Andrea M. Storås
Looking into Concept Explanation Methods for Diabetic Retinopathy Classification
Oct 04, 2024Abstract:Diabetic retinopathy is a common complication of diabetes, and monitoring the progression of retinal abnormalities using fundus imaging is crucial. Because the images must be interpreted by a medical expert, it is infeasible to screen all individuals with diabetes for diabetic retinopathy. Deep learning has shown impressive results for automatic analysis and grading of fundus images. One drawback is, however, the lack of interpretability, which hampers the implementation of such systems in the clinic. Explainable artificial intelligence methods can be applied to explain the deep neural networks. Explanations based on concepts have shown to be intuitive for humans to understand, but have not yet been explored in detail for diabetic retinopathy grading. This work investigates and compares two concept-based explanation techniques for explaining deep neural networks developed for automatic diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy: Quantitative Testing with Concept Activation Vectors and Concept Bottleneck Models. We found that both methods have strengths and weaknesses, and choice of method should take the available data and the end user's preferences into account.
* Accepted for publication at the Journal of Machine Learning for Biomedical Imaging (MELBA) https://melba-journal.org/2024:021
VISEM-Tracking: Human Spermatozoa Tracking Dataset
Dec 23, 2022Abstract:A manual assessment of sperm motility requires microscopy observation, which is challenging due to the fast-moving spermatozoa in the field of view. To obtain correct results, manual evaluation requires extensive training. Therefore, computer-assisted sperm analysis (CASA) has become increasingly used in clinics. Despite this, more data is needed to train supervised machine learning approaches in order to improve accuracy and reliability in the assessment of sperm motility and kinematics. In this regard, we provide a dataset called VISEM-Tracking with 20 video recordings of 30 seconds of wet sperm preparations with manually annotated bounding-box coordinates and a set of sperm characteristics analyzed by experts in the domain. In addition to the annotated data, we provide unlabeled video clips for easy-to-use access and analysis of the data via methods such as self- or unsupervised learning. As part of this paper, we present baseline sperm detection performances using the YOLOv5 deep learning model trained on the VISEM-Tracking dataset. As a result, we show that the dataset can be used to train complex deep learning models to analyze spermatozoa. The dataset is publicly available at https://zenodo.org/record/7293726.
MLC at HECKTOR 2022: The Effect and Importance of Training Data when Analyzing Cases of Head and Neck Tumors using Machine Learning
Nov 30, 2022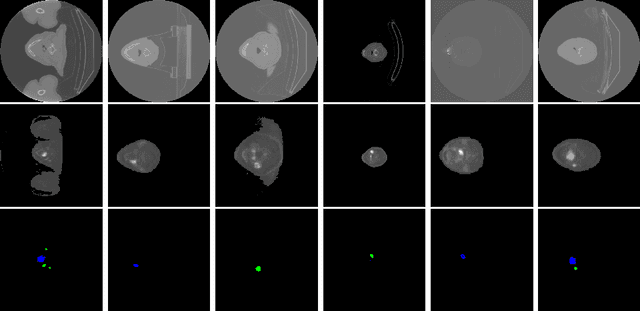
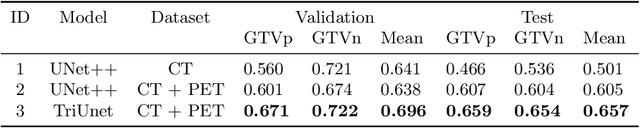
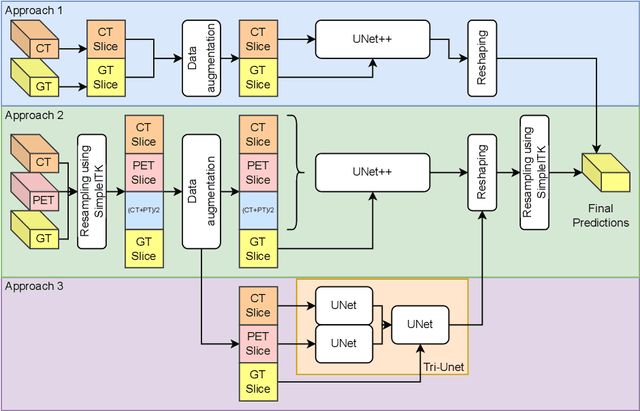
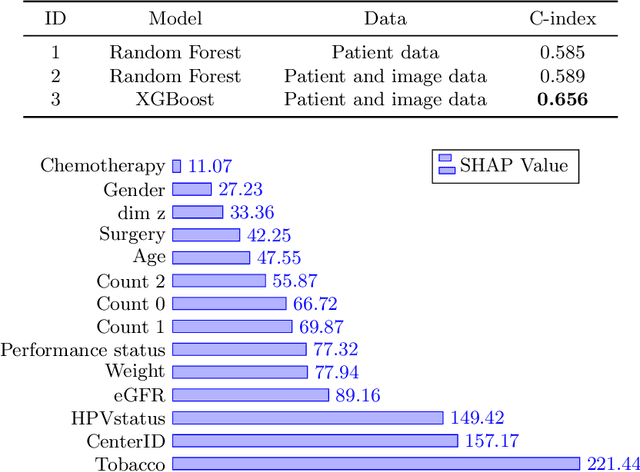
Abstract:Head and neck cancers are the fifth most common cancer worldwide, and recently, analysis of Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Computed Tomography (CT) images has been proposed to identify patients with a prognosis. Even though the results look promising, more research is needed to further validate and improve the results. This paper presents the work done by team MLC for the 2022 version of the HECKTOR grand challenge held at MICCAI 2022. For Task 1, the automatic segmentation task, our approach was, in contrast to earlier solutions using 3D segmentation, to keep it as simple as possible using a 2D model, analyzing every slice as a standalone image. In addition, we were interested in understanding how different modalities influence the results. We proposed two approaches; one using only the CT scans to make predictions and another using a combination of the CT and PET scans. For Task 2, the prediction of recurrence-free survival, we first proposed two approaches, one where we only use patient data and one where we combined the patient data with segmentations from the image model. For the prediction of the first two approaches, we used Random Forest. In our third approach, we combined patient data and image data using XGBoost. Low kidney function might worsen cancer prognosis. In this approach, we therefore estimated the kidney function of the patients and included it as a feature. Overall, we conclude that our simple methods were not able to compete with the highest-ranking submissions, but we still obtained reasonably good scores. We also got interesting insights into how the combination of different modalities can influence the segmentation and predictions.
PolypConnect: Image inpainting for generating realistic gastrointestinal tract images with polyps
May 30, 2022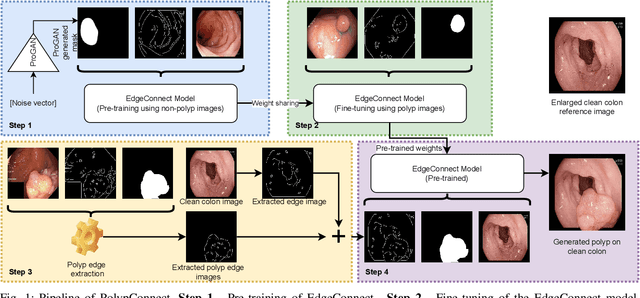
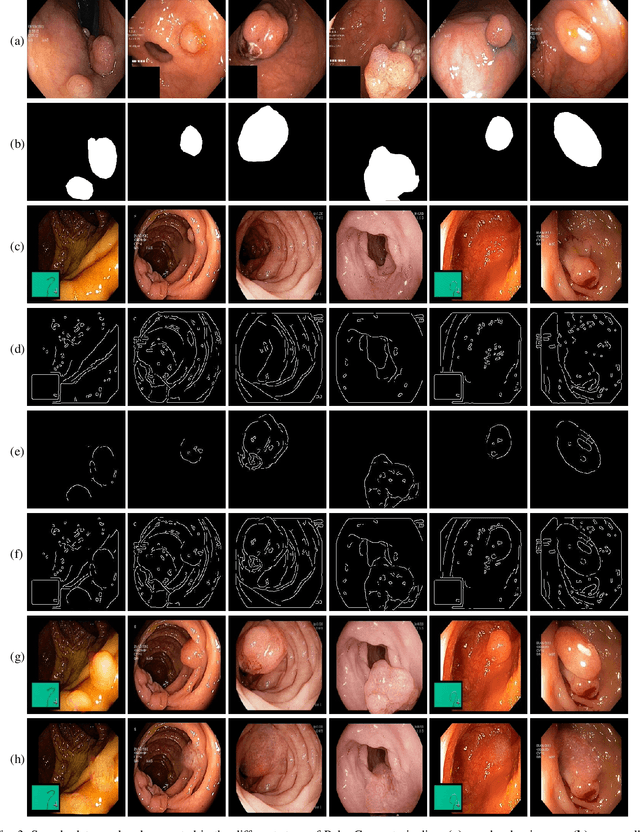
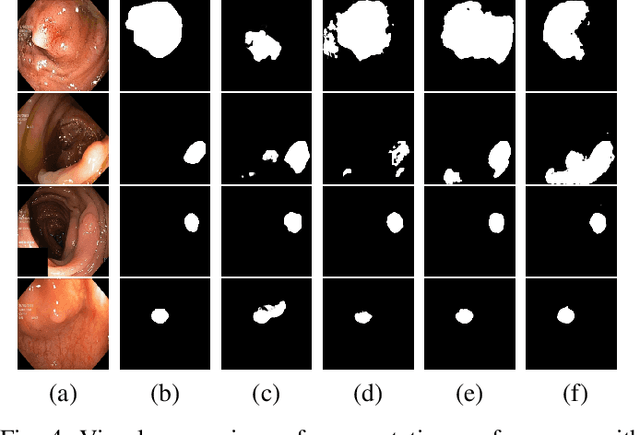
Abstract:Early identification of a polyp in the lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract can lead to prevention of life-threatening colorectal cancer. Developing computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems to detect polyps can improve detection accuracy and efficiency and save the time of the domain experts called endoscopists. Lack of annotated data is a common challenge when building CAD systems. Generating synthetic medical data is an active research area to overcome the problem of having relatively few true positive cases in the medical domain. To be able to efficiently train machine learning (ML) models, which are the core of CAD systems, a considerable amount of data should be used. In this respect, we propose the PolypConnect pipeline, which can convert non-polyp images into polyp images to increase the size of training datasets for training. We present the whole pipeline with quantitative and qualitative evaluations involving endoscopists. The polyp segmentation model trained using synthetic data, and real data shows a 5.1% improvement of mean intersection over union (mIOU), compared to the model trained only using real data. The codes of all the experiments are available on GitHub to reproduce the results.
Predicting tacrolimus exposure in kidney transplanted patients using machine learning
May 09, 2022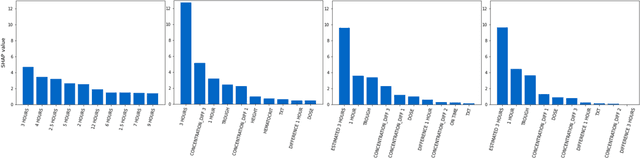



Abstract:Tacrolimus is one of the cornerstone immunosuppressive drugs in most transplantation centers worldwide following solid organ transplantation. Therapeutic drug monitoring of tacrolimus is necessary in order to avoid rejection of the transplanted organ or severe side effects. However, finding the right dose for a given patient is challenging, even for experienced clinicians. Consequently, a tool that can accurately estimate the drug exposure for individual dose adaptions would be of high clinical value. In this work, we propose a new technique using machine learning to estimate the tacrolimus exposure in kidney transplant recipients. Our models achieve predictive errors that are at the same level as an established population pharmacokinetic model, but are faster to develop and require less knowledge about the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug.
Artificial Intelligence in Dry Eye Disease
Sep 02, 2021Abstract:Dry eye disease (DED) has a prevalence of between 5 and 50\%, depending on the diagnostic criteria used and population under study. However, it remains one of the most underdiagnosed and undertreated conditions in ophthalmology. Many tests used in the diagnosis of DED rely on an experienced observer for image interpretation, which may be considered subjective and result in variation in diagnosis. Since artificial intelligence (AI) systems are capable of advanced problem solving, use of such techniques could lead to more objective diagnosis. Although the term `AI' is commonly used, recent success in its applications to medicine is mainly due to advancements in the sub-field of machine learning, which has been used to automatically classify images and predict medical outcomes. Powerful machine learning techniques have been harnessed to understand nuances in patient data and medical images, aiming for consistent diagnosis and stratification of disease severity. This is the first literature review on the use of AI in DED. We provide a brief introduction to AI, report its current use in DED research and its potential for application in the clinic. Our review found that AI has been employed in a wide range of DED clinical tests and research applications, primarily for interpretation of interferometry, slit-lamp and meibography images. While initial results are promising, much work is still needed on model development, clinical testing and standardisation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge