Lei Wei
Tencent Robotics X
FadeMem: Biologically-Inspired Forgetting for Efficient Agent Memory
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Large language models deployed as autonomous agents face critical memory limitations, lacking selective forgetting mechanisms that lead to either catastrophic forgetting at context boundaries or information overload within them. While human memory naturally balances retention and forgetting through adaptive decay processes, current AI systems employ binary retention strategies that preserve everything or lose it entirely. We propose FadeMem, a biologically-inspired agent memory architecture that incorporates active forgetting mechanisms mirroring human cognitive efficiency. FadeMem implements differential decay rates across a dual-layer memory hierarchy, where retention is governed by adaptive exponential decay functions modulated by semantic relevance, access frequency, and temporal patterns. Through LLM-guided conflict resolution and intelligent memory fusion, our system consolidates related information while allowing irrelevant details to fade. Experiments on Multi-Session Chat, LoCoMo, and LTI-Bench demonstrate superior multi-hop reasoning and retrieval with 45\% storage reduction, validating the effectiveness of biologically-inspired forgetting in agent memory systems.
Think-Augmented Function Calling: Improving LLM Parameter Accuracy Through Embedded Reasoning
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in function calling for autonomous agents, yet current mechanisms lack explicit reasoning transparency during parameter generation, particularly for complex functions with interdependent parameters. While existing approaches like chain-of-thought prompting operate at the agent level, they fail to provide fine-grained reasoning guidance for individual function parameters. To address these limitations, we propose Think-Augmented Function Calling (TAFC), a novel framework that enhances function calling accuracy through explicit reasoning at both function and parameter levels. Our method introduces a universal "think" parameter augmentation that enables models to articulate their decision-making process, with dynamic optimization for parameter descriptions to improve reasoning quality. For complex parameters, TAFC automatically triggers granular reasoning based on complexity scoring, ensuring appropriate justification for critical decisions. Additionally, we propose reasoning-guided optimization to align generated reasoning with human expectations. TAFC requires no architectural modifications to existing LLMs while maintaining full API compatibility. Evaluation on ToolBench across proprietary and open-source models demonstrates significant improvements in parameter generation accuracy and reasoning coherence for multi-parameter functions, while providing enhanced interpretability for debugging AI agent behaviors.
Hybrid Long and Short Range Flows for Point Cloud Filtering
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Point cloud capture processes are error-prone and introduce noisy artifacts that necessitate filtering/denoising. Recent filtering methods often suffer from point clustering or noise retaining issues. In this paper, we propose Hybrid Point Cloud Filtering ($\textbf{HybridPF}$) that considers both short-range and long-range filtering trajectories when removing noise. It is well established that short range scores, given by $\nabla_{x}\log p(x_t)$, may provide the necessary displacements to move noisy points to the underlying clean surface. By contrast, long range velocity flows approximate constant displacements directed from a high noise variant patch $x_0$ towards the corresponding clean surface $x_1$. Here, noisy patches $x_t$ are viewed as intermediate states between the high noise variant and the clean patches. Our intuition is that long range information from velocity flow models can guide the short range scores to align more closely with the clean points. In turn, score models generally provide a quicker convergence to the clean surface. Specifically, we devise two parallel modules, the ShortModule and LongModule, each consisting of an Encoder-Decoder pair to respectively account for short-range scores and long-range flows. We find that short-range scores, guided by long-range features, yield filtered point clouds with good point distributions and convergence near the clean surface. We design a joint loss function to simultaneously train the ShortModule and LongModule, in an end-to-end manner. Finally, we identify a key weakness in current displacement based methods, limitations on the decoder architecture, and propose a dynamic graph convolutional decoder to improve the inference process. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our HybridPF achieves state-of-the-art results while enabling faster inference speed.
DrVD-Bench: Do Vision-Language Models Reason Like Human Doctors in Medical Image Diagnosis?
May 30, 2025Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) exhibit strong zero-shot generalization on natural images and show early promise in interpretable medical image analysis. However, existing benchmarks do not systematically evaluate whether these models truly reason like human clinicians or merely imitate superficial patterns. To address this gap, we propose DrVD-Bench, the first multimodal benchmark for clinical visual reasoning. DrVD-Bench consists of three modules: Visual Evidence Comprehension, Reasoning Trajectory Assessment, and Report Generation Evaluation, comprising a total of 7,789 image-question pairs. Our benchmark covers 20 task types, 17 diagnostic categories, and five imaging modalities-CT, MRI, ultrasound, radiography, and pathology. DrVD-Bench is explicitly structured to reflect the clinical reasoning workflow from modality recognition to lesion identification and diagnosis. We benchmark 19 VLMs, including general-purpose and medical-specific, open-source and proprietary models, and observe that performance drops sharply as reasoning complexity increases. While some models begin to exhibit traces of human-like reasoning, they often still rely on shortcut correlations rather than grounded visual understanding. DrVD-Bench offers a rigorous and structured evaluation framework to guide the development of clinically trustworthy VLMs.
Object-level Cross-view Geo-localization with Location Enhancement and Multi-Head Cross Attention
May 23, 2025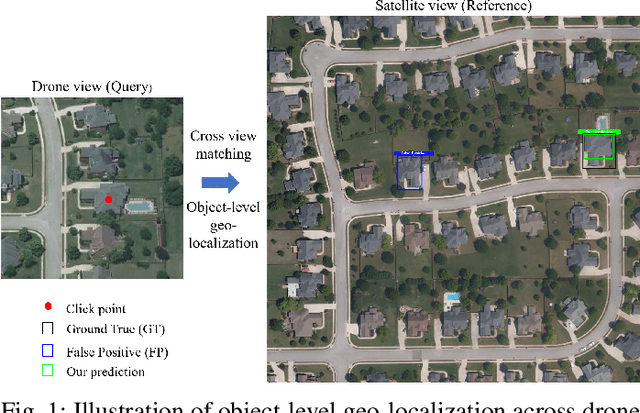
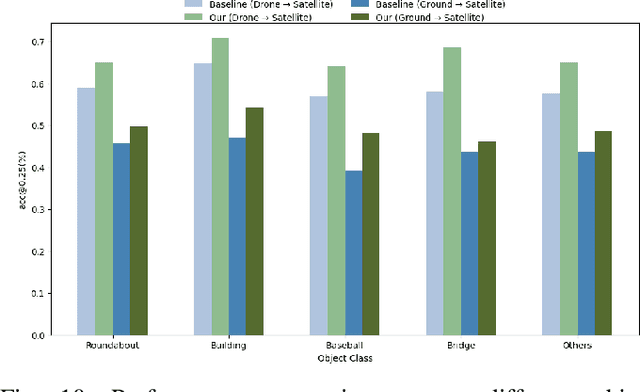
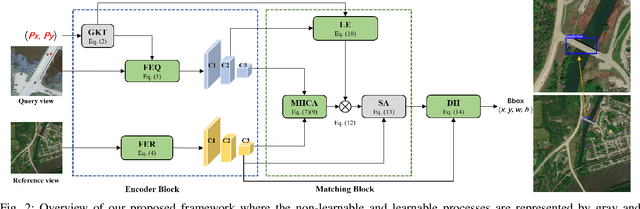
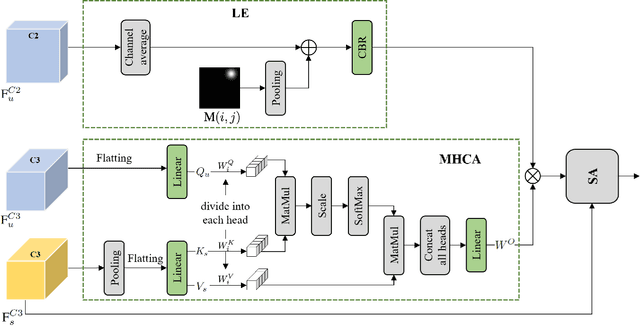
Abstract:Cross-view geo-localization determines the location of a query image, captured by a drone or ground-based camera, by matching it to a geo-referenced satellite image. While traditional approaches focus on image-level localization, many applications, such as search-and-rescue, infrastructure inspection, and precision delivery, demand object-level accuracy. This enables users to prompt a specific object with a single click on a drone image to retrieve precise geo-tagged information of the object. However, variations in viewpoints, timing, and imaging conditions pose significant challenges, especially when identifying visually similar objects in extensive satellite imagery. To address these challenges, we propose an Object-level Cross-view Geo-localization Network (OCGNet). It integrates user-specified click locations using Gaussian Kernel Transfer (GKT) to preserve location information throughout the network. This cue is dually embedded into the feature encoder and feature matching blocks, ensuring robust object-specific localization. Additionally, OCGNet incorporates a Location Enhancement (LE) module and a Multi-Head Cross Attention (MHCA) module to adaptively emphasize object-specific features or expand focus to relevant contextual regions when necessary. OCGNet achieves state-of-the-art performance on a public dataset, CVOGL. It also demonstrates few-shot learning capabilities, effectively generalizing from limited examples, making it suitable for diverse applications (https://github.com/ZheyangH/OCGNet).
Benchmarking AI scientists in omics data-driven biological research
May 13, 2025Abstract:The rise of large language models and multi-agent systems has sparked growing interest in AI scientists capable of autonomous biological research. However, existing benchmarks either focus on reasoning without data or on data analysis with predefined statistical answers, lacking realistic, data-driven evaluation settings. Here, we introduce the Biological AI Scientist Benchmark (BaisBench), a benchmark designed to assess AI scientists' ability to generate biological discoveries through data analysis and reasoning with external knowledge. BaisBench comprises two tasks: cell type annotation on 31 expert-labeled single-cell datasets, and scientific discovery through answering 198 multiple-choice questions derived from the biological insights of 41 recent single-cell studies. Systematic experiments on state-of-the-art AI scientists and LLM agents showed that while promising, current models still substantially underperform human experts on both tasks. We hope BaisBench will fill this gap and serve as a foundation for advancing and evaluating AI models for scientific discovery. The benchmark can be found at: https://github.com/EperLuo/BaisBench.
Intelligent Spatial Perception by Building Hierarchical 3D Scene Graphs for Indoor Scenarios with the Help of LLMs
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses the high demand in advanced intelligent robot navigation for a more holistic understanding of spatial environments, by introducing a novel system that harnesses the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) to construct hierarchical 3D Scene Graphs (3DSGs) for indoor scenarios. The proposed framework constructs 3DSGs consisting of a fundamental layer with rich metric-semantic information, an object layer featuring precise point-cloud representation of object nodes as well as visual descriptors, and higher layers of room, floor, and building nodes. Thanks to the innovative application of LLMs, not only object nodes but also nodes of higher layers, e.g., room nodes, are annotated in an intelligent and accurate manner. A polling mechanism for room classification using LLMs is proposed to enhance the accuracy and reliability of the room node annotation. Thorough numerical experiments demonstrate the system's ability to integrate semantic descriptions with geometric data, creating an accurate and comprehensive representation of the environment instrumental for context-aware navigation and task planning.
QueST: Querying Functional and Structural Niches on Spatial Transcriptomics Data via Contrastive Subgraph Embedding
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:The functional or structural spatial regions within tissues, referred to as spatial niches, are elements for illustrating the spatial contexts of multicellular organisms. A key challenge is querying shared niches across diverse tissues, which is crucial for achieving a comprehensive understanding of the organization and phenotypes of cell populations. However, current data analysis methods predominantly focus on creating spatial-aware embeddings for cells, neglecting the development of niche-level representations for effective querying. To address this gap, we introduce QueST, a novel niche representation learning model designed for querying spatial niches across multiple samples. QueST utilizes a novel subgraph contrastive learning approach to explicitly capture niche-level characteristics and incorporates adversarial training to mitigate batch effects. We evaluate QueST on established benchmarks using human and mouse datasets, demonstrating its superiority over state-of-the-art graph representation learning methods in accurate niche queries. Overall, QueST offers a specialized model for spatial niche queries, paving the way for deeper insights into the patterns and mechanisms of cell spatial organization across tissues. Source code can be found at https://github.com/cmhimself/QueST.
StraightPCF: Straight Point Cloud Filtering
May 14, 2024Abstract:Point cloud filtering is a fundamental 3D vision task, which aims to remove noise while recovering the underlying clean surfaces. State-of-the-art methods remove noise by moving noisy points along stochastic trajectories to the clean surfaces. These methods often require regularization within the training objective and/or during post-processing, to ensure fidelity. In this paper, we introduce StraightPCF, a new deep learning based method for point cloud filtering. It works by moving noisy points along straight paths, thus reducing discretization errors while ensuring faster convergence to the clean surfaces. We model noisy patches as intermediate states between high noise patch variants and their clean counterparts, and design the VelocityModule to infer a constant flow velocity from the former to the latter. This constant flow leads to straight filtering trajectories. In addition, we introduce a DistanceModule that scales the straight trajectory using an estimated distance scalar to attain convergence near the clean surface. Our network is lightweight and only has $\sim530K$ parameters, being 17% of IterativePFN (a most recent point cloud filtering network). Extensive experiments on both synthetic and real-world data show our method achieves state-of-the-art results. Our method also demonstrates nice distributions of filtered points without the need for regularization. The implementation code can be found at: https://github.com/ddsediri/StraightPCF.
scDiffusion: conditional generation of high-quality single-cell data using diffusion model
Jan 08, 2024



Abstract:Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data are important for studying the biology of development or diseases at single-cell level. To better understand the properties of the data, to build controlled benchmark data for testing downstream methods, and to augment data when collecting sufficient real data is challenging, generative models have been proposed to computationally generate synthetic scRNA-seq data. However, the data generated with current models are not very realistic yet, especially when we need to generate data with controlled conditions. In the meantime, the Diffusion models have shown their power in generating data in computer vision at high fidelity, providing a new opportunity for scRNA-seq generation. In this study, we developed scDiffusion, a diffusion-based model to generate high-quality scRNA-seq data with controlled conditions. We designed multiple classifiers to guide the diffusion process simultaneously, enabling scDiffusion to generate data under multiple condition combinations. We also proposed a new control strategy called Gradient Interpolation. This strategy allows the model to generate continuous trajectories of cell development from a given cell state. Experiments showed that scDiffusion can generate single-cell gene expression data closely resembling real scRNA-seq data, surpassing state-of-the-art models in multiple metrics. Also, scDiffusion can conditionally produce data on specific cell types including rare cell types. Furthermore, we could use the multiple-condition generation of scDiffusion to generate cell type that was out of the training data. Leveraging the Gradient Interpolation strategy, we generated a continuous developmental trajectory of mouse embryonic cells. These experiments demonstrate that scDiffusion is a powerful tool for augmenting the real scRNA-seq data and can provide insights into cell fate research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge