Shaobo Liu
Privacy-Preserving Hybrid Ensemble Model for Network Anomaly Detection: Balancing Security and Data Protection
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:Privacy-preserving network anomaly detection has become an essential area of research due to growing concerns over the protection of sensitive data. Traditional anomaly de- tection models often prioritize accuracy while neglecting the critical aspect of privacy. In this work, we propose a hybrid ensemble model that incorporates privacy-preserving techniques to address both detection accuracy and data protection. Our model combines the strengths of several machine learning algo- rithms, including K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Support Vector Machines (SVM), XGBoost, and Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), to create a robust system capable of identifying network anomalies while ensuring privacy. The proposed approach in- tegrates advanced preprocessing techniques that enhance data quality and address the challenges of small sample sizes and imbalanced datasets. By embedding privacy measures into the model design, our solution offers a significant advancement over existing methods, ensuring both enhanced detection performance and strong privacy safeguards.
Research on Key Technologies for Cross-Cloud Federated Training of Large Language Models
Oct 24, 2024Abstract:With the rapid development of natural language processing technology, large language models have demonstrated exceptional performance in various application scenarios. However, training these models requires significant computational resources and data processing capabilities. Cross-cloud federated training offers a new approach to addressing the resource bottlenecks of a single cloud platform, allowing the computational resources of multiple clouds to collaboratively complete the training tasks of large models. This study analyzes the key technologies of cross-cloud federated training, including data partitioning and distribution, communication optimization, model aggregation algorithms, and the compatibility of heterogeneous cloud platforms. Additionally, the study examines data security and privacy protection strategies in cross-cloud training, particularly the application of data encryption and differential privacy techniques. Through experimental validation, the proposed technical framework demonstrates enhanced training efficiency, ensured data security, and reduced training costs, highlighting the broad application prospects of cross-cloud federated training.
TRIZ Method for Urban Building Energy Optimization: GWO-SARIMA-LSTM Forecasting model
Oct 20, 2024



Abstract:With the advancement of global climate change and sustainable development goals, urban building energy consumption optimization and carbon emission reduction have become the focus of research. Traditional energy consumption prediction methods often lack accuracy and adaptability due to their inability to fully consider complex energy consumption patterns, especially in dealing with seasonal fluctuations and dynamic changes. This study proposes a hybrid deep learning model that combines TRIZ innovation theory with GWO, SARIMA and LSTM to improve the accuracy of building energy consumption prediction. TRIZ plays a key role in model design, providing innovative solutions to achieve an effective balance between energy efficiency, cost and comfort by systematically analyzing the contradictions in energy consumption optimization. GWO is used to optimize the parameters of the model to ensure that the model maintains high accuracy under different conditions. The SARIMA model focuses on capturing seasonal trends in the data, while the LSTM model handles short-term and long-term dependencies in the data, further improving the accuracy of the prediction. The main contribution of this research is the development of a robust model that leverages the strengths of TRIZ and advanced deep learning techniques, improving the accuracy of energy consumption predictions. Our experiments demonstrate a significant 15% reduction in prediction error compared to existing models. This innovative approach not only enhances urban energy management but also provides a new framework for optimizing energy use and reducing carbon emissions, contributing to sustainable development.
Balancing Innovation and Privacy: Data Security Strategies in Natural Language Processing Applications
Oct 11, 2024



Abstract:This research addresses privacy protection in Natural Language Processing (NLP) by introducing a novel algorithm based on differential privacy, aimed at safeguarding user data in common applications such as chatbots, sentiment analysis, and machine translation. With the widespread application of NLP technology, the security and privacy protection of user data have become important issues that need to be solved urgently. This paper proposes a new privacy protection algorithm designed to effectively prevent the leakage of user sensitive information. By introducing a differential privacy mechanism, our model ensures the accuracy and reliability of data analysis results while adding random noise. This method not only reduces the risk caused by data leakage but also achieves effective processing of data while protecting user privacy. Compared to traditional privacy methods like data anonymization and homomorphic encryption, our approach offers significant advantages in terms of computational efficiency and scalability while maintaining high accuracy in data analysis. The proposed algorithm's efficacy is demonstrated through performance metrics such as accuracy (0.89), precision (0.85), and recall (0.88), outperforming other methods in balancing privacy and utility. As privacy protection regulations become increasingly stringent, enterprises and developers must take effective measures to deal with privacy risks. Our research provides an important reference for the application of privacy protection technology in the field of NLP, emphasizing the need to achieve a balance between technological innovation and user privacy. In the future, with the continuous advancement of technology, privacy protection will become a core element of data-driven applications and promote the healthy development of the entire industry.
Applying Hybrid Graph Neural Networks to Strengthen Credit Risk Analysis
Oct 05, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a novel approach to credit risk prediction by employing Graph Convolutional Neural Networks (GCNNs) to assess the creditworthiness of borrowers. Leveraging the power of big data and artificial intelligence, the proposed method addresses the challenges faced by traditional credit risk assessment models, particularly in handling imbalanced datasets and extracting meaningful features from complex relationships. The paper begins by transforming raw borrower data into graph-structured data, where borrowers and their relationships are represented as nodes and edges, respectively. A classic subgraph convolutional model is then applied to extract local features, followed by the introduction of a hybrid GCNN model that integrates both local and global convolutional operators to capture a comprehensive representation of node features. The hybrid model incorporates an attention mechanism to adaptively select features, mitigating issues of over-smoothing and insufficient feature consideration. The study demonstrates the potential of GCNNs in improving the accuracy of credit risk prediction, offering a robust solution for financial institutions seeking to enhance their lending decision-making processes.
Toward Pedestrian Head Tracking: A Benchmark Dataset and an Information Fusion Network
Aug 12, 2024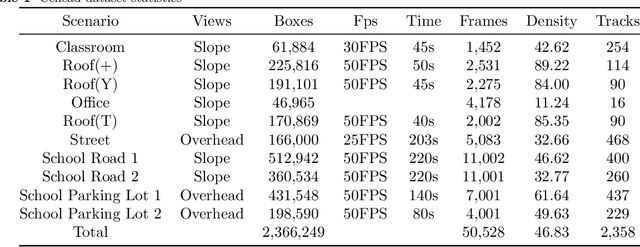


Abstract:Pedestrian detection and tracking in crowded video sequences have a wide range of applications, including autonomous driving, robot navigation and pedestrian flow surveillance. However, detecting and tracking pedestrians in high-density crowds face many challenges, including intra-class occlusions, complex motions, and diverse poses. Although deep learning models have achieved remarkable progress in head detection, head tracking datasets and methods are extremely lacking. Existing head datasets have limited coverage of complex pedestrian flows and scenes (e.g., pedestrian interactions, occlusions, and object interference). It is of great importance to develop new head tracking datasets and methods. To address these challenges, we present a Chinese Large-scale Cross-scene Pedestrian Head Tracking dataset (Cchead) and a Multi-Source Information Fusion Network (MIFN). Our dataset has features that are of considerable interest, including 10 diverse scenes of 50,528 frames with over 2,366,249 heads and 2,358 tracks annotated. Our dataset contains diverse human moving speeds, directions, and complex crowd pedestrian flows with collision avoidance behaviors. We provide a comprehensive analysis and comparison with existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) algorithms. Moreover, our MIFN is the first end-to-end CNN-based head detection and tracking network that jointly trains RGB frames, pixel-level motion information (optical flow and frame difference maps), depth maps, and density maps in videos. Compared with SOTA pedestrian detection and tracking methods, MIFN achieves superior performance on our Cchead dataset. We believe our datasets and baseline will become valuable resources towards developing pedestrian tracking in dense crowds.
Multi-Scenario Combination Based on Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning to Optimize the Advertising Recommendation System
Jul 03, 2024



Abstract:This paper explores multi-scenario optimization on large platforms using multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL). We address this by treating scenarios like search, recommendation, and advertising as a cooperative, partially observable multi-agent decision problem. We introduce the Multi-Agent Recurrent Deterministic Policy Gradient (MARDPG) algorithm, which aligns different scenarios under a shared objective and allows for strategy communication to boost overall performance. Our results show marked improvements in metrics such as click-through rate (CTR), conversion rate, and total sales, confirming our method's efficacy in practical settings.
Application Of Vision-Language Models For Assessing Osteoarthritis Disease Severity
Jan 12, 2024Abstract:Osteoarthritis (OA) poses a global health challenge, demanding precise diagnostic methods. Current radiographic assessments are time consuming and prone to variability, prompting the need for automated solutions. The existing deep learning models for OA assessment are unimodal single task systems and they don't incorporate relevant text information such as patient demographics, disease history, or physician reports. This study investigates employing Vision Language Processing (VLP) models to predict OA severity using Xray images and corresponding reports. Our method leverages Xray images of the knee and diverse report templates generated from tabular OA scoring values to train a CLIP (Contrastive Language Image PreTraining) style VLP model. Furthermore, we incorporate additional contrasting captions to enforce the model to discriminate between positive and negative reports. Results demonstrate the efficacy of these models in learning text image representations and their contextual relationships, showcase potential advancement in OA assessment, and establish a foundation for specialized vision language models in medical contexts.
Disentangle-based Continual Graph Representation Learning
Oct 06, 2020
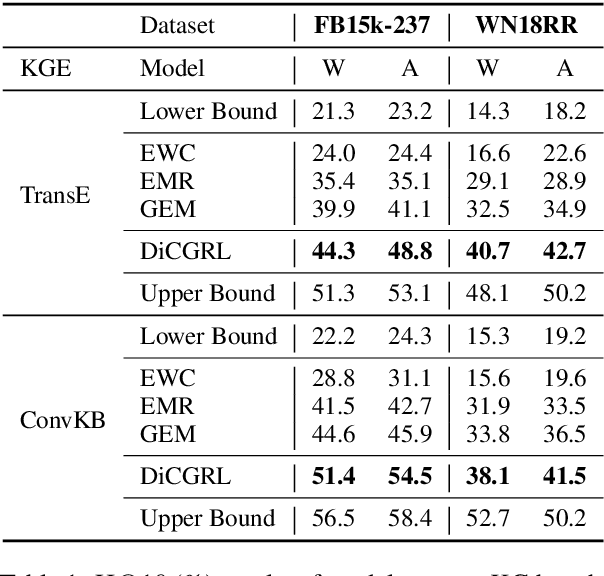
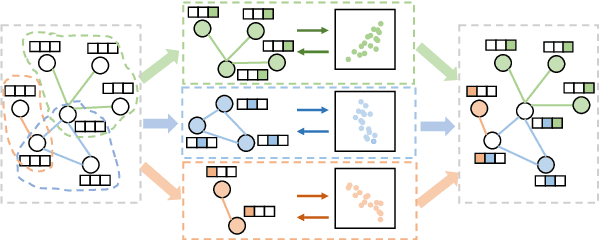

Abstract:Graph embedding (GE) methods embed nodes (and/or edges) in graph into a low-dimensional semantic space, and have shown its effectiveness in modeling multi-relational data. However, existing GE models are not practical in real-world applications since it overlooked the streaming nature of incoming data. To address this issue, we study the problem of continual graph representation learning which aims to continually train a GE model on new data to learn incessantly emerging multi-relational data while avoiding catastrophically forgetting old learned knowledge. Moreover, we propose a disentangle-based continual graph representation learning (DiCGRL) framework inspired by the human's ability to learn procedural knowledge. The experimental results show that DiCGRL could effectively alleviate the catastrophic forgetting problem and outperform state-of-the-art continual learning models. The code and datasets are released on https://github.com/KXY-PUBLIC/DiCGRL.
Exploiting Contextual Information via Dynamic Memory Network for Event Detection
Oct 03, 2018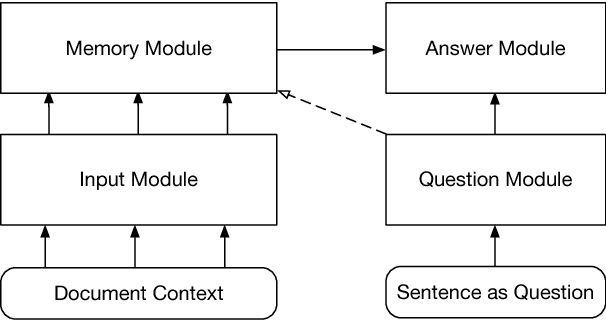
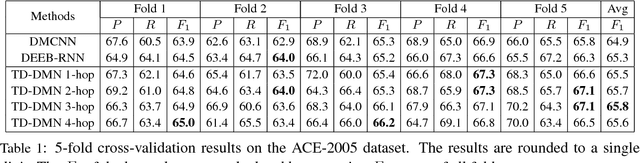
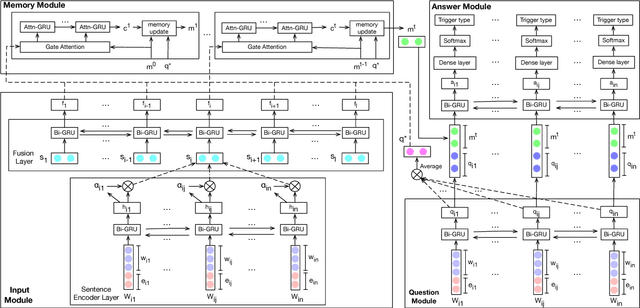
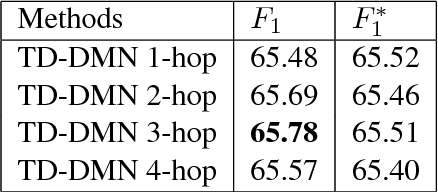
Abstract:The task of event detection involves identifying and categorizing event triggers. Contextual information has been shown effective on the task. However, existing methods which utilize contextual information only process the context once. We argue that the context can be better exploited by processing the context multiple times, allowing the model to perform complex reasoning and to generate better context representation, thus improving the overall performance. Meanwhile, dynamic memory network (DMN) has demonstrated promising capability in capturing contextual information and has been applied successfully to various tasks. In light of the multi-hop mechanism of the DMN to model the context, we propose the trigger detection dynamic memory network (TD-DMN) to tackle the event detection problem. We performed a five-fold cross-validation on the ACE-2005 dataset and experimental results show that the multi-hop mechanism does improve the performance and the proposed model achieves best $F_1$ score compared to the state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge