Steven Hicks
Medical Imaging AI Competitions Lack Fairness
Dec 19, 2025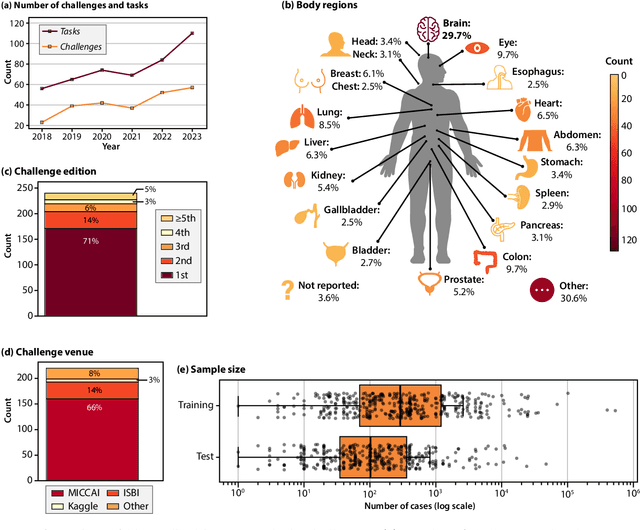
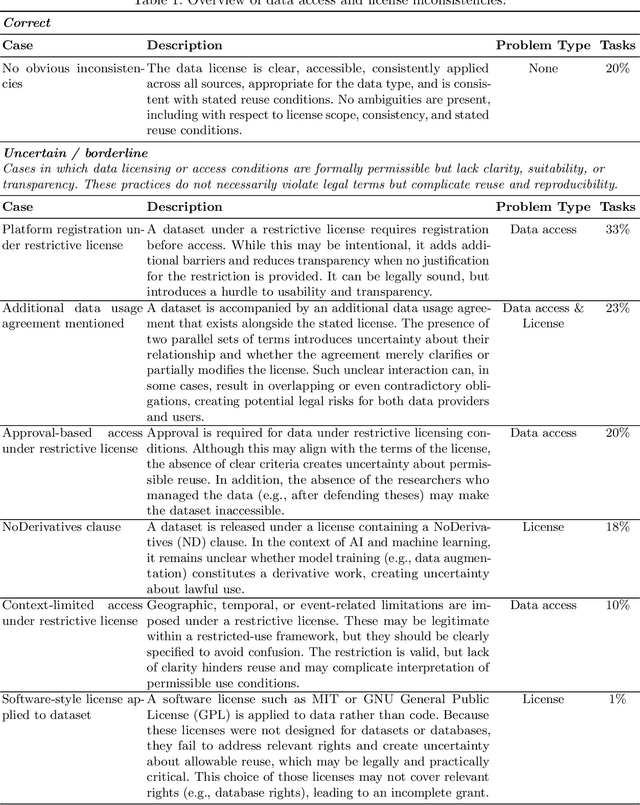
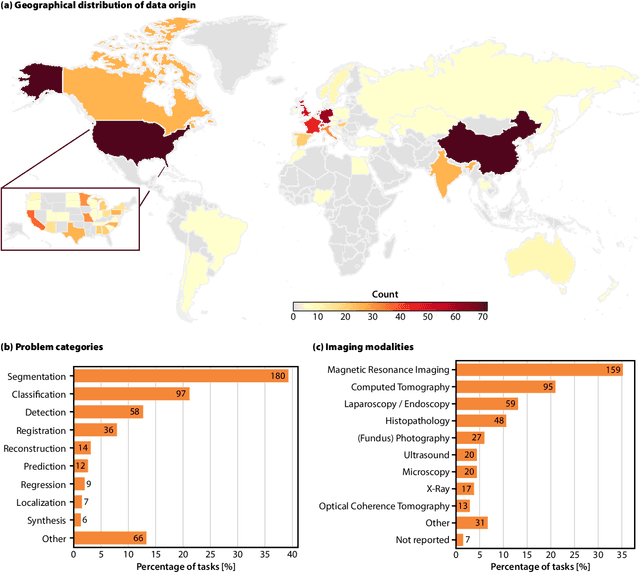
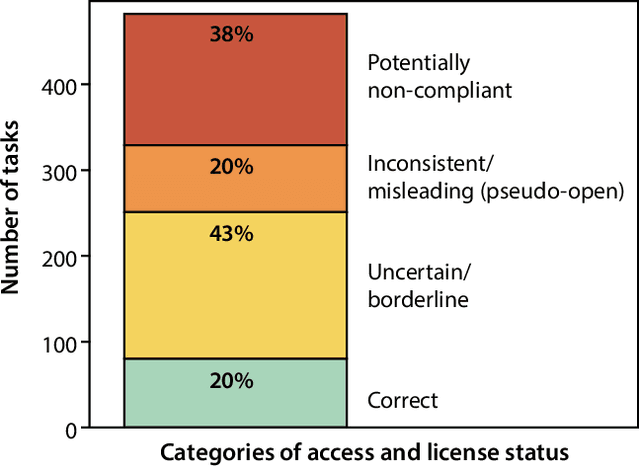
Abstract:Benchmarking competitions are central to the development of artificial intelligence (AI) in medical imaging, defining performance standards and shaping methodological progress. However, it remains unclear whether these benchmarks provide data that are sufficiently representative, accessible, and reusable to support clinically meaningful AI. In this work, we assess fairness along two complementary dimensions: (1) whether challenge datasets are representative of real-world clinical diversity, and (2) whether they are accessible and legally reusable in line with the FAIR principles. To address this question, we conducted a large-scale systematic study of 241 biomedical image analysis challenges comprising 458 tasks across 19 imaging modalities. Our findings show substantial biases in dataset composition, including geographic location, modality-, and problem type-related biases, indicating that current benchmarks do not adequately reflect real-world clinical diversity. Despite their widespread influence, challenge datasets were frequently constrained by restrictive or ambiguous access conditions, inconsistent or non-compliant licensing practices, and incomplete documentation, limiting reproducibility and long-term reuse. Together, these shortcomings expose foundational fairness limitations in our benchmarking ecosystem and highlight a disconnect between leaderboard success and clinical relevance.
Prompt to Polyp: Medical Text-Conditioned Image Synthesis with Diffusion Models
May 12, 2025Abstract:The generation of realistic medical images from text descriptions has significant potential to address data scarcity challenges in healthcare AI while preserving patient privacy. This paper presents a comprehensive study of text-to-image synthesis in the medical domain, comparing two distinct approaches: (1) fine-tuning large pre-trained latent diffusion models and (2) training small, domain-specific models. We introduce a novel model named MSDM, an optimized architecture based on Stable Diffusion that integrates a clinical text encoder, variational autoencoder, and cross-attention mechanisms to better align medical text prompts with generated images. Our study compares two approaches: fine-tuning large pre-trained models (FLUX, Kandinsky) versus training compact domain-specific models (MSDM). Evaluation across colonoscopy (MedVQA-GI) and radiology (ROCOv2) datasets reveals that while large models achieve higher fidelity, our optimized MSDM delivers comparable quality with lower computational costs. Quantitative metrics and qualitative evaluations by medical experts reveal strengths and limitations of each approach.
Prompt to Polyp: Clinically-Aware Medical Image Synthesis with Diffusion Models
May 08, 2025Abstract:The generation of realistic medical images from text descriptions has significant potential to address data scarcity challenges in healthcare AI while preserving patient privacy. This paper presents a comprehensive study of text-to-image synthesis in the medical domain, comparing two distinct approaches: (1) fine-tuning large pre-trained latent diffusion models and (2) training small, domain-specific models. We introduce a novel model named MSDM, an optimized architecture based on Stable Diffusion that integrates a clinical text encoder, variational autoencoder, and cross-attention mechanisms to better align medical text prompts with generated images. Our study compares two approaches: fine-tuning large pre-trained models (FLUX, Kandinsky) versus training compact domain-specific models (MSDM). Evaluation across colonoscopy (MedVQA-GI) and radiology (ROCOv2) datasets reveals that while large models achieve higher fidelity, our optimized MSDM delivers comparable quality with lower computational costs. Quantitative metrics and qualitative evaluations by medical experts reveal strengths and limitations of each approach.
Interplay between Federated Learning and Explainable Artificial Intelligence: a Scoping Review
Nov 07, 2024



Abstract:The joint implementation of Federated learning (FL) and Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) will allow training models from distributed data and explaining their inner workings while preserving important aspects of privacy. Towards establishing the benefits and tensions associated with their interplay, this scoping review maps those publications that jointly deal with FL and XAI, focusing on publications where an interplay between FL and model interpretability or post-hoc explanations was found. In total, 37 studies met our criteria, with more papers focusing on explanation methods (mainly feature relevance) than on interpretability (mainly algorithmic transparency). Most works used simulated horizontal FL setups involving 10 or fewer data centers. Only one study explicitly and quantitatively analyzed the influence of FL on model explanations, revealing a significant research gap. Aggregation of interpretability metrics across FL nodes created generalized global insights at the expense of node-specific patterns being diluted. 8 papers addressed the benefits of incorporating explanation methods as a component of the FL algorithm. Studies using established FL libraries or following reporting guidelines are a minority. More quantitative research and structured, transparent practices are needed to fully understand their mutual impact and under which conditions it happens.
GastroVision: A Multi-class Endoscopy Image Dataset for Computer Aided Gastrointestinal Disease Detection
Jul 16, 2023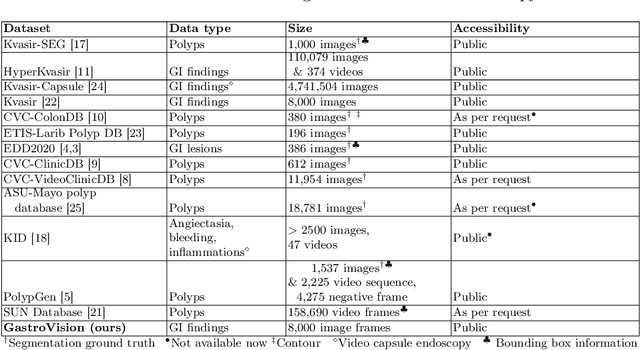
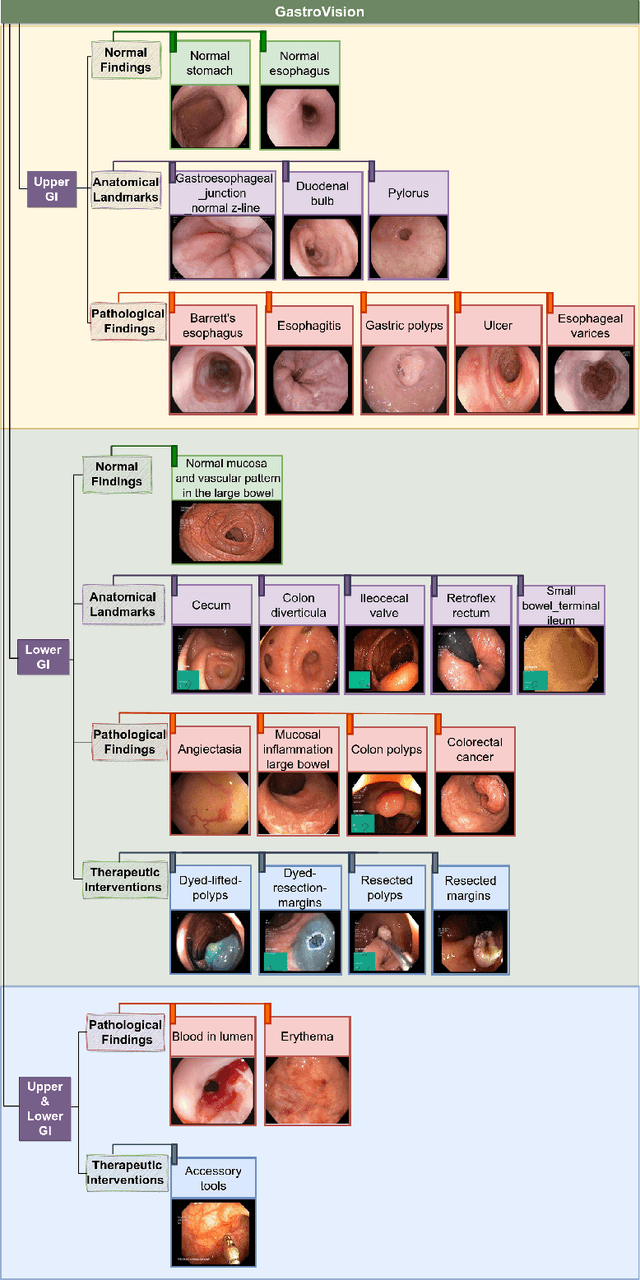
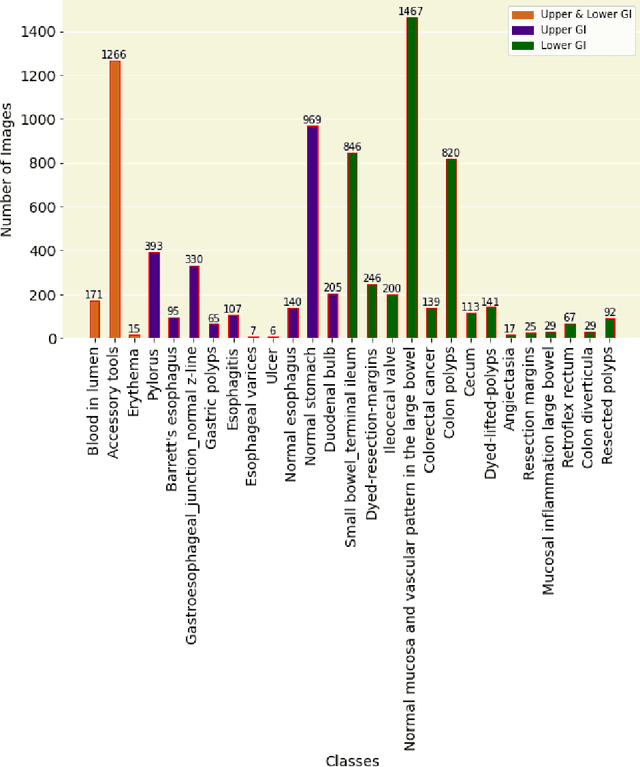
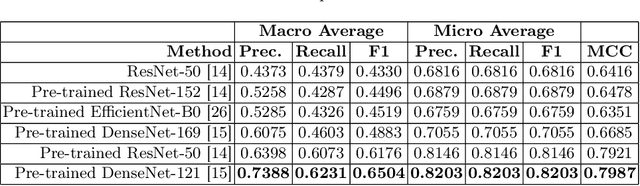
Abstract:Integrating real-time artificial intelligence (AI) systems in clinical practices faces challenges such as scalability and acceptance. These challenges include data availability, biased outcomes, data quality, lack of transparency, and underperformance on unseen datasets from different distributions. The scarcity of large-scale, precisely labeled, and diverse datasets are the major challenge for clinical integration. This scarcity is also due to the legal restrictions and extensive manual efforts required for accurate annotations from clinicians. To address these challenges, we present GastroVision, a multi-center open-access gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy dataset that includes different anatomical landmarks, pathological abnormalities, polyp removal cases and normal findings (a total of 24 classes) from the GI tract. The dataset comprises 8,000 images acquired from B{\ae}rum Hospital in Norway and Karolinska University in Sweden and was annotated and verified by experienced GI endoscopists. Furthermore, we validate the significance of our dataset with extensive benchmarking based on the popular deep learning based baseline models. We believe our dataset can facilitate the development of AI-based algorithms for GI disease detection and classification. Our dataset is available at https://osf.io/84e7f/.
Visual explanations for polyp detection: How medical doctors assess intrinsic versus extrinsic explanations
Mar 23, 2022
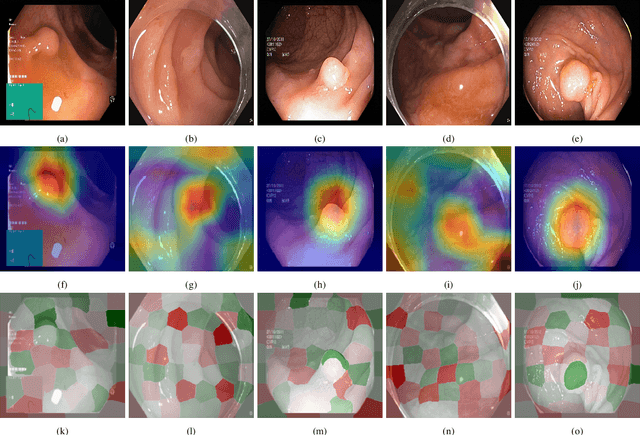
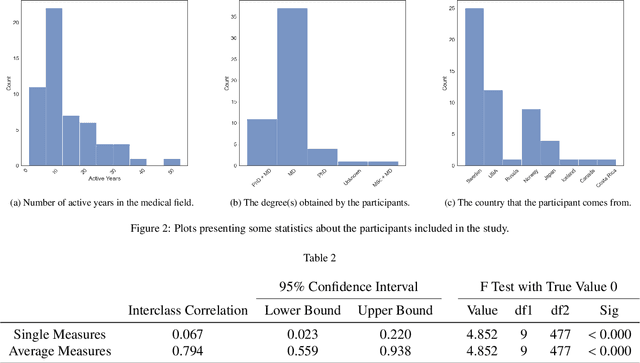
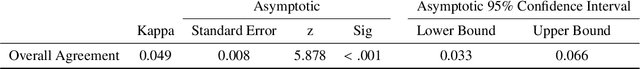
Abstract:Deep learning has in recent years achieved immense success in all areas of computer vision and has the potential of assisting medical doctors in analyzing visual content for disease and other abnormalities. However, the current state of deep learning is very much a black box, making medical professionals highly skeptical about integrating these methods into clinical practice. Several methods have been proposed in order to shine some light onto these black boxes, but there is no consensus on the opinion of the medical doctors that will consume these explanations. This paper presents a study asking medical doctors about their opinion of current state-of-the-art explainable artificial intelligence methods when applied to a gastrointestinal disease detection use case. We compare two different categories of explanation methods, intrinsic and extrinsic, and gauge their opinion of the current value of these explanations. The results indicate that intrinsic explanations are preferred and that explanation.
Assessing generalisability of deep learning-based polyp detection and segmentation methods through a computer vision challenge
Feb 24, 2022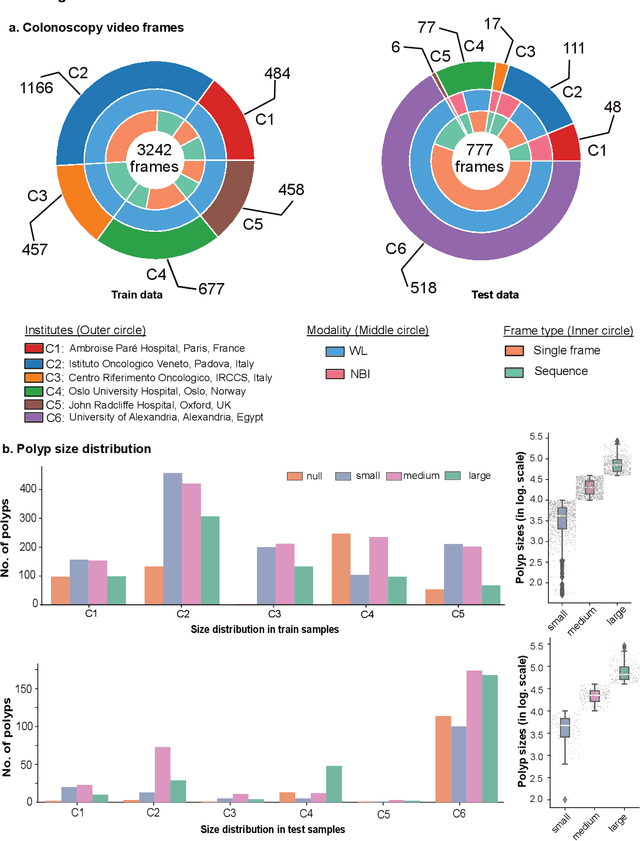
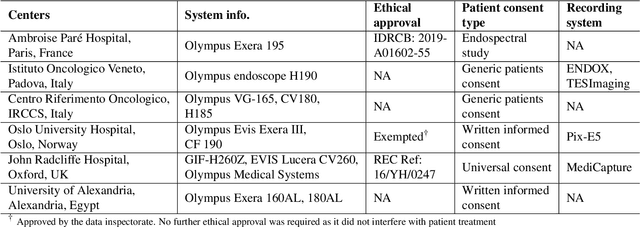
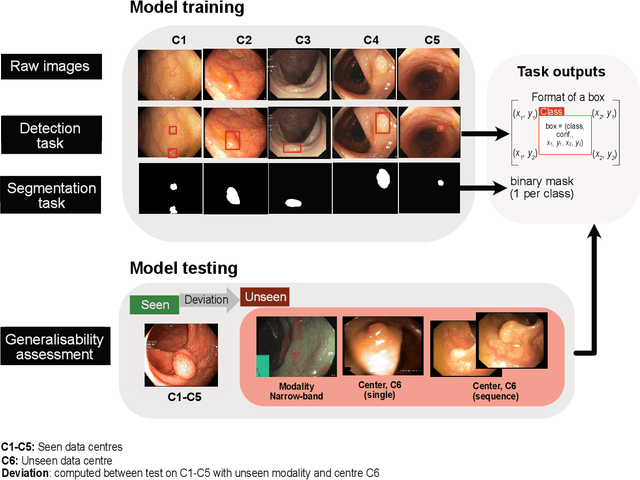
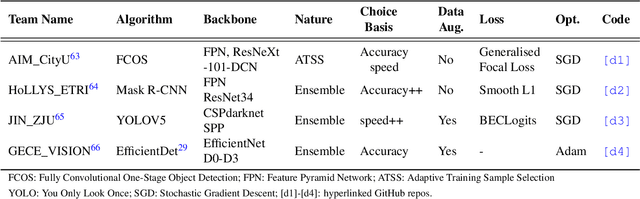
Abstract:Polyps are well-known cancer precursors identified by colonoscopy. However, variability in their size, location, and surface largely affect identification, localisation, and characterisation. Moreover, colonoscopic surveillance and removal of polyps (referred to as polypectomy ) are highly operator-dependent procedures. There exist a high missed detection rate and incomplete removal of colonic polyps due to their variable nature, the difficulties to delineate the abnormality, the high recurrence rates, and the anatomical topography of the colon. There have been several developments in realising automated methods for both detection and segmentation of these polyps using machine learning. However, the major drawback in most of these methods is their ability to generalise to out-of-sample unseen datasets that come from different centres, modalities and acquisition systems. To test this hypothesis rigorously we curated a multi-centre and multi-population dataset acquired from multiple colonoscopy systems and challenged teams comprising machine learning experts to develop robust automated detection and segmentation methods as part of our crowd-sourcing Endoscopic computer vision challenge (EndoCV) 2021. In this paper, we analyse the detection results of the four top (among seven) teams and the segmentation results of the five top teams (among 16). Our analyses demonstrate that the top-ranking teams concentrated on accuracy (i.e., accuracy > 80% on overall Dice score on different validation sets) over real-time performance required for clinical applicability. We further dissect the methods and provide an experiment-based hypothesis that reveals the need for improved generalisability to tackle diversity present in multi-centre datasets.
Visual Sentiment Analysis: A Natural DisasterUse-case Task at MediaEval 2021
Nov 22, 2021Abstract:The Visual Sentiment Analysis task is being offered for the first time at MediaEval. The main purpose of the task is to predict the emotional response to images of natural disasters shared on social media. Disaster-related images are generally complex and often evoke an emotional response, making them an ideal use case of visual sentiment analysis. We believe being able to perform meaningful analysis of natural disaster-related data could be of great societal importance, and a joint effort in this regard can open several interesting directions for future research. The task is composed of three sub-tasks, each aiming to explore a different aspect of the challenge. In this paper, we provide a detailed overview of the task, the general motivation of the task, and an overview of the dataset and the metrics to be used for the evaluation of the proposed solutions.
Few-shot segmentation of medical images based on meta-learning with implicit gradients
Jun 06, 2021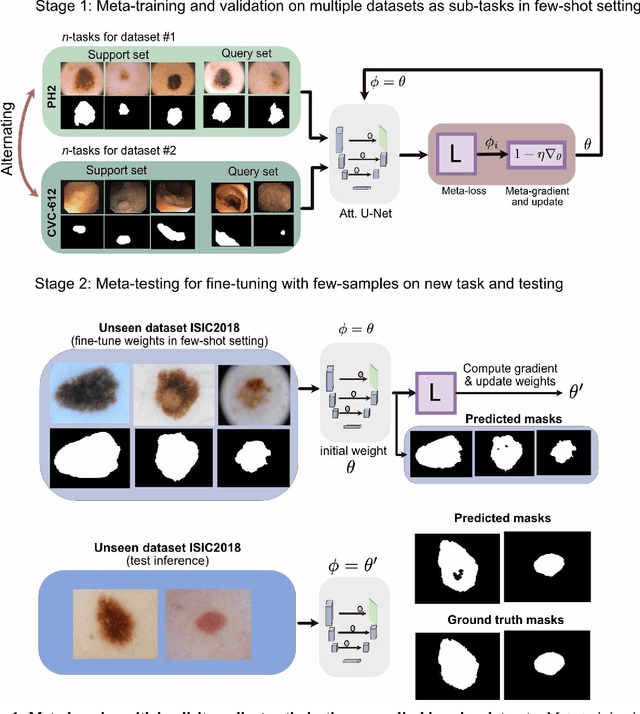
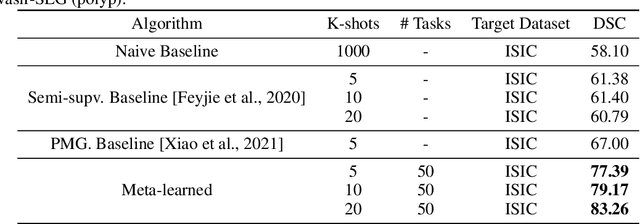
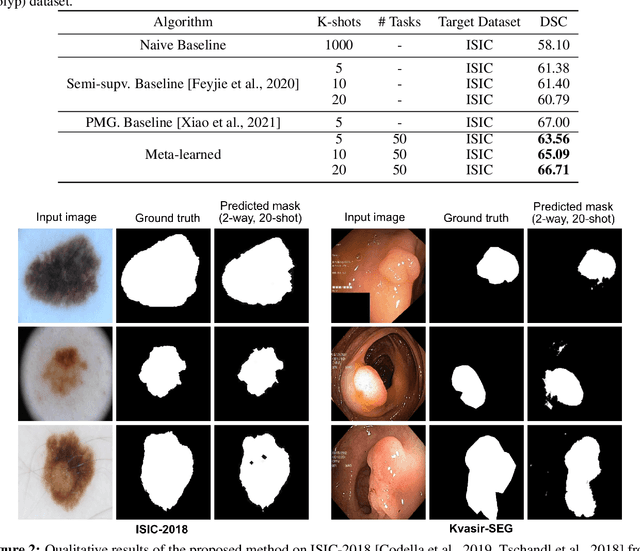

Abstract:Classical supervised methods commonly used often suffer from the requirement of an abudant number of training samples and are unable to generalize on unseen datasets. As a result, the broader application of any trained model is very limited in clinical settings. However, few-shot approaches can minimize the need for enormous reliable ground truth labels that are both labor intensive and expensive. To this end, we propose to exploit an optimization-based implicit model agnostic meta-learning {iMAML} algorithm in a few-shot setting for medical image segmentation. Our approach can leverage the learned weights from a diverse set of training samples and can be deployed on a new unseen dataset. We show that unlike classical few-shot learning approaches, our method has improved generalization capability. To our knowledge, this is the first work that exploits iMAML for medical image segmentation. Our quantitative results on publicly available skin and polyp datasets show that the proposed method outperforms the naive supervised baseline model and two recent few-shot segmentation approaches by large margins.
Pyramid-Focus-Augmentation: Medical Image Segmentation with Step-Wise Focus
Dec 14, 2020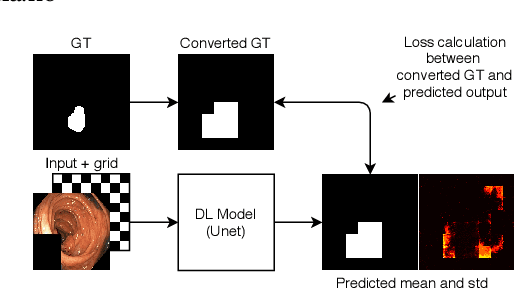
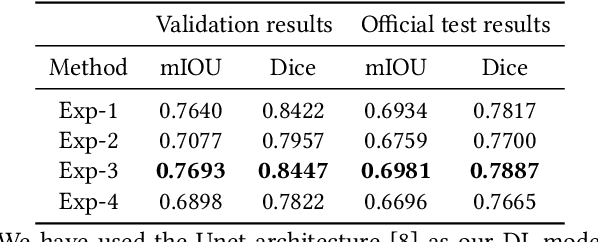

Abstract:Segmentation of findings in the gastrointestinal tract is a challenging but also an important task which is an important building stone for sufficient automatic decision support systems. In this work, we present our solution for the Medico 2020 task, which focused on the problem of colon polyp segmentation. We present our simple but efficient idea of using an augmentation method that uses grids in a pyramid-like manner (large to small) for segmentation. Our results show that the proposed methods work as indented and can also lead to comparable results when competing with other methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge