Ala Al-Fuqaha
GuardEval: A Multi-Perspective Benchmark for Evaluating Safety, Fairness, and Robustness in LLM Moderators
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) become deeply embedded in daily life, the urgent need for safer moderation systems, distinguishing between naive from harmful requests while upholding appropriate censorship boundaries, has never been greater. While existing LLMs can detect harmful or unsafe content, they often struggle with nuanced cases such as implicit offensiveness, subtle gender and racial biases, and jailbreak prompts, due to the subjective and context-dependent nature of these issues. Furthermore, their heavy reliance on training data can reinforce societal biases, resulting in inconsistent and ethically problematic outputs. To address these challenges, we introduce GuardEval, a unified multi-perspective benchmark dataset designed for both training and evaluation, containing 106 fine-grained categories spanning human emotions, offensive and hateful language, gender and racial bias, and broader safety concerns. We also present GemmaGuard (GGuard), a QLoRA fine-tuned version of Gemma3-12B trained on GuardEval, to assess content moderation with fine-grained labels. Our evaluation shows that GGuard achieves a macro F1 score of 0.832, substantially outperforming leading moderation models, including OpenAI Moderator (0.64) and Llama Guard (0.61). We show that multi-perspective, human-centered safety benchmarks are critical for reducing biased and inconsistent moderation decisions. GuardEval and GGuard together demonstrate that diverse, representative data materially improve safety, fairness, and robustness on complex, borderline cases.
Large Language Model Enhanced Particle Swarm Optimization for Hyperparameter Tuning for Deep Learning Models
Apr 19, 2025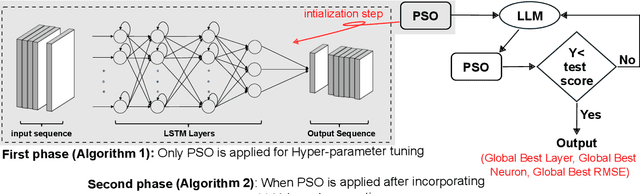
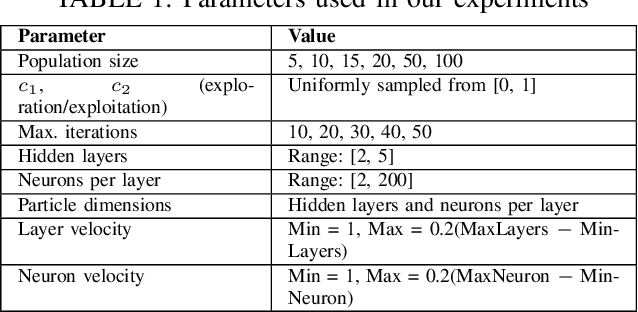
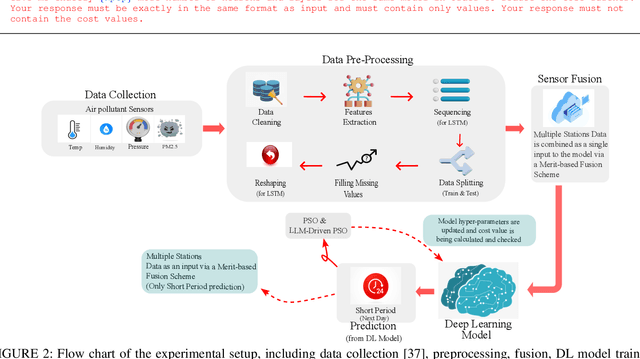

Abstract:Determining the ideal architecture for deep learning models, such as the number of layers and neurons, is a difficult and resource-intensive process that frequently relies on human tuning or computationally costly optimization approaches. While Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and Large Language Models (LLMs) have been individually applied in optimization and deep learning, their combined use for enhancing convergence in numerical optimization tasks remains underexplored. Our work addresses this gap by integrating LLMs into PSO to reduce model evaluations and improve convergence for deep learning hyperparameter tuning. The proposed LLM-enhanced PSO method addresses the difficulties of efficiency and convergence by using LLMs (particularly ChatGPT-3.5 and Llama3) to improve PSO performance, allowing for faster achievement of target objectives. Our method speeds up search space exploration by substituting underperforming particle placements with best suggestions offered by LLMs. Comprehensive experiments across three scenarios -- (1) optimizing the Rastrigin function, (2) using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks for time series regression, and (3) using Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for material classification -- show that the method significantly improves convergence rates and lowers computational costs. Depending on the application, computational complexity is lowered by 20% to 60% compared to traditional PSO methods. Llama3 achieved a 20% to 40% reduction in model calls for regression tasks, whereas ChatGPT-3.5 reduced model calls by 60% for both regression and classification tasks, all while preserving accuracy and error rates. This groundbreaking methodology offers a very efficient and effective solution for optimizing deep learning models, leading to substantial computational performance improvements across a wide range of applications.
A Survey of Social Cybersecurity: Techniques for Attack Detection, Evaluations, Challenges, and Future Prospects
Apr 06, 2025



Abstract:In today's digital era, the Internet, especially social media platforms, plays a significant role in shaping public opinions, attitudes, and beliefs. Unfortunately, the credibility of scientific information sources is often undermined by the spread of misinformation through various means, including technology-driven tools like bots, cyborgs, trolls, sock-puppets, and deep fakes. This manipulation of public discourse serves antagonistic business agendas and compromises civil society. In response to this challenge, a new scientific discipline has emerged: social cybersecurity.
A Multi-Agent DRL-Based Framework for Optimal Resource Allocation and Twin Migration in the Multi-Tier Vehicular Metaverse
Feb 26, 2025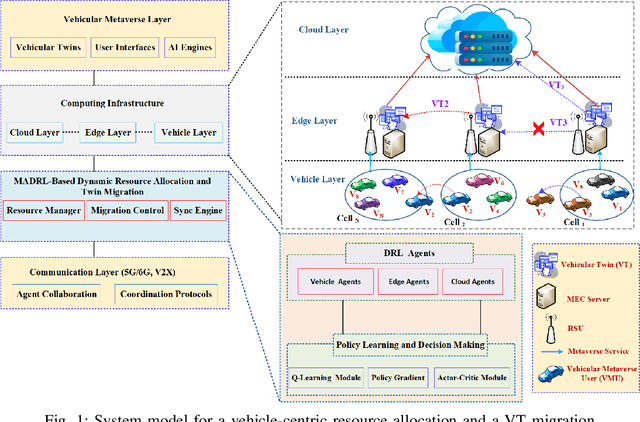
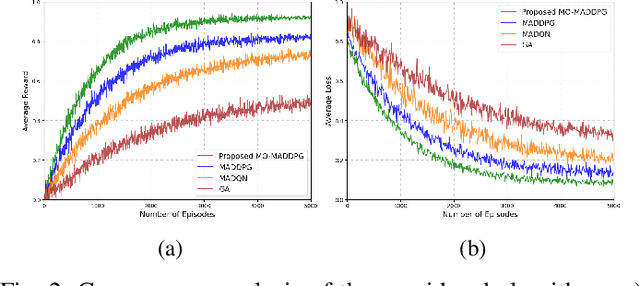
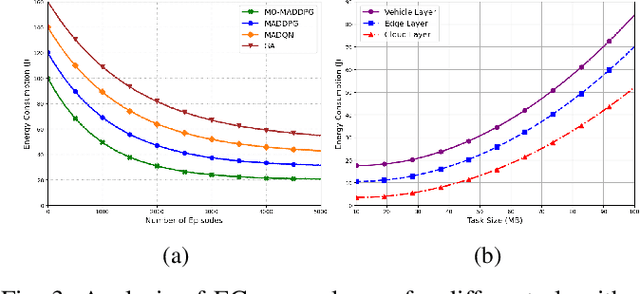
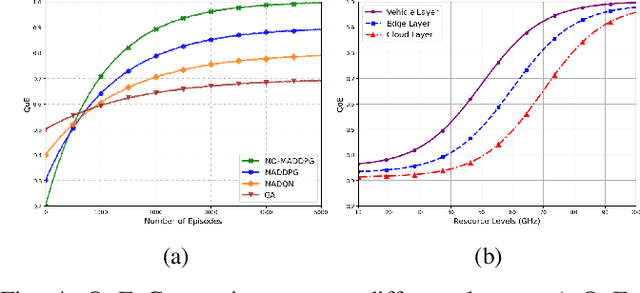
Abstract:Although multi-tier vehicular Metaverse promises to transform vehicles into essential nodes -- within an interconnected digital ecosystem -- using efficient resource allocation and seamless vehicular twin (VT) migration, this can hardly be achieved by the existing techniques operating in a highly dynamic vehicular environment, since they can hardly balance multi-objective optimization problems such as latency reduction, resource utilization, and user experience (UX). To address these challenges, we introduce a novel multi-tier resource allocation and VT migration framework that integrates Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs), a hierarchical Stackelberg game-based incentive mechanism, and Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning (MADRL). The GCN-based model captures both spatial and temporal dependencies within the vehicular network; the Stackelberg game-based incentive mechanism fosters cooperation between vehicles and infrastructure; and the MADRL algorithm jointly optimizes resource allocation and VT migration in real time. By modeling this dynamic and multi-tier vehicular Metaverse as a Markov Decision Process (MDP), we develop a MADRL-based algorithm dubbed the Multi-Objective Multi-Agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (MO-MADDPG), which can effectively balances the various conflicting objectives. Extensive simulations validate the effectiveness of this algorithm that is demonstrated to enhance scalability, reliability, and efficiency while considerably improving latency, resource utilization, migration cost, and overall UX by 12.8%, 9.7%, 14.2%, and 16.1%, respectively.
Safeguarding connected autonomous vehicle communication: Protocols, intra- and inter-vehicular attacks and defenses
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:The advancements in autonomous driving technology, coupled with the growing interest from automotive manufacturers and tech companies, suggest a rising adoption of Connected Autonomous Vehicles (CAVs) in the near future. Despite some evidence of higher accident rates in AVs, these incidents tend to result in less severe injuries compared to traditional vehicles due to cooperative safety measures. However, the increased complexity of CAV systems exposes them to significant security vulnerabilities, potentially compromising their performance and communication integrity. This paper contributes by presenting a detailed analysis of existing security frameworks and protocols, focusing on intra- and inter-vehicle communications. We systematically evaluate the effectiveness of these frameworks in addressing known vulnerabilities and propose a set of best practices for enhancing CAV communication security. The paper also provides a comprehensive taxonomy of attack vectors in CAV ecosystems and suggests future research directions for designing more robust security mechanisms. Our key contributions include the development of a new classification system for CAV security threats, the proposal of practical security protocols, and the introduction of use cases that demonstrate how these protocols can be integrated into real-world CAV applications. These insights are crucial for advancing secure CAV adoption and ensuring the safe integration of autonomous vehicles into intelligent transportation systems.
Open Foundation Models in Healthcare: Challenges, Paradoxes, and Opportunities with GenAI Driven Personalized Prescription
Feb 04, 2025Abstract:In response to the success of proprietary Large Language Models (LLMs) such as OpenAI's GPT-4, there is a growing interest in developing open, non-proprietary LLMs and AI foundation models (AIFMs) for transparent use in academic, scientific, and non-commercial applications. Despite their inability to match the refined functionalities of their proprietary counterparts, open models hold immense potential to revolutionize healthcare applications. In this paper, we examine the prospects of open-source LLMs and AIFMs for developing healthcare applications and make two key contributions. Firstly, we present a comprehensive survey of the current state-of-the-art open-source healthcare LLMs and AIFMs and introduce a taxonomy of these open AIFMs, categorizing their utility across various healthcare tasks. Secondly, to evaluate the general-purpose applications of open LLMs in healthcare, we present a case study on personalized prescriptions. This task is particularly significant due to its critical role in delivering tailored, patient-specific medications that can greatly improve treatment outcomes. In addition, we compare the performance of open-source models with proprietary models in settings with and without Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). Our findings suggest that, although less refined, open LLMs can achieve performance comparable to proprietary models when paired with grounding techniques such as RAG. Furthermore, to highlight the clinical significance of LLMs-empowered personalized prescriptions, we perform subjective assessment through an expert clinician. We also elaborate on ethical considerations and potential risks associated with the misuse of powerful LLMs and AIFMs, highlighting the need for a cautious and responsible implementation in healthcare.
Multi-UAV Multi-RIS QoS-Aware Aerial Communication Systems using DRL and PSO
Jun 16, 2024



Abstract:Recently, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) have attracted the attention of researchers in academia and industry for providing wireless services to ground users in diverse scenarios like festivals, large sporting events, natural and man-made disasters due to their advantages in terms of versatility and maneuverability. However, the limited resources of UAVs (e.g., energy budget and different service requirements) can pose challenges for adopting UAVs for such applications. Our system model considers a UAV swarm that navigates an area, providing wireless communication to ground users with RIS support to improve the coverage of the UAVs. In this work, we introduce an optimization model with the aim of maximizing the throughput and UAVs coverage through optimal path planning of UAVs and multi-RIS phase configurations. The formulated optimization is challenging to solve using standard linear programming techniques, limiting its applicability in real-time decision-making. Therefore, we introduce a two-step solution using deep reinforcement learning and particle swarm optimization. We conduct extensive simulations and compare our approach to two competitive solutions presented in the recent literature. Our simulation results demonstrate that our adopted approach is 20 \% better than the brute-force approach and 30\% better than the baseline solution in terms of QoS.
Meta Reinforcement Learning for Strategic IoT Deployments Coverage in Disaster-Response UAV Swarms
Jan 20, 2024



Abstract:In the past decade, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) have grabbed the attention of researchers in academia and industry for their potential use in critical emergency applications, such as providing wireless services to ground users and collecting data from areas affected by disasters, due to their advantages in terms of maneuverability and movement flexibility. The UAVs' limited resources, energy budget, and strict mission completion time have posed challenges in adopting UAVs for these applications. Our system model considers a UAV swarm that navigates an area collecting data from ground IoT devices focusing on providing better service for strategic locations and allowing UAVs to join and leave the swarm (e.g., for recharging) in a dynamic way. In this work, we introduce an optimization model with the aim of minimizing the total energy consumption and provide the optimal path planning of UAVs under the constraints of minimum completion time and transmit power. The formulated optimization is NP-hard making it not applicable for real-time decision making. Therefore, we introduce a light-weight meta-reinforcement learning solution that can also cope with sudden changes in the environment through fast convergence. We conduct extensive simulations and compare our approach to three state-of-the-art learning models. Our simulation results prove that our introduced approach is better than the three state-of-the-art algorithms in providing coverage to strategic locations with fast convergence.
Empowering HWNs with Efficient Data Labeling: A Clustered Federated Semi-Supervised Learning Approach
Jan 19, 2024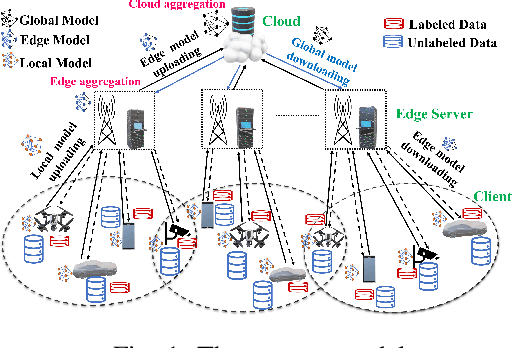
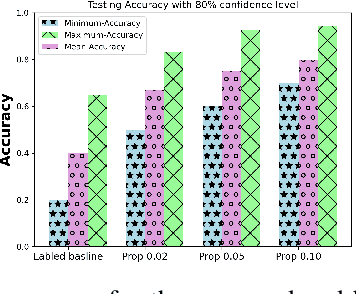
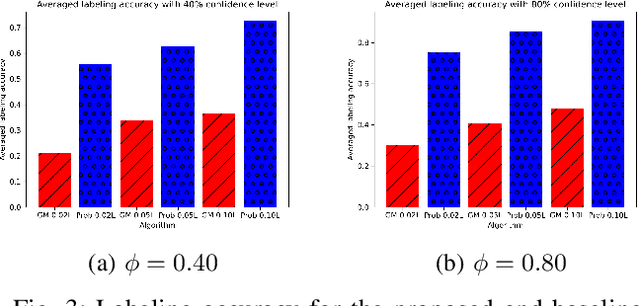
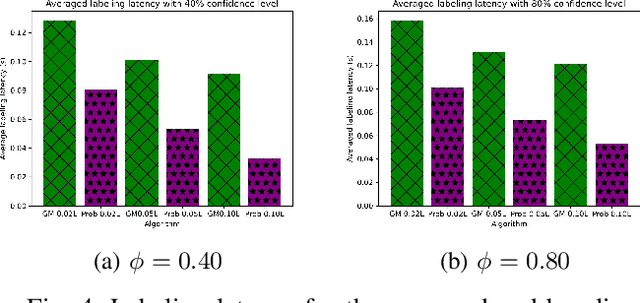
Abstract:Clustered Federated Multitask Learning (CFL) has gained considerable attention as an effective strategy for overcoming statistical challenges, particularly when dealing with non independent and identically distributed (non IID) data across multiple users. However, much of the existing research on CFL operates under the unrealistic premise that devices have access to accurate ground truth labels. This assumption becomes especially problematic in hierarchical wireless networks (HWNs), where edge networks contain a large amount of unlabeled data, resulting in slower convergence rates and increased processing times, particularly when dealing with two layers of model aggregation. To address these issues, we introduce a novel framework, Clustered Federated Semi-Supervised Learning (CFSL), designed for more realistic HWN scenarios. Our approach leverages a best-performing specialized model algorithm, wherein each device is assigned a specialized model that is highly adept at generating accurate pseudo-labels for unlabeled data, even when the data stems from diverse environments. We validate the efficacy of CFSL through extensive experiments, comparing it with existing methods highlighted in recent literature. Our numerical results demonstrate that CFSL significantly improves upon key metrics such as testing accuracy, labeling accuracy, and labeling latency under varying proportions of labeled and unlabeled data while also accommodating the non-IID nature of the data and the unique characteristics of wireless edge networks.
Adversarial Machine Learning for Social Good: Reframing the Adversary as an Ally
Oct 05, 2023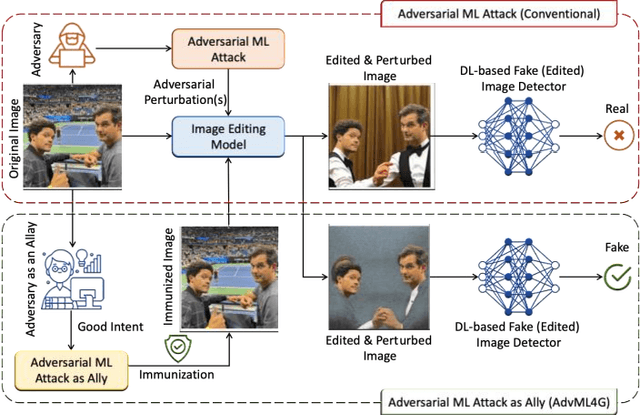
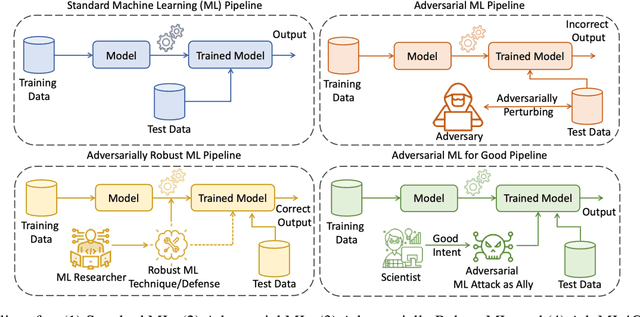
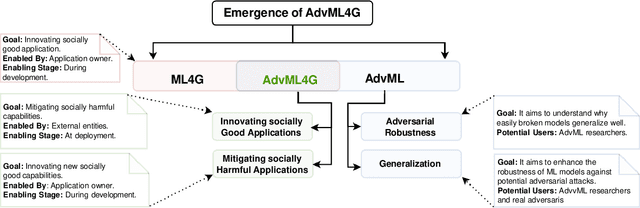
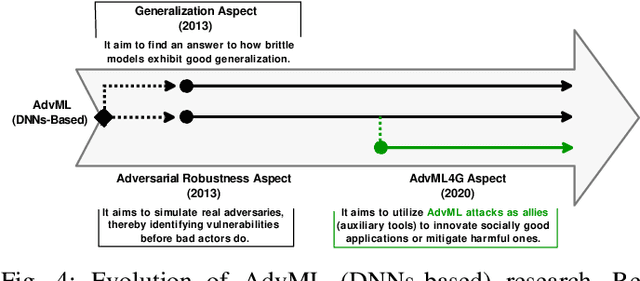
Abstract:Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) have been the driving force behind many of the recent advances in machine learning. However, research has shown that DNNs are vulnerable to adversarial examples -- input samples that have been perturbed to force DNN-based models to make errors. As a result, Adversarial Machine Learning (AdvML) has gained a lot of attention, and researchers have investigated these vulnerabilities in various settings and modalities. In addition, DNNs have also been found to incorporate embedded bias and often produce unexplainable predictions, which can result in anti-social AI applications. The emergence of new AI technologies that leverage Large Language Models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT and GPT-4, increases the risk of producing anti-social applications at scale. AdvML for Social Good (AdvML4G) is an emerging field that repurposes the AdvML bug to invent pro-social applications. Regulators, practitioners, and researchers should collaborate to encourage the development of pro-social applications and hinder the development of anti-social ones. In this work, we provide the first comprehensive review of the emerging field of AdvML4G. This paper encompasses a taxonomy that highlights the emergence of AdvML4G, a discussion of the differences and similarities between AdvML4G and AdvML, a taxonomy covering social good-related concepts and aspects, an exploration of the motivations behind the emergence of AdvML4G at the intersection of ML4G and AdvML, and an extensive summary of the works that utilize AdvML4G as an auxiliary tool for innovating pro-social applications. Finally, we elaborate upon various challenges and open research issues that require significant attention from the research community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge