Yaosi Hu
LongCaptioning: Unlocking the Power of Long Caption Generation in Large Multimodal Models
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:Large multimodal models (LMMs) have shown remarkable performance in video understanding tasks and can even process videos longer than one hour. However, despite their ability to handle long inputs, generating outputs with corresponding levels of richness remains a challenge. In this paper, we explore the issue of long outputs in LMMs using video captioning as a proxy task, and we find that open-source LMMs struggle to consistently generate outputs exceeding about 300 words. Through controlled experiments, we find that the scarcity of paired examples with long-captions during training is the primary factor limiting the model's output length. However, manually annotating long-caption examples is time-consuming and expensive. To address this, we propose the LongCaption-Agent, a framework that synthesizes long caption data by aggregating multi-level descriptions. Using LongCaption-Agent, we curated a new long-caption dataset, LongCaption-10K. We also develop LongCaption-Bench, a benchmark designed to comprehensively evaluate the quality of long captions generated by LMMs. By incorporating LongCaption-10K into training, we enable LMMs to generate captions exceeding 1,000 words, while maintaining high output quality. In LongCaption-Bench, our 8B parameter model achieved state-of-the-art performance, even surpassing larger proprietary models. We will release the dataset and code after publication.
Remote Sensing Semantic Segmentation Quality Assessment based on Vision Language Model
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:The complexity of scenes and variations in image quality result in significant variability in the performance of semantic segmentation methods of remote sensing imagery (RSI) in supervised real-world scenarios. This makes the evaluation of semantic segmentation quality in such scenarios an issue to be resolved. However, most of the existing evaluation metrics are developed based on expert-labeled object-level annotations, which are not applicable in such scenarios. To address this issue, we propose RS-SQA, an unsupervised quality assessment model for RSI semantic segmentation based on vision language model (VLM). This framework leverages a pre-trained RS VLM for semantic understanding and utilizes intermediate features from segmentation methods to extract implicit information about segmentation quality. Specifically, we introduce CLIP-RS, a large-scale pre-trained VLM trained with purified text to reduce textual noise and capture robust semantic information in the RS domain. Feature visualizations confirm that CLIP-RS can effectively differentiate between various levels of segmentation quality. Semantic features and low-level segmentation features are effectively integrated through a semantic-guided approach to enhance evaluation accuracy. To further support the development of RS semantic segmentation quality assessment, we present RS-SQED, a dedicated dataset sampled from four major RS semantic segmentation datasets and annotated with segmentation accuracy derived from the inference results of 8 representative segmentation methods. Experimental results on the established dataset demonstrate that RS-SQA significantly outperforms state-of-the-art quality assessment models. This provides essential support for predicting segmentation accuracy and high-quality semantic segmentation interpretation, offering substantial practical value.
TIV-Diffusion: Towards Object-Centric Movement for Text-driven Image to Video Generation
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Text-driven Image to Video Generation (TI2V) aims to generate controllable video given the first frame and corresponding textual description. The primary challenges of this task lie in two parts: (i) how to identify the target objects and ensure the consistency between the movement trajectory and the textual description. (ii) how to improve the subjective quality of generated videos. To tackle the above challenges, we propose a new diffusion-based TI2V framework, termed TIV-Diffusion, via object-centric textual-visual alignment, intending to achieve precise control and high-quality video generation based on textual-described motion for different objects. Concretely, we enable our TIV-Diffuion model to perceive the textual-described objects and their motion trajectory by incorporating the fused textual and visual knowledge through scale-offset modulation. Moreover, to mitigate the problems of object disappearance and misaligned objects and motion, we introduce an object-centric textual-visual alignment module, which reduces the risk of misaligned objects/motion by decoupling the objects in the reference image and aligning textual features with each object individually. Based on the above innovations, our TIV-Diffusion achieves state-of-the-art high-quality video generation compared with existing TI2V methods.
SubjectDrive: Scaling Generative Data in Autonomous Driving via Subject Control
Mar 28, 2024



Abstract:Autonomous driving progress relies on large-scale annotated datasets. In this work, we explore the potential of generative models to produce vast quantities of freely-labeled data for autonomous driving applications and present SubjectDrive, the first model proven to scale generative data production in a way that could continuously improve autonomous driving applications. We investigate the impact of scaling up the quantity of generative data on the performance of downstream perception models and find that enhancing data diversity plays a crucial role in effectively scaling generative data production. Therefore, we have developed a novel model equipped with a subject control mechanism, which allows the generative model to leverage diverse external data sources for producing varied and useful data. Extensive evaluations confirm SubjectDrive's efficacy in generating scalable autonomous driving training data, marking a significant step toward revolutionizing data production methods in this field.
LaMD: Latent Motion Diffusion for Video Generation
Apr 23, 2023Abstract:Generating coherent and natural movement is the key challenge in video generation. This research proposes to condense video generation into a problem of motion generation, to improve the expressiveness of motion and make video generation more manageable. This can be achieved by breaking down the video generation process into latent motion generation and video reconstruction. We present a latent motion diffusion (LaMD) framework, which consists of a motion-decomposed video autoencoder and a diffusion-based motion generator, to implement this idea. Through careful design, the motion-decomposed video autoencoder can compress patterns in movement into a concise latent motion representation. Meanwhile, the diffusion-based motion generator is able to efficiently generate realistic motion on a continuous latent space under multi-modal conditions, at a cost that is similar to that of image diffusion models. Results show that LaMD generates high-quality videos with a wide range of motions, from stochastic dynamics to highly controllable movements. It achieves new state-of-the-art performance on benchmark datasets, including BAIR, Landscape and CATER-GENs, for Image-to-Video (I2V) and Text-Image-to-Video (TI2V) generation. The source code of LaMD will be made available soon.
Learning Human Cognitive Appraisal Through Reinforcement Memory Unit
Aug 06, 2022



Abstract:We propose a novel memory-enhancing mechanism for recurrent neural networks that exploits the effect of human cognitive appraisal in sequential assessment tasks. We conceptualize the memory-enhancing mechanism as Reinforcement Memory Unit (RMU) that contains an appraisal state together with two positive and negative reinforcement memories. The two reinforcement memories are decayed or strengthened by stronger stimulus. Thereafter the appraisal state is updated through the competition of positive and negative reinforcement memories. Therefore, RMU can learn the appraisal variation under violent changing of the stimuli for estimating human affective experience. As shown in the experiments of video quality assessment and video quality of experience tasks, the proposed reinforcement memory unit achieves superior performance among recurrent neural networks, that demonstrates the effectiveness of RMU for modeling human cognitive appraisal.
Make It Move: Controllable Image-to-Video Generation with Text Descriptions
Dec 06, 2021



Abstract:Generating controllable videos conforming to user intentions is an appealing yet challenging topic in computer vision. To enable maneuverable control in line with user intentions, a novel video generation task, named Text-Image-to-Video generation (TI2V), is proposed. With both controllable appearance and motion, TI2V aims at generating videos from a static image and a text description. The key challenges of TI2V task lie both in aligning appearance and motion from different modalities, and in handling uncertainty in text descriptions. To address these challenges, we propose a Motion Anchor-based video GEnerator (MAGE) with an innovative motion anchor (MA) structure to store appearance-motion aligned representation. To model the uncertainty and increase the diversity, it further allows the injection of explicit condition and implicit randomness. Through three-dimensional axial transformers, MA is interacted with given image to generate next frames recursively with satisfying controllability and diversity. Accompanying the new task, we build two new video-text paired datasets based on MNIST and CATER for evaluation. Experiments conducted on these datasets verify the effectiveness of MAGE and show appealing potentials of TI2V task. Source code for model and datasets will be available soon.
Predicate correlation learning for scene graph generation
Jul 06, 2021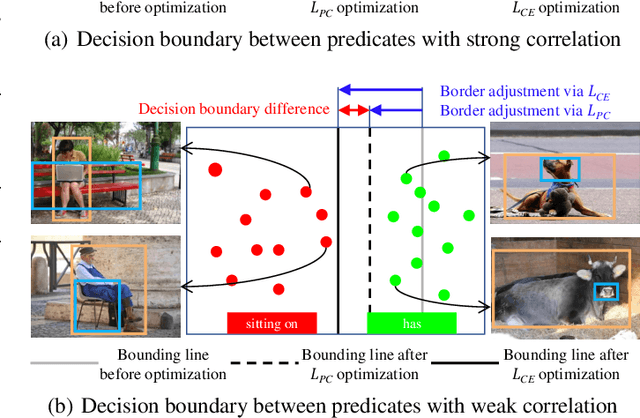
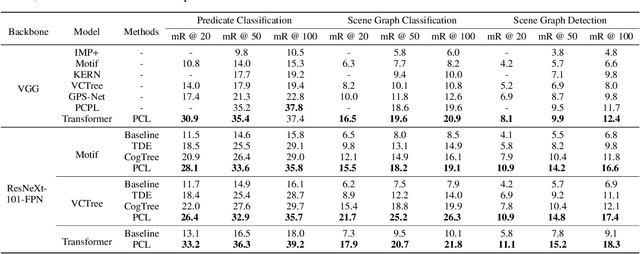
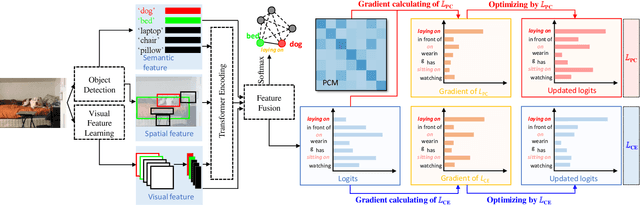
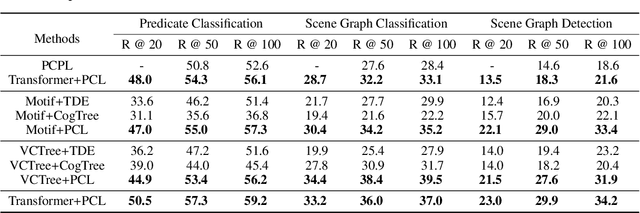
Abstract:For a typical Scene Graph Generation (SGG) method, there is often a large gap in the performance of the predicates' head classes and tail classes. This phenomenon is mainly caused by the semantic overlap between different predicates as well as the long-tailed data distribution. In this paper, a Predicate Correlation Learning (PCL) method for SGG is proposed to address the above two problems by taking the correlation between predicates into consideration. To describe the semantic overlap between strong-correlated predicate classes, a Predicate Correlation Matrix (PCM) is defined to quantify the relationship between predicate pairs, which is dynamically updated to remove the matrix's long-tailed bias. In addition, PCM is integrated into a Predicate Correlation Loss function ($L_{PC}$) to reduce discouraging gradients of unannotated classes. The proposed method is evaluated on Visual Genome benchmark, where the performance of the tail classes is significantly improved when built on the existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge