Empowering HWNs with Efficient Data Labeling: A Clustered Federated Semi-Supervised Learning Approach
Paper and Code
Jan 19, 2024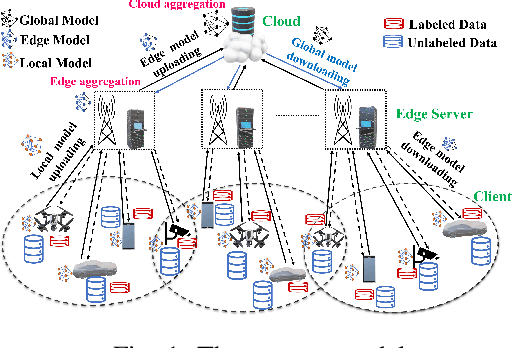
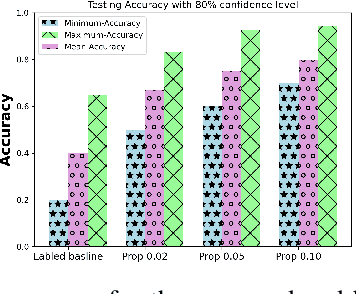
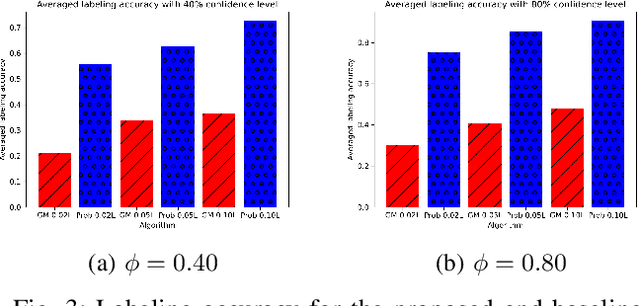
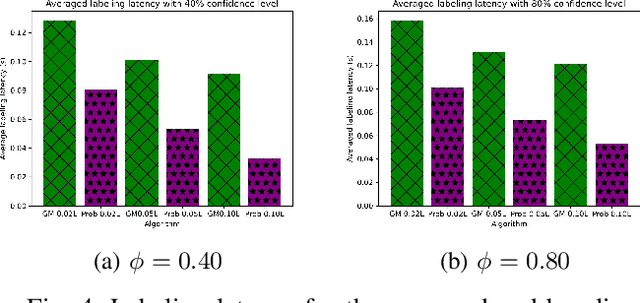
Clustered Federated Multitask Learning (CFL) has gained considerable attention as an effective strategy for overcoming statistical challenges, particularly when dealing with non independent and identically distributed (non IID) data across multiple users. However, much of the existing research on CFL operates under the unrealistic premise that devices have access to accurate ground truth labels. This assumption becomes especially problematic in hierarchical wireless networks (HWNs), where edge networks contain a large amount of unlabeled data, resulting in slower convergence rates and increased processing times, particularly when dealing with two layers of model aggregation. To address these issues, we introduce a novel framework, Clustered Federated Semi-Supervised Learning (CFSL), designed for more realistic HWN scenarios. Our approach leverages a best-performing specialized model algorithm, wherein each device is assigned a specialized model that is highly adept at generating accurate pseudo-labels for unlabeled data, even when the data stems from diverse environments. We validate the efficacy of CFSL through extensive experiments, comparing it with existing methods highlighted in recent literature. Our numerical results demonstrate that CFSL significantly improves upon key metrics such as testing accuracy, labeling accuracy, and labeling latency under varying proportions of labeled and unlabeled data while also accommodating the non-IID nature of the data and the unique characteristics of wireless edge networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge