Xiao Du
Gated Rotary-Enhanced Linear Attention for Long-term Sequential Recommendation
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:In Sequential Recommendation Systems (SRSs), Transformer models show remarkable performance but face computation cost challenges when modeling long-term user behavior sequences due to the quadratic complexity of the dot-product attention mechanism. By approximating the dot-product attention, linear attention provides an efficient option with linear complexity. However, existing linear attention methods face two limitations: 1) they often use learnable position encodings, which incur extra computational costs in long-term sequence scenarios, and 2) they may not consider the user's fine-grained local preferences and confuse these with the actual change of long-term interests. To remedy these drawbacks, we propose a long-term sequential Recommendation model with Gated Rotary Enhanced Linear Attention (RecGRELA). Specifically, we first propose a Rotary-Enhanced Linear Attention (RELA) module to model long-range dependency within the user's historical information using rotary position encodings. We then introduce a local short operation to incorporate local preferences and demonstrate the theoretical insight. We further introduce a SiLU-based Gated mechanism for RELA (GRELA) to help the model determine whether a user's behavior indicates local interest or a genuine shift in long-term preferences. Experimental results on four public datasets demonstrate that our RecGRELA achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to existing SRSs while maintaining low memory overhead.
FitLight: Federated Imitation Learning for Plug-and-Play Autonomous Traffic Signal Control
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Although Reinforcement Learning (RL)-based Traffic Signal Control (TSC) methods have been extensively studied, their practical applications still raise some serious issues such as high learning cost and poor generalizability. This is because the ``trial-and-error'' training style makes RL agents extremely dependent on the specific traffic environment, which also requires a long convergence time. To address these issues, we propose a novel Federated Imitation Learning (FIL)-based framework for multi-intersection TSC, named FitLight, which allows RL agents to plug-and-play for any traffic environment without additional pre-training cost. Unlike existing imitation learning approaches that rely on pre-training RL agents with demonstrations, FitLight allows real-time imitation learning and seamless transition to reinforcement learning. Due to our proposed knowledge-sharing mechanism and novel hybrid pressure-based agent design, RL agents can quickly find a best control policy with only a few episodes. Moreover, for resource-constrained TSC scenarios, FitLight supports model pruning and heterogeneous model aggregation, such that RL agents can work on a micro-controller with merely 16{\it KB} RAM and 32{\it KB} ROM. Extensive experiments demonstrate that, compared to state-of-the-art methods, FitLight not only provides a superior starting point but also converges to a better final solution on both real-world and synthetic datasets, even under extreme resource limitations.
SAFL: Structure-Aware Personalized Federated Learning via Client-Specific Clustering and SCSI-Guided Model Pruning
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) enables clients to collaboratively train machine learning models without sharing local data, preserving privacy in diverse environments. While traditional FL approaches preserve privacy, they often struggle with high computational and communication overhead. To address these issues, model pruning is introduced as a strategy to streamline computations. However, existing pruning methods, when applied solely based on local data, often produce sub-models that inadequately reflect clients' specific tasks due to data insufficiency. To overcome these challenges, this paper introduces SAFL (Structure-Aware Federated Learning), a novel framework that enhances personalized federated learning through client-specific clustering and Similar Client Structure Information (SCSI)-guided model pruning. SAFL employs a two-stage process: initially, it groups clients based on data similarities and uses aggregated pruning criteria to guide the pruning process, facilitating the identification of optimal sub-models. Subsequently, clients train these pruned models and engage in server-based aggregation, ensuring tailored and efficient models for each client. This method significantly reduces computational overhead while improving inference accuracy. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SAFL markedly diminishes model size and improves performance, making it highly effective in federated environments characterized by heterogeneous data.
When Foresight Pruning Meets Zeroth-Order Optimization: Efficient Federated Learning for Low-Memory Devices
May 08, 2024



Abstract:Although Federated Learning (FL) enables collaborative learning in Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT) design, it fails to work on low-memory AIoT devices due to its heavy memory usage. To address this problem, various federated pruning methods are proposed to reduce memory usage during inference. However, few of them can substantially mitigate the memory burdens during pruning and training. As an alternative, zeroth-order or backpropagation-free (BP-Free) methods can partially alleviate the memory consumption, but they suffer from scaling up and large computation overheads, since the gradient estimation error and floating point operations (FLOPs) increase as the dimensionality of the model parameters grows. In this paper, we propose a federated foresight pruning method based on Neural Tangent Kernel (NTK), which can seamlessly integrate with federated BP-Free training frameworks. We present an approximation to the computation of federated NTK by using the local NTK matrices. Moreover, we demonstrate that the data-free property of our method can substantially reduce the approximation error in extreme data heterogeneity scenarios. Since our approach improves the performance of the vanilla BP-Free method with fewer FLOPs and truly alleviates memory pressure during training and inference, it makes FL more friendly to low-memory devices. Comprehensive experimental results obtained from simulation- and real test-bed-based platforms show that our federated foresight-pruning method not only preserves the ability of the dense model with a memory reduction up to 9x but also boosts the performance of the vanilla BP-Free method with dramatically fewer FLOPs.
Situation-Dependent Causal Influence-Based Cooperative Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning
Dec 15, 2023



Abstract:Learning to collaborate has witnessed significant progress in multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL). However, promoting coordination among agents and enhancing exploration capabilities remain challenges. In multi-agent environments, interactions between agents are limited in specific situations. Effective collaboration between agents thus requires a nuanced understanding of when and how agents' actions influence others. To this end, in this paper, we propose a novel MARL algorithm named Situation-Dependent Causal Influence-Based Cooperative Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning (SCIC), which incorporates a novel Intrinsic reward mechanism based on a new cooperation criterion measured by situation-dependent causal influence among agents. Our approach aims to detect inter-agent causal influences in specific situations based on the criterion using causal intervention and conditional mutual information. This effectively assists agents in exploring states that can positively impact other agents, thus promoting cooperation between agents. The resulting update links coordinated exploration and intrinsic reward distribution, which enhance overall collaboration and performance. Experimental results on various MARL benchmarks demonstrate the superiority of our method compared to state-of-the-art approaches.
FAIR: Frequency-aware Image Restoration for Industrial Visual Anomaly Detection
Sep 13, 2023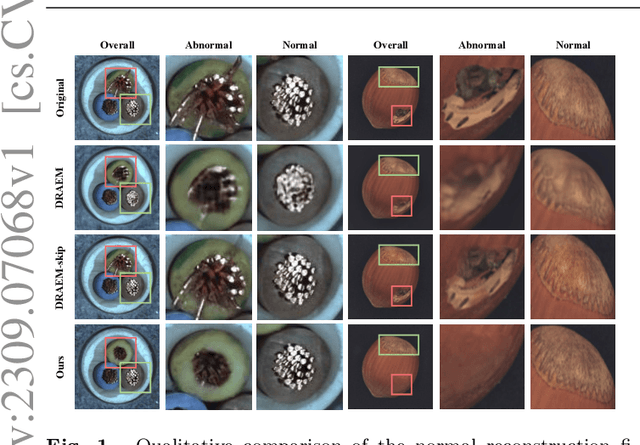
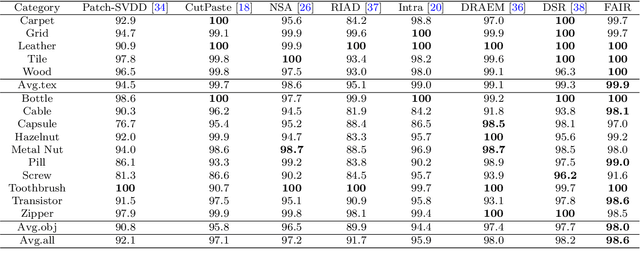
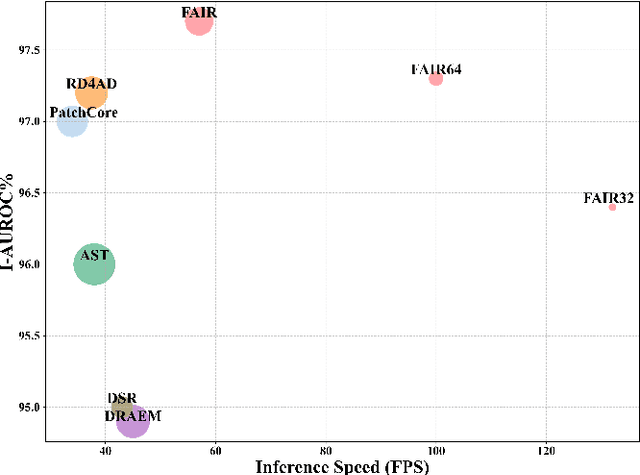
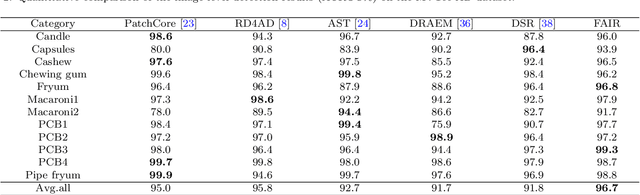
Abstract:Image reconstruction-based anomaly detection models are widely explored in industrial visual inspection. However, existing models usually suffer from the trade-off between normal reconstruction fidelity and abnormal reconstruction distinguishability, which damages the performance. In this paper, we find that the above trade-off can be better mitigated by leveraging the distinct frequency biases between normal and abnormal reconstruction errors. To this end, we propose Frequency-aware Image Restoration (FAIR), a novel self-supervised image restoration task that restores images from their high-frequency components. It enables precise reconstruction of normal patterns while mitigating unfavorable generalization to anomalies. Using only a simple vanilla UNet, FAIR achieves state-of-the-art performance with higher efficiency on various defect detection datasets. Code: https://github.com/liutongkun/FAIR.
Component-aware anomaly detection framework for adjustable and logical industrial visual inspection
May 15, 2023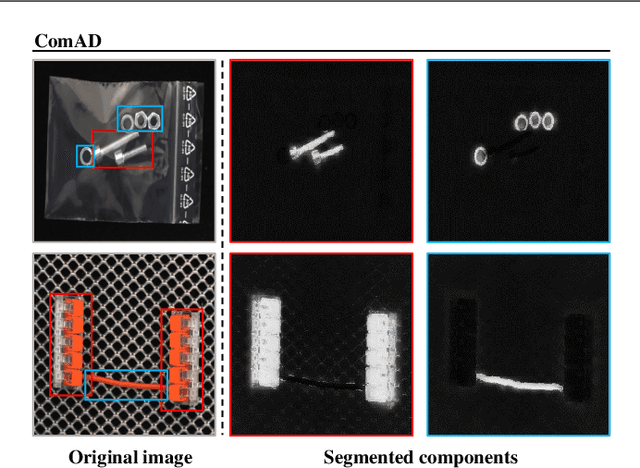
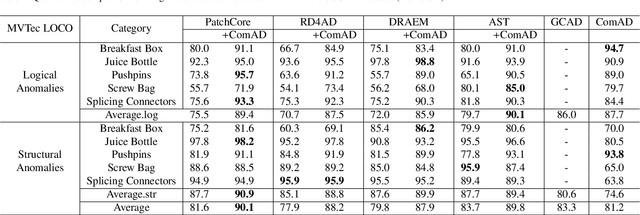
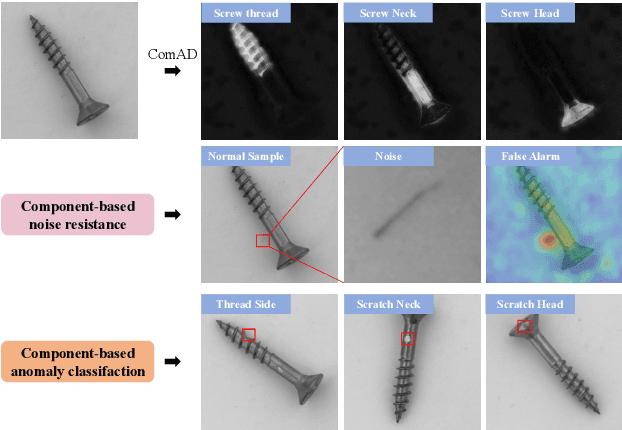
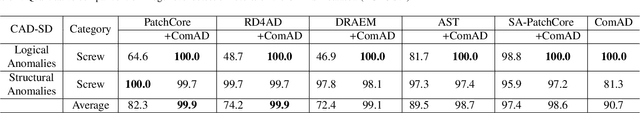
Abstract:Industrial visual inspection aims at detecting surface defects in products during the manufacturing process. Although existing anomaly detection models have shown great performance on many public benchmarks, their limited adjustability and ability to detect logical anomalies hinder their broader use in real-world settings. To this end, in this paper, we propose a novel component-aware anomaly detection framework (ComAD) which can simultaneously achieve adjustable and logical anomaly detection for industrial scenarios. Specifically, we propose to segment images into multiple components based on a lightweight and nearly training-free unsupervised semantic segmentation model. Then, we design an interpretable logical anomaly detection model through modeling the metrological features of each component and their relationships. Despite its simplicity, our framework achieves state-of-the-art performance on image-level logical anomaly detection. Meanwhile, segmenting a product image into multiple components provides a novel perspective for industrial visual inspection, demonstrating great potential in model customization, noise resistance, and anomaly classification. The code will be available at https://github.com/liutongkun/ComAD.
Reconstruction from edge image combined with color and gradient difference for industrial surface anomaly detection
Oct 26, 2022

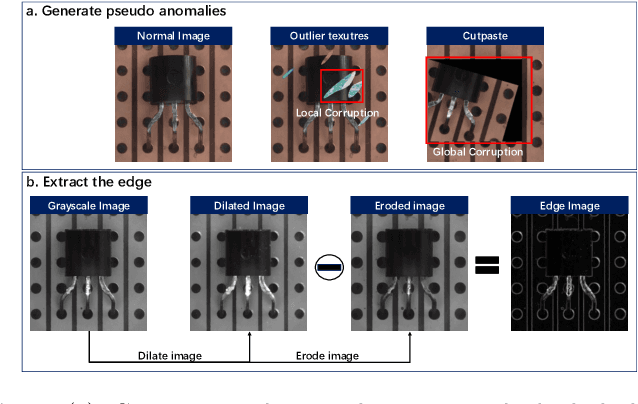
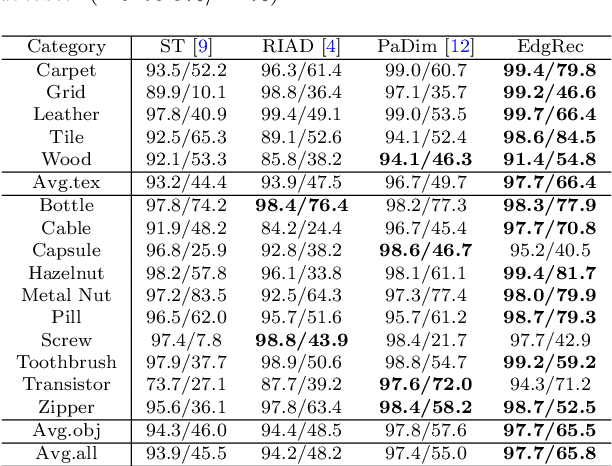
Abstract:Reconstruction-based methods are widely explored in industrial visual anomaly detection. Such methods commonly require the model to well reconstruct the normal patterns but fail in the anomalies, and thus the anomalies can be detected by evaluating the reconstruction errors. However, in practice, it's usually difficult to control the generalization boundary of the model. The model with an overly strong generalization capability can even well reconstruct the abnormal regions, making them less distinguishable, while the model with a poor generalization capability can not reconstruct those changeable high-frequency components in the normal regions, which ultimately leads to false positives. To tackle the above issue, we propose a new reconstruction network where we reconstruct the original RGB image from its gray value edges (EdgRec). Specifically, this is achieved by an UNet-type denoising autoencoder with skip connections. The input edge and skip connections can well preserve the high-frequency information in the original image. Meanwhile, the proposed restoration task can force the network to memorize the normal low-frequency and color information. Besides, the denoising design can prevent the model from directly copying the original high-frequent components. To evaluate the anomalies, we further propose a new interpretable hand-crafted evaluation function that considers both the color and gradient differences. Our method achieves competitive results on the challenging benchmark MVTec AD (97.8\% for detection and 97.7\% for localization, AUROC). In addition, we conduct experiments on the MVTec 3D-AD dataset and show convincing results using RGB images only. Our code will be available at https://github.com/liutongkun/EdgRec.
Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning for Dynamic Resource Management in 6G in-X Subnetworks
May 10, 2022

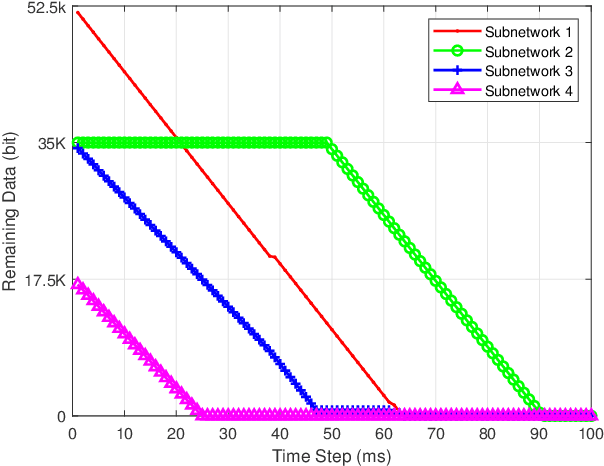
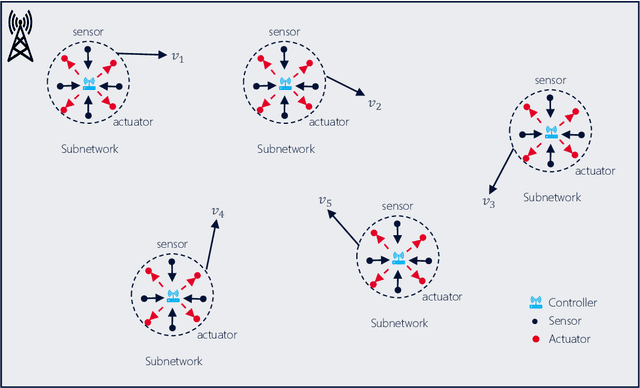
Abstract:The 6G network enables a subnetwork-wide evolution, resulting in a "network of subnetworks". However, due to the dynamic mobility of wireless subnetworks, the data transmission of intra-subnetwork and inter-subnetwork will inevitably interfere with each other, which poses a great challenge to radio resource management. Moreover, most of the existing approaches require the instantaneous channel gain between subnetworks, which are usually difficult to be collected. To tackle these issues, in this paper we propose a novel effective intelligent radio resource management method using multi-agent deep reinforcement learning (MARL), which only needs the sum of received power, named received signal strength indicator (RSSI), on each channel instead of channel gains. However, to directly separate individual interference from RSSI is an almost impossible thing. To this end, we further propose a novel MARL architecture, named GA-Net, which integrates a hard attention layer to model the importance distribution of inter-subnetwork relationships based on RSSI and exclude the impact of unrelated subnetworks, and employs a graph attention network with a multi-head attention layer to exact the features and calculate their weights that will impact individual throughput. Experimental results prove that our proposed framework significantly outperforms both traditional and MARL-based methods in various aspects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge