Taewook Kim
Conditional Text-to-Image Generation with Reference Guidance
Nov 22, 2024Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models have demonstrated tremendous success in synthesizing visually stunning images given textual instructions. Despite remarkable progress in creating high-fidelity visuals, text-to-image models can still struggle with precisely rendering subjects, such as text spelling. To address this challenge, this paper explores using additional conditions of an image that provides visual guidance of the particular subjects for diffusion models to generate. In addition, this reference condition empowers the model to be conditioned in ways that the vocabularies of the text tokenizer cannot adequately represent, and further extends the model's generalization to novel capabilities such as generating non-English text spellings. We develop several small-scale expert plugins that efficiently endow a Stable Diffusion model with the capability to take different references. Each plugin is trained with auxiliary networks and loss functions customized for applications such as English scene-text generation, multi-lingual scene-text generation, and logo-image generation. Our expert plugins demonstrate superior results than the existing methods on all tasks, each containing only 28.55M trainable parameters.
Steering AI-Driven Personalization of Scientific Text for General Audiences
Nov 15, 2024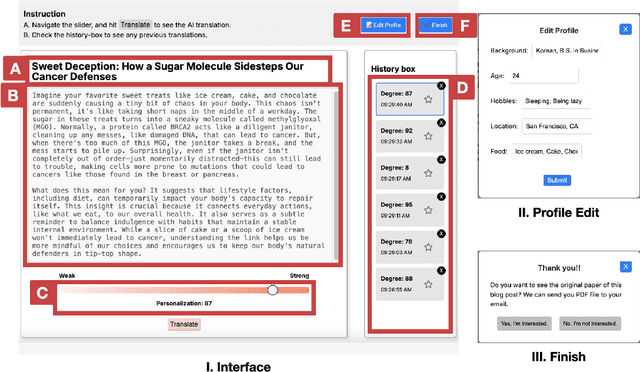
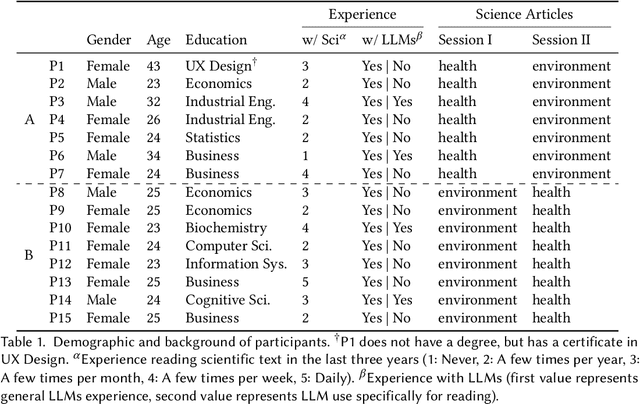

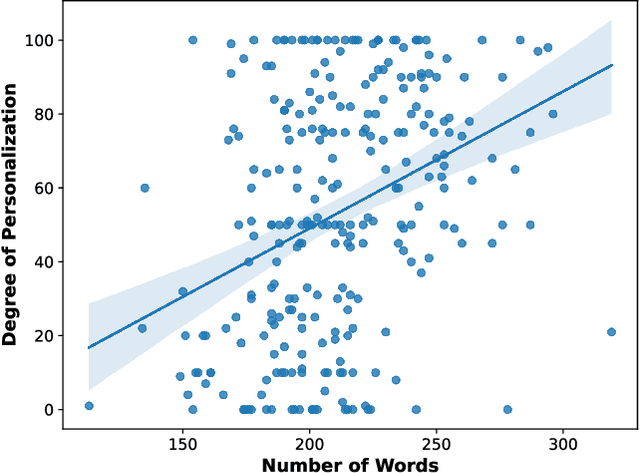
Abstract:Digital media platforms (e.g., social media, science blogs) offer opportunities to communicate scientific content to general audiences at scale. However, these audiences vary in their scientific expertise, literacy levels, and personal backgrounds, making effective science communication challenging. To address this challenge, we designed TranSlider, an AI-powered tool that generates personalized translations of scientific text based on individual user profiles (e.g., hobbies, location, and education). Our tool features an interactive slider that allows users to steer the degree of personalization from 0 (weakly relatable) to 100 (strongly relatable), leveraging LLMs to generate the translations with given degrees. Through an exploratory study with 15 participants, we investigated both the utility of these AI-personalized translations and how interactive reading features influenced users' understanding and reading experiences. We found that participants who preferred higher degrees of personalization appreciated the relatable and contextual translations, while those who preferred lower degrees valued concise translations with subtle contextualization. Furthermore, participants reported the compounding effect of multiple translations on their understanding of scientific content. Given these findings, we discuss several implications of AI-personalized translation tools in facilitating communication in collaborative contexts.
Learning to Customize Text-to-Image Diffusion In Diverse Context
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:Most text-to-image customization techniques fine-tune models on a small set of \emph{personal concept} images captured in minimal contexts. This often results in the model becoming overfitted to these training images and unable to generalize to new contexts in future text prompts. Existing customization methods are built on the success of effectively representing personal concepts as textual embeddings. Thus, in this work, we resort to diversifying the context of these personal concepts \emph{solely} within the textual space by simply creating a contextually rich set of text prompts, together with a widely used self-supervised learning objective. Surprisingly, this straightforward and cost-effective method significantly improves semantic alignment in the textual space, and this effect further extends to the image space, resulting in higher prompt fidelity for generated images. Additionally, our approach does not require any architectural modifications, making it highly compatible with existing text-to-image customization methods. We demonstrate the broad applicability of our approach by combining it with four different baseline methods, achieving notable CLIP score improvements.
Authors' Values and Attitudes Towards AI-bridged Scalable Personalization of Creative Language Arts
Mar 01, 2024Abstract:Generative AI has the potential to create a new form of interactive media: AI-bridged creative language arts (CLA), which bridge the author and audience by personalizing the author's vision to the audience's context and taste at scale. However, it is unclear what the authors' values and attitudes would be regarding AI-bridged CLA. To identify these values and attitudes, we conducted an interview study with 18 authors across eight genres (e.g., poetry, comics) by presenting speculative but realistic AI-bridged CLA scenarios. We identified three benefits derived from the dynamics between author, artifact, and audience: those that 1) authors get from the process, 2) audiences get from the artifact, and 3) authors get from the audience. We found how AI-bridged CLA would either promote or reduce these benefits, along with authors' concerns. We hope our investigation hints at how AI can provide intriguing experiences to CLA audiences while promoting authors' values.
Suppressing Spoof-irrelevant Factors for Domain-agnostic Face Anti-spoofing
Dec 02, 2020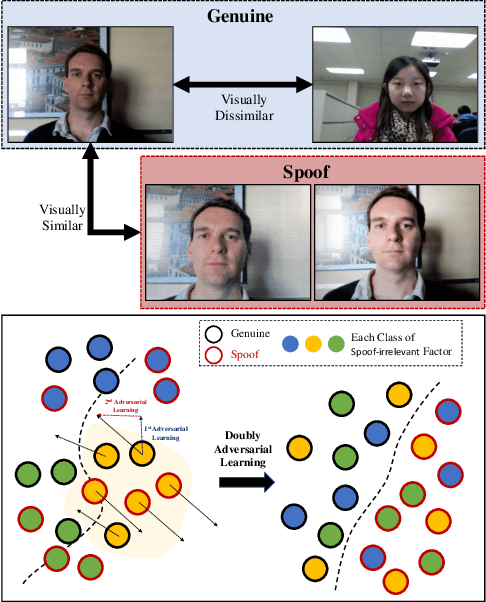
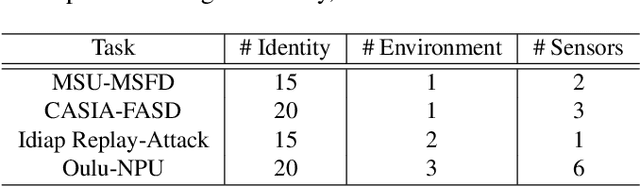
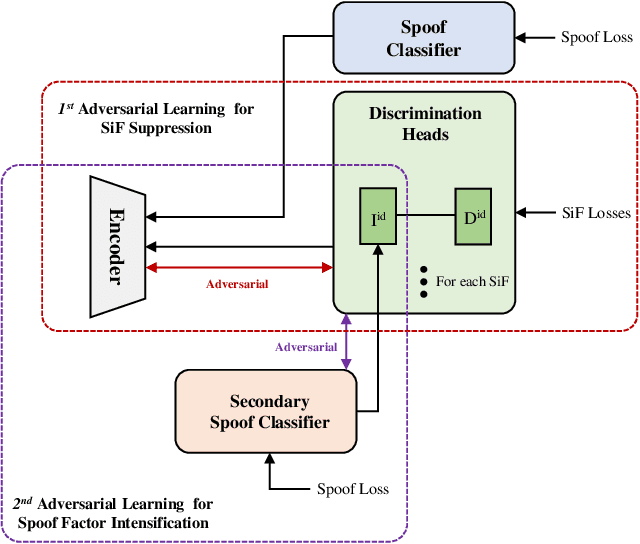
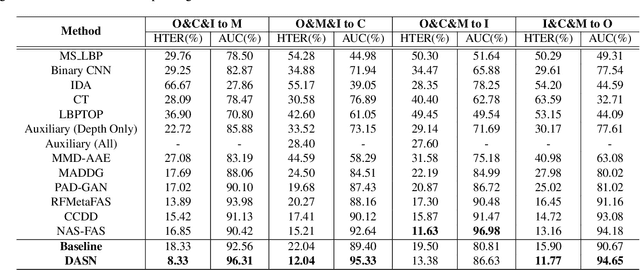
Abstract:Face anti-spoofing aims to prevent false authentications of face recognition systems by distinguishing whether an image is originated from a human face or a spoof medium. We propose a novel method called Doubly Adversarial Suppression Network (DASN) for domain-agnostic face anti-spoofing; DASN improves the generalization ability to unseen domains by learning to effectively suppress spoof-irrelevant factors (SiFs) (e.g., camera sensors, illuminations). To achieve our goal, we introduce two types of adversarial learning schemes. In the first adversarial learning scheme, multiple SiFs are suppressed by deploying multiple discrimination heads that are trained against an encoder. In the second adversarial learning scheme, each of the discrimination heads is also adversarially trained to suppress a spoof factor, and the group of the secondary spoof classifier and the encoder aims to intensify the spoof factor by overcoming the suppression. We evaluate the proposed method on four public benchmark datasets, and achieve remarkable evaluation results. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
BAN: Focusing on Boundary Context for Object Detection
Nov 13, 2018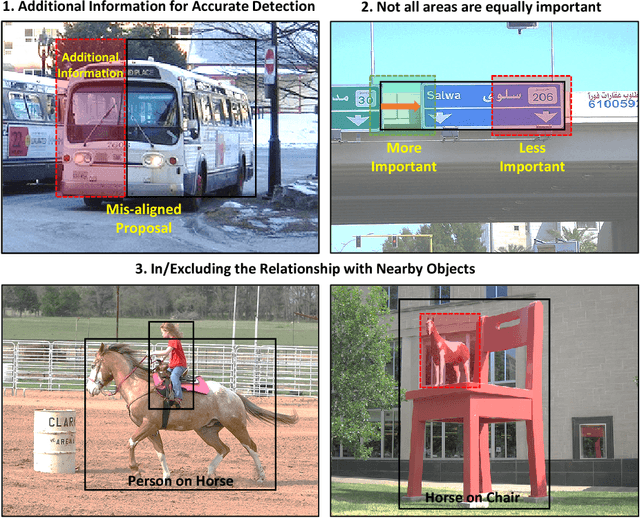
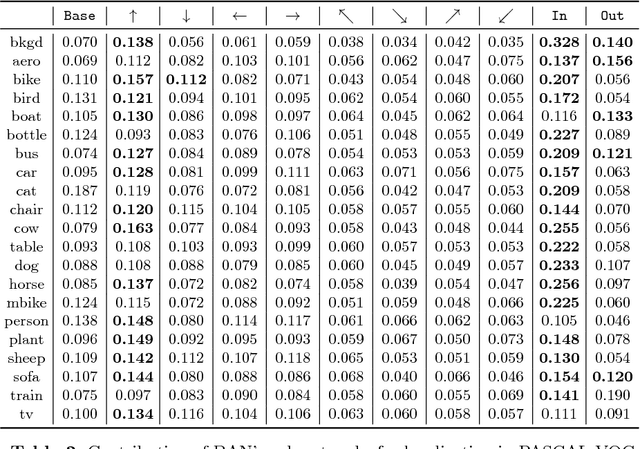
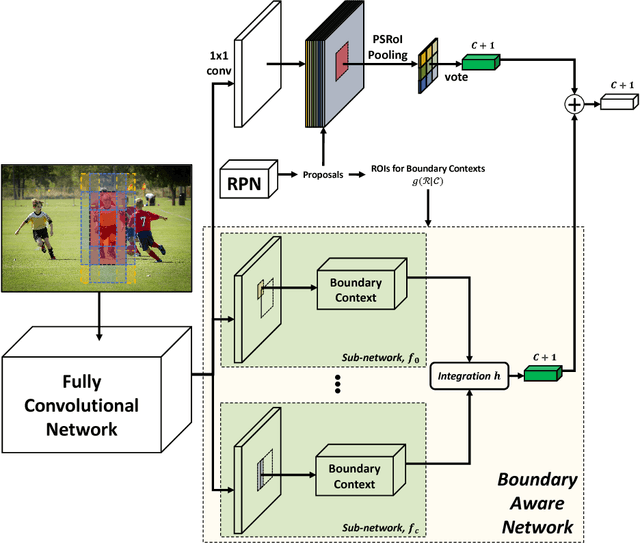
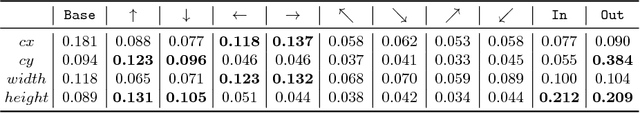
Abstract:Visual context is one of the important clue for object detection and the context information for boundaries of an object is especially valuable. We propose a boundary aware network (BAN) designed to exploit the visual contexts including boundary information and surroundings, named boundary context, and define three types of the boundary contexts: side, vertex and in/out-boundary context. Our BAN consists of 10 sub-networks for the area belonging to the boundary contexts. The detection head of BAN is defined as an ensemble of these sub-networks with different contributions depending on the sub-problem of detection. To verify our method, we visualize the activation of the sub-networks according to the boundary contexts and empirically show that the sub-networks contribute more to the related sub-problem in detection. We evaluate our method on PASCAL VOC detection benchmark and MS COCO dataset. The proposed method achieves the mean Average Precision (mAP) of 83.4% on PASCAL VOC and 36.9% on MS COCO. BAN allows the convolution network to provide an additional source of contexts for detection and selectively focus on the more important contexts, and it can be generally applied to many other detection methods as well to enhance the accuracy in detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge