Xiaoqing Guo
Engineering Mathematics, University of Bristol, affiliated with the Bristol Robotics Lab, United Kingdom
Where MLLMs Attend and What They Rely On: Explaining Autoregressive Token Generation
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in aligning visual inputs with natural language outputs. Yet, the extent to which generated tokens depend on visual modalities remains poorly understood, limiting interpretability and reliability. In this work, we present EAGLE, a lightweight black-box framework for explaining autoregressive token generation in MLLMs. EAGLE attributes any selected tokens to compact perceptual regions while quantifying the relative influence of language priors and perceptual evidence. The framework introduces an objective function that unifies sufficiency (insight score) and indispensability (necessity score), optimized via greedy search over sparsified image regions for faithful and efficient attribution. Beyond spatial attribution, EAGLE performs modality-aware analysis that disentangles what tokens rely on, providing fine-grained interpretability of model decisions. Extensive experiments across open-source MLLMs show that EAGLE consistently outperforms existing methods in faithfulness, localization, and hallucination diagnosis, while requiring substantially less GPU memory. These results highlight its effectiveness and practicality for advancing the interpretability of MLLMs. The code is available at https://github.com/RuoyuChen10/EAGLE.
U2-BENCH: Benchmarking Large Vision-Language Models on Ultrasound Understanding
May 23, 2025Abstract:Ultrasound is a widely-used imaging modality critical to global healthcare, yet its interpretation remains challenging due to its varying image quality on operators, noises, and anatomical structures. Although large vision-language models (LVLMs) have demonstrated impressive multimodal capabilities across natural and medical domains, their performance on ultrasound remains largely unexplored. We introduce U2-BENCH, the first comprehensive benchmark to evaluate LVLMs on ultrasound understanding across classification, detection, regression, and text generation tasks. U2-BENCH aggregates 7,241 cases spanning 15 anatomical regions and defines 8 clinically inspired tasks, such as diagnosis, view recognition, lesion localization, clinical value estimation, and report generation, across 50 ultrasound application scenarios. We evaluate 20 state-of-the-art LVLMs, both open- and closed-source, general-purpose and medical-specific. Our results reveal strong performance on image-level classification, but persistent challenges in spatial reasoning and clinical language generation. U2-BENCH establishes a rigorous and unified testbed to assess and accelerate LVLM research in the uniquely multimodal domain of medical ultrasound imaging.
IterMask3D: Unsupervised Anomaly Detection and Segmentation with Test-Time Iterative Mask Refinement in 3D Brain MR
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:Unsupervised anomaly detection and segmentation methods train a model to learn the training distribution as 'normal'. In the testing phase, they identify patterns that deviate from this normal distribution as 'anomalies'. To learn the `normal' distribution, prevailing methods corrupt the images and train a model to reconstruct them. During testing, the model attempts to reconstruct corrupted inputs based on the learned 'normal' distribution. Deviations from this distribution lead to high reconstruction errors, which indicate potential anomalies. However, corrupting an input image inevitably causes information loss even in normal regions, leading to suboptimal reconstruction and an increased risk of false positives. To alleviate this, we propose IterMask3D, an iterative spatial mask-refining strategy designed for 3D brain MRI. We iteratively spatially mask areas of the image as corruption and reconstruct them, then shrink the mask based on reconstruction error. This process iteratively unmasks 'normal' areas to the model, whose information further guides reconstruction of 'normal' patterns under the mask to be reconstructed accurately, reducing false positives. In addition, to achieve better reconstruction performance, we also propose using high-frequency image content as additional structural information to guide the reconstruction of the masked area. Extensive experiments on the detection of both synthetic and real-world imaging artifacts, as well as segmentation of various pathological lesions across multiple MRI sequences, consistently demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
Bridge the Gap Between Visual and Linguistic Comprehension for Generalized Zero-shot Semantic Segmentation
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Generalized zero-shot semantic segmentation (GZS3) aims to achieve the human-level capability of segmenting not only seen classes but also novel class regions unseen in the training data through introducing the bridge of semantic representations, e.g., word vector. While effective, the way of utilizing one semantic representation to associate the corresponding class and to enable the knowledge transfer from seen to unseen classes is insufficient as well as incompatible with human cognition. Inspired by the observation that humans often use some `part' and `state' information to comprehend the seen objects and imagine unseen classes, we decouple each class into detailed descriptions, including object parts and states. Based on the decoupling formulation, we propose a Decoupled Vision-Language Matching (DeVLMatch) framework, composed of spatial-part (SPMatch) and channel-state (CSMatch) matching modules, for GZS3. In SPMatch, we comprehend objects with spatial part information from both visual and linguistic perspectives and perform graph matching to bridge the gap. In CSMatch, states of objects from the linguistic perspective are matched to compatible channel information from the visual perspective. By decoupling and matching objects across visual and linguistic comprehension, we can explicitly introspect the relationship between seen and unseen classes in fine-grained object part and state levels, thereby facilitating the knowledge transfer from seen to unseen classes in visual space. The proposed DeVLMatch framework surpasses the previous GZS3 methods on standard benchmarks, including PASCAL VOC, COCO-Stuff, and CATARACTS, demonstrating its effectiveness.
Pose-GuideNet: Automatic Scanning Guidance for Fetal Head Ultrasound from Pose Estimation
Aug 19, 2024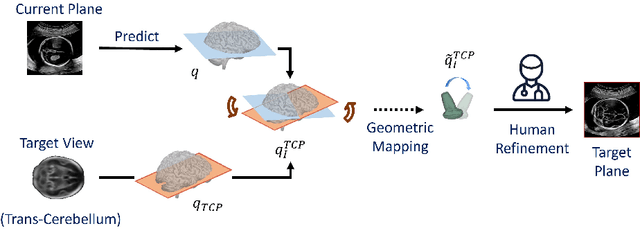
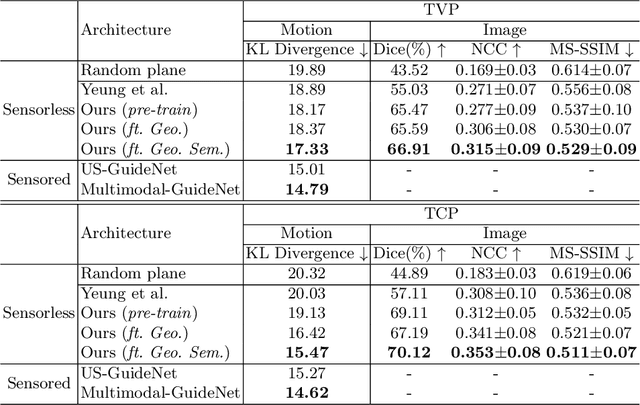
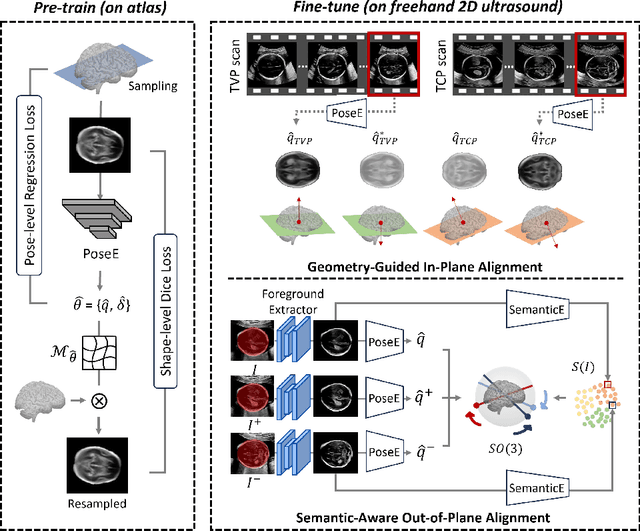
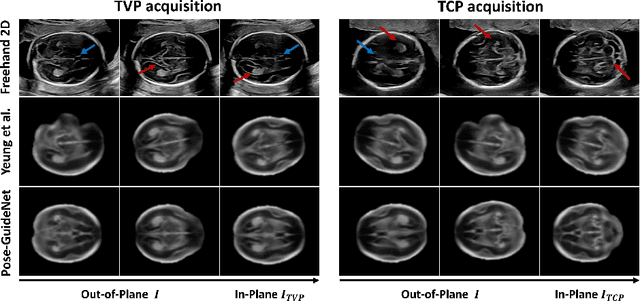
Abstract:3D pose estimation from a 2D cross-sectional view enables healthcare professionals to navigate through the 3D space, and such techniques initiate automatic guidance in many image-guided radiology applications. In this work, we investigate how estimating 3D fetal pose from freehand 2D ultrasound scanning can guide a sonographer to locate a head standard plane. Fetal head pose is estimated by the proposed Pose-GuideNet, a novel 2D/3D registration approach to align freehand 2D ultrasound to a 3D anatomical atlas without the acquisition of 3D ultrasound. To facilitate the 2D to 3D cross-dimensional projection, we exploit the prior knowledge in the atlas to align the standard plane frame in a freehand scan. A semantic-aware contrastive-based approach is further proposed to align the frames that are off standard planes based on their anatomical similarity. In the experiment, we enhance the existing assessment of freehand image localization by comparing the transformation of its estimated pose towards standard plane with the corresponding probe motion, which reflects the actual view change in 3D anatomy. Extensive results on two clinical head biometry tasks show that Pose-GuideNet not only accurately predicts pose but also successfully predicts the direction of the fetal head. Evaluations with probe motions further demonstrate the feasibility of adopting Pose-GuideNet for freehand ultrasound-assisted navigation in a sensor-free environment.
MMSummary: Multimodal Summary Generation for Fetal Ultrasound Video
Aug 07, 2024



Abstract:We present the first automated multimodal summary generation system, MMSummary, for medical imaging video, particularly with a focus on fetal ultrasound analysis. Imitating the examination process performed by a human sonographer, MMSummary is designed as a three-stage pipeline, progressing from keyframe detection to keyframe captioning and finally anatomy segmentation and measurement. In the keyframe detection stage, an innovative automated workflow is proposed to progressively select a concise set of keyframes, preserving sufficient video information without redundancy. Subsequently, we adapt a large language model to generate meaningful captions for fetal ultrasound keyframes in the keyframe captioning stage. If a keyframe is captioned as fetal biometry, the segmentation and measurement stage estimates biometric parameters by segmenting the region of interest according to the textual prior. The MMSummary system provides comprehensive summaries for fetal ultrasound examinations and based on reported experiments is estimated to reduce scanning time by approximately 31.5%, thereby suggesting the potential to enhance clinical workflow efficiency.
IterMask2: Iterative Unsupervised Anomaly Segmentation via Spatial and Frequency Masking for Brain Lesions in MRI
Jun 04, 2024Abstract:Unsupervised anomaly segmentation approaches to pathology segmentation train a model on images of healthy subjects, that they define as the 'normal' data distribution. At inference, they aim to segment any pathologies in new images as 'anomalies', as they exhibit patterns that deviate from those in 'normal' training data. Prevailing methods follow the 'corrupt-and-reconstruct' paradigm. They intentionally corrupt an input image, reconstruct it to follow the learned 'normal' distribution, and subsequently segment anomalies based on reconstruction error. Corrupting an input image, however, inevitably leads to suboptimal reconstruction even of normal regions, causing false positives. To alleviate this, we propose a novel iterative spatial mask-refining strategy IterMask2. We iteratively mask areas of the image, reconstruct them, and update the mask based on reconstruction error. This iterative process progressively adds information about areas that are confidently normal as per the model. The increasing content guides reconstruction of nearby masked areas, improving reconstruction of normal tissue under these areas, reducing false positives. We also use high-frequency image content as an auxiliary input to provide additional structural information for masked areas. This further improves reconstruction error of normal in comparison to anomalous areas, facilitating segmentation of the latter. We conduct experiments on several brain lesion datasets and demonstrate effectiveness of our method. Code is available at: https://github.com/ZiyunLiang/IterMasks2
Diversified and Personalized Multi-rater Medical Image Segmentation
Mar 20, 2024Abstract:Annotation ambiguity due to inherent data uncertainties such as blurred boundaries in medical scans and different observer expertise and preferences has become a major obstacle for training deep-learning based medical image segmentation models. To address it, the common practice is to gather multiple annotations from different experts, leading to the setting of multi-rater medical image segmentation. Existing works aim to either merge different annotations into the "groundtruth" that is often unattainable in numerous medical contexts, or generate diverse results, or produce personalized results corresponding to individual expert raters. Here, we bring up a more ambitious goal for multi-rater medical image segmentation, i.e., obtaining both diversified and personalized results. Specifically, we propose a two-stage framework named D-Persona (first Diversification and then Personalization). In Stage I, we exploit multiple given annotations to train a Probabilistic U-Net model, with a bound-constrained loss to improve the prediction diversity. In this way, a common latent space is constructed in Stage I, where different latent codes denote diversified expert opinions. Then, in Stage II, we design multiple attention-based projection heads to adaptively query the corresponding expert prompts from the shared latent space, and then perform the personalized medical image segmentation. We evaluated the proposed model on our in-house Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma dataset and the public lung nodule dataset (i.e., LIDC-IDRI). Extensive experiments demonstrated our D-Persona can provide diversified and personalized results at the same time, achieving new SOTA performance for multi-rater medical image segmentation. Our code will be released at https://github.com/ycwu1997/D-Persona.
TIMS: A Tactile Internet-Based Micromanipulation System with Haptic Guidance for Surgical Training
Mar 07, 2023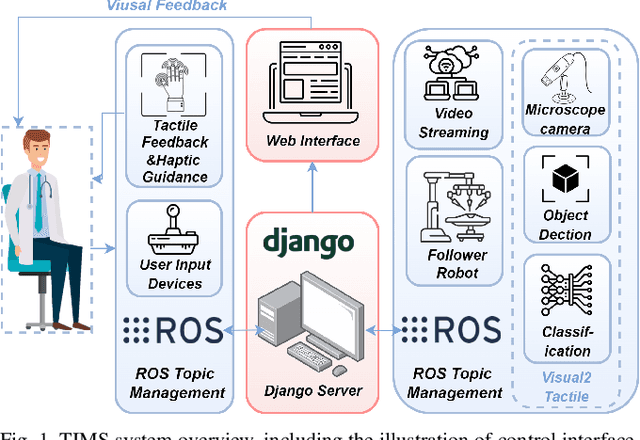
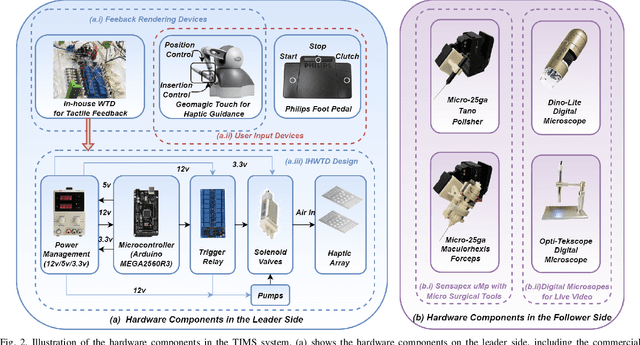
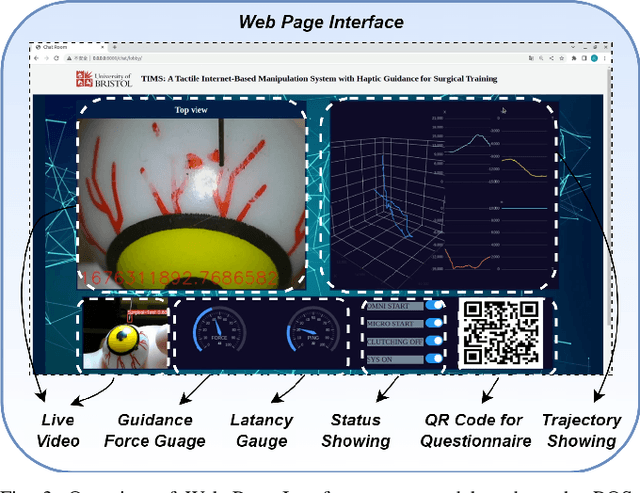
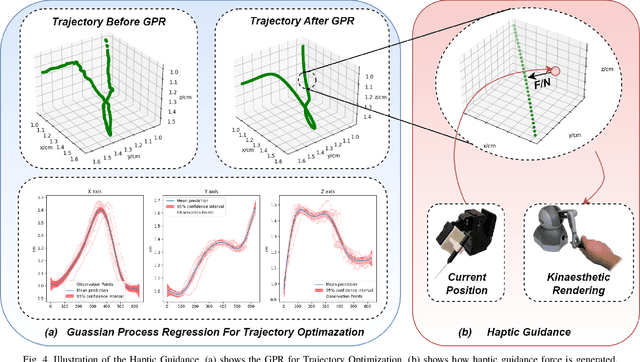
Abstract:Microsurgery involves the dexterous manipulation of delicate tissue or fragile structures such as small blood vessels, nerves, etc., under a microscope. To address the limitation of imprecise manipulation of human hands, robotic systems have been developed to assist surgeons in performing complex microsurgical tasks with greater precision and safety. However, the steep learning curve for robot-assisted microsurgery (RAMS) and the shortage of well-trained surgeons pose significant challenges to the widespread adoption of RAMS. Therefore, the development of a versatile training system for RAMS is necessary, which can bring tangible benefits to both surgeons and patients. In this paper, we present a Tactile Internet-Based Micromanipulation System (TIMS) based on a ROS-Django web-based architecture for microsurgical training. This system can provide tactile feedback to operators via a wearable tactile display (WTD), while real-time data is transmitted through the internet via a ROS-Django framework. In addition, TIMS integrates haptic guidance to `guide' the trainees to follow a desired trajectory provided by expert surgeons. Learning from demonstration based on Gaussian Process Regression (GPR) was used to generate the desired trajectory. User studies were also conducted to verify the effectiveness of our proposed TIMS, comparing users' performance with and without tactile feedback and/or haptic guidance.
Joint Class-Affinity Loss Correction for Robust Medical Image Segmentation with Noisy Labels
Jun 16, 2022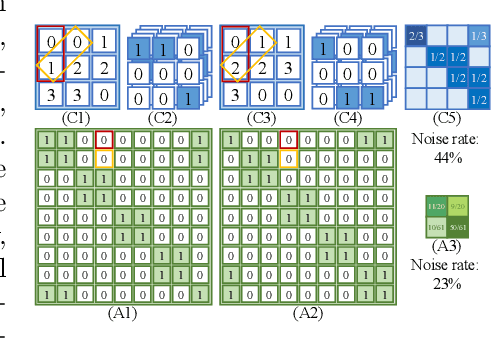
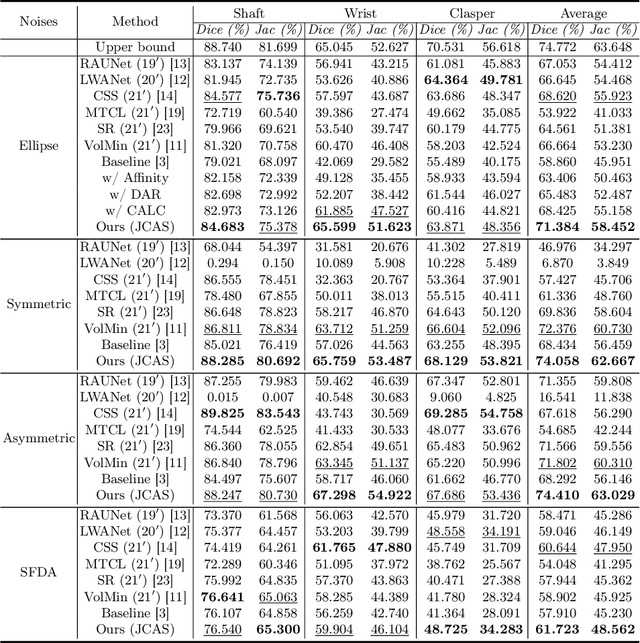
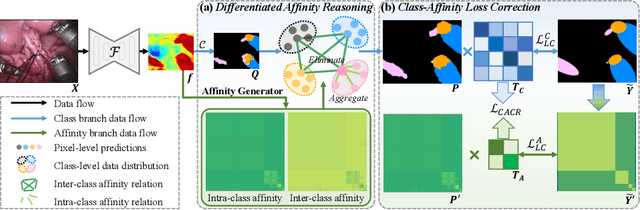

Abstract:Noisy labels collected with limited annotation cost prevent medical image segmentation algorithms from learning precise semantic correlations. Previous segmentation arts of learning with noisy labels merely perform a pixel-wise manner to preserve semantics, such as pixel-wise label correction, but neglect the pair-wise manner. In fact, we observe that the pair-wise manner capturing affinity relations between pixels can greatly reduce the label noise rate. Motivated by this observation, we present a novel perspective for noisy mitigation by incorporating both pixel-wise and pair-wise manners, where supervisions are derived from noisy class and affinity labels, respectively. Unifying the pixel-wise and pair-wise manners, we propose a robust Joint Class-Affinity Segmentation (JCAS) framework to combat label noise issues in medical image segmentation. Considering the affinity in pair-wise manner incorporates contextual dependencies, a differentiated affinity reasoning (DAR) module is devised to rectify the pixel-wise segmentation prediction by reasoning about intra-class and inter-class affinity relations. To further enhance the noise resistance, a class-affinity loss correction (CALC) strategy is designed to correct supervision signals via the modeled noise label distributions in class and affinity labels. Meanwhile, CALC strategy interacts the pixel-wise and pair-wise manners through the theoretically derived consistency regularization. Extensive experiments under both synthetic and real-world noisy labels corroborate the efficacy of the proposed JCAS framework with a minimum gap towards the upper bound performance. The source code is available at \url{https://github.com/CityU-AIM-Group/JCAS}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge