Jiang Wang
Unsupervised Single-Channel Audio Separation with Diffusion Source Priors
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Single-channel audio separation aims to separate individual sources from a single-channel mixture. Most existing methods rely on supervised learning with synthetically generated paired data. However, obtaining high-quality paired data in real-world scenarios is often difficult. This data scarcity can degrade model performance under unseen conditions and limit generalization ability. To this end, in this work, we approach this problem from an unsupervised perspective, framing it as a probabilistic inverse problem. Our method requires only diffusion priors trained on individual sources. Separation is then achieved by iteratively guiding an initial state toward the solution through reconstruction guidance. Importantly, we introduce an advanced inverse problem solver specifically designed for separation, which mitigates gradient conflicts caused by interference between the diffusion prior and reconstruction guidance during inverse denoising. This design ensures high-quality and balanced separation performance across individual sources. Additionally, we find that initializing the denoising process with an augmented mixture instead of pure Gaussian noise provides an informative starting point that significantly improves the final performance. To further enhance audio prior modeling, we design a novel time-frequency attention-based network architecture that demonstrates strong audio modeling capability. Collectively, these improvements lead to significant performance gains, as validated across speech-sound event, sound event, and speech separation tasks.
Observability-Aware Active Calibration of Multi-Sensor Extrinsics for Ground Robots via Online Trajectory Optimization
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Accurate calibration of sensor extrinsic parameters for ground robotic systems (i.e., relative poses) is crucial for ensuring spatial alignment and achieving high-performance perception. However, existing calibration methods typically require complex and often human-operated processes to collect data. Moreover, most frameworks neglect acoustic sensors, thereby limiting the associated systems' auditory perception capabilities. To alleviate these issues, we propose an observability-aware active calibration method for ground robots with multimodal sensors, including a microphone array, a LiDAR (exteroceptive sensors), and wheel encoders (proprioceptive sensors). Unlike traditional approaches, our method enables active trajectory optimization for online data collection and calibration, contributing to the development of more intelligent robotic systems. Specifically, we leverage the Fisher information matrix (FIM) to quantify parameter observability and adopt its minimum eigenvalue as an optimization metric for trajectory generation via B-spline curves. Through planning and replanning of robot trajectory online, the method enhances the observability of multi-sensor extrinsic parameters. The effectiveness and advantages of our method have been demonstrated through numerical simulations and real-world experiments. For the benefit of the community, we have also open-sourced our code and data at https://github.com/AISLAB-sustech/Multisensor-Calibration.
Single-Channel Target Speech Extraction Utilizing Distance and Room Clues
May 20, 2025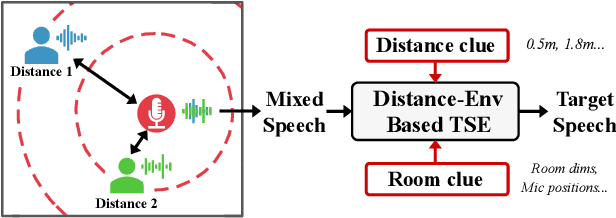
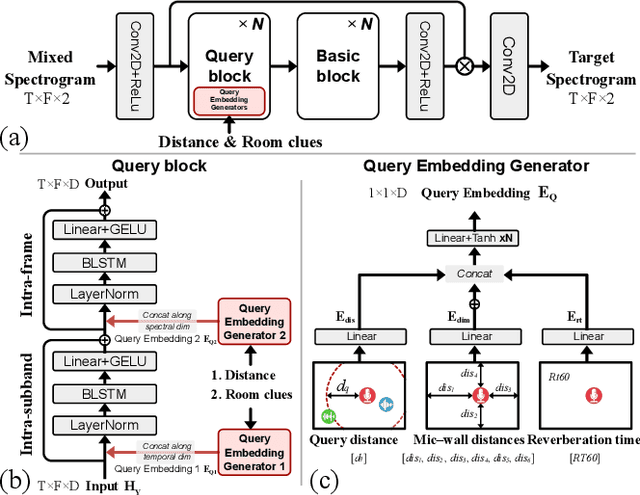
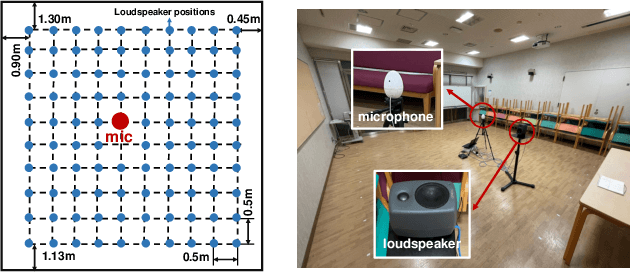
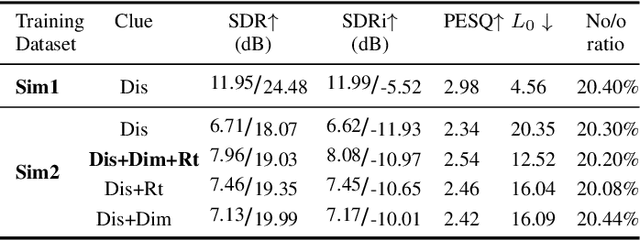
Abstract:This paper aims to achieve single-channel target speech extraction (TSE) in enclosures utilizing distance clues and room information. Recent works have verified the feasibility of distance clues for the TSE task, which can imply the sound source's direct-to-reverberation ratio (DRR) and thus can be utilized for speech separation and TSE systems. However, such distance clue is significantly influenced by the room's acoustic characteristics, such as dimension and reverberation time, making it challenging for TSE systems that rely solely on distance clues to generalize across a variety of different rooms. To solve this, we suggest providing room environmental information (room dimensions and reverberation time) for distance-based TSE for better generalization capabilities. Especially, we propose a distance and environment-based TSE model in the time-frequency (TF) domain with learnable distance and room embedding. Results on both simulated and real collected datasets demonstrate its feasibility. Demonstration materials are available at https://runwushi.github.io/distance-room-demo-page/.
Improved Extrinsic Calibration of Acoustic Cameras via Batch Optimization
Feb 10, 2025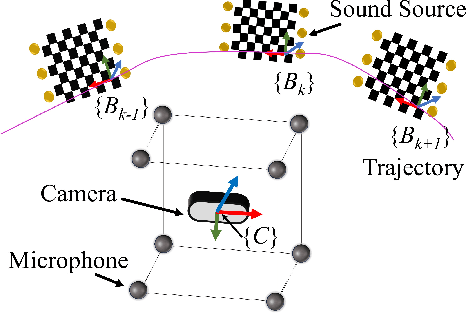
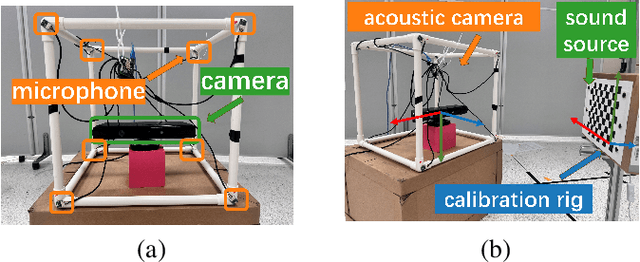
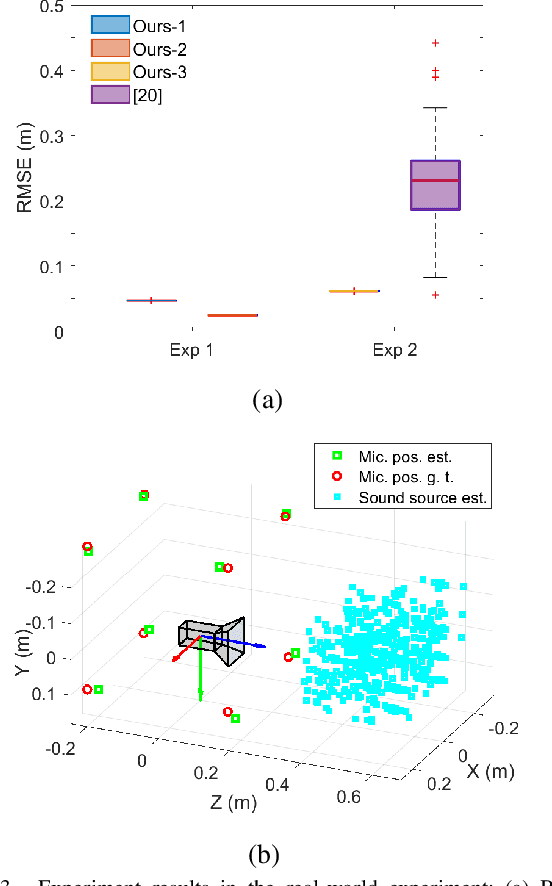
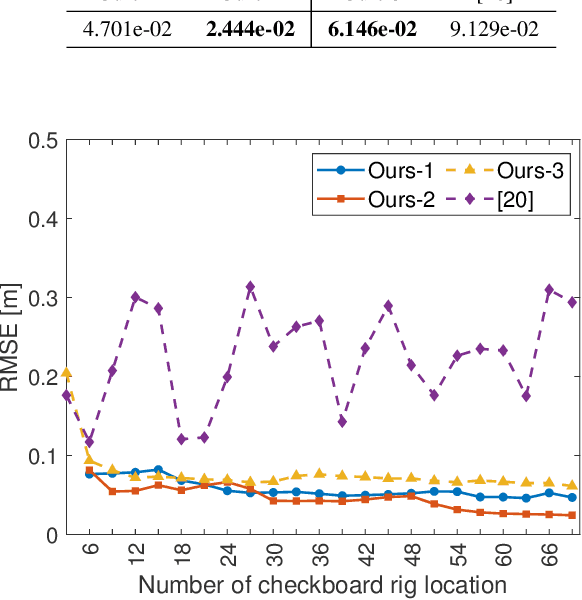
Abstract:Acoustic cameras have found many applications in practice. Accurate and reliable extrinsic calibration of the microphone array and visual sensors within acoustic cameras is crucial for fusing visual and auditory measurements. Existing calibration methods either require prior knowledge of the microphone array geometry or rely on grid search which suffers from slow iteration speed or poor convergence. To overcome these limitations, in this paper, we propose an automatic calibration technique using a calibration board with both visual and acoustic markers to identify each microphone position in the camera frame. We formulate the extrinsic calibration problem (between microphones and the visual sensor) as a nonlinear least squares problem and employ a batch optimization strategy to solve the associated problem. Extensive numerical simulations and realworld experiments show that the proposed method improves both the accuracy and robustness of extrinsic parameter calibration for acoustic cameras, in comparison to existing methods. To benefit the community, we open-source all the codes and data at https://github.com/AISLAB-sustech/AcousticCamera.
Conditional Text-to-Image Generation with Reference Guidance
Nov 22, 2024Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models have demonstrated tremendous success in synthesizing visually stunning images given textual instructions. Despite remarkable progress in creating high-fidelity visuals, text-to-image models can still struggle with precisely rendering subjects, such as text spelling. To address this challenge, this paper explores using additional conditions of an image that provides visual guidance of the particular subjects for diffusion models to generate. In addition, this reference condition empowers the model to be conditioned in ways that the vocabularies of the text tokenizer cannot adequately represent, and further extends the model's generalization to novel capabilities such as generating non-English text spellings. We develop several small-scale expert plugins that efficiently endow a Stable Diffusion model with the capability to take different references. Each plugin is trained with auxiliary networks and loss functions customized for applications such as English scene-text generation, multi-lingual scene-text generation, and logo-image generation. Our expert plugins demonstrate superior results than the existing methods on all tasks, each containing only 28.55M trainable parameters.
SLAM-based Joint Calibration of Multiple Asynchronous Microphone Arrays and Sound Source Localization
May 30, 2024



Abstract:Robot audition systems with multiple microphone arrays have many applications in practice. However, accurate calibration of multiple microphone arrays remains challenging because there are many unknown parameters to be identified, including the relative transforms (i.e., orientation, translation) and asynchronous factors (i.e., initial time offset and sampling clock difference) between microphone arrays. To tackle these challenges, in this paper, we adopt batch simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) for joint calibration of multiple asynchronous microphone arrays and sound source localization. Using the Fisher information matrix (FIM) approach, we first conduct the observability analysis (i.e., parameter identifiability) of the above-mentioned calibration problem and establish necessary/sufficient conditions under which the FIM and the Jacobian matrix have full column rank, which implies the identifiability of the unknown parameters. We also discover several scenarios where the unknown parameters are not uniquely identifiable. Subsequently, we propose an effective framework to initialize the unknown parameters, which is used as the initial guess in batch SLAM for multiple microphone arrays calibration, aiming to further enhance optimization accuracy and convergence. Extensive numerical simulations and real experiments have been conducted to verify the performance of the proposed method. The experiment results show that the proposed pipeline achieves higher accuracy with fast convergence in comparison to methods that use the noise-corrupted ground truth of the unknown parameters as the initial guess in the optimization and other existing frameworks.
LLM-AD: Large Language Model based Audio Description System
May 02, 2024Abstract:The development of Audio Description (AD) has been a pivotal step forward in making video content more accessible and inclusive. Traditionally, AD production has demanded a considerable amount of skilled labor, while existing automated approaches still necessitate extensive training to integrate multimodal inputs and tailor the output from a captioning style to an AD style. In this paper, we introduce an automated AD generation pipeline that harnesses the potent multimodal and instruction-following capacities of GPT-4V(ision). Notably, our methodology employs readily available components, eliminating the need for additional training. It produces ADs that not only comply with established natural language AD production standards but also maintain contextually consistent character information across frames, courtesy of a tracking-based character recognition module. A thorough analysis on the MAD dataset reveals that our approach achieves a performance on par with learning-based methods in automated AD production, as substantiated by a CIDEr score of 20.5.
Asynchronous Microphone Array Calibration using Hybrid TDOA Information
Mar 12, 2024



Abstract:Asynchronous Microphone array calibration is a prerequisite for most audition robot applications. In practice, the calibration requires estimating microphone positions, time offsets, clock drift rates, and sound event locations simultaneously. The existing method proposed Graph-based Simultaneous Localisation and Mapping (Graph-SLAM) utilizing common TDOA, time difference of arrival between two microphones (TDOA-M), and odometry measurement, however, it heavily depends on the initial value. In this paper, we propose a novel TDOA, time difference of arrival between adjacent sound events (TDOA-S), combine it with TDOA-M, called hybrid TDOA, and add odometry measurement to construct Graph-SLAM and use the Gauss-Newton (GN) method to solve. TDOA-S is simple and efficient because it eliminates time offset without generating new variables. Simulation and real-world experiment results consistently show that our method is independent of microphone number, insensitive to initial values, and has better calibration accuracy and stability under various TDOA noises. In addition, the simulation result demonstrates that our method has a lower Cram\'er-Rao lower bound (CRLB) for microphone parameters, which explains the advantages of my method.
RefineVIS: Video Instance Segmentation with Temporal Attention Refinement
Jun 07, 2023Abstract:We introduce a novel framework called RefineVIS for Video Instance Segmentation (VIS) that achieves good object association between frames and accurate segmentation masks by iteratively refining the representations using sequence context. RefineVIS learns two separate representations on top of an off-the-shelf frame-level image instance segmentation model: an association representation responsible for associating objects across frames and a segmentation representation that produces accurate segmentation masks. Contrastive learning is utilized to learn temporally stable association representations. A Temporal Attention Refinement (TAR) module learns discriminative segmentation representations by exploiting temporal relationships and a novel temporal contrastive denoising technique. Our method supports both online and offline inference. It achieves state-of-the-art video instance segmentation accuracy on YouTube-VIS 2019 (64.4 AP), Youtube-VIS 2021 (61.4 AP), and OVIS (46.1 AP) datasets. The visualization shows that the TAR module can generate more accurate instance segmentation masks, particularly for challenging cases such as highly occluded objects.
Adaptive Human Matting for Dynamic Videos
Apr 12, 2023



Abstract:The most recent efforts in video matting have focused on eliminating trimap dependency since trimap annotations are expensive and trimap-based methods are less adaptable for real-time applications. Despite the latest tripmap-free methods showing promising results, their performance often degrades when dealing with highly diverse and unstructured videos. We address this limitation by introducing Adaptive Matting for Dynamic Videos, termed AdaM, which is a framework designed for simultaneously differentiating foregrounds from backgrounds and capturing alpha matte details of human subjects in the foreground. Two interconnected network designs are employed to achieve this goal: (1) an encoder-decoder network that produces alpha mattes and intermediate masks which are used to guide the transformer in adaptively decoding foregrounds and backgrounds, and (2) a transformer network in which long- and short-term attention combine to retain spatial and temporal contexts, facilitating the decoding of foreground details. We benchmark and study our methods on recently introduced datasets, showing that our model notably improves matting realism and temporal coherence in complex real-world videos and achieves new best-in-class generalizability. Further details and examples are available at https://github.com/microsoft/AdaM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge