Qin Chen
East China Normal University
Mimic Human Cognition, Master Multi-Image Reasoning: A Meta-Action Framework for Enhanced Visual Understanding
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) excel at single-image understanding, they exhibit significantly degraded performance in multi-image reasoning scenarios. Multi-image reasoning presents fundamental challenges including complex inter-relationships between images and scattered critical information across image sets. Inspired by human cognitive processes, we propose the Cognition-Inspired Meta-Action Framework (CINEMA), a novel approach that decomposes multi-image reasoning into five structured meta-actions: Global, Focus, Hint, Think, and Answer which explicitly modeling the sequential cognitive steps humans naturally employ. For cold-start training, we introduce a Retrieval-Based Tree Sampling strategy that generates high-quality meta-action trajectories to bootstrap the model with reasoning patterns. During reinforcement learning, we adopt a two-stage paradigm: an exploration phase with Diversity-Preserving Strategy to avoid entropy collapse, followed by an annealed exploitation phase with DAPO to gradually strengthen exploitation. To train our model, we construct a dataset of 57k cold-start and 58k reinforcement learning instances spanning multi-image, multi-frame, and single-image tasks. We conduct extensive evaluations on multi-image reasoning benchmarks, video understanding benchmarks, and single-image benchmarks, achieving competitive state-of-the-art performance on several key benchmarks. Our model surpasses GPT-4o on the MUIR and MVMath benchmarks and notably outperforms specialized video reasoning models on video understanding benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness and generalizability of our human cognition-inspired reasoning framework.
PsychEval: A Multi-Session and Multi-Therapy Benchmark for High-Realism AI Psychological Counselor
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:To develop a reliable AI for psychological assessment, we introduce \texttt{PsychEval}, a multi-session, multi-therapy, and highly realistic benchmark designed to address three key challenges: \textbf{1) Can we train a highly realistic AI counselor?} Realistic counseling is a longitudinal task requiring sustained memory and dynamic goal tracking. We propose a multi-session benchmark (spanning 6-10 sessions across three distinct stages) that demands critical capabilities such as memory continuity, adaptive reasoning, and longitudinal planning. The dataset is annotated with extensive professional skills, comprising over 677 meta-skills and 4577 atomic skills. \textbf{2) How to train a multi-therapy AI counselor?} While existing models often focus on a single therapy, complex cases frequently require flexible strategies among various therapies. We construct a diverse dataset covering five therapeutic modalities (Psychodynamic, Behaviorism, CBT, Humanistic Existentialist, and Postmodernist) alongside an integrative therapy with a unified three-stage clinical framework across six core psychological topics. \textbf{3) How to systematically evaluate an AI counselor?} We establish a holistic evaluation framework with 18 therapy-specific and therapy-shared metrics across Client-Level and Counselor-Level dimensions. To support this, we also construct over 2,000 diverse client profiles. Extensive experimental analysis fully validates the superior quality and clinical fidelity of our dataset. Crucially, \texttt{PsychEval} transcends static benchmarking to serve as a high-fidelity reinforcement learning environment that enables the self-evolutionary training of clinically responsible and adaptive AI counselors.
Black-box Model Merging for Language-Model-as-a-Service with Massive Model Repositories
Sep 16, 2025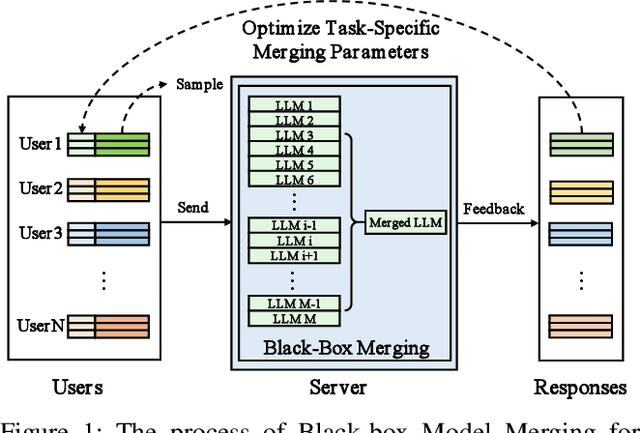
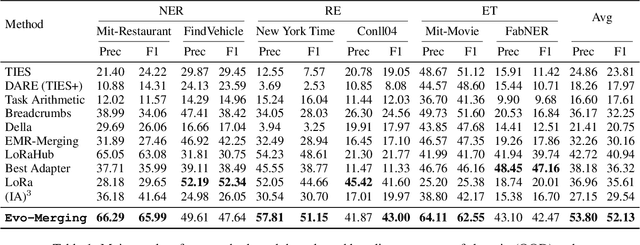
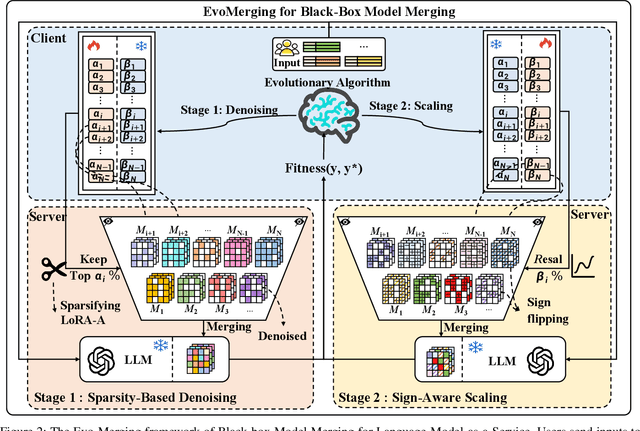
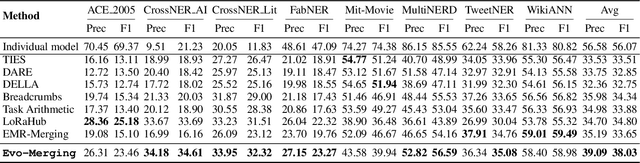
Abstract:Model merging refers to the process of integrating multiple distinct models into a unified model that preserves and combines the strengths and capabilities of the individual models. Most existing approaches rely on task vectors to combine models, typically under the assumption that model parameters are accessible. However, for extremely large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-4, which are often provided solely as black-box services through API interfaces (Language-Model-as-a-Service), model weights are not available to end users. This presents a significant challenge, which we refer to as black-box model merging (BMM) with massive LLMs. To address this challenge, we propose a derivative-free optimization framework based on the evolutionary algorithm (Evo-Merging) that enables effective model merging using only inference-time API queries. Our method consists of two key components: (1) sparsity-based denoising, designed to identify and filter out irrelevant or redundant information across models, and (2) sign-aware scaling, which dynamically computes optimal combination weights for the relevant models based on their performance. We also provide a formal justification, along with a theoretical analysis, for our asymmetric sparsification. Extensive experimental evaluations demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art results on a range of tasks, significantly outperforming existing strong baselines.
Mitigating Strategy Preference Bias in Emotional Support Conversation via Uncertainty Estimations
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Emotional support conversation (ESC) aims to alleviate distress through empathetic dialogue, yet large language models (LLMs) face persistent challenges in delivering effective ESC due to low accuracy in strategy planning. Moreover, there is a considerable preference bias towards specific strategies. Prior methods using fine-tuned strategy planners have shown potential in reducing such bias, while the underlying causes of the preference bias in LLMs have not well been studied. To address these issues, we first reveal the fundamental causes of the bias by identifying the knowledge boundaries of LLMs in strategy planning. Then, we propose an approach to mitigate the bias by reinforcement learning with a dual reward function, which optimizes strategy planning via both accuracy and entropy-based confidence for each region according to the knowledge boundaries. Experiments on the ESCov and ExTES datasets with multiple LLM backbones show that our approach outperforms the baselines, confirming the effectiveness of our approach.
Forget What's Sensitive, Remember What Matters: Token-Level Differential Privacy in Memory Sculpting for Continual Learning
Sep 16, 2025
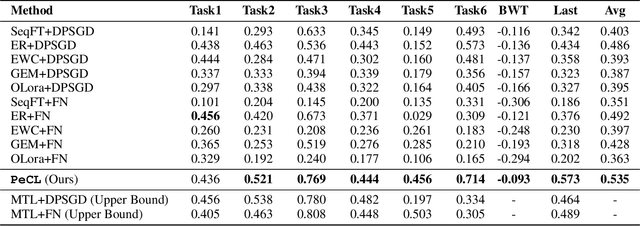
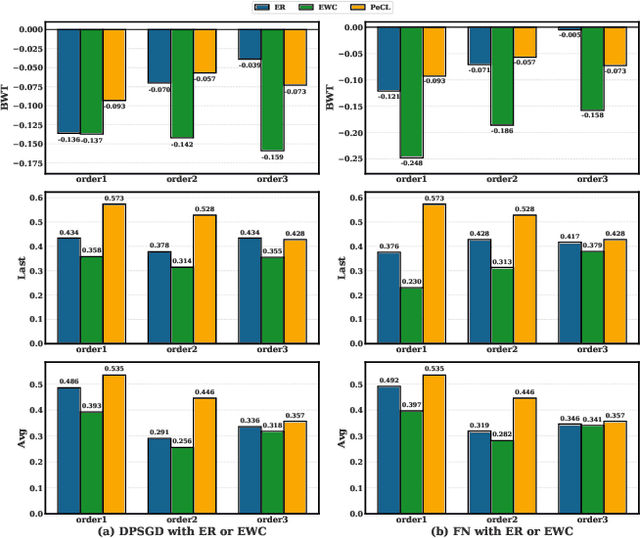
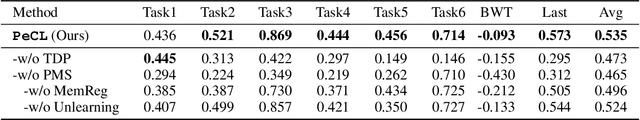
Abstract:Continual Learning (CL) models, while adept at sequential knowledge acquisition, face significant and often overlooked privacy challenges due to accumulating diverse information. Traditional privacy methods, like a uniform Differential Privacy (DP) budget, indiscriminately protect all data, leading to substantial model utility degradation and hindering CL deployment in privacy-sensitive areas. To overcome this, we propose a privacy-enhanced continual learning (PeCL) framework that forgets what's sensitive and remembers what matters. Our approach first introduces a token-level dynamic Differential Privacy strategy that adaptively allocates privacy budgets based on the semantic sensitivity of individual tokens. This ensures robust protection for private entities while minimizing noise injection for non-sensitive, general knowledge. Second, we integrate a privacy-guided memory sculpting module. This module leverages the sensitivity analysis from our dynamic DP mechanism to intelligently forget sensitive information from the model's memory and parameters, while explicitly preserving the task-invariant historical knowledge crucial for mitigating catastrophic forgetting. Extensive experiments show that PeCL achieves a superior balance between privacy preserving and model utility, outperforming baseline models by maintaining high accuracy on previous tasks while ensuring robust privacy.
SheetDesigner: MLLM-Powered Spreadsheet Layout Generation with Rule-Based and Vision-Based Reflection
Sep 09, 2025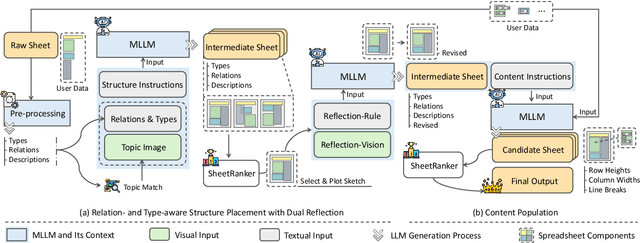
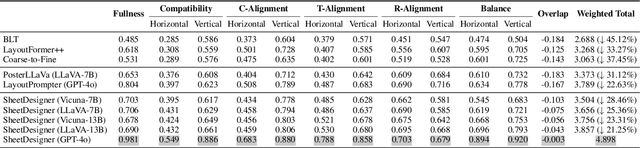
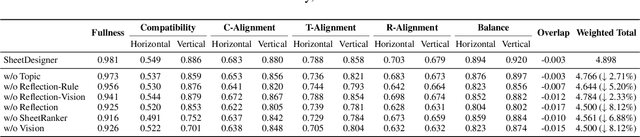
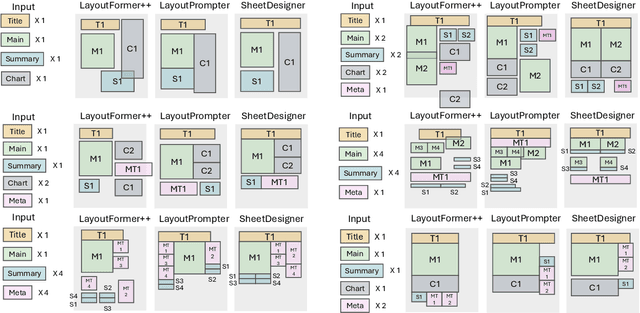
Abstract:Spreadsheets are critical to data-centric tasks, with rich, structured layouts that enable efficient information transmission. Given the time and expertise required for manual spreadsheet layout design, there is an urgent need for automated solutions. However, existing automated layout models are ill-suited to spreadsheets, as they often (1) treat components as axis-aligned rectangles with continuous coordinates, overlooking the inherently discrete, grid-based structure of spreadsheets; and (2) neglect interrelated semantics, such as data dependencies and contextual links, unique to spreadsheets. In this paper, we first formalize the spreadsheet layout generation task, supported by a seven-criterion evaluation protocol and a dataset of 3,326 spreadsheets. We then introduce SheetDesigner, a zero-shot and training-free framework using Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) that combines rule and vision reflection for component placement and content population. SheetDesigner outperforms five baselines by at least 22.6\%. We further find that through vision modality, MLLMs handle overlap and balance well but struggle with alignment, necessitates hybrid rule and visual reflection strategies. Our codes and data is available at Github.
Building Self-Evolving Agents via Experience-Driven Lifelong Learning: A Framework and Benchmark
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:As AI advances toward general intelligence, the focus is shifting from systems optimized for static tasks to creating open-ended agents that learn continuously. In this paper, we introduce Experience-driven Lifelong Learning (ELL), a framework for building self-evolving agents capable of continuous growth through real-world interaction. The framework is built on four core principles: (1) Experience Exploration: Agents learn through continuous, self-motivated interaction with dynamic environments, navigating interdependent tasks and generating rich experiential trajectories. (2) Long-term Memory: Agents preserve and structure historical knowledge, including personal experiences, domain expertise, and commonsense reasoning, into a persistent memory system. (3) Skill Learning: Agents autonomously improve by abstracting recurring patterns from experience into reusable skills, which are actively refined and validated for application in new tasks. (4) Knowledge Internalization: Agents internalize explicit and discrete experiences into implicit and intuitive capabilities as "second nature". We also introduce StuLife, a benchmark dataset for ELL that simulates a student's holistic college journey, from enrollment to academic and personal development, across three core phases and ten detailed sub-scenarios. StuLife is designed around three key paradigm shifts: From Passive to Proactive, From Context to Memory, and From Imitation to Learning. In this dynamic environment, agents must acquire and distill practical skills and maintain persistent memory to make decisions based on evolving state variables. StuLife provides a comprehensive platform for evaluating lifelong learning capabilities, including memory retention, skill transfer, and self-motivated behavior. Beyond evaluating SOTA LLMs on the StuLife benchmark, we also explore the role of context engineering in advancing AGI.
Protein-SE(3): Benchmarking SE(3)-based Generative Models for Protein Structure Design
Jul 27, 2025Abstract:SE(3)-based generative models have shown great promise in protein geometry modeling and effective structure design. However, the field currently lacks a modularized benchmark to enable comprehensive investigation and fair comparison of different methods. In this paper, we propose Protein-SE(3), a new benchmark based on a unified training framework, which comprises protein scaffolding tasks, integrated generative models, high-level mathematical abstraction, and diverse evaluation metrics. Recent advanced generative models designed for protein scaffolding, from multiple perspectives like DDPM (Genie1 and Genie2), Score Matching (FrameDiff and RfDiffusion) and Flow Matching (FoldFlow and FrameFlow) are integrated into our framework. All integrated methods are fairly investigated with the same training dataset and evaluation metrics. Furthermore, we provide a high-level abstraction of the mathematical foundations behind the generative models, enabling fast prototyping of future algorithms without reliance on explicit protein structures. Accordingly, we release the first comprehensive benchmark built upon unified training framework for SE(3)-based protein structure design, which is publicly accessible at https://github.com/BruthYU/protein-se3.
Large Language Models for Predictive Analysis: How Far Are They?
May 22, 2025Abstract:Predictive analysis is a cornerstone of modern decision-making, with applications in various domains. Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as powerful tools in enabling nuanced, knowledge-intensive conversations, thus aiding in complex decision-making tasks. With the burgeoning expectation to harness LLMs for predictive analysis, there is an urgent need to systematically assess their capability in this domain. However, there is a lack of relevant evaluations in existing studies. To bridge this gap, we introduce the \textbf{PredictiQ} benchmark, which integrates 1130 sophisticated predictive analysis queries originating from 44 real-world datasets of 8 diverse fields. We design an evaluation protocol considering text analysis, code generation, and their alignment. Twelve renowned LLMs are evaluated, offering insights into their practical use in predictive analysis. Generally, we believe that existing LLMs still face considerable challenges in conducting predictive analysis. See \href{https://github.com/Cqkkkkkk/PredictiQ}{Github}.
Task-Core Memory Management and Consolidation for Long-term Continual Learning
May 15, 2025



Abstract:In this paper, we focus on a long-term continual learning (CL) task, where a model learns sequentially from a stream of vast tasks over time, acquiring new knowledge while retaining previously learned information in a manner akin to human learning. Unlike traditional CL settings, long-term CL involves handling a significantly larger number of tasks, which exacerbates the issue of catastrophic forgetting. Our work seeks to address two critical questions: 1) How do existing CL methods perform in the context of long-term CL? and 2) How can we mitigate the catastrophic forgetting that arises from prolonged sequential updates? To tackle these challenges, we propose a novel framework inspired by human memory mechanisms for long-term continual learning (Long-CL). Specifically, we introduce a task-core memory management strategy to efficiently index crucial memories and adaptively update them as learning progresses. Additionally, we develop a long-term memory consolidation mechanism that selectively retains hard and discriminative samples, ensuring robust knowledge retention. To facilitate research in this area, we construct and release two multi-modal and textual benchmarks, MMLongCL-Bench and TextLongCL-Bench, providing a valuable resource for evaluating long-term CL approaches. Experimental results show that Long-CL outperforms the previous state-of-the-art by 7.4\% and 6.5\% AP on the two benchmarks, respectively, demonstrating the effectiveness of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge