Eytan Adar
Selecting Fine-Tuning Examples by Quizzing VLMs
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:A challenge in fine-tuning text-to-image diffusion models for specific topics is to select good examples. Fine-tuning from image sets of varying quality, such as Wikipedia Commons, will often produce poor output. However, training images that \textit{do} exemplify the target concept (e.g., a \textit{female Mountain Bluebird}) help ensure that the generated images are similarly representative (e.g., have the prototypical blue-wings and gray chest). In this work, we propose QZLoRA, a framework to select images for low-rank adaptation (LoRA). The approach leverages QuizRank, a method to automatically rank images by treating them as an `educational intervention' and `quizzing' a VLM. We demonstrate that QZLoRA can produce better aligned, photorealistic images with fewer samples. We also show that these fine-tuned models can produce stylized that are similarly representative (i.e., illustrations). Our results highlight the promise of combining automated visual reasoning with parameter-efficient fine-tuning for topic-adaptive generative modeling.
Through the Judge's Eyes: Inferred Thinking Traces Improve Reliability of LLM Raters
Oct 29, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used as raters for evaluation tasks. However, their reliability is often limited for subjective tasks, when human judgments involve subtle reasoning beyond annotation labels. Thinking traces, the reasoning behind a judgment, are highly informative but challenging to collect and curate. We present a human-LLM collaborative framework to infer thinking traces from label-only annotations. The proposed framework uses a simple and effective rejection sampling method to reconstruct these traces at scale. These inferred thinking traces are applied to two complementary tasks: (1) fine-tuning open LLM raters; and (2) synthesizing clearer annotation guidelines for proprietary LLM raters. Across multiple datasets, our methods lead to significantly improved LLM-human agreement. Additionally, the refined annotation guidelines increase agreement among different LLM models. These results suggest that LLMs can serve as practical proxies for otherwise unrevealed human thinking traces, enabling label-only corpora to be extended into thinking-trace-augmented resources that enhance the reliability of LLM raters.
QuizRank: Picking Images by Quizzing VLMs
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Images play a vital role in improving the readability and comprehension of Wikipedia articles by serving as `illustrative aids.' However, not all images are equally effective and not all Wikipedia editors are trained in their selection. We propose QuizRank, a novel method of image selection that leverages large language models (LLMs) and vision language models (VLMs) to rank images as learning interventions. Our approach transforms textual descriptions of the article's subject into multiple-choice questions about important visual characteristics of the concept. We utilize these questions to quiz the VLM: the better an image can help answer questions, the higher it is ranked. To further improve discrimination between visually similar items, we introduce a Contrastive QuizRank that leverages differences in the features of target (e.g., a Western Bluebird) and distractor concepts (e.g., Mountain Bluebird) to generate questions. We demonstrate the potential of VLMs as effective visual evaluators by showing a high congruence with human quiz-takers and an effective discriminative ranking of images.
Seeing Like an AI: How LLMs Apply (and Misapply) Wikipedia Neutrality Norms
Jul 04, 2024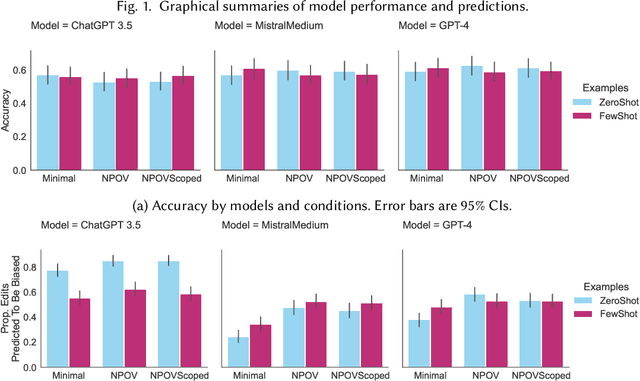
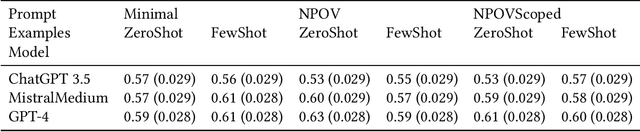
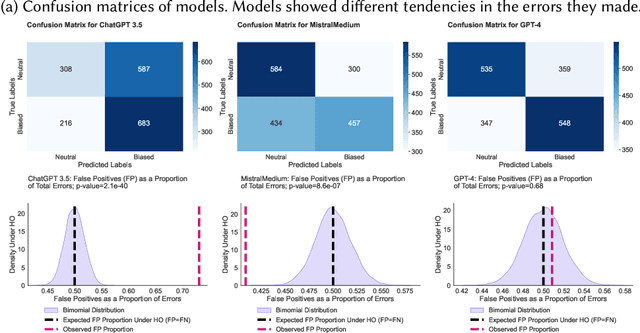
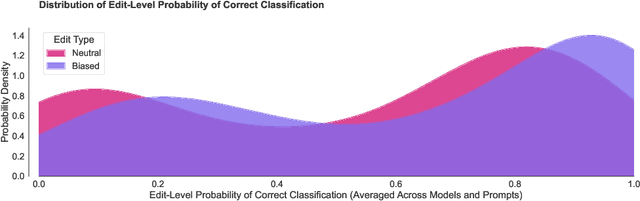
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are trained on broad corpora and then used in communities with specialized norms. Is providing LLMs with community rules enough for models to follow these norms? We evaluate LLMs' capacity to detect (Task 1) and correct (Task 2) biased Wikipedia edits according to Wikipedia's Neutral Point of View (NPOV) policy. LLMs struggled with bias detection, achieving only 64% accuracy on a balanced dataset. Models exhibited contrasting biases (some under- and others over-predicted bias), suggesting distinct priors about neutrality. LLMs performed better at generation, removing 79% of words removed by Wikipedia editors. However, LLMs made additional changes beyond Wikipedia editors' simpler neutralizations, resulting in high-recall but low-precision editing. Interestingly, crowdworkers rated AI rewrites as more neutral (70%) and fluent (61%) than Wikipedia-editor rewrites. Qualitative analysis found LLMs sometimes applied NPOV more comprehensively than Wikipedia editors but often made extraneous non-NPOV-related changes (such as grammar). LLMs may apply rules in ways that resonate with the public but diverge from community experts. While potentially effective for generation, LLMs may reduce editor agency and increase moderation workload (e.g., verifying additions). Even when rules are easy to articulate, having LLMs apply them like community members may still be difficult.
One vs. Many: Comprehending Accurate Information from Multiple Erroneous and Inconsistent AI Generations
May 09, 2024
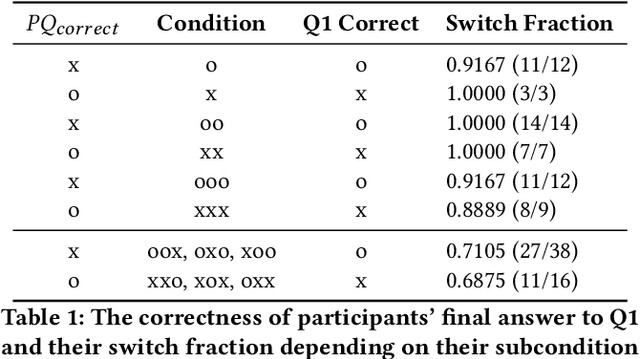
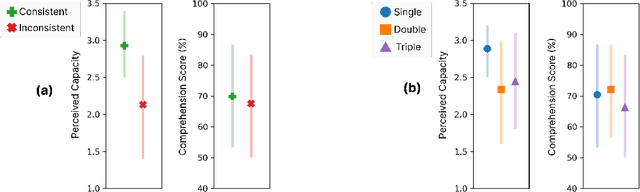
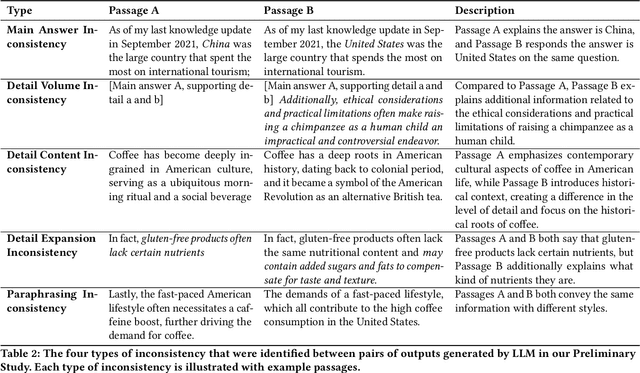
Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) are nondeterministic, the same input can generate different outputs, some of which may be incorrect or hallucinated. If run again, the LLM may correct itself and produce the correct answer. Unfortunately, most LLM-powered systems resort to single results which, correct or not, users accept. Having the LLM produce multiple outputs may help identify disagreements or alternatives. However, it is not obvious how the user will interpret conflicts or inconsistencies. To this end, we investigate how users perceive the AI model and comprehend the generated information when they receive multiple, potentially inconsistent, outputs. Through a preliminary study, we identified five types of output inconsistencies. Based on these categories, we conducted a study (N=252) in which participants were given one or more LLM-generated passages to an information-seeking question. We found that inconsistency within multiple LLM-generated outputs lowered the participants' perceived AI capacity, while also increasing their comprehension of the given information. Specifically, we observed that this positive effect of inconsistencies was most significant for participants who read two passages, compared to those who read three. Based on these findings, we present design implications that, instead of regarding LLM output inconsistencies as a drawback, we can reveal the potential inconsistencies to transparently indicate the limitations of these models and promote critical LLM usage.
Authors' Values and Attitudes Towards AI-bridged Scalable Personalization of Creative Language Arts
Mar 01, 2024Abstract:Generative AI has the potential to create a new form of interactive media: AI-bridged creative language arts (CLA), which bridge the author and audience by personalizing the author's vision to the audience's context and taste at scale. However, it is unclear what the authors' values and attitudes would be regarding AI-bridged CLA. To identify these values and attitudes, we conducted an interview study with 18 authors across eight genres (e.g., poetry, comics) by presenting speculative but realistic AI-bridged CLA scenarios. We identified three benefits derived from the dynamics between author, artifact, and audience: those that 1) authors get from the process, 2) audiences get from the artifact, and 3) authors get from the audience. We found how AI-bridged CLA would either promote or reduce these benefits, along with authors' concerns. We hope our investigation hints at how AI can provide intriguing experiences to CLA audiences while promoting authors' values.
PromptPaint: Steering Text-to-Image Generation Through Paint Medium-like Interactions
Aug 09, 2023



Abstract:While diffusion-based text-to-image (T2I) models provide a simple and powerful way to generate images, guiding this generation remains a challenge. For concepts that are difficult to describe through language, users may struggle to create prompts. Moreover, many of these models are built as end-to-end systems, lacking support for iterative shaping of the image. In response, we introduce PromptPaint, which combines T2I generation with interactions that model how we use colored paints. PromptPaint allows users to go beyond language to mix prompts that express challenging concepts. Just as we iteratively tune colors through layered placements of paint on a physical canvas, PromptPaint similarly allows users to apply different prompts to different canvas areas and times of the generative process. Through a set of studies, we characterize different approaches for mixing prompts, design trade-offs, and socio-technical challenges for generative models. With PromptPaint we provide insight into future steerable generative tools.
Sensible AI: Re-imagining Interpretability and Explainability using Sensemaking Theory
May 10, 2022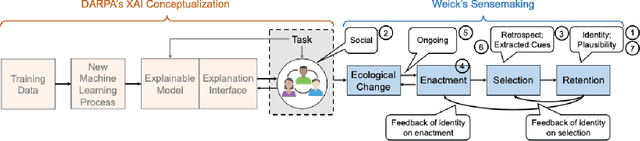
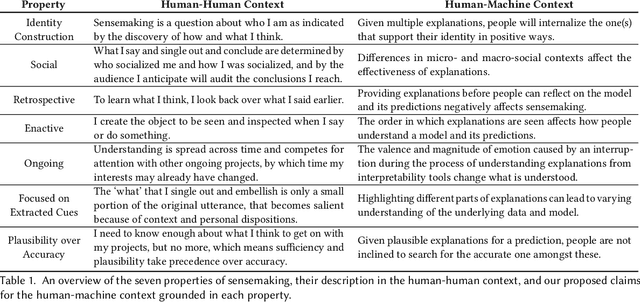
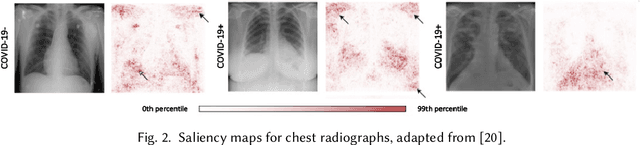
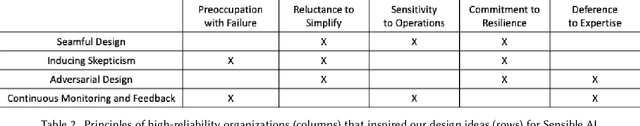
Abstract:Understanding how ML models work is a prerequisite for responsibly designing, deploying, and using ML-based systems. With interpretability approaches, ML can now offer explanations for its outputs to aid human understanding. Though these approaches rely on guidelines for how humans explain things to each other, they ultimately solve for improving the artifact -- an explanation. In this paper, we propose an alternate framework for interpretability grounded in Weick's sensemaking theory, which focuses on who the explanation is intended for. Recent work has advocated for the importance of understanding stakeholders' needs -- we build on this by providing concrete properties (e.g., identity, social context, environmental cues, etc.) that shape human understanding. We use an application of sensemaking in organizations as a template for discussing design guidelines for Sensible AI, AI that factors in the nuances of human cognition when trying to explain itself.
Towards A Process Model for Co-Creating AI Experiences
May 06, 2021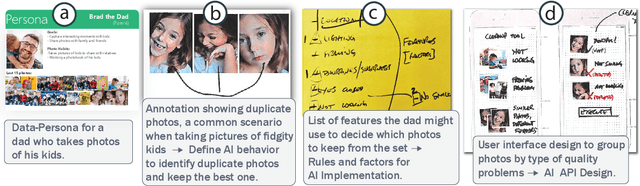
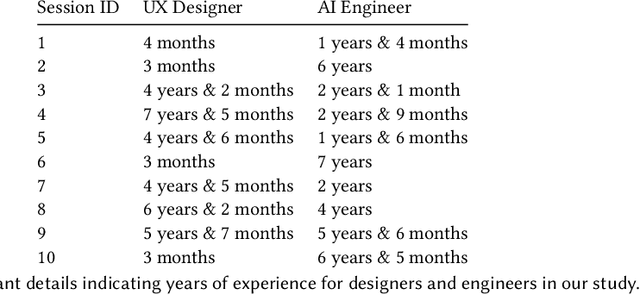

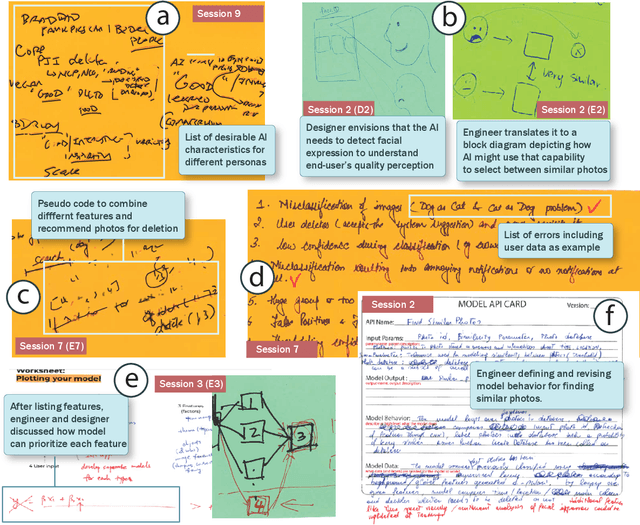
Abstract:Thinking of technology as a design material is appealing. It encourages designers to explore the material's properties to understand its capabilities and limitations, a prerequisite to generative design thinking. However, as a material, AI resists this approach because its properties emerge as part of the design process itself. Therefore, designers and AI engineers must collaborate in new ways to create both the material and its application experience. We investigate the co-creation process through a design study with 10 pairs of designers and engineers. We find that design 'probes' with user data are a useful tool in defining AI materials. Through data probes, designers construct designerly representations of the envisioned AI experience (AIX) to identify desirable AI characteristics. Data probes facilitate divergent thinking, material testing, and design validation. Based on our findings, we propose a process model for co-creating AIX and offer design considerations for incorporating data probes in design tools.
LAMVI-2: A Visual Tool for Comparing and Tuning Word Embedding Models
Oct 22, 2018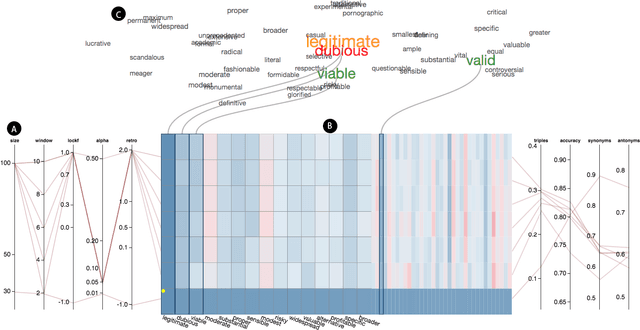
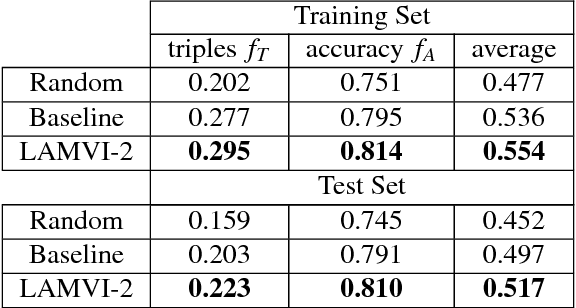
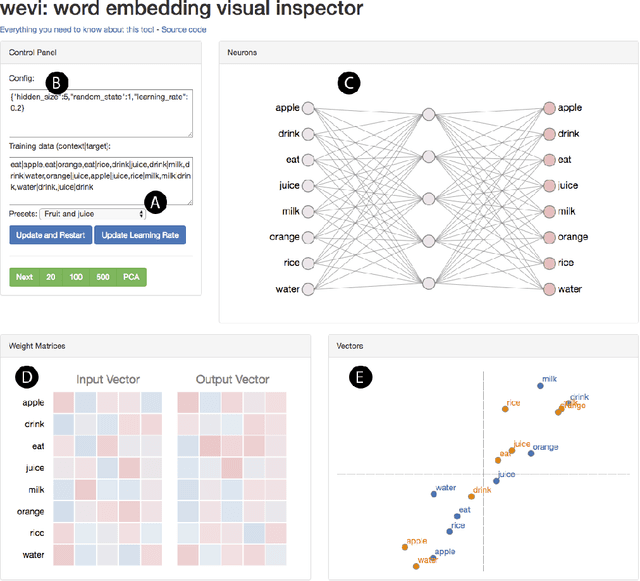
Abstract:Tuning machine learning models, particularly deep learning architectures, is a complex process. Automated hyperparameter tuning algorithms often depend on specific optimization metrics. However, in many situations, a developer trades one metric against another: accuracy versus overfitting, precision versus recall, smaller models and accuracy, etc. With deep learning, not only are the model's representations opaque, the model's behavior when parameters "knobs" are changed may also be unpredictable. Thus, picking the "best" model often requires time-consuming model comparison. In this work, we introduce LAMVI-2, a visual analytics system to support a developer in comparing hyperparameter settings and outcomes. By focusing on word-embedding models ("deep learning for text") we integrate views to compare both high-level statistics as well as internal model behaviors (e.g., comparing word 'distances'). We demonstrate how developers can work with LAMVI-2 to more quickly and accurately narrow down an appropriate and effective application-specific model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge