Peng Chu
LLM-AD: Large Language Model based Audio Description System
May 02, 2024Abstract:The development of Audio Description (AD) has been a pivotal step forward in making video content more accessible and inclusive. Traditionally, AD production has demanded a considerable amount of skilled labor, while existing automated approaches still necessitate extensive training to integrate multimodal inputs and tailor the output from a captioning style to an AD style. In this paper, we introduce an automated AD generation pipeline that harnesses the potent multimodal and instruction-following capacities of GPT-4V(ision). Notably, our methodology employs readily available components, eliminating the need for additional training. It produces ADs that not only comply with established natural language AD production standards but also maintain contextually consistent character information across frames, courtesy of a tracking-based character recognition module. A thorough analysis on the MAD dataset reveals that our approach achieves a performance on par with learning-based methods in automated AD production, as substantiated by a CIDEr score of 20.5.
RefineVIS: Video Instance Segmentation with Temporal Attention Refinement
Jun 07, 2023Abstract:We introduce a novel framework called RefineVIS for Video Instance Segmentation (VIS) that achieves good object association between frames and accurate segmentation masks by iteratively refining the representations using sequence context. RefineVIS learns two separate representations on top of an off-the-shelf frame-level image instance segmentation model: an association representation responsible for associating objects across frames and a segmentation representation that produces accurate segmentation masks. Contrastive learning is utilized to learn temporally stable association representations. A Temporal Attention Refinement (TAR) module learns discriminative segmentation representations by exploiting temporal relationships and a novel temporal contrastive denoising technique. Our method supports both online and offline inference. It achieves state-of-the-art video instance segmentation accuracy on YouTube-VIS 2019 (64.4 AP), Youtube-VIS 2021 (61.4 AP), and OVIS (46.1 AP) datasets. The visualization shows that the TAR module can generate more accurate instance segmentation masks, particularly for challenging cases such as highly occluded objects.
Consistent Video Instance Segmentation with Inter-Frame Recurrent Attention
Jun 14, 2022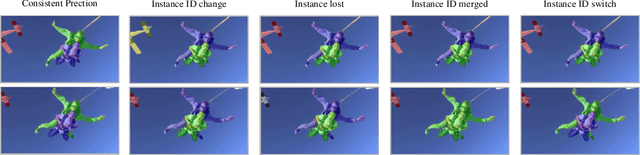
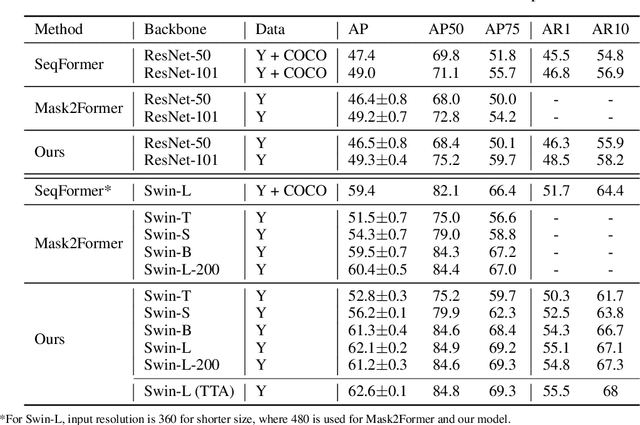
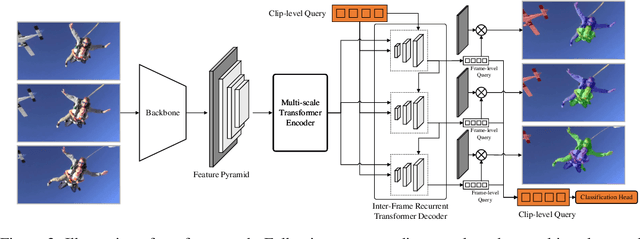
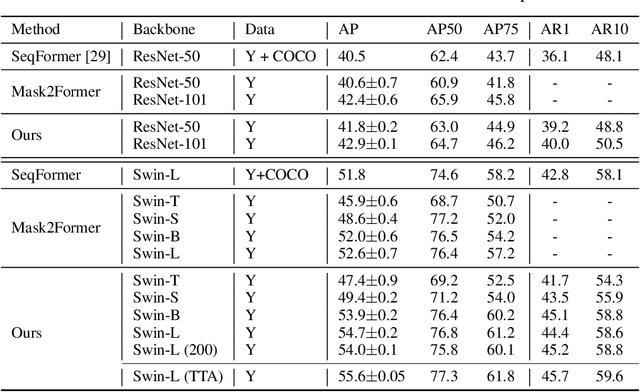
Abstract:Video instance segmentation aims at predicting object segmentation masks for each frame, as well as associating the instances across multiple frames. Recent end-to-end video instance segmentation methods are capable of performing object segmentation and instance association together in a direct parallel sequence decoding/prediction framework. Although these methods generally predict higher quality object segmentation masks, they can fail to associate instances in challenging cases because they do not explicitly model the temporal instance consistency for adjacent frames. We propose a consistent end-to-end video instance segmentation framework with Inter-Frame Recurrent Attention to model both the temporal instance consistency for adjacent frames and the global temporal context. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that the Inter-Frame Recurrent Attention significantly improves temporal instance consistency while maintaining the quality of the object segmentation masks. Our model achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on both YouTubeVIS-2019 (62.1\%) and YouTubeVIS-2021 (54.7\%) datasets. In addition, quantitative and qualitative results show that the proposed methods predict more temporally consistent instance segmentation masks.
Deep Frequency Filtering for Domain Generalization
Mar 23, 2022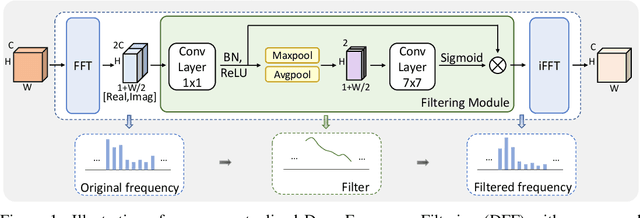
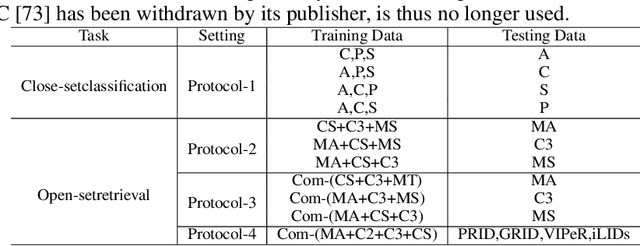
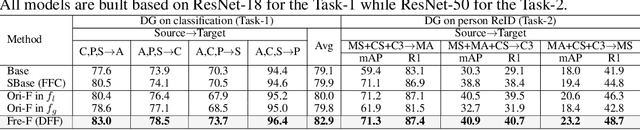
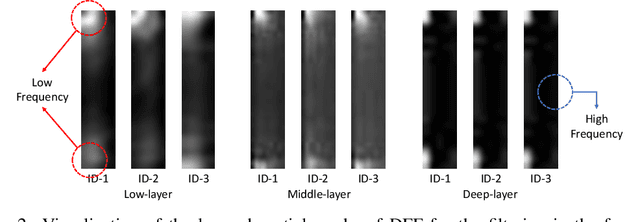
Abstract:Improving the generalization capability of Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) is critical for their practical uses, which has been a longstanding challenge. Some theoretical studies have revealed that DNNs have preferences to different frequency components in the learning process and indicated that this may affect the robustness of learned features. In this paper, we propose Deep Frequency Filtering (DFF) for learning domain-generalizable features, which is the first endeavour to explicitly modulate frequency components of different transfer difficulties across domains during training. To achieve this, we perform Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) on feature maps at different layers, then adopt a light-weight module to learn the attention masks from frequency representations after FFT to enhance transferable frequency components while suppressing the components not conductive to generalization. Further, we empirically compare different types of attention for implementing our conceptualized DFF. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed DFF and show that applying DFF on a plain baseline outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on different domain generalization tasks, including close-set classification and open-set retrieval.
Lifelong Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Person Re-identification with Coordinated Anti-forgetting and Adaptation
Dec 13, 2021
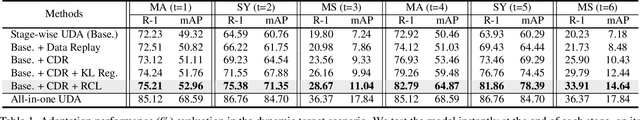
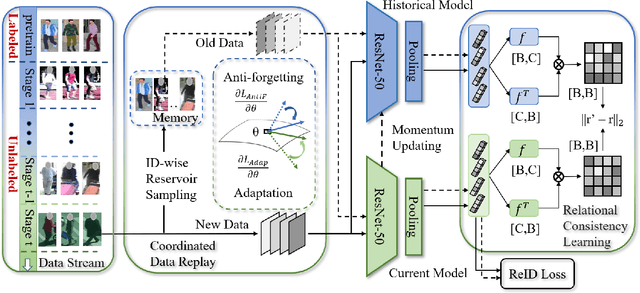
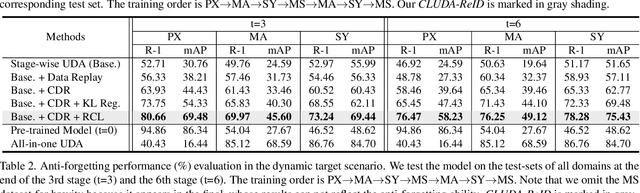
Abstract:Unsupervised domain adaptive person re-identification (ReID) has been extensively investigated to mitigate the adverse effects of domain gaps. Those works assume the target domain data can be accessible all at once. However, for the real-world streaming data, this hinders the timely adaptation to changing data statistics and sufficient exploitation of increasing samples. In this paper, to address more practical scenarios, we propose a new task, Lifelong Unsupervised Domain Adaptive (LUDA) person ReID. This is challenging because it requires the model to continuously adapt to unlabeled data of the target environments while alleviating catastrophic forgetting for such a fine-grained person retrieval task. We design an effective scheme for this task, dubbed CLUDA-ReID, where the anti-forgetting is harmoniously coordinated with the adaptation. Specifically, a meta-based Coordinated Data Replay strategy is proposed to replay old data and update the network with a coordinated optimization direction for both adaptation and memorization. Moreover, we propose Relational Consistency Learning for old knowledge distillation/inheritance in line with the objective of retrieval-based tasks. We set up two evaluation settings to simulate the practical application scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our CLUDA-ReID for both scenarios with stationary target streams and scenarios with dynamic target streams.
MMPTRACK: Large-scale Densely Annotated Multi-camera Multiple People Tracking Benchmark
Nov 30, 2021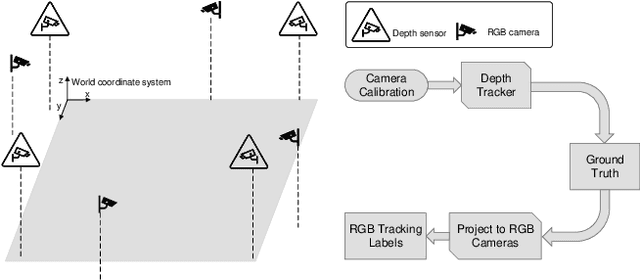
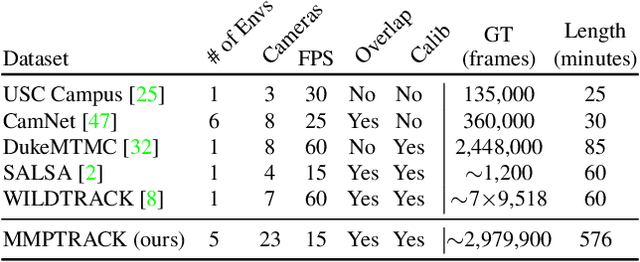

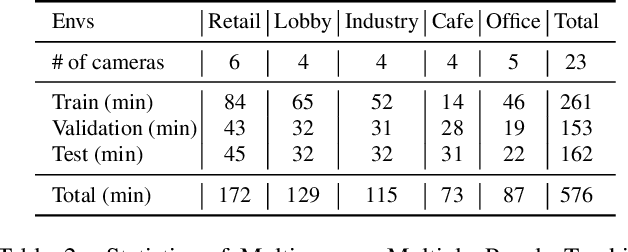
Abstract:Multi-camera tracking systems are gaining popularity in applications that demand high-quality tracking results, such as frictionless checkout because monocular multi-object tracking (MOT) systems often fail in cluttered and crowded environments due to occlusion. Multiple highly overlapped cameras can significantly alleviate the problem by recovering partial 3D information. However, the cost of creating a high-quality multi-camera tracking dataset with diverse camera settings and backgrounds has limited the dataset scale in this domain. In this paper, we provide a large-scale densely-labeled multi-camera tracking dataset in five different environments with the help of an auto-annotation system. The system uses overlapped and calibrated depth and RGB cameras to build a high-performance 3D tracker that automatically generates the 3D tracking results. The 3D tracking results are projected to each RGB camera view using camera parameters to create 2D tracking results. Then, we manually check and correct the 3D tracking results to ensure the label quality, which is much cheaper than fully manual annotation. We have conducted extensive experiments using two real-time multi-camera trackers and a person re-identification (ReID) model with different settings. This dataset provides a more reliable benchmark of multi-camera, multi-object tracking systems in cluttered and crowded environments. Also, our results demonstrate that adapting the trackers and ReID models on this dataset significantly improves their performance. Our dataset will be publicly released upon the acceptance of this work.
TransMOT: Spatial-Temporal Graph Transformer for Multiple Object Tracking
Apr 03, 2021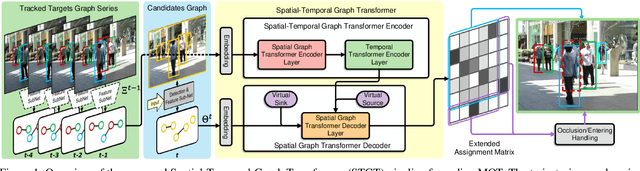
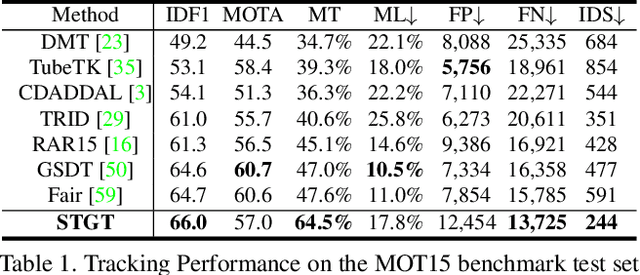
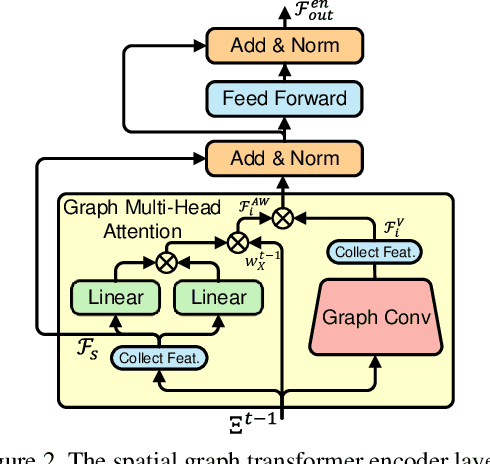
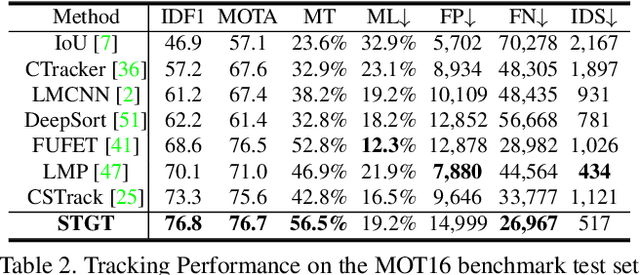
Abstract:Tracking multiple objects in videos relies on modeling the spatial-temporal interactions of the objects. In this paper, we propose a solution named TransMOT, which leverages powerful graph transformers to efficiently model the spatial and temporal interactions among the objects. TransMOT effectively models the interactions of a large number of objects by arranging the trajectories of the tracked objects as a set of sparse weighted graphs, and constructing a spatial graph transformer encoder layer, a temporal transformer encoder layer, and a spatial graph transformer decoder layer based on the graphs. TransMOT is not only more computationally efficient than the traditional Transformer, but it also achieves better tracking accuracy. To further improve the tracking speed and accuracy, we propose a cascade association framework to handle low-score detections and long-term occlusions that require large computational resources to model in TransMOT. The proposed method is evaluated on multiple benchmark datasets including MOT15, MOT16, MOT17, and MOT20, and it achieves state-of-the-art performance on all the datasets.
GMOT-40: A Benchmark for Generic Multiple Object Tracking
Dec 02, 2020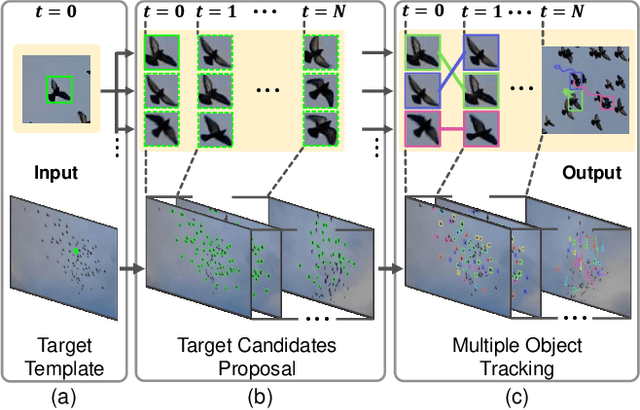
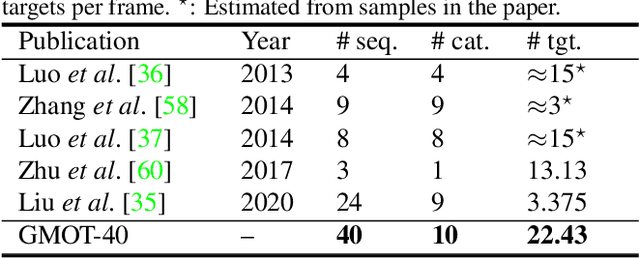
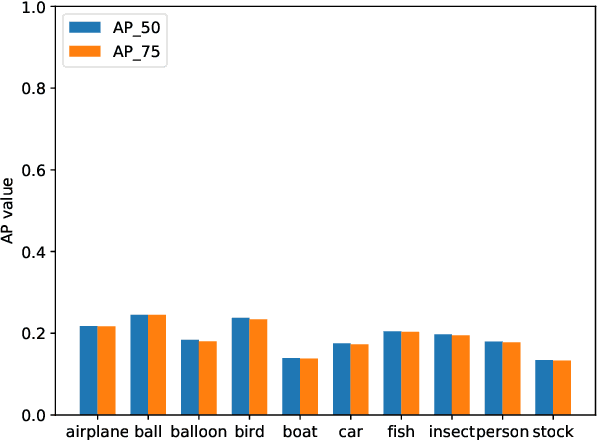
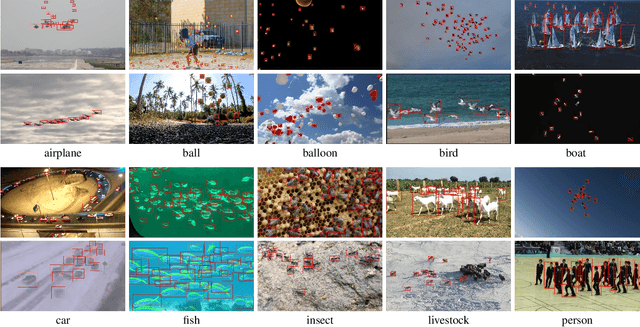
Abstract:Multiple Object Tracking (MOT) has witnessed remarkable advances in recent years. However, existing studies dominantly request prior knowledge of the tracking target, and hence may not generalize well to unseen categories. In contrast, Generic Multiple Object Tracking (GMOT), which requires little prior information about the target, is largely under-explored. In this paper, we make contributions to boost the study of GMOT in three aspects. First, we construct the first public GMOT dataset, dubbed GMOT-40, which contains 40 carefully annotated sequences evenly distributed among 10 object categories. In addition, two tracking protocols are adopted to evaluate different characteristics of tracking algorithms. Second, by noting the lack of devoted tracking algorithms, we have designed a series of baseline GMOT algorithms. Third, we perform a thorough evaluation on GMOT-40, involving popular MOT algorithms (with necessary modifications) and the proposed baselines. We will release the GMOT-40 benchmark, the evaluation results, as well as the baseline algorithm to the public upon the publication of the paper.
LaSOT: A High-quality Large-scale Single Object Tracking Benchmark
Sep 12, 2020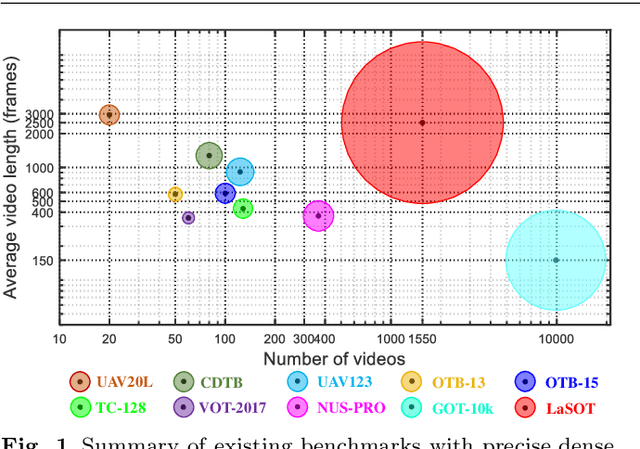
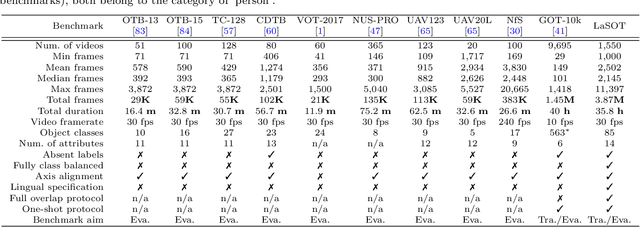
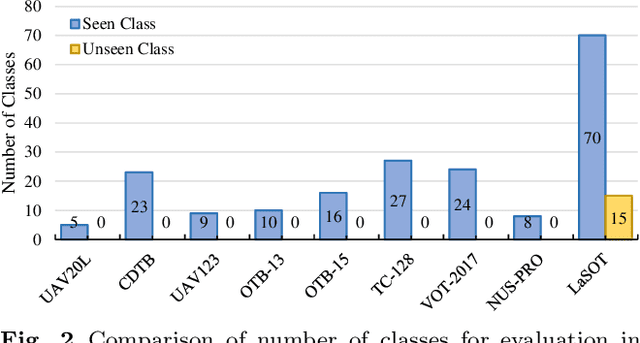
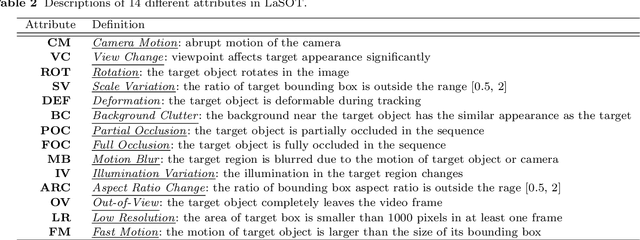
Abstract:Despite great recent advances in visual tracking, its further development, including both algorithm design and evaluation, is limited due to lack of dedicated large-scale benchmarks. To address this problem, we present LaSOT, a high-quality Large-scale Single Object Tracking benchmark. LaSOT contains a diverse selection of 85 object classes, and offers 1,550 totaling more than 3.87 million frames. Each video frame is carefully and manually annotated with a bounding box. This makes LaSOT, to our knowledge, the largest densely annotated tracking benchmark. Our goal in releasing LaSOT is to provide a dedicated high quality platform for both training and evaluation of trackers. The average video length of LaSOT is around 2,500 frames, where each video contains various challenge factors that exist in real world video footage,such as the targets disappearing and re-appearing. These longer video lengths allow for the assessment of long-term trackers. To take advantage of the close connection between visual appearance and natural language, we provide language specification for each video in LaSOT. We believe such additions will allow for future research to use linguistic features to improve tracking. Two protocols, full-overlap and one-shot, are designated for flexible assessment of trackers. We extensively evaluate 48 baseline trackers on LaSOT with in-depth analysis, and results reveal that there still exists significant room for improvement. The complete benchmark, tracking results as well as analysis are available at http://vision.cs.stonybrook.edu/~lasot/.
Feature Space Augmentation for Long-Tailed Data
Aug 09, 2020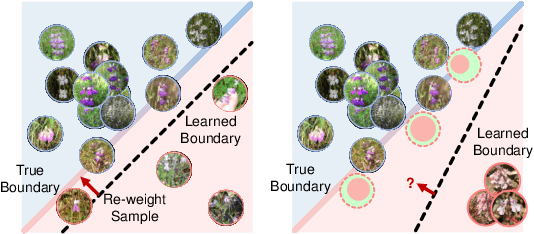
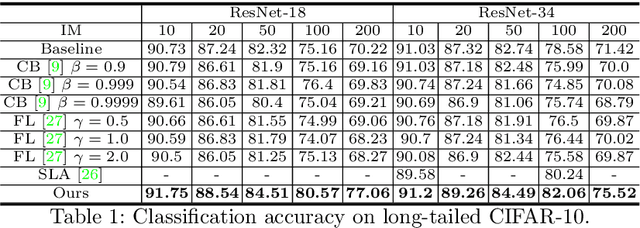
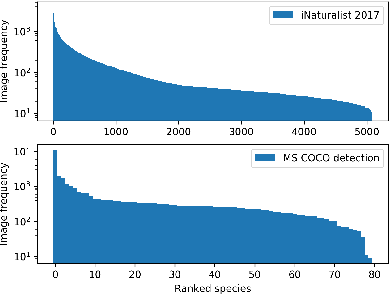
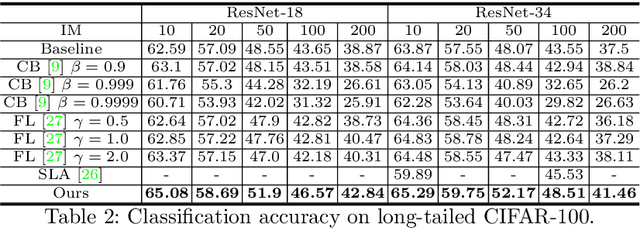
Abstract:Real-world data often follow a long-tailed distribution as the frequency of each class is typically different. For example, a dataset can have a large number of under-represented classes and a few classes with more than sufficient data. However, a model to represent the dataset is usually expected to have reasonably homogeneous performances across classes. Introducing class-balanced loss and advanced methods on data re-sampling and augmentation are among the best practices to alleviate the data imbalance problem. However, the other part of the problem about the under-represented classes will have to rely on additional knowledge to recover the missing information. In this work, we present a novel approach to address the long-tailed problem by augmenting the under-represented classes in the feature space with the features learned from the classes with ample samples. In particular, we decompose the features of each class into a class-generic component and a class-specific component using class activation maps. Novel samples of under-represented classes are then generated on the fly during training stages by fusing the class-specific features from the under-represented classes with the class-generic features from confusing classes. Our results on different datasets such as iNaturalist, ImageNet-LT, Places-LT and a long-tailed version of CIFAR have shown the state of the art performances.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge