Sijin Chen
DSPv2: Improved Dense Policy for Effective and Generalizable Whole-body Mobile Manipulation
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Learning whole-body mobile manipulation via imitation is essential for generalizing robotic skills to diverse environments and complex tasks. However, this goal is hindered by significant challenges, particularly in effectively processing complex observation, achieving robust generalization, and generating coherent actions. To address these issues, we propose DSPv2, a novel policy architecture. DSPv2 introduces an effective encoding scheme that aligns 3D spatial features with multi-view 2D semantic features. This fusion enables the policy to achieve broad generalization while retaining the fine-grained perception necessary for precise control. Furthermore, we extend the Dense Policy paradigm to the whole-body mobile manipulation domain, demonstrating its effectiveness in generating coherent and precise actions for the whole-body robotic platform. Extensive experiments show that our method significantly outperforms existing approaches in both task performance and generalization ability. Project page is available at: https://selen-suyue.github.io/DSPv2Net/.
OmniSVG: A Unified Scalable Vector Graphics Generation Model
Apr 08, 2025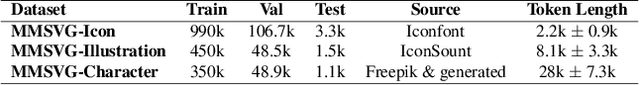
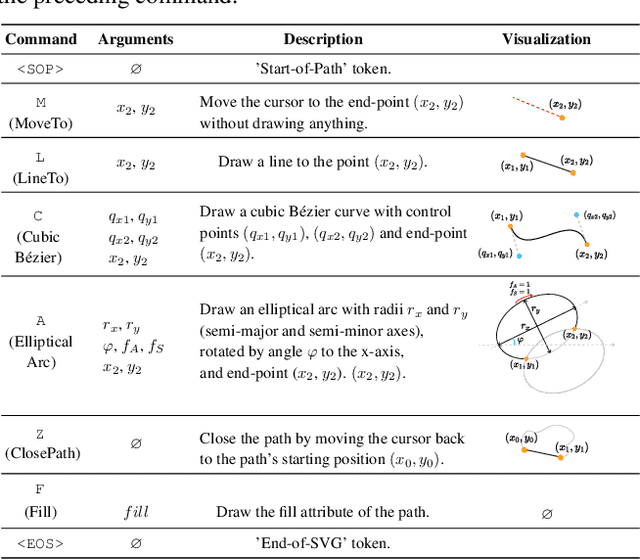
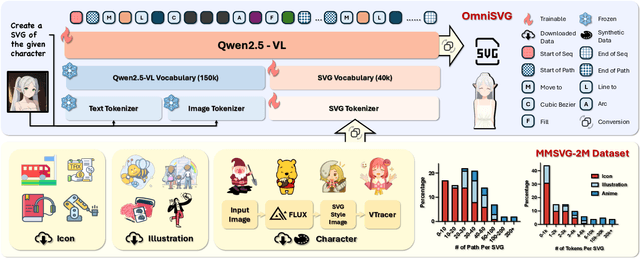
Abstract:Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) is an important image format widely adopted in graphic design because of their resolution independence and editability. The study of generating high-quality SVG has continuously drawn attention from both designers and researchers in the AIGC community. However, existing methods either produces unstructured outputs with huge computational cost or is limited to generating monochrome icons of over-simplified structures. To produce high-quality and complex SVG, we propose OmniSVG, a unified framework that leverages pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) for end-to-end multimodal SVG generation. By parameterizing SVG commands and coordinates into discrete tokens, OmniSVG decouples structural logic from low-level geometry for efficient training while maintaining the expressiveness of complex SVG structure. To further advance the development of SVG synthesis, we introduce MMSVG-2M, a multimodal dataset with two million richly annotated SVG assets, along with a standardized evaluation protocol for conditional SVG generation tasks. Extensive experiments show that OmniSVG outperforms existing methods and demonstrates its potential for integration into professional SVG design workflows.
Decoding Game: On Minimax Optimality of Heuristic Text Generation Strategies
Oct 04, 2024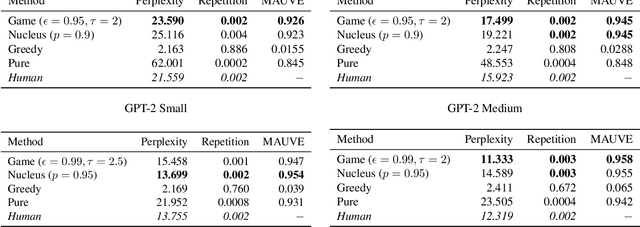
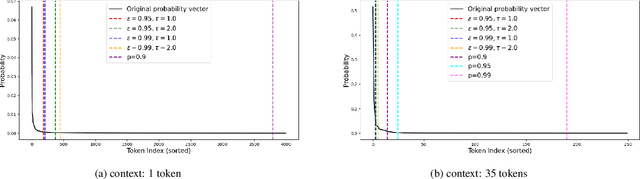
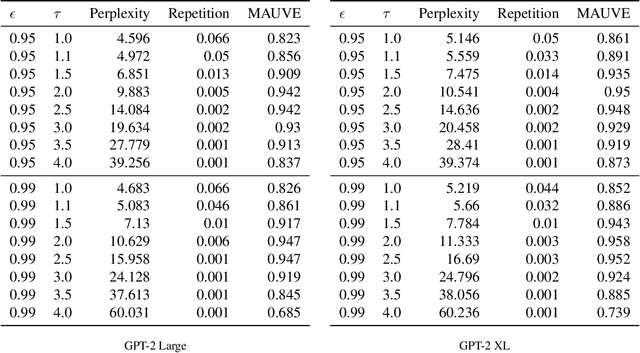
Abstract:Decoding strategies play a pivotal role in text generation for modern language models, yet a puzzling gap divides theory and practice. Surprisingly, strategies that should intuitively be optimal, such as Maximum a Posteriori (MAP), often perform poorly in practice. Meanwhile, popular heuristic approaches like Top-$k$ and Nucleus sampling, which employ truncation and normalization of the conditional next-token probabilities, have achieved great empirical success but lack theoretical justifications. In this paper, we propose Decoding Game, a comprehensive theoretical framework which reimagines text generation as a two-player zero-sum game between Strategist, who seeks to produce text credible in the true distribution, and Nature, who distorts the true distribution adversarially. After discussing the decomposibility of multi-step generation, we derive the optimal strategy in closed form for one-step Decoding Game. It is shown that the adversarial Nature imposes an implicit regularization on likelihood maximization, and truncation-normalization methods are first-order approximations to the optimal strategy under this regularization. Additionally, by generalizing the objective and parameters of Decoding Game, near-optimal strategies encompass diverse methods such as greedy search, temperature scaling, and hybrids thereof. Numerical experiments are conducted to complement our theoretical analysis.
Takin: A Cohort of Superior Quality Zero-shot Speech Generation Models
Sep 18, 2024



Abstract:With the advent of the big data and large language model era, zero-shot personalized rapid customization has emerged as a significant trend. In this report, we introduce Takin AudioLLM, a series of techniques and models, mainly including Takin TTS, Takin VC, and Takin Morphing, specifically designed for audiobook production. These models are capable of zero-shot speech production, generating high-quality speech that is nearly indistinguishable from real human speech and facilitating individuals to customize the speech content according to their own needs. Specifically, we first introduce Takin TTS, a neural codec language model that builds upon an enhanced neural speech codec and a multi-task training framework, capable of generating high-fidelity natural speech in a zero-shot way. For Takin VC, we advocate an effective content and timbre joint modeling approach to improve the speaker similarity, while advocating for a conditional flow matching based decoder to further enhance its naturalness and expressiveness. Last, we propose the Takin Morphing system with highly decoupled and advanced timbre and prosody modeling approaches, which enables individuals to customize speech production with their preferred timbre and prosody in a precise and controllable manner. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness and robustness of our Takin AudioLLM series models. For detailed demos, please refer to https://takinaudiollm.github.io.
MeshAnything: Artist-Created Mesh Generation with Autoregressive Transformers
Jun 14, 2024



Abstract:Recently, 3D assets created via reconstruction and generation have matched the quality of manually crafted assets, highlighting their potential for replacement. However, this potential is largely unrealized because these assets always need to be converted to meshes for 3D industry applications, and the meshes produced by current mesh extraction methods are significantly inferior to Artist-Created Meshes (AMs), i.e., meshes created by human artists. Specifically, current mesh extraction methods rely on dense faces and ignore geometric features, leading to inefficiencies, complicated post-processing, and lower representation quality. To address these issues, we introduce MeshAnything, a model that treats mesh extraction as a generation problem, producing AMs aligned with specified shapes. By converting 3D assets in any 3D representation into AMs, MeshAnything can be integrated with various 3D asset production methods, thereby enhancing their application across the 3D industry. The architecture of MeshAnything comprises a VQ-VAE and a shape-conditioned decoder-only transformer. We first learn a mesh vocabulary using the VQ-VAE, then train the shape-conditioned decoder-only transformer on this vocabulary for shape-conditioned autoregressive mesh generation. Our extensive experiments show that our method generates AMs with hundreds of times fewer faces, significantly improving storage, rendering, and simulation efficiencies, while achieving precision comparable to previous methods.
MeshXL: Neural Coordinate Field for Generative 3D Foundation Models
May 31, 2024



Abstract:The polygon mesh representation of 3D data exhibits great flexibility, fast rendering speed, and storage efficiency, which is widely preferred in various applications. However, given its unstructured graph representation, the direct generation of high-fidelity 3D meshes is challenging. Fortunately, with a pre-defined ordering strategy, 3D meshes can be represented as sequences, and the generation process can be seamlessly treated as an auto-regressive problem. In this paper, we validate the Neural Coordinate Field (NeurCF), an explicit coordinate representation with implicit neural embeddings, is a simple-yet-effective representation for large-scale sequential mesh modeling. After that, we present MeshXL, a family of generative pre-trained auto-regressive models, which addresses the process of 3D mesh generation with modern large language model approaches. Extensive experiments show that MeshXL is able to generate high-quality 3D meshes, and can also serve as foundation models for various down-stream applications.
M3DBench: Let's Instruct Large Models with Multi-modal 3D Prompts
Dec 17, 2023



Abstract:Recently, 3D understanding has become popular to facilitate autonomous agents to perform further decisionmaking. However, existing 3D datasets and methods are often limited to specific tasks. On the other hand, recent progress in Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multimodal Language Models (MLMs) have demonstrated exceptional general language and imagery tasking performance. Therefore, it is interesting to unlock MLM's potential to be 3D generalist for wider tasks. However, current MLMs' research has been less focused on 3D tasks due to a lack of large-scale 3D instruction-following datasets. In this work, we introduce a comprehensive 3D instructionfollowing dataset called M3DBench, which possesses the following characteristics: 1) It supports general multimodal instructions interleaved with text, images, 3D objects, and other visual prompts. 2) It unifies diverse 3D tasks at both region and scene levels, covering a variety of fundamental abilities in real-world 3D environments. 3) It is a large-scale 3D instruction-following dataset with over 320k instruction-response pairs. Furthermore, we establish a new benchmark for assessing the performance of large models in understanding multi-modal 3D prompts. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our dataset and baseline, supporting general 3D-centric tasks, which can inspire future research.
LL3DA: Visual Interactive Instruction Tuning for Omni-3D Understanding, Reasoning, and Planning
Nov 30, 2023


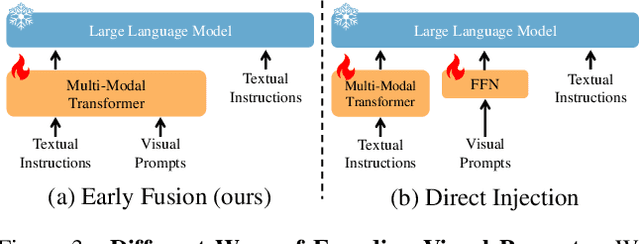
Abstract:Recent advances in Large Multimodal Models (LMM) have made it possible for various applications in human-machine interactions. However, developing LMMs that can comprehend, reason, and plan in complex and diverse 3D environments remains a challenging topic, especially considering the demand for understanding permutation-invariant point cloud 3D representations of the 3D scene. Existing works seek help from multi-view images, and project 2D features to 3D space as 3D scene representations. This, however, leads to huge computational overhead and performance degradation. In this paper, we present LL3DA, a Large Language 3D Assistant that takes point cloud as direct input and respond to both textual-instructions and visual-prompts. This help LMMs better comprehend human interactions and further help to remove the ambiguities in cluttered 3D scenes. Experiments show that LL3DA achieves remarkable results, and surpasses various 3D vision-language models on both 3D Dense Captioning and 3D Question Answering.
Escaping Saddle Points in Heterogeneous Federated Learning via Distributed SGD with Communication Compression
Oct 29, 2023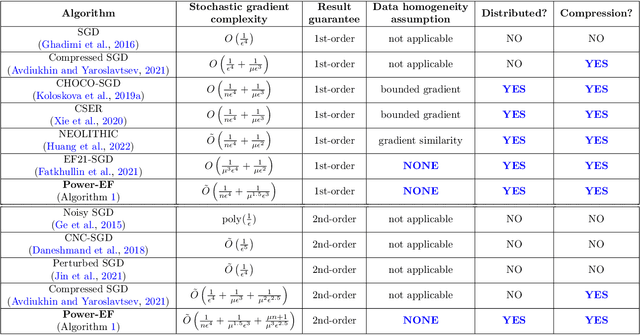
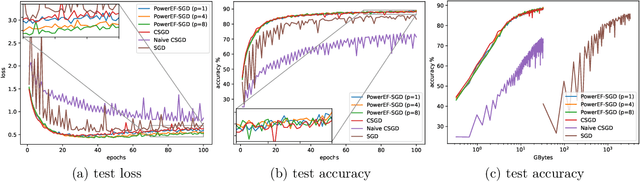
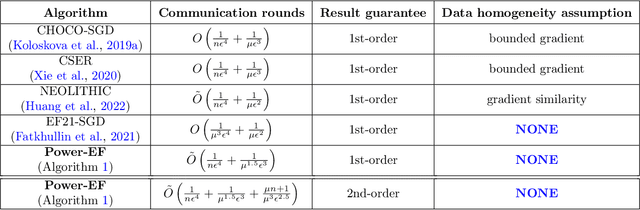
Abstract:We consider the problem of finding second-order stationary points of heterogeneous federated learning (FL). Previous works in FL mostly focus on first-order convergence guarantees, which do not rule out the scenario of unstable saddle points. Meanwhile, it is a key bottleneck of FL to achieve communication efficiency without compensating the learning accuracy, especially when local data are highly heterogeneous across different clients. Given this, we propose a novel algorithm Power-EF that only communicates compressed information via a novel error-feedback scheme. To our knowledge, Power-EF is the first distributed and compressed SGD algorithm that provably escapes saddle points in heterogeneous FL without any data homogeneity assumptions. In particular, Power-EF improves to second-order stationary points after visiting first-order (possibly saddle) points, using additional gradient queries and communication rounds only of almost the same order required by first-order convergence, and the convergence rate exhibits a linear speedup in terms of the number of workers. Our theory improves/recovers previous results, while extending to much more tolerant settings on the local data. Numerical experiments are provided to complement the theory.
Vote2Cap-DETR++: Decoupling Localization and Describing for End-to-End 3D Dense Captioning
Sep 06, 2023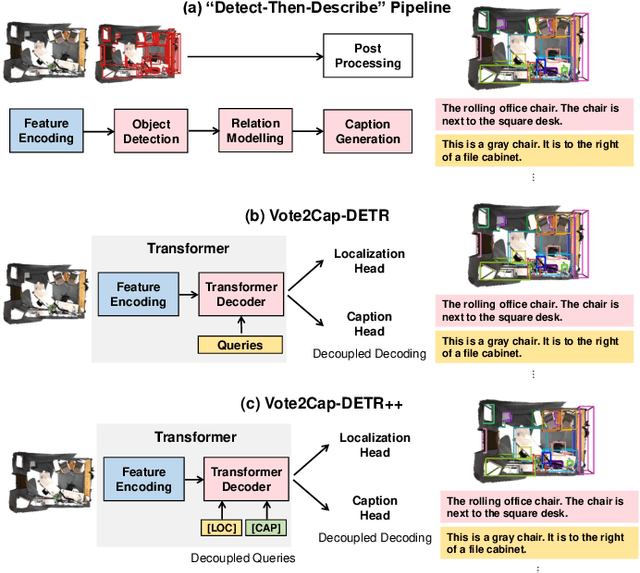
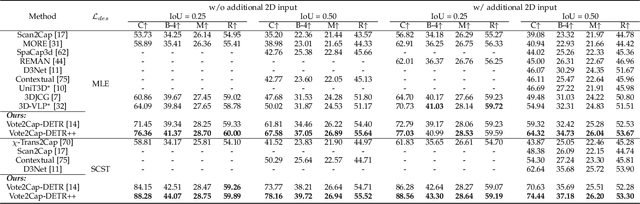
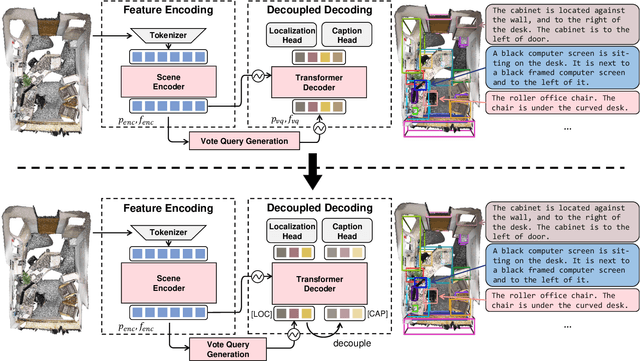
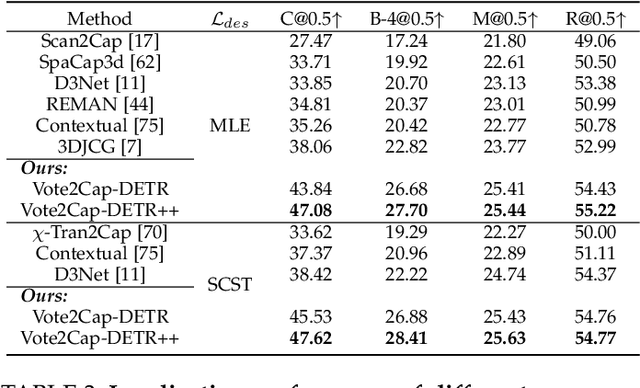
Abstract:3D dense captioning requires a model to translate its understanding of an input 3D scene into several captions associated with different object regions. Existing methods adopt a sophisticated "detect-then-describe" pipeline, which builds explicit relation modules upon a 3D detector with numerous hand-crafted components. While these methods have achieved initial success, the cascade pipeline tends to accumulate errors because of duplicated and inaccurate box estimations and messy 3D scenes. In this paper, we first propose Vote2Cap-DETR, a simple-yet-effective transformer framework that decouples the decoding process of caption generation and object localization through parallel decoding. Moreover, we argue that object localization and description generation require different levels of scene understanding, which could be challenging for a shared set of queries to capture. To this end, we propose an advanced version, Vote2Cap-DETR++, which decouples the queries into localization and caption queries to capture task-specific features. Additionally, we introduce the iterative spatial refinement strategy to vote queries for faster convergence and better localization performance. We also insert additional spatial information to the caption head for more accurate descriptions. Without bells and whistles, extensive experiments on two commonly used datasets, ScanRefer and Nr3D, demonstrate Vote2Cap-DETR and Vote2Cap-DETR++ surpass conventional "detect-then-describe" methods by a large margin. Codes will be made available at https://github.com/ch3cook-fdu/Vote2Cap-DETR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge