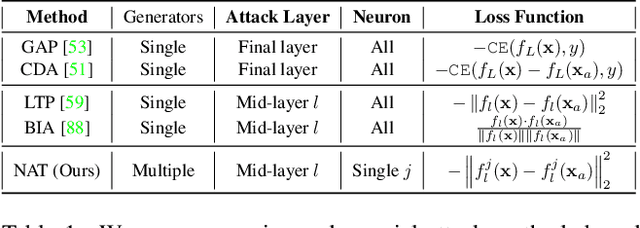

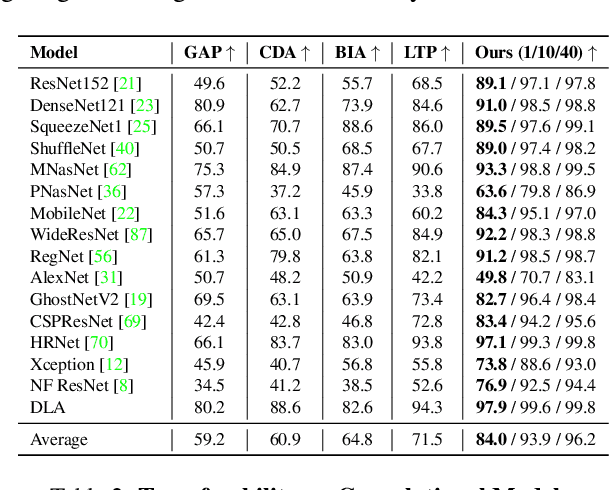
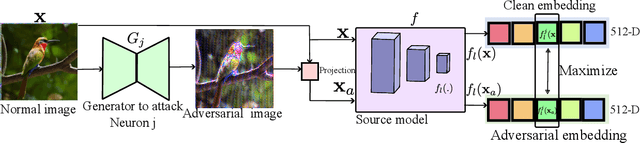
Abstract:The generation of transferable adversarial perturbations typically involves training a generator to maximize embedding separation between clean and adversarial images at a single mid-layer of a source model. In this work, we build on this approach and introduce Neuron Attack for Transferability (NAT), a method designed to target specific neuron within the embedding. Our approach is motivated by the observation that previous layer-level optimizations often disproportionately focus on a few neurons representing similar concepts, leaving other neurons within the attacked layer minimally affected. NAT shifts the focus from embedding-level separation to a more fundamental, neuron-specific approach. We find that targeting individual neurons effectively disrupts the core units of the neural network, providing a common basis for transferability across different models. Through extensive experiments on 41 diverse ImageNet models and 9 fine-grained models, NAT achieves fooling rates that surpass existing baselines by over 14\% in cross-model and 4\% in cross-domain settings. Furthermore, by leveraging the complementary attacking capabilities of the trained generators, we achieve impressive fooling rates within just 10 queries. Our code is available at: https://krishnakanthnakka.github.io/NAT/
OmniTraj: Pre-Training on Heterogeneous Data for Adaptive and Zero-Shot Human Trajectory Prediction
Jul 31, 2025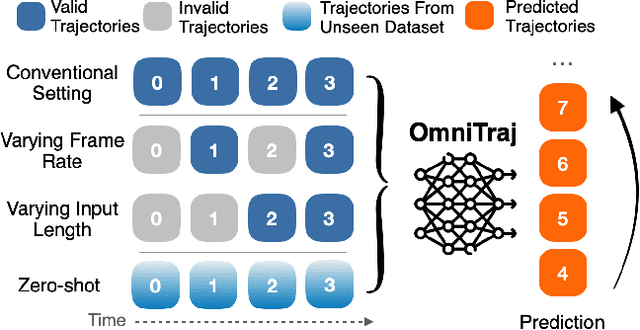

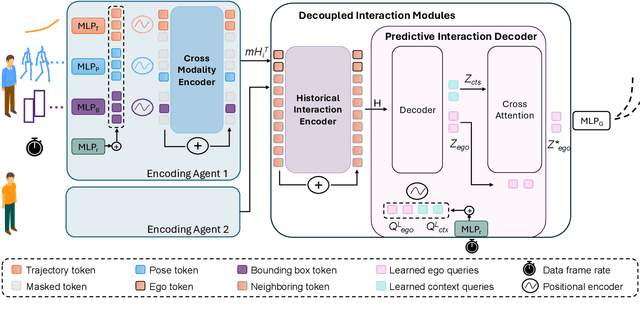
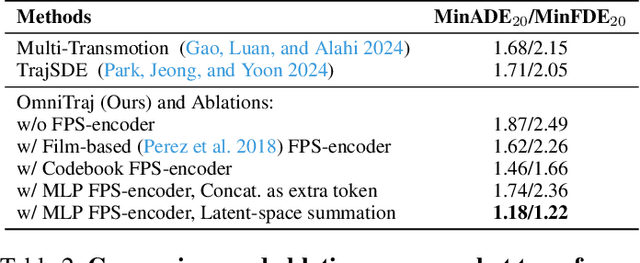
Abstract:While large-scale pre-training has advanced human trajectory prediction, a critical challenge remains: zero-shot transfer to unseen dataset with varying temporal dynamics. State-of-the-art pre-trained models often require fine-tuning to adapt to new datasets with different frame rates or observation horizons, limiting their scalability and practical utility. In this work, we systematically investigate this limitation and propose a robust solution. We first demonstrate that existing data-aware discrete models struggle when transferred to new scenarios with shifted temporal setups. We then isolate the temporal generalization from dataset shift, revealing that a simple, explicit conditioning mechanism for temporal metadata is a highly effective solution. Based on this insight, we present OmniTraj, a Transformer-based model pre-trained on a large-scale, heterogeneous dataset. Our experiments show that explicitly conditioning on the frame rate enables OmniTraj to achieve state-of-the-art zero-shot transfer performance, reducing prediction error by over 70\% in challenging cross-setup scenarios. After fine-tuning, OmniTraj achieves state-of-the-art results on four datasets, including NBA, JTA, WorldPose, and ETH-UCY. The code is publicly available: https://github.com/vita-epfl/omnitraj
Social-Pose: Enhancing Trajectory Prediction with Human Body Pose
Jul 30, 2025
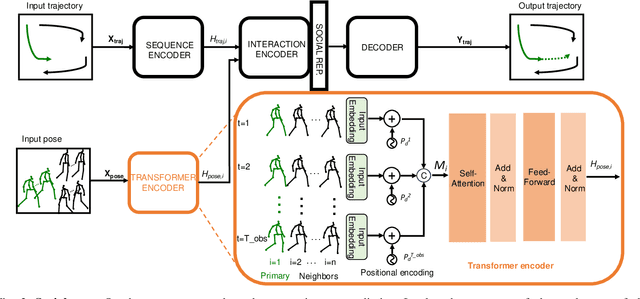
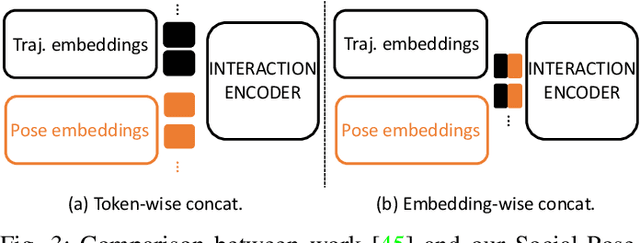
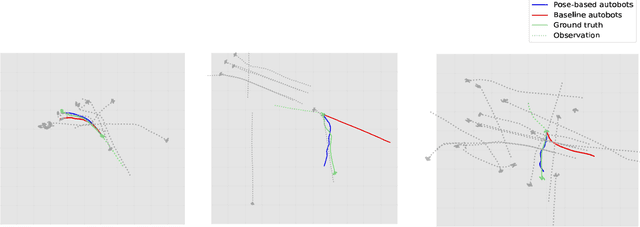
Abstract:Accurate human trajectory prediction is one of the most crucial tasks for autonomous driving, ensuring its safety. Yet, existing models often fail to fully leverage the visual cues that humans subconsciously communicate when navigating the space. In this work, we study the benefits of predicting human trajectories using human body poses instead of solely their Cartesian space locations in time. We propose `Social-pose', an attention-based pose encoder that effectively captures the poses of all humans in a scene and their social relations. Our method can be integrated into various trajectory prediction architectures. We have conducted extensive experiments on state-of-the-art models (based on LSTM, GAN, MLP, and Transformer), and showed improvements over all of them on synthetic (Joint Track Auto) and real (Human3.6M, Pedestrians and Cyclists in Road Traffic, and JRDB) datasets. We also explored the advantages of using 2D versus 3D poses, as well as the effect of noisy poses and the application of our pose-based predictor in robot navigation scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge