Syed Zohaib Hassan
Enhancing Naturalness in LLM-Generated Utterances through Disfluency Insertion
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:Disfluencies are a natural feature of spontaneous human speech but are typically absent from the outputs of Large Language Models (LLMs). This absence can diminish the perceived naturalness of synthesized speech, which is an important criteria when building conversational agents that aim to mimick human behaviours. We show how the insertion of disfluencies can alleviate this shortcoming. The proposed approach involves (1) fine-tuning an LLM with Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) to incorporate various types of disfluencies into LLM-generated utterances and (2) synthesizing those utterances using a text-to-speech model that supports the generation of speech phenomena such as disfluencies. We evaluated the quality of the generated speech across two metrics: intelligibility and perceived spontaneity. We demonstrate through a user study that the insertion of disfluencies significantly increase the perceived spontaneity of the generated speech. This increase came, however, along with a slight reduction in intelligibility.
Visual Sentiment Analysis: A Natural DisasterUse-case Task at MediaEval 2021
Nov 22, 2021Abstract:The Visual Sentiment Analysis task is being offered for the first time at MediaEval. The main purpose of the task is to predict the emotional response to images of natural disasters shared on social media. Disaster-related images are generally complex and often evoke an emotional response, making them an ideal use case of visual sentiment analysis. We believe being able to perform meaningful analysis of natural disaster-related data could be of great societal importance, and a joint effort in this regard can open several interesting directions for future research. The task is composed of three sub-tasks, each aiming to explore a different aspect of the challenge. In this paper, we provide a detailed overview of the task, the general motivation of the task, and an overview of the dataset and the metrics to be used for the evaluation of the proposed solutions.
Sentiment Analysis of Users' Reviews on COVID-19 Contact Tracing Apps with a Benchmark Dataset
Mar 01, 2021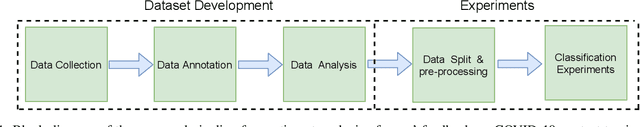
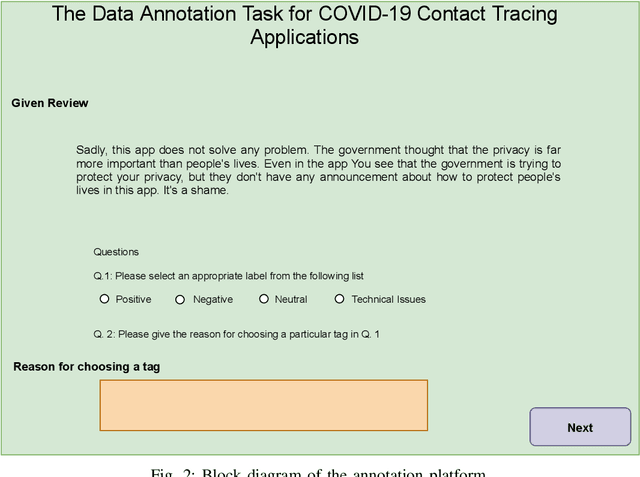
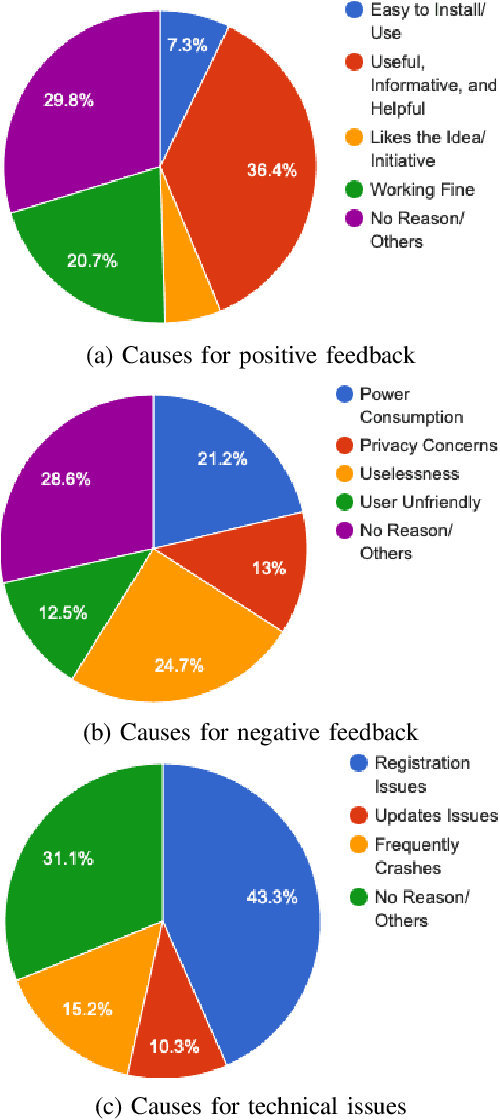
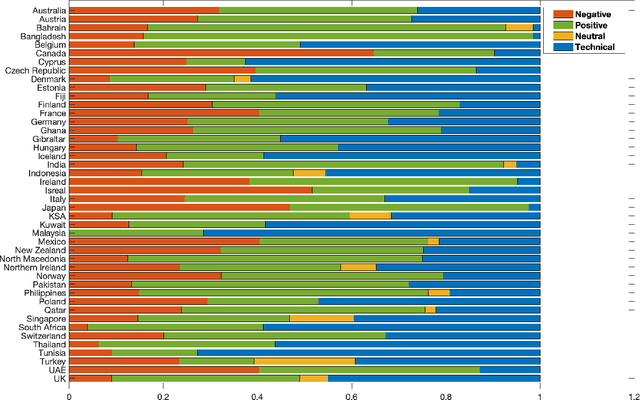
Abstract:Contact tracing has been globally adopted in the fight to control the infection rate of COVID-19. Thanks to digital technologies, such as smartphones and wearable devices, contacts of COVID-19 patients can be easily traced and informed about their potential exposure to the virus. To this aim, several interesting mobile applications have been developed. However, there are ever-growing concerns over the working mechanism and performance of these applications. The literature already provides some interesting exploratory studies on the community's response to the applications by analyzing information from different sources, such as news and users' reviews of the applications. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no existing solution that automatically analyzes users' reviews and extracts the evoked sentiments. In this work, we propose a pipeline starting from manual annotation via a crowd-sourcing study and concluding on the development and training of AI models for automatic sentiment analysis of users' reviews. In total, we employ eight different methods achieving up to an average F1-Scores 94.8% indicating the feasibility of automatic sentiment analysis of users' reviews on the COVID-19 contact tracing applications. We also highlight the key advantages, drawbacks, and users' concerns over the applications. Moreover, we also collect and annotate a large-scale dataset composed of 34,534 reviews manually annotated from the contract tracing applications of 46 distinct countries. The presented analysis and the dataset are expected to provide a baseline/benchmark for future research in the domain.
Visual Sentiment Analysis from Disaster Images in Social Media
Sep 04, 2020
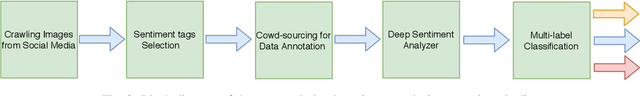
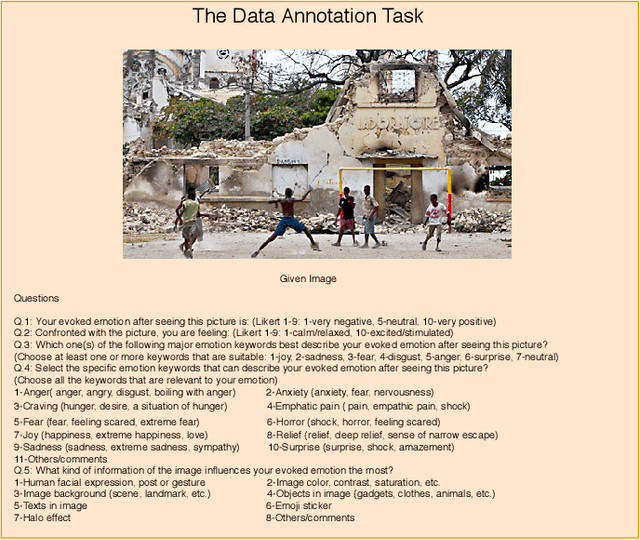
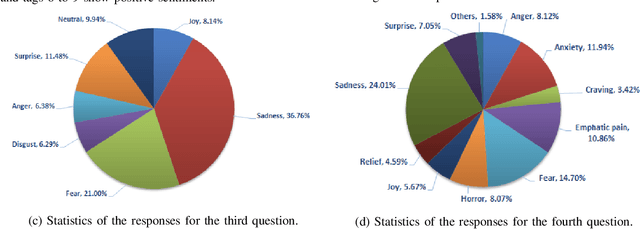
Abstract:The increasing popularity of social networks and users' tendency towards sharing their feelings, expressions, and opinions in text, visual, and audio content, have opened new opportunities and challenges in sentiment analysis. While sentiment analysis of text streams has been widely explored in literature, sentiment analysis from images and videos is relatively new. This article focuses on visual sentiment analysis in a societal important domain, namely disaster analysis in social media. To this aim, we propose a deep visual sentiment analyzer for disaster related images, covering different aspects of visual sentiment analysis starting from data collection, annotation, model selection, implementation, and evaluations. For data annotation, and analyzing peoples' sentiments towards natural disasters and associated images in social media, a crowd-sourcing study has been conducted with a large number of participants worldwide. The crowd-sourcing study resulted in a large-scale benchmark dataset with four different sets of annotations, each aiming a separate task. The presented analysis and the associated dataset will provide a baseline/benchmark for future research in the domain. We believe the proposed system can contribute toward more livable communities by helping different stakeholders, such as news broadcasters, humanitarian organizations, as well as the general public.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge