Pengyu Zhang
Koopman Autoencoders with Continuous-Time Latent Dynamics for Fluid Dynamics Forecasting
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Data-driven surrogate models have emerged as powerful tools for accelerating the simulation of turbulent flows. However, classical approaches which perform autoregressive rollouts often trade off between strong short-term accuracy and long-horizon stability. Koopman autoencoders, inspired by Koopman operator theory, provide a physics-based alternative by mapping nonlinear dynamics into a latent space where linear evolution is conducted. In practice, most existing formulations operate in a discrete-time setting, limiting temporal flexibility. In this work, we introduce a continuous-time Koopman framework that models latent evolution through numerical integration schemes. By allowing variable timesteps at inference, the method demonstrates robustness to temporal resolution and generalizes beyond training regimes. In addition, the learned dynamics closely adhere to the analytical matrix exponential solution, enabling efficient long-horizon forecasting. We evaluate the approach on classical CFD benchmarks and report accuracy, stability, and extrapolation properties.
Capsizing-Guided Trajectory Optimization for Autonomous Navigation with Rough Terrain
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:It is a challenging task for ground robots to autonomously navigate in harsh environments due to the presence of non-trivial obstacles and uneven terrain. This requires trajectory planning that balances safety and efficiency. The primary challenge is to generate a feasible trajectory that prevents robot from tip-over while ensuring effective navigation. In this paper, we propose a capsizing-aware trajectory planner (CAP) to achieve trajectory planning on the uneven terrain. The tip-over stability of the robot on rough terrain is analyzed. Based on the tip-over stability, we define the traversable orientation, which indicates the safe range of robot orientations. This orientation is then incorporated into a capsizing-safety constraint for trajectory optimization. We employ a graph-based solver to compute a robust and feasible trajectory while adhering to the capsizing-safety constraint. Extensive simulation and real-world experiments validate the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed method. The results demonstrate that CAP outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches, providing enhanced navigation performance on uneven terrains.
Using Large Language Models to Tackle Fundamental Challenges in Graph Learning: A Comprehensive Survey
May 24, 2025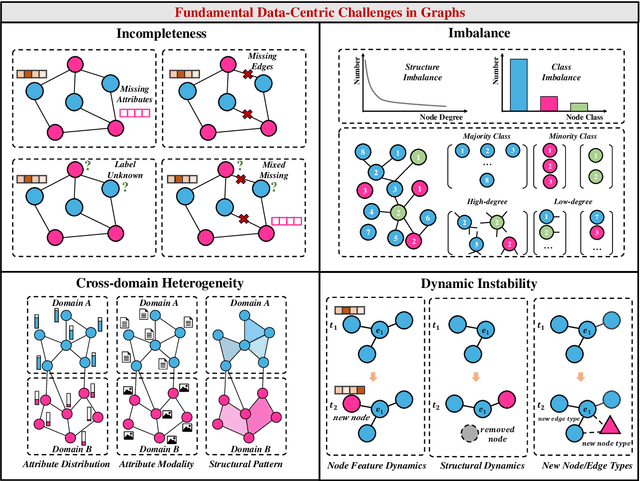
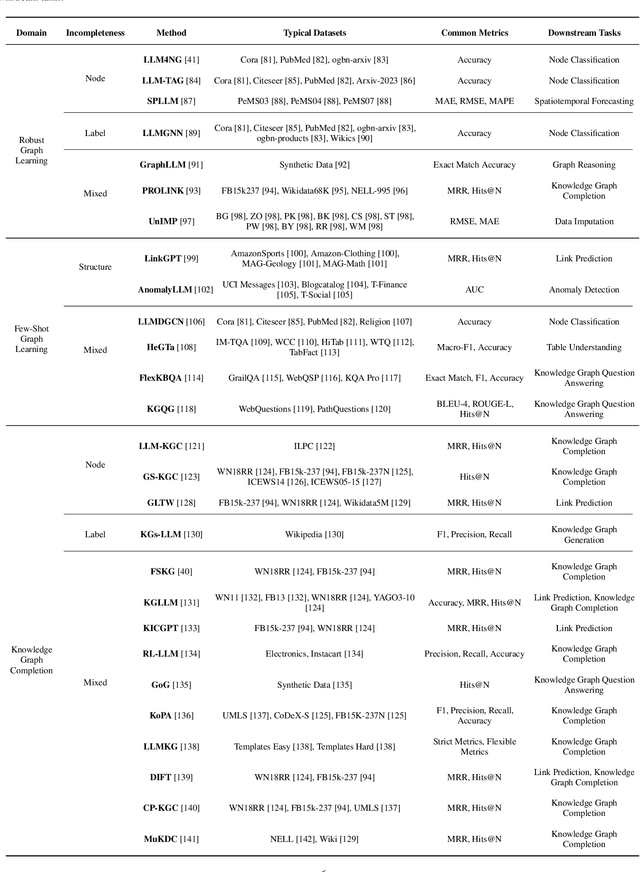
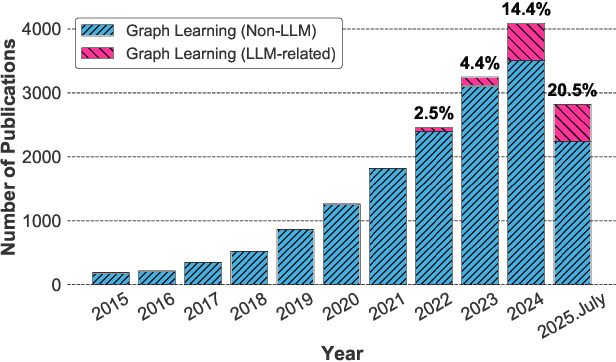
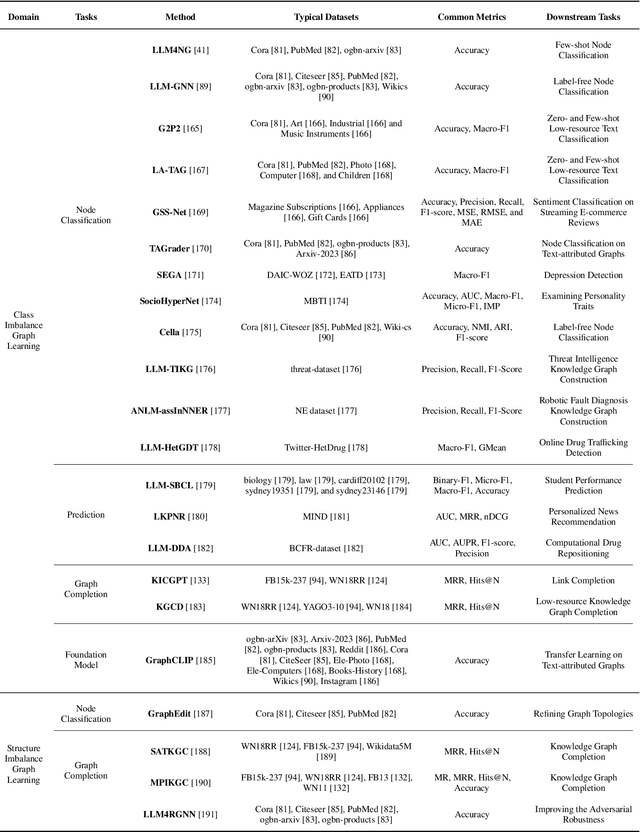
Abstract:Graphs are a widely used paradigm for representing non-Euclidean data, with applications ranging from social network analysis to biomolecular prediction. Conventional graph learning approaches typically rely on fixed structural assumptions or fully observed data, limiting their effectiveness in more complex, noisy, or evolving settings. Consequently, real-world graph data often violates the assumptions of traditional graph learning methods, in particular, it leads to four fundamental challenges: (1) Incompleteness, real-world graphs have missing nodes, edges, or attributes; (2) Imbalance, the distribution of the labels of nodes or edges and their structures for real-world graphs are highly skewed; (3) Cross-domain Heterogeneity, graphs from different domains exhibit incompatible feature spaces or structural patterns; and (4) Dynamic Instability, graphs evolve over time in unpredictable ways. Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) offer the potential to tackle these challenges by leveraging rich semantic reasoning and external knowledge. This survey provides a comprehensive review of how LLMs can be integrated with graph learning to address the aforementioned challenges. For each challenge, we review both traditional solutions and modern LLM-driven approaches, highlighting how LLMs contribute unique advantages. Finally, we discuss open research questions and promising future directions in this emerging interdisciplinary field. To support further exploration, we have curated a repository of recent advances on graph learning challenges: https://github.com/limengran98/Awesome-Literature-Graph-Learning-Challenges.
EDENet: Echo Direction Encoding Network for Place Recognition Based on Ground Penetrating Radar
Feb 28, 2025



Abstract:Ground penetrating radar (GPR) based localization has gained significant recognition in robotics due to its ability to detect stable subsurface features, offering advantages in environments where traditional sensors like cameras and LiDAR may struggle. However, existing methods are primarily focused on small-scale place recognition (PR), leaving the challenges of PR in large-scale maps unaddressed. These challenges include the inherent sparsity of underground features and the variability in underground dielectric constants, which complicate robust localization. In this work, we investigate the geometric relationship between GPR echo sequences and underground scenes, leveraging the robustness of directional features to inform our network design. We introduce learnable Gabor filters for the precise extraction of directional responses, coupled with a direction-aware attention mechanism for effective geometric encoding. To further enhance performance, we incorporate a shift-invariant unit and a multi-scale aggregation strategy to better accommodate variations in di-electric constants. Experiments conducted on public datasets demonstrate that our proposed EDENet not only surpasses existing solutions in terms of PR performance but also offers advantages in model size and computational efficiency.
Explainable Federated Bayesian Causal Inference and Its Application in Advanced Manufacturing
Jan 10, 2025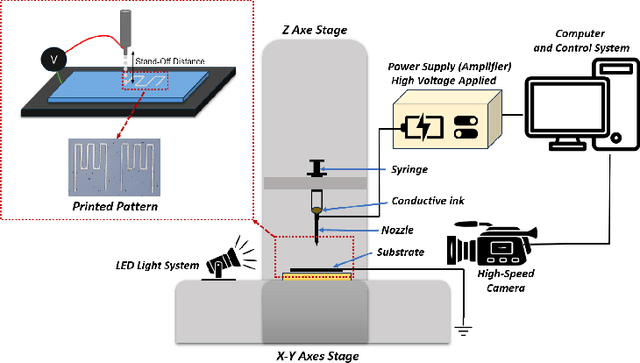
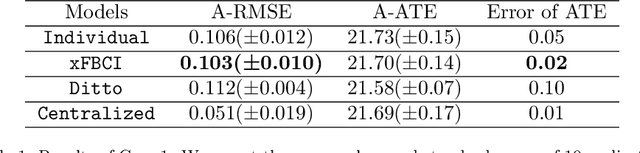
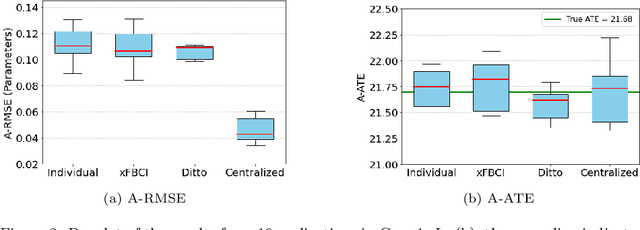
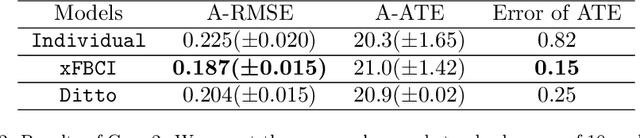
Abstract:Causal inference has recently gained notable attention across various fields like biology, healthcare, and environmental science, especially within explainable artificial intelligence (xAI) systems, for uncovering the causal relationships among multiple variables and outcomes. Yet, it has not been fully recognized and deployed in the manufacturing systems. In this paper, we introduce an explainable, scalable, and flexible federated Bayesian learning framework, \texttt{xFBCI}, designed to explore causality through treatment effect estimation in distributed manufacturing systems. By leveraging federated Bayesian learning, we efficiently estimate posterior of local parameters to derive the propensity score for each client without accessing local private data. These scores are then used to estimate the treatment effect using propensity score matching (PSM). Through simulations on various datasets and a real-world Electrohydrodynamic (EHD) printing data, we demonstrate that our approach outperforms standard Bayesian causal inference methods and several state-of-the-art federated learning benchmarks.
Hyperbolic Contrastive Learning for Hierarchical 3D Point Cloud Embedding
Jan 07, 2025



Abstract:Hyperbolic spaces allow for more efficient modeling of complex, hierarchical structures, which is particularly beneficial in tasks involving multi-modal data. Although hyperbolic geometries have been proven effective for language-image pre-training, their capabilities to unify language, image, and 3D Point Cloud modalities are under-explored. We extend the 3D Point Cloud modality in hyperbolic multi-modal contrastive pre-training. Additionally, we explore the entailment, modality gap, and alignment regularizers for learning hierarchical 3D embeddings and facilitating the transfer of knowledge from both Text and Image modalities. These regularizers enable the learning of intra-modal hierarchy within each modality and inter-modal hierarchy across text, 2D images, and 3D Point Clouds. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed training strategy yields an outstanding 3D Point Cloud encoder, and the obtained 3D Point Cloud hierarchical embeddings significantly improve performance on various downstream tasks.
TIGER: Temporally Improved Graph Entity Linker
Oct 11, 2024



Abstract:Knowledge graphs change over time, for example, when new entities are introduced or entity descriptions change. This impacts the performance of entity linking, a key task in many uses of knowledge graphs such as web search and recommendation. Specifically, entity linking models exhibit temporal degradation - their performance decreases the further a knowledge graph moves from its original state on which an entity linking model was trained. To tackle this challenge, we introduce \textbf{TIGER}: a \textbf{T}emporally \textbf{I}mproved \textbf{G}raph \textbf{E}ntity Linke\textbf{r}. By incorporating structural information between entities into the model, we enhance the learned representation, making entities more distinguishable over time. The core idea is to integrate graph-based information into text-based information, from which both distinct and shared embeddings are based on an entity's feature and structural relationships and their interaction. Experiments on three datasets show that our model can effectively prevent temporal degradation, demonstrating a 16.24\% performance boost over the state-of-the-art in a temporal setting when the time gap is one year and an improvement to 20.93\% as the gap expands to three years. The code and data are made available at \url{https://github.com/pengyu-zhang/TIGER-Temporally-Improved-Graph-Entity-Linker}.
CYCLE: Cross-Year Contrastive Learning in Entity-Linking
Oct 11, 2024



Abstract:Knowledge graphs constantly evolve with new entities emerging, existing definitions being revised, and entity relationships changing. These changes lead to temporal degradation in entity linking models, characterized as a decline in model performance over time. To address this issue, we propose leveraging graph relationships to aggregate information from neighboring entities across different time periods. This approach enhances the ability to distinguish similar entities over time, thereby minimizing the impact of temporal degradation. We introduce \textbf{CYCLE}: \textbf{C}ross-\textbf{Y}ear \textbf{C}ontrastive \textbf{L}earning for \textbf{E}ntity-Linking. This model employs a novel graph contrastive learning method to tackle temporal performance degradation in entity linking tasks. Our contrastive learning method treats newly added graph relationships as \textit{positive} samples and newly removed ones as \textit{negative} samples. This approach helps our model effectively prevent temporal degradation, achieving a 13.90\% performance improvement over the state-of-the-art from 2023 when the time gap is one year, and a 17.79\% improvement as the gap expands to three years. Further analysis shows that CYCLE is particularly robust for low-degree entities, which are less resistant to temporal degradation due to their sparse connectivity, making them particularly suitable for our method. The code and data are made available at \url{https://github.com/pengyu-zhang/CYCLE-Cross-Year-Contrastive-Learning-in-Entity-Linking}.
EvSign: Sign Language Recognition and Translation with Streaming Events
Jul 17, 2024


Abstract:Sign language is one of the most effective communication tools for people with hearing difficulties. Most existing works focus on improving the performance of sign language tasks on RGB videos, which may suffer from degraded recording conditions, such as fast movement of hands with motion blur and textured signer's appearance. The bio-inspired event camera, which asynchronously captures brightness change with high speed, could naturally perceive dynamic hand movements, providing rich manual clues for sign language tasks. In this work, we aim at exploring the potential of event camera in continuous sign language recognition (CSLR) and sign language translation (SLT). To promote the research, we first collect an event-based benchmark EvSign for those tasks with both gloss and spoken language annotations. EvSign dataset offers a substantial amount of high-quality event streams and an extensive vocabulary of glosses and words, thereby facilitating the development of sign language tasks. In addition, we propose an efficient transformer-based framework for event-based SLR and SLT tasks, which fully leverages the advantages of streaming events. The sparse backbone is employed to extract visual features from sparse events. Then, the temporal coherence is effectively utilized through the proposed local token fusion and gloss-aware temporal aggregation modules. Extensive experimental results are reported on both simulated (PHOENIX14T) and EvSign datasets. Our method performs favorably against existing state-of-the-art approaches with only 0.34% computational cost (0.84G FLOPS per video) and 44.2% network parameters. The project is available at https://zhang-pengyu.github.io/EVSign.
Deciphering public attention to geoengineering and climate issues using machine learning and dynamic analysis
May 11, 2024



Abstract:As the conversation around using geoengineering to combat climate change intensifies, it is imperative to engage the public and deeply understand their perspectives on geoengineering research, development, and potential deployment. Through a comprehensive data-driven investigation, this paper explores the types of news that captivate public interest in geoengineering. We delved into 30,773 English-language news articles from the BBC and the New York Times, combined with Google Trends data spanning 2018 to 2022, to explore how public interest in geoengineering fluctuates in response to news coverage of broader climate issues. Using BERT-based topic modeling, sentiment analysis, and time-series regression models, we found that positive sentiment in energy-related news serves as a good predictor of heightened public interest in geoengineering, a trend that persists over time. Our findings suggest that public engagement with geoengineering and climate action is not uniform, with some topics being more potent in shaping interest over time, such as climate news related to energy, disasters, and politics. Understanding these patterns is crucial for scientists, policymakers, and educators aiming to craft effective strategies for engaging with the public and fostering dialogue around emerging climate technologies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge