Pierre Lison
Re-identification of De-identified Documents with Autoregressive Infilling
May 19, 2025Abstract:Documents revealing sensitive information about individuals must typically be de-identified. This de-identification is often done by masking all mentions of personally identifiable information (PII), thereby making it more difficult to uncover the identity of the person(s) in question. To investigate the robustness of de-identification methods, we present a novel, RAG-inspired approach that attempts the reverse process of re-identification based on a database of documents representing background knowledge. Given a text in which personal identifiers have been masked, the re-identification proceeds in two steps. A retriever first selects from the background knowledge passages deemed relevant for the re-identification. Those passages are then provided to an infilling model which seeks to infer the original content of each text span. This process is repeated until all masked spans are replaced. We evaluate the re-identification on three datasets (Wikipedia biographies, court rulings and clinical notes). Results show that (1) as many as 80% of de-identified text spans can be successfully recovered and (2) the re-identification accuracy increases along with the level of background knowledge.
Incremental Dialogue Management: Survey, Discussion, and Implications for HRI
Jan 01, 2025



Abstract:Efforts towards endowing robots with the ability to speak have benefited from recent advancements in NLP, in particular large language models. However, as powerful as current models have become, they still operate on sentence or multi-sentence level input, not on the word-by-word input that humans operate on, affecting the degree of responsiveness that they offer, which is critical in situations where humans interact with robots using speech. In this paper, we review the literature on interactive systems that operate incrementally (i.e., at the word level or below it). We motivate the need for incremental systems, survey incremental modeling of important aspects of dialogue like speech recognition and language generation. Primary focus is on the part of the system that makes decisions, known as the dialogue manager. We find that there is very little research on incremental dialogue management, offer some requirements for practical incremental dialogue management, and the implications of incremental dialogue for embodied, robotic platforms.
Enhancing Naturalness in LLM-Generated Utterances through Disfluency Insertion
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:Disfluencies are a natural feature of spontaneous human speech but are typically absent from the outputs of Large Language Models (LLMs). This absence can diminish the perceived naturalness of synthesized speech, which is an important criteria when building conversational agents that aim to mimick human behaviours. We show how the insertion of disfluencies can alleviate this shortcoming. The proposed approach involves (1) fine-tuning an LLM with Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) to incorporate various types of disfluencies into LLM-generated utterances and (2) synthesizing those utterances using a text-to-speech model that supports the generation of speech phenomena such as disfluencies. We evaluated the quality of the generated speech across two metrics: intelligibility and perceived spontaneity. We demonstrate through a user study that the insertion of disfluencies significantly increase the perceived spontaneity of the generated speech. This increase came, however, along with a slight reduction in intelligibility.
Truthful Text Sanitization Guided by Inference Attacks
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:The purpose of text sanitization is to rewrite those text spans in a document that may directly or indirectly identify an individual, to ensure they no longer disclose personal information. Text sanitization must strike a balance between preventing the leakage of personal information (privacy protection) while also retaining as much of the document's original content as possible (utility preservation). We present an automated text sanitization strategy based on generalizations, which are more abstract (but still informative) terms that subsume the semantic content of the original text spans. The approach relies on instruction-tuned large language models (LLMs) and is divided into two stages. The LLM is first applied to obtain truth-preserving replacement candidates and rank them according to their abstraction level. Those candidates are then evaluated for their ability to protect privacy by conducting inference attacks with the LLM. Finally, the system selects the most informative replacement shown to be resistant to those attacks. As a consequence of this two-stage process, the chosen replacements effectively balance utility and privacy. We also present novel metrics to automatically evaluate these two aspects without the need to manually annotate data. Empirical results on the Text Anonymization Benchmark show that the proposed approach leads to enhanced utility, with only a marginal increase in the risk of re-identifying protected individuals compared to fully suppressing the original information. Furthermore, the selected replacements are shown to be more truth-preserving and abstractive than previous methods.
Neural Text Sanitization with Privacy Risk Indicators: An Empirical Analysis
Oct 22, 2023Abstract:Text sanitization is the task of redacting a document to mask all occurrences of (direct or indirect) personal identifiers, with the goal of concealing the identity of the individual(s) referred in it. In this paper, we consider a two-step approach to text sanitization and provide a detailed analysis of its empirical performance on two recently published datasets: the Text Anonymization Benchmark (Pil\'an et al., 2022) and a collection of Wikipedia biographies (Papadopoulou et al., 2022). The text sanitization process starts with a privacy-oriented entity recognizer that seeks to determine the text spans expressing identifiable personal information. This privacy-oriented entity recognizer is trained by combining a standard named entity recognition model with a gazetteer populated by person-related terms extracted from Wikidata. The second step of the text sanitization process consists in assessing the privacy risk associated with each detected text span, either isolated or in combination with other text spans. We present five distinct indicators of the re-identification risk, respectively based on language model probabilities, text span classification, sequence labelling, perturbations, and web search. We provide a contrastive analysis of each privacy indicator and highlight their benefits and limitations, notably in relation to the available labeled data.
Retrieval-Augmented Neural Response Generation Using Logical Reasoning and Relevance Scoring
Oct 20, 2023



Abstract:Constructing responses in task-oriented dialogue systems typically relies on information sources such the current dialogue state or external databases. This paper presents a novel approach to knowledge-grounded response generation that combines retrieval-augmented language models with logical reasoning. The approach revolves around a knowledge graph representing the current dialogue state and background information, and proceeds in three steps. The knowledge graph is first enriched with logically derived facts inferred using probabilistic logical programming. A neural model is then employed at each turn to score the conversational relevance of each node and edge of this extended graph. Finally, the elements with highest relevance scores are converted to a natural language form, and are integrated into the prompt for the neural conversational model employed to generate the system response. We investigate the benefits of the proposed approach on two datasets (KVRET and GraphWOZ) along with a human evaluation. Experimental results show that the combination of (probabilistic) logical reasoning with conversational relevance scoring does increase both the factuality and fluency of the responses.
Conversational Feedback in Scripted versus Spontaneous Dialogues: A Comparative Analysis
Sep 27, 2023Abstract:Scripted dialogues such as movie and TV subtitles constitute a widespread source of training data for conversational NLP models. However, the linguistic characteristics of those dialogues are notably different from those observed in corpora of spontaneous interactions. This difference is particularly marked for communicative feedback and grounding phenomena such as backchannels, acknowledgments, or clarification requests. Such signals are known to constitute a key part of the conversation flow and are used by the dialogue participants to provide feedback to one another on their perception of the ongoing interaction. This paper presents a quantitative analysis of such communicative feedback phenomena in both subtitles and spontaneous conversations. Based on dialogue data in English, French, German, Hungarian, Italian, Japanese, Norwegian and Chinese, we extract both lexical statistics and classification outputs obtained with a neural dialogue act tagger. Two main findings of this empirical study are that (1) conversational feedback is markedly less frequent in subtitles than in spontaneous dialogues and (2) subtitles contain a higher proportion of negative feedback. Furthermore, we show that dialogue responses generated by large language models also follow the same underlying trends and include comparatively few occurrences of communicative feedback, except when those models are explicitly fine-tuned on spontaneous dialogues.
Constructing a Knowledge Graph from Textual Descriptions of Software Vulnerabilities in the National Vulnerability Database
May 15, 2023



Abstract:Knowledge graphs have shown promise for several cybersecurity tasks, such as vulnerability assessment and threat analysis. In this work, we present a new method for constructing a vulnerability knowledge graph from information in the National Vulnerability Database (NVD). Our approach combines named entity recognition (NER), relation extraction (RE), and entity prediction using a combination of neural models, heuristic rules, and knowledge graph embeddings. We demonstrate how our method helps to fix missing entities in knowledge graphs used for cybersecurity and evaluate the performance.
Who's in Charge? Roles and Responsibilities of Decision-Making Components in Conversational Robots
Mar 15, 2023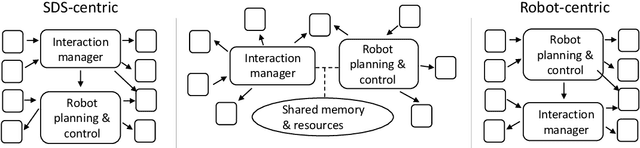
Abstract:Software architectures for conversational robots typically consist of multiple modules, each designed for a particular processing task or functionality. Some of these modules are developed for the purpose of making decisions about the next action that the robot ought to perform in the current context. Those actions may relate to physical movements, such as driving forward or grasping an object, but may also correspond to communicative acts, such as asking a question to the human user. In this position paper, we reflect on the organization of those decision modules in human-robot interaction platforms. We discuss the relative benefits and limitations of modular vs. end-to-end architectures, and argue that, despite the increasing popularity of end-to-end approaches, modular architectures remain preferable when developing conversational robots designed to execute complex tasks in collaboration with human users. We also show that most practical HRI architectures tend to be either robot-centric or dialogue-centric, depending on where developers wish to place the ``command center'' of their system. While those design choices may be justified in some application domains, they also limit the robot's ability to flexibly interleave physical movements and conversational behaviours. We contend that architectures placing ``action managers'' and ``interaction managers'' on an equal footing may provide the best path forward for future human-robot interaction systems.
GraphWOZ: Dialogue Management with Conversational Knowledge Graphs
Nov 23, 2022



Abstract:We present a new approach to dialogue management using conversational knowledge graphs as core representation of the dialogue state. To this end, we introduce a new dataset, GraphWOZ, which comprises Wizard-of-Oz dialogues in which human participants interact with a robot acting as a receptionist. In contrast to most existing work on dialogue management, GraphWOZ relies on a dialogue state explicitly represented as a dynamic knowledge graph instead of a fixed set of slots. This graph is composed of a varying number of entities (such as individuals, places, events, utterances and mentions) and relations between them (such as persons being part of a group or attending an event). The graph is then regularly updated on the basis of new observations and system actions. GraphWOZ is released along with detailed manual annotations related to the user intents, system responses, and reference relations occurring in both user and system turns. Based on GraphWOZ, we present experimental results for two dialogue management tasks, namely conversational entity linking and response ranking. For conversational entity linking, we show how to connect utterance mentions to their corresponding entity in the knowledge graph with a neural model relying on a combination of both string and graph-based features. Response ranking is then performed by summarizing the relevant content of the graph into a text, which is concatenated with the dialogue history and employed as input to score possible responses to a given dialogue state.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge