Benjamin Yen
Unsupervised Single-Channel Audio Separation with Diffusion Source Priors
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Single-channel audio separation aims to separate individual sources from a single-channel mixture. Most existing methods rely on supervised learning with synthetically generated paired data. However, obtaining high-quality paired data in real-world scenarios is often difficult. This data scarcity can degrade model performance under unseen conditions and limit generalization ability. To this end, in this work, we approach this problem from an unsupervised perspective, framing it as a probabilistic inverse problem. Our method requires only diffusion priors trained on individual sources. Separation is then achieved by iteratively guiding an initial state toward the solution through reconstruction guidance. Importantly, we introduce an advanced inverse problem solver specifically designed for separation, which mitigates gradient conflicts caused by interference between the diffusion prior and reconstruction guidance during inverse denoising. This design ensures high-quality and balanced separation performance across individual sources. Additionally, we find that initializing the denoising process with an augmented mixture instead of pure Gaussian noise provides an informative starting point that significantly improves the final performance. To further enhance audio prior modeling, we design a novel time-frequency attention-based network architecture that demonstrates strong audio modeling capability. Collectively, these improvements lead to significant performance gains, as validated across speech-sound event, sound event, and speech separation tasks.
Single-Channel Target Speech Extraction Utilizing Distance and Room Clues
May 20, 2025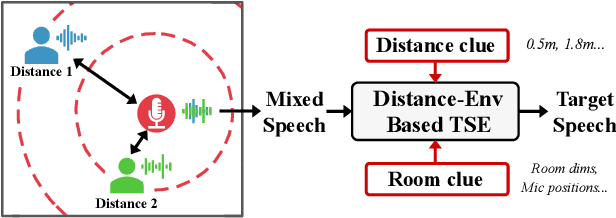
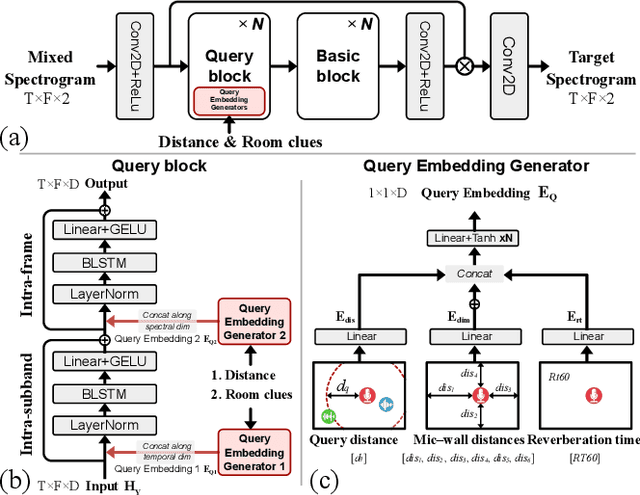
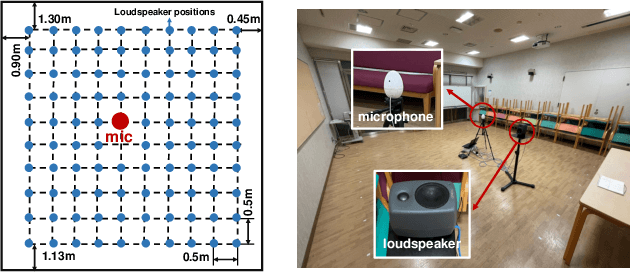
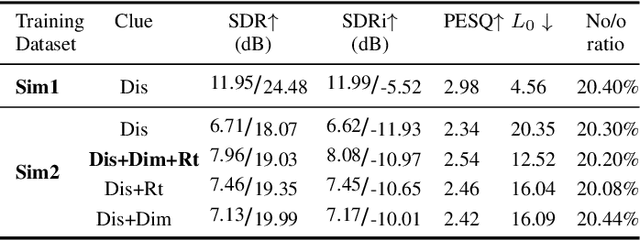
Abstract:This paper aims to achieve single-channel target speech extraction (TSE) in enclosures utilizing distance clues and room information. Recent works have verified the feasibility of distance clues for the TSE task, which can imply the sound source's direct-to-reverberation ratio (DRR) and thus can be utilized for speech separation and TSE systems. However, such distance clue is significantly influenced by the room's acoustic characteristics, such as dimension and reverberation time, making it challenging for TSE systems that rely solely on distance clues to generalize across a variety of different rooms. To solve this, we suggest providing room environmental information (room dimensions and reverberation time) for distance-based TSE for better generalization capabilities. Especially, we propose a distance and environment-based TSE model in the time-frequency (TF) domain with learnable distance and room embedding. Results on both simulated and real collected datasets demonstrate its feasibility. Demonstration materials are available at https://runwushi.github.io/distance-room-demo-page/.
Distance Based Single-Channel Target Speech Extraction
Dec 28, 2024



Abstract:This paper aims to achieve single-channel target speech extraction (TSE) in enclosures by solely utilizing distance information. This is the first work that utilizes only distance cues without using speaker physiological information for single-channel TSE. Inspired by recent single-channel Distance-based separation and extraction methods, we introduce a novel model that efficiently fuses distance information with time-frequency (TF) bins for TSE. Experimental results in both single-room and multi-room scenarios demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of our approach. This method can also be employed to estimate the distances of different speakers in mixed speech. Online demos are available at https://runwushi.github.io/distance-demo-page.
UAV-Enhanced Combination to Application: Comprehensive Analysis and Benchmarking of a Human Detection Dataset for Disaster Scenarios
Aug 09, 2024



Abstract:Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have revolutionized search and rescue (SAR) operations, but the lack of specialized human detection datasets for training machine learning models poses a significant challenge.To address this gap, this paper introduces the Combination to Application (C2A) dataset, synthesized by overlaying human poses onto UAV-captured disaster scenes. Through extensive experimentation with state-of-the-art detection models, we demonstrate that models fine-tuned on the C2A dataset exhibit substantial performance improvements compared to those pre-trained on generic aerial datasets. Furthermore, we highlight the importance of combining the C2A dataset with general human datasets to achieve optimal performance and generalization across various scenarios. This points out the crucial need for a tailored dataset to enhance the effectiveness of SAR operations. Our contributions also include developing dataset creation pipeline and integrating diverse human poses and disaster scenes information to assess the severity of disaster scenarios. Our findings advocate for future developments, to ensure that SAR operations benefit from the most realistic and effective AI-assisted interventions possible.
From Blurry to Brilliant Detection: YOLOv5-Based Aerial Object Detection with Super Resolution
Jan 26, 2024Abstract:The demand for accurate object detection in aerial imagery has surged with the widespread use of drones and satellite technology. Traditional object detection models, trained on datasets biased towards large objects, struggle to perform optimally in aerial scenarios where small, densely clustered objects are prevalent. To address this challenge, we present an innovative approach that combines super-resolution and an adapted lightweight YOLOv5 architecture. We employ a range of datasets, including VisDrone-2023, SeaDroneSee, VEDAI, and NWPU VHR-10, to evaluate our model's performance. Our Super Resolved YOLOv5 architecture features Transformer encoder blocks, allowing the model to capture global context and context information, leading to improved detection results, especially in high-density, occluded conditions. This lightweight model not only delivers improved accuracy but also ensures efficient resource utilization, making it well-suited for real-time applications. Our experimental results demonstrate the model's superior performance in detecting small and densely clustered objects, underlining the significance of dataset choice and architectural adaptation for this specific task. In particular, the method achieves 52.5% mAP on VisDrone, exceeding top prior works. This approach promises to significantly advance object detection in aerial imagery, contributing to more accurate and reliable results in a variety of real-world applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge