Cuiling Lan
Stepwise Think-Critique: A Unified Framework for Robust and Interpretable LLM Reasoning
Dec 17, 2025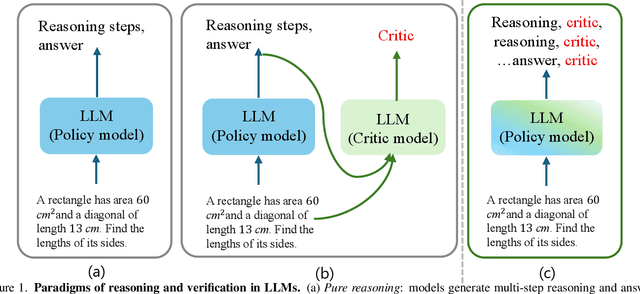
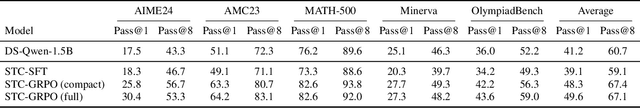
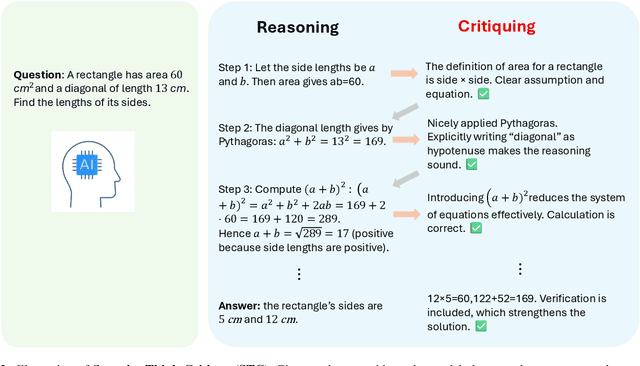
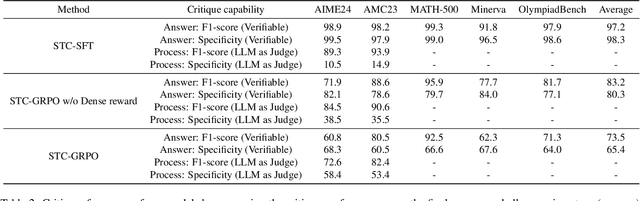
Abstract:Human beings solve complex problems through critical thinking, where reasoning and evaluation are intertwined to converge toward correct solutions. However, most existing large language models (LLMs) decouple reasoning from verification: they either generate reasoning without explicit self-checking or rely on external verifiers to detect errors post hoc. The former lacks immediate feedback, while the latter increases system complexity and hinders synchronized learning. Motivated by human critical thinking, we propose Stepwise Think-Critique (STC), a unified framework that interleaves reasoning and self-critique at each step within a single model. STC is trained with a hybrid reinforcement learning objective combining reasoning rewards and critique-consistency rewards to jointly optimize reasoning quality and self-evaluation. Experiments on mathematical reasoning benchmarks show that STC demonstrates strong critic-thinking capabilities and produces more interpretable reasoning traces, representing a step toward LLMs with built-in critical thinking.
BRIGHT: A globally distributed multimodal building damage assessment dataset with very-high-resolution for all-weather disaster response
Jan 10, 2025



Abstract:Disaster events occur around the world and cause significant damage to human life and property. Earth observation (EO) data enables rapid and comprehensive building damage assessment (BDA), an essential capability in the aftermath of a disaster to reduce human casualties and to inform disaster relief efforts. Recent research focuses on the development of AI models to achieve accurate mapping of unseen disaster events, mostly using optical EO data. However, solutions based on optical data are limited to clear skies and daylight hours, preventing a prompt response to disasters. Integrating multimodal (MM) EO data, particularly the combination of optical and SAR imagery, makes it possible to provide all-weather, day-and-night disaster responses. Despite this potential, the development of robust multimodal AI models has been constrained by the lack of suitable benchmark datasets. In this paper, we present a BDA dataset using veRy-hIGH-resoluTion optical and SAR imagery (BRIGHT) to support AI-based all-weather disaster response. To the best of our knowledge, BRIGHT is the first open-access, globally distributed, event-diverse MM dataset specifically curated to support AI-based disaster response. It covers five types of natural disasters and two types of man-made disasters across 12 regions worldwide, with a particular focus on developing countries where external assistance is most needed. The optical and SAR imagery in BRIGHT, with a spatial resolution between 0.3-1 meters, provides detailed representations of individual buildings, making it ideal for precise BDA. In our experiments, we have tested seven advanced AI models trained with our BRIGHT to validate the transferability and robustness. The dataset and code are available at https://github.com/ChenHongruixuan/BRIGHT. BRIGHT also serves as the official dataset for the 2025 IEEE GRSS Data Fusion Contest.
GSemSplat: Generalizable Semantic 3D Gaussian Splatting from Uncalibrated Image Pairs
Dec 22, 2024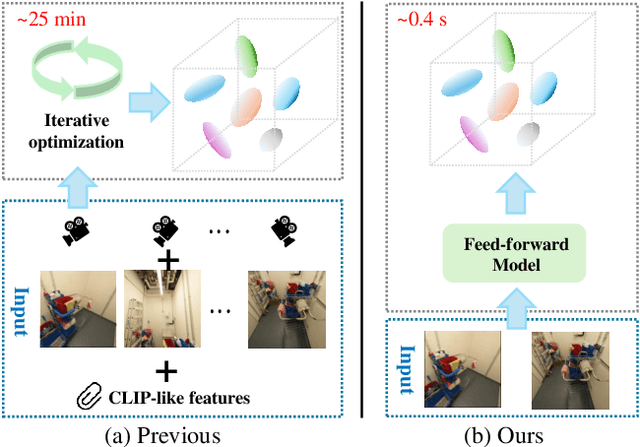
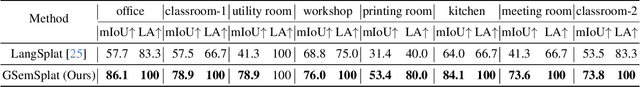
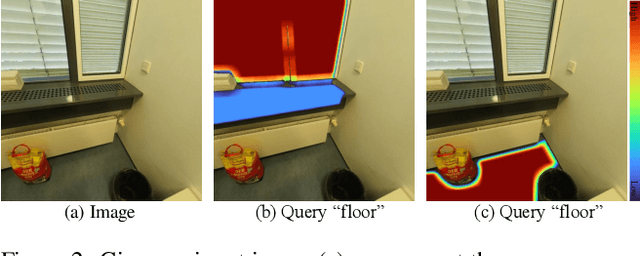
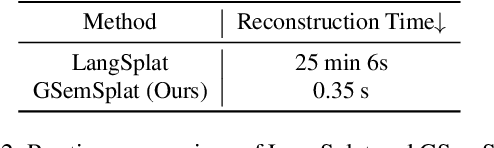
Abstract:Modeling and understanding the 3D world is crucial for various applications, from augmented reality to robotic navigation. Recent advancements based on 3D Gaussian Splatting have integrated semantic information from multi-view images into Gaussian primitives. However, these methods typically require costly per-scene optimization from dense calibrated images, limiting their practicality. In this paper, we consider the new task of generalizable 3D semantic field modeling from sparse, uncalibrated image pairs. Building upon the Splatt3R architecture, we introduce GSemSplat, a framework that learns open-vocabulary semantic representations linked to 3D Gaussians without the need for per-scene optimization, dense image collections or calibration. To ensure effective and reliable learning of semantic features in 3D space, we employ a dual-feature approach that leverages both region-specific and context-aware semantic features as supervision in the 2D space. This allows us to capitalize on their complementary strengths. Experimental results on the ScanNet++ dataset demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our approach compared to the traditional scene-specific method. We hope our work will inspire more research into generalizable 3D understanding.
TIV-Diffusion: Towards Object-Centric Movement for Text-driven Image to Video Generation
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Text-driven Image to Video Generation (TI2V) aims to generate controllable video given the first frame and corresponding textual description. The primary challenges of this task lie in two parts: (i) how to identify the target objects and ensure the consistency between the movement trajectory and the textual description. (ii) how to improve the subjective quality of generated videos. To tackle the above challenges, we propose a new diffusion-based TI2V framework, termed TIV-Diffusion, via object-centric textual-visual alignment, intending to achieve precise control and high-quality video generation based on textual-described motion for different objects. Concretely, we enable our TIV-Diffuion model to perceive the textual-described objects and their motion trajectory by incorporating the fused textual and visual knowledge through scale-offset modulation. Moreover, to mitigate the problems of object disappearance and misaligned objects and motion, we introduce an object-centric textual-visual alignment module, which reduces the risk of misaligned objects/motion by decoupling the objects in the reference image and aligning textual features with each object individually. Based on the above innovations, our TIV-Diffusion achieves state-of-the-art high-quality video generation compared with existing TI2V methods.
UCIP: A Universal Framework for Compressed Image Super-Resolution using Dynamic Prompt
Jul 18, 2024



Abstract:Compressed Image Super-resolution (CSR) aims to simultaneously super-resolve the compressed images and tackle the challenging hybrid distortions caused by compression. However, existing works on CSR usually focuses on a single compression codec, i.e., JPEG, ignoring the diverse traditional or learning-based codecs in the practical application, e.g., HEVC, VVC, HIFIC, etc. In this work, we propose the first universal CSR framework, dubbed UCIP, with dynamic prompt learning, intending to jointly support the CSR distortions of any compression codecs/modes. Particularly, an efficient dynamic prompt strategy is proposed to mine the content/spatial-aware task-adaptive contextual information for the universal CSR task, using only a small amount of prompts with spatial size 1x1. To simplify contextual information mining, we introduce the novel MLP-like framework backbone for our UCIP by adapting the Active Token Mixer (ATM) to CSR tasks for the first time, where the global information modeling is only taken in horizontal and vertical directions with offset prediction. We also build an all-in-one benchmark dataset for the CSR task by collecting the datasets with the popular 6 diverse traditional and learning-based codecs, including JPEG, HEVC, VVC, HIFIC, etc., resulting in 23 common degradations. Extensive experiments have shown the consistent and excellent performance of our UCIP on universal CSR tasks. The project can be found in https://lixinustc.github.io/UCIP.github.io
Text Grouping Adapter: Adapting Pre-trained Text Detector for Layout Analysis
May 13, 2024



Abstract:Significant progress has been made in scene text detection models since the rise of deep learning, but scene text layout analysis, which aims to group detected text instances as paragraphs, has not kept pace. Previous works either treated text detection and grouping using separate models, or train a model from scratch while using a unified one. All of them have not yet made full use of the already well-trained text detectors and easily obtainable detection datasets. In this paper, we present Text Grouping Adapter (TGA), a module that can enable the utilization of various pre-trained text detectors to learn layout analysis, allowing us to adopt a well-trained text detector right off the shelf or just fine-tune it efficiently. Designed to be compatible with various text detector architectures, TGA takes detected text regions and image features as universal inputs to assemble text instance features. To capture broader contextual information for layout analysis, we propose to predict text group masks from text instance features by one-to-many assignment. Our comprehensive experiments demonstrate that, even with frozen pre-trained models, incorporating our TGA into various pre-trained text detectors and text spotters can achieve superior layout analysis performance, simultaneously inheriting generalized text detection ability from pre-training. In the case of full parameter fine-tuning, we can further improve layout analysis performance.
Slot-VLM: SlowFast Slots for Video-Language Modeling
Feb 20, 2024Abstract:Video-Language Models (VLMs), powered by the advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs), are charting new frontiers in video understanding. A pivotal challenge is the development of an efficient method to encapsulate video content into a set of representative tokens to align with LLMs. In this work, we introduce Slot-VLM, a novel framework designed to generate semantically decomposed video tokens, in terms of object-wise and event-wise visual representations, to facilitate LLM inference. Particularly, we design a SlowFast Slots module, i.e., SF-Slots, that adaptively aggregates the dense video tokens from the CLIP vision encoder to a set of representative slots. In order to take into account both the spatial object details and the varied temporal dynamics, SF-Slots is built with a dual-branch structure. The Slow-Slots branch focuses on extracting object-centric slots from features at high spatial resolution but low (slow) frame sample rate, emphasizing detailed object information. Conversely, Fast-Slots branch is engineered to learn event-centric slots from high temporal sample rate but low spatial resolution features. These complementary slots are combined to form the vision context, serving as the input to the LLM for efficient question answering. Our experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our Slot-VLM, which achieves the state-of-the-art performance on video question-answering.
Diffusion Model with Cross Attention as an Inductive Bias for Disentanglement
Feb 15, 2024



Abstract:Disentangled representation learning strives to extract the intrinsic factors within observed data. Factorizing these representations in an unsupervised manner is notably challenging and usually requires tailored loss functions or specific structural designs. In this paper, we introduce a new perspective and framework, demonstrating that diffusion models with cross-attention can serve as a powerful inductive bias to facilitate the learning of disentangled representations. We propose to encode an image to a set of concept tokens and treat them as the condition of the latent diffusion for image reconstruction, where cross-attention over the concept tokens is used to bridge the interaction between the encoder and diffusion. Without any additional regularization, this framework achieves superior disentanglement performance on the benchmark datasets, surpassing all previous methods with intricate designs. We have conducted comprehensive ablation studies and visualization analysis, shedding light on the functioning of this model. This is the first work to reveal the potent disentanglement capability of diffusion models with cross-attention, requiring no complex designs. We anticipate that our findings will inspire more investigation on exploring diffusion for disentangled representation learning towards more sophisticated data analysis and understanding.
Retrieval-based Video Language Model for Efficient Long Video Question Answering
Dec 08, 2023



Abstract:The remarkable natural language understanding, reasoning, and generation capabilities of large language models (LLMs) have made them attractive for application to video question answering (Video QA) tasks, utilizing video tokens as contextual input. However, employing LLMs for long video understanding presents significant challenges and remains under-explored. The extensive number of video tokens leads to considerable computational costs for LLMs while using aggregated tokens results in loss of vision details. Moreover, the presence of abundant question-irrelevant tokens introduces noise to the video QA process. To address these issues, we introduce a simple yet effective retrieval-based video language model (R-VLM) for efficient and interpretable long video QA. Specifically, given a question (query) and a long video, our model identifies and selects the most relevant $K$ video chunks and uses their associated visual tokens to serve as context for the LLM inference. This effectively reduces the number of video tokens, eliminates noise interference, and enhances system performance. Our experimental results validate the effectiveness of our framework for comprehending long videos. Furthermore, based on the retrieved chunks, our model is interpretable that provides the justifications on where we get the answers.
Land-cover change detection using paired OpenStreetMap data and optical high-resolution imagery via object-guided Transformer
Oct 04, 2023



Abstract:Optical high-resolution imagery and OpenStreetMap (OSM) data are two important data sources for land-cover change detection. Previous studies in these two data sources focus on utilizing the information in OSM data to aid the change detection on multi-temporal optical high-resolution images. This paper pioneers the direct detection of land-cover changes utilizing paired OSM data and optical imagery, thereby broadening the horizons of change detection tasks to encompass more dynamic earth observations. To this end, we propose an object-guided Transformer (ObjFormer) architecture by naturally combining the prevalent object-based image analysis (OBIA) technique with the advanced vision Transformer architecture. The introduction of OBIA can significantly reduce the computational overhead and memory burden in the self-attention module. Specifically, the proposed ObjFormer has a hierarchical pseudo-siamese encoder consisting of object-guided self-attention modules that extract representative features of different levels from OSM data and optical images; a decoder consisting of object-guided cross-attention modules can progressively recover the land-cover changes from the extracted heterogeneous features. In addition to the basic supervised binary change detection task, this paper raises a new semi-supervised semantic change detection task that does not require any manually annotated land-cover labels of optical images to train semantic change detectors. Two lightweight semantic decoders are added to ObjFormer to accomplish this task efficiently. A converse cross-entropy loss is designed to fully utilize the negative samples, thereby contributing to the great performance improvement in this task. The first large-scale benchmark dataset containing 1,287 map-image pairs (1024$\times$ 1024 pixels for each sample) covering 40 regions on six continents ...(see the manuscript for the full abstract)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge