Ilhem Berrou
Open Foundation Models in Healthcare: Challenges, Paradoxes, and Opportunities with GenAI Driven Personalized Prescription
Feb 04, 2025Abstract:In response to the success of proprietary Large Language Models (LLMs) such as OpenAI's GPT-4, there is a growing interest in developing open, non-proprietary LLMs and AI foundation models (AIFMs) for transparent use in academic, scientific, and non-commercial applications. Despite their inability to match the refined functionalities of their proprietary counterparts, open models hold immense potential to revolutionize healthcare applications. In this paper, we examine the prospects of open-source LLMs and AIFMs for developing healthcare applications and make two key contributions. Firstly, we present a comprehensive survey of the current state-of-the-art open-source healthcare LLMs and AIFMs and introduce a taxonomy of these open AIFMs, categorizing their utility across various healthcare tasks. Secondly, to evaluate the general-purpose applications of open LLMs in healthcare, we present a case study on personalized prescriptions. This task is particularly significant due to its critical role in delivering tailored, patient-specific medications that can greatly improve treatment outcomes. In addition, we compare the performance of open-source models with proprietary models in settings with and without Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). Our findings suggest that, although less refined, open LLMs can achieve performance comparable to proprietary models when paired with grounding techniques such as RAG. Furthermore, to highlight the clinical significance of LLMs-empowered personalized prescriptions, we perform subjective assessment through an expert clinician. We also elaborate on ethical considerations and potential risks associated with the misuse of powerful LLMs and AIFMs, highlighting the need for a cautious and responsible implementation in healthcare.
Robust Surgical Tools Detection in Endoscopic Videos with Noisy Data
Jul 03, 2023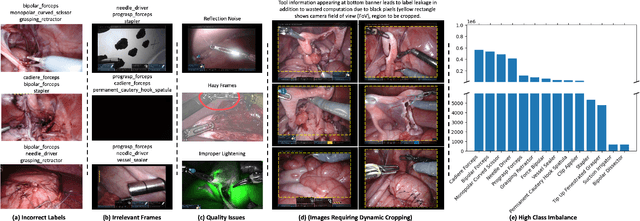
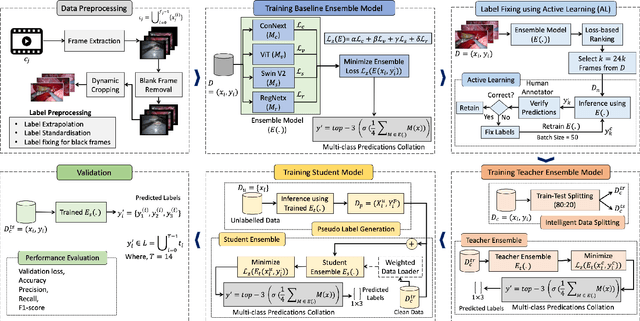
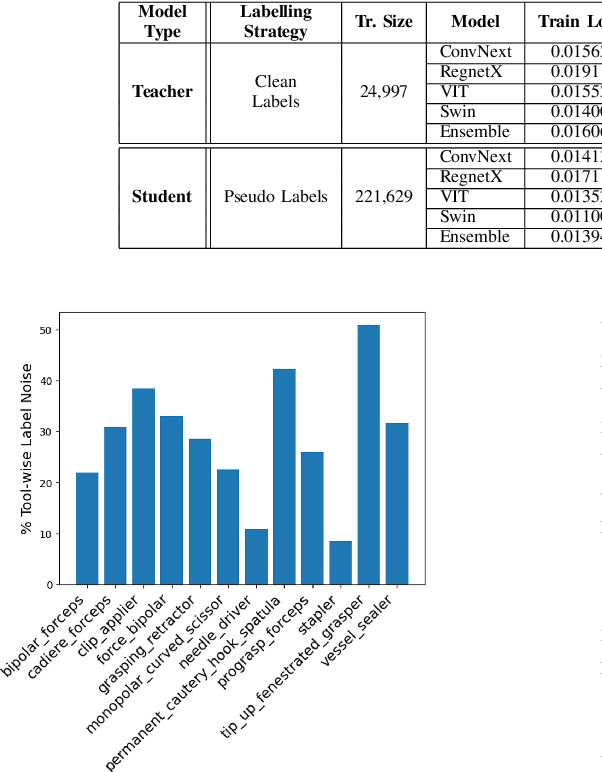
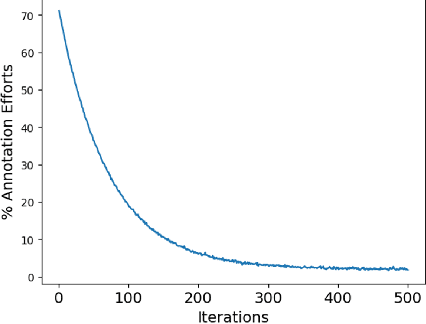
Abstract:Over the past few years, surgical data science has attracted substantial interest from the machine learning (ML) community. Various studies have demonstrated the efficacy of emerging ML techniques in analysing surgical data, particularly recordings of procedures, for digitizing clinical and non-clinical functions like preoperative planning, context-aware decision-making, and operating skill assessment. However, this field is still in its infancy and lacks representative, well-annotated datasets for training robust models in intermediate ML tasks. Also, existing datasets suffer from inaccurate labels, hindering the development of reliable models. In this paper, we propose a systematic methodology for developing robust models for surgical tool detection using noisy data. Our methodology introduces two key innovations: (1) an intelligent active learning strategy for minimal dataset identification and label correction by human experts; and (2) an assembling strategy for a student-teacher model-based self-training framework to achieve the robust classification of 14 surgical tools in a semi-supervised fashion. Furthermore, we employ weighted data loaders to handle difficult class labels and address class imbalance issues. The proposed methodology achieves an average F1-score of 85.88\% for the ensemble model-based self-training with class weights, and 80.88\% without class weights for noisy labels. Also, our proposed method significantly outperforms existing approaches, which effectively demonstrates its effectiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge