Tae Soo Kim
"When to Hand Off, When to Work Together": Expanding Human-Agent Co-Creative Collaboration through Concurrent Interaction
Mar 02, 2026Abstract:Human collaborators coordinate dynamically through process visibility and workspace awareness, yet AI agents typically either provide only final outputs or expose read-only execution processes (e.g., planning, reasoning) without interpreting concurrent user actions on shared artifacts. Building on mixed-initiative interaction principles, we explore whether agents can achieve collaborative context awareness -- interpreting concurrent user actions on shared artifacts and adapting in real-time. Study 1 (N=10 professional designers) revealed that process visibility enabled reasoning about agent actions but exposed conflicts when agents could not distinguish feedback from independent work. We developed CLEO, which interprets collaborative intent and adapts in real-time. Study 2 (N=10, two-day with stimulated recall interviews) analyzed 214 turns, identifying five action patterns, six triggers, and four enabling factors explaining when designers choose delegation (70.1%), direction (28.5%), or concurrent work (31.8%). We present a decision model with six interaction loops, design implications, and an annotated dataset.
DiscoverLLM: From Executing Intents to Discovering Them
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:To handle ambiguous and open-ended requests, Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly trained to interact with users to surface intents they have not yet expressed (e.g., ask clarification questions). However, users are often ambiguous because they have not yet formed their intents: they must observe and explore outcomes to discover what they want. Simply asking "what kind of tone do you want?" fails when users themselves do not know. We introduce DiscoverLLM, a novel and generalizable framework that trains LLMs to help users form and discover their intents. Central to our approach is a novel user simulator that models cognitive state with a hierarchy of intents that progressively concretize as the model surfaces relevant options -- where the degree of concretization serves as a reward signal that models can be trained to optimize. Resulting models learn to collaborate with users by adaptively diverging (i.e., explore options) when intents are unclear, and converging (i.e., refine and implement) when intents concretize. Across proposed interactive benchmarks in creative writing, technical writing, and SVG drawing, DiscoverLLM achieves over 10% higher task performance while reducing conversation length by up to 40%. In a user study with 75 human participants, DiscoverLLM improved conversation satisfaction and efficiency compared to baselines.
ClearFairy: Capturing Creative Workflows through Decision Structuring, In-Situ Questioning, and Rationale Inference
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Capturing professionals' decision-making in creative workflows is essential for reflection, collaboration, and knowledge sharing, yet existing methods often leave rationales incomplete and implicit decisions hidden. To address this, we present CLEAR framework that structures reasoning into cognitive decision steps-linked units of actions, artifacts, and self-explanations that make decisions traceable. Building on this framework, we introduce ClearFairy, a think-aloud AI assistant for UI design that detects weak explanations, asks lightweight clarifying questions, and infers missing rationales to ease the knowledge-sharing burden. In a study with twelve creative professionals, 85% of ClearFairy's inferred rationales were accepted, increasing strong explanations from 14% to over 83% of decision steps without adding cognitive demand. The captured steps also enhanced generative AI agents in Figma, yielding next-action predictions better aligned with professionals and producing more coherent design outcomes. For future research on human knowledge-grounded creative AI agents, we release a dataset of captured 417 decision steps.
SelectiveKD: A semi-supervised framework for cancer detection in DBT through Knowledge Distillation and Pseudo-labeling
Sep 25, 2024Abstract:When developing Computer Aided Detection (CAD) systems for Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT), the complexity arising from the volumetric nature of the modality poses significant technical challenges for obtaining large-scale accurate annotations. Without access to large-scale annotations, the resulting model may not generalize to different domains. Given the costly nature of obtaining DBT annotations, how to effectively increase the amount of data used for training DBT CAD systems remains an open challenge. In this paper, we present SelectiveKD, a semi-supervised learning framework for building cancer detection models for DBT, which only requires a limited number of annotated slices to reach high performance. We achieve this by utilizing unlabeled slices available in a DBT stack through a knowledge distillation framework in which the teacher model provides a supervisory signal to the student model for all slices in the DBT volume. Our framework mitigates the potential noise in the supervisory signal from a sub-optimal teacher by implementing a selective dataset expansion strategy using pseudo labels. We evaluate our approach with a large-scale real-world dataset of over 10,000 DBT exams collected from multiple device manufacturers and locations. The resulting SelectiveKD process effectively utilizes unannotated slices from a DBT stack, leading to significantly improved cancer classification performance (AUC) and generalization performance.
Is user feedback always informative? Retrieval Latent Defending for Semi-Supervised Domain Adaptation without Source Data
Jul 22, 2024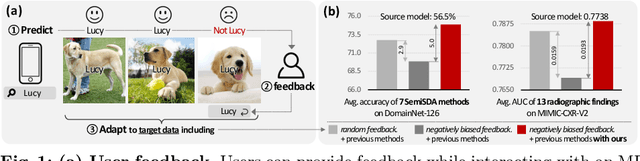
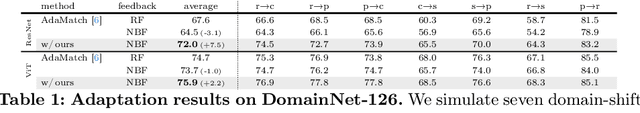
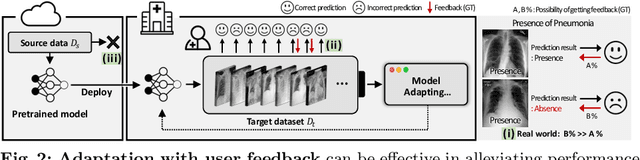
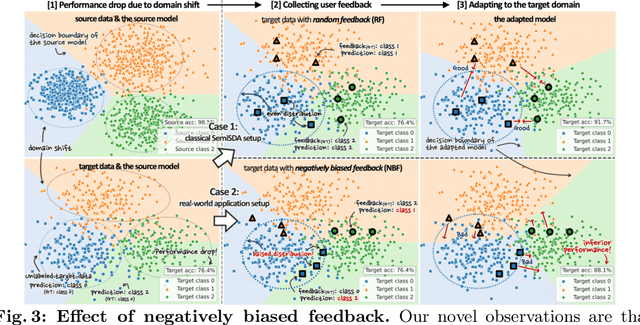
Abstract:This paper aims to adapt the source model to the target environment, leveraging small user feedback (i.e., labeled target data) readily available in real-world applications. We find that existing semi-supervised domain adaptation (SemiSDA) methods often suffer from poorly improved adaptation performance when directly utilizing such feedback data, as shown in Figure 1. We analyze this phenomenon via a novel concept called Negatively Biased Feedback (NBF), which stems from the observation that user feedback is more likely for data points where the model produces incorrect predictions. To leverage this feedback while avoiding the issue, we propose a scalable adapting approach, Retrieval Latent Defending. This approach helps existing SemiSDA methods to adapt the model with a balanced supervised signal by utilizing latent defending samples throughout the adaptation process. We demonstrate the problem caused by NBF and the efficacy of our approach across various benchmarks, including image classification, semantic segmentation, and a real-world medical imaging application. Our extensive experiments reveal that integrating our approach with multiple state-of-the-art SemiSDA methods leads to significant performance improvements.
One vs. Many: Comprehending Accurate Information from Multiple Erroneous and Inconsistent AI Generations
May 09, 2024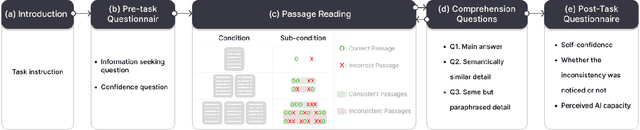
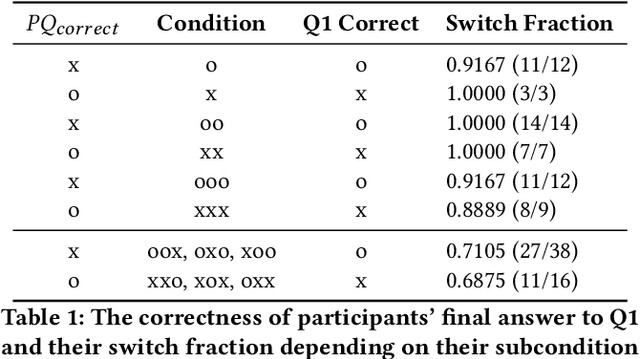
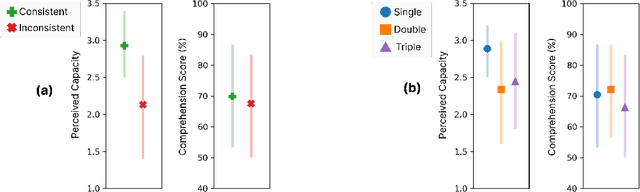
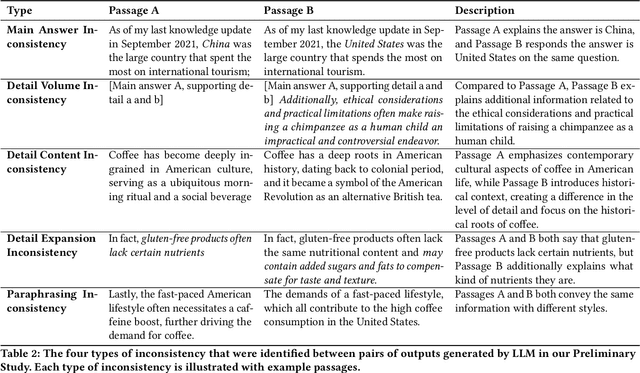
Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) are nondeterministic, the same input can generate different outputs, some of which may be incorrect or hallucinated. If run again, the LLM may correct itself and produce the correct answer. Unfortunately, most LLM-powered systems resort to single results which, correct or not, users accept. Having the LLM produce multiple outputs may help identify disagreements or alternatives. However, it is not obvious how the user will interpret conflicts or inconsistencies. To this end, we investigate how users perceive the AI model and comprehend the generated information when they receive multiple, potentially inconsistent, outputs. Through a preliminary study, we identified five types of output inconsistencies. Based on these categories, we conducted a study (N=252) in which participants were given one or more LLM-generated passages to an information-seeking question. We found that inconsistency within multiple LLM-generated outputs lowered the participants' perceived AI capacity, while also increasing their comprehension of the given information. Specifically, we observed that this positive effect of inconsistencies was most significant for participants who read two passages, compared to those who read three. Based on these findings, we present design implications that, instead of regarding LLM output inconsistencies as a drawback, we can reveal the potential inconsistencies to transparently indicate the limitations of these models and promote critical LLM usage.
EvalLM: Interactive Evaluation of Large Language Model Prompts on User-Defined Criteria
Sep 24, 2023Abstract:By simply composing prompts, developers can prototype novel generative applications with Large Language Models (LLMs). To refine prototypes into products, however, developers must iteratively revise prompts by evaluating outputs to diagnose weaknesses. Formative interviews (N=8) revealed that developers invest significant effort in manually evaluating outputs as they assess context-specific and subjective criteria. We present EvalLM, an interactive system for iteratively refining prompts by evaluating multiple outputs on user-defined criteria. By describing criteria in natural language, users can employ the system's LLM-based evaluator to get an overview of where prompts excel or fail, and improve these based on the evaluator's feedback. A comparative study (N=12) showed that EvalLM, when compared to manual evaluation, helped participants compose more diverse criteria, examine twice as many outputs, and reach satisfactory prompts with 59% fewer revisions. Beyond prompts, our work can be extended to augment model evaluation and alignment in specific application contexts.
ELVIS: Empowering Locality of Vision Language Pre-training with Intra-modal Similarity
Apr 11, 2023



Abstract:Deep learning has shown great potential in assisting radiologists in reading chest X-ray (CXR) images, but its need for expensive annotations for improving performance prevents widespread clinical application. Visual language pre-training (VLP) can alleviate the burden and cost of annotation by leveraging routinely generated reports for radiographs, which exist in large quantities as well as in paired form (imagetext pairs). Additionally, extensions to localization-aware VLPs are being proposed to address the needs of accurate localization of abnormalities for CAD in CXR. However, we find that the formulation proposed by locality-aware VLP literatures actually leads to loss in spatial relationships required for downstream localization tasks. Therefore, we propose Empowering Locality of VLP with Intra-modal Similarity, ELVIS, a VLP aware of intra-modal locality, to better preserve the locality within radiographs or reports, which enhances the ability to comprehend location references in text reports. Our locality-aware VLP method significantly outperforms state-of-the art baselines in multiple segmentation tasks and the MS-CXR phrase grounding task. Qualitatively, ELVIS is able to focus well on regions of interest described in the report text compared to prior approaches, allowing for enhanced interpretability.
LMCanvas: Object-Oriented Interaction to Personalize Large Language Model-Powered Writing Environments
Mar 27, 2023Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) can enhance writing by automating or supporting specific tasks in writers' workflows (e.g., paraphrasing, creating analogies). Leveraging this capability, a collection of interfaces have been developed that provide LLM-powered tools for specific writing tasks. However, these interfaces provide limited support for writers to create personal tools for their own unique tasks, and may not comprehensively fulfill a writer's needs -- requiring them to continuously switch between interfaces during writing. In this work, we envision LMCanvas, an interface that enables writers to create their own LLM-powered writing tools and arrange their personal writing environment by interacting with "blocks" in a canvas. In this interface, users can create text blocks to encapsulate writing and LLM prompts, model blocks for model parameter configurations, and connect these to create pipeline blocks that output generations. In this workshop paper, we discuss the design for LMCanvas and our plans to develop this concept.
The Semantic Reader Project: Augmenting Scholarly Documents through AI-Powered Interactive Reading Interfaces
Mar 25, 2023
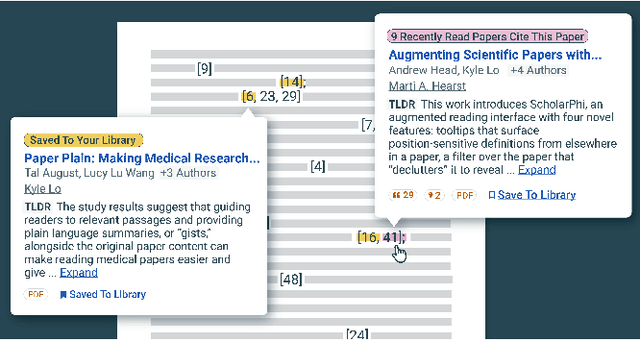
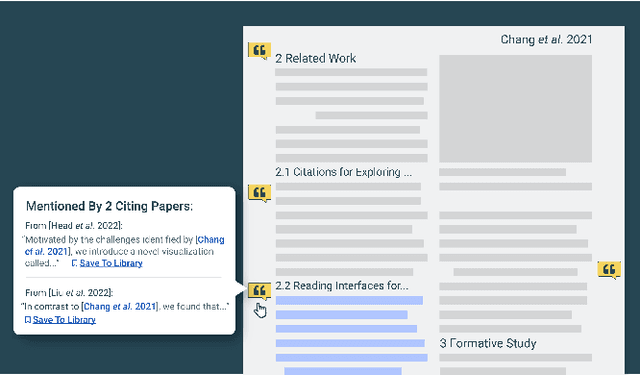
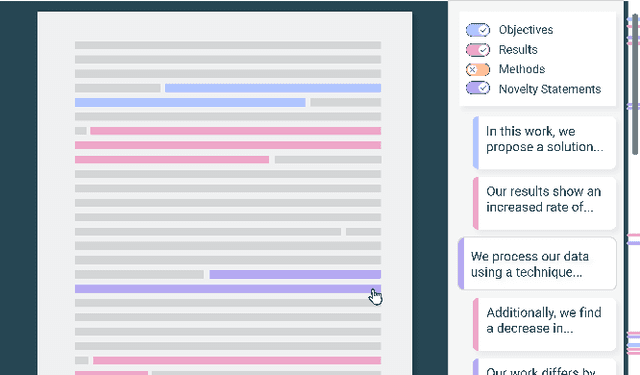
Abstract:Scholarly publications are key to the transfer of knowledge from scholars to others. However, research papers are information-dense, and as the volume of the scientific literature grows, the need for new technology to support the reading process grows. In contrast to the process of finding papers, which has been transformed by Internet technology, the experience of reading research papers has changed little in decades. The PDF format for sharing research papers is widely used due to its portability, but it has significant downsides including: static content, poor accessibility for low-vision readers, and difficulty reading on mobile devices. This paper explores the question "Can recent advances in AI and HCI power intelligent, interactive, and accessible reading interfaces -- even for legacy PDFs?" We describe the Semantic Reader Project, a collaborative effort across multiple institutions to explore automatic creation of dynamic reading interfaces for research papers. Through this project, we've developed ten research prototype interfaces and conducted usability studies with more than 300 participants and real-world users showing improved reading experiences for scholars. We've also released a production reading interface for research papers that will incorporate the best features as they mature. We structure this paper around challenges scholars and the public face when reading research papers -- Discovery, Efficiency, Comprehension, Synthesis, and Accessibility -- and present an overview of our progress and remaining open challenges.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge