Zhuo Zhao
GeoRAG: A Question-Answering Approach from a Geographical Perspective
Apr 03, 2025



Abstract:Geographic Question Answering (GeoQA) addresses natural language queries in geographic domains to fulfill complex user demands and improve information retrieval efficiency. Traditional QA systems, however, suffer from limited comprehension, low retrieval accuracy, weak interactivity, and inadequate handling of complex tasks, hindering precise information acquisition. This study presents GeoRAG, a knowledge-enhanced QA framework integrating domain-specific fine-tuning and prompt engineering with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technology to enhance geographic knowledge retrieval accuracy and user interaction. The methodology involves four components: (1) A structured geographic knowledge base constructed from 3267 corpora (research papers, monographs, and technical reports), categorized via a multi-agent approach into seven dimensions: semantic understanding, spatial location, geometric morphology, attribute characteristics, feature relationships, evolutionary processes, and operational mechanisms. This yielded 145234 classified entries and 875432 multi-dimensional QA pairs. (2) A multi-label text classifier based on BERT-Base-Chinese, trained to analyze query types through geographic dimension classification. (3) A retrieval evaluator leveraging QA pair data to assess query-document relevance, optimizing retrieval precision. (4) GeoPrompt templates engineered to dynamically integrate user queries with retrieved information, enhancing response quality through dimension-specific prompting. Comparative experiments demonstrate GeoRAG's superior performance over conventional RAG across multiple base models, validating its generalizability. This work advances geographic AI by proposing a novel paradigm for deploying large language models in domain-specific contexts, with implications for improving GeoQA systems scalability and accuracy in real-world applications.
Path-GPTOmic: A Balanced Multi-modal Learning Framework for Survival Outcome Prediction
Mar 18, 2024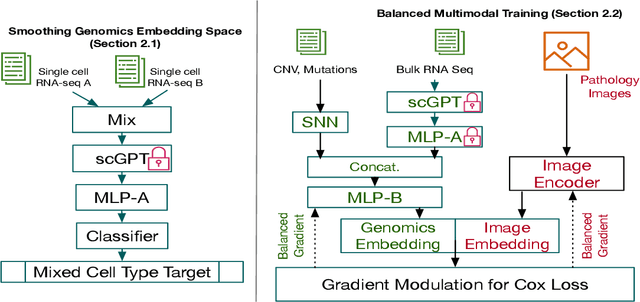
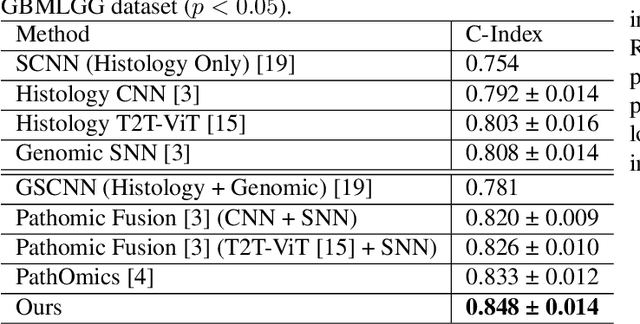

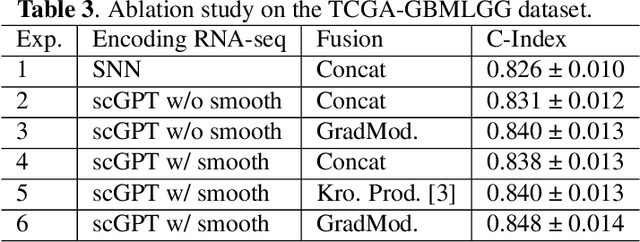
Abstract:For predicting cancer survival outcomes, standard approaches in clinical research are often based on two main modalities: pathology images for observing cell morphology features, and genomic (e.g., bulk RNA-seq) for quantifying gene expressions. However, existing pathology-genomic multi-modal algorithms face significant challenges: (1) Valuable biological insights regarding genes and gene-gene interactions are frequently overlooked; (2) one modality often dominates the optimization process, causing inadequate training for the other modality. In this paper, we introduce a new multi-modal ``Path-GPTOmic" framework for cancer survival outcome prediction. First, to extract valuable biological insights, we regulate the embedding space of a foundation model, scGPT, initially trained on single-cell RNA-seq data, making it adaptable for bulk RNA-seq data. Second, to address the imbalance-between-modalities problem, we propose a gradient modulation mechanism tailored to the Cox partial likelihood loss for survival prediction. The contributions of the modalities are dynamically monitored and adjusted during the training process, encouraging that both modalities are sufficiently trained. Evaluated on two TCGA(The Cancer Genome Atlas) datasets, our model achieves substantially improved survival prediction accuracy.
SHMC-Net: A Mask-guided Feature Fusion Network for Sperm Head Morphology Classification
Feb 07, 2024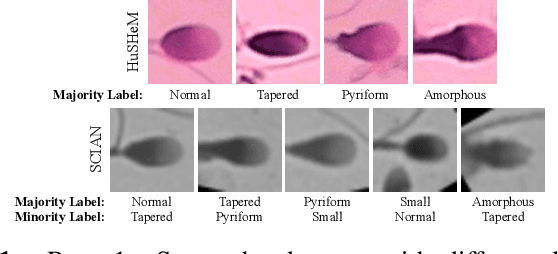
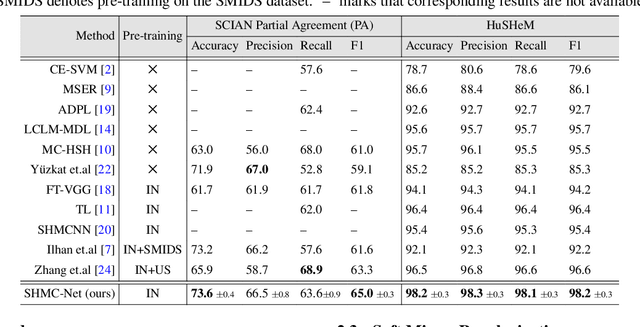
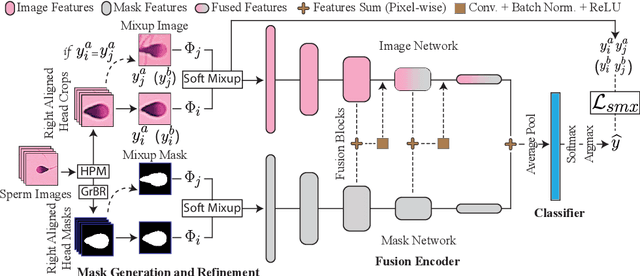
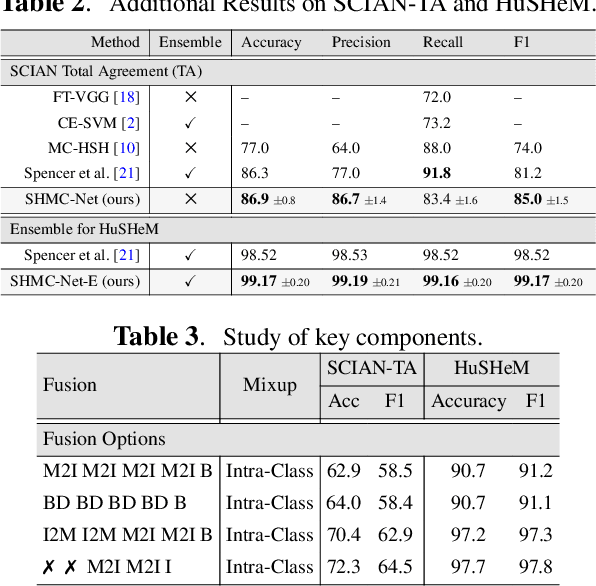
Abstract:Male infertility accounts for about one-third of global infertility cases. Manual assessment of sperm abnormalities through head morphology analysis encounters issues of observer variability and diagnostic discrepancies among experts. Its alternative, Computer-Assisted Semen Analysis (CASA), suffers from low-quality sperm images, small datasets, and noisy class labels. We propose a new approach for sperm head morphology classification, called SHMC-Net, which uses segmentation masks of sperm heads to guide the morphology classification of sperm images. SHMC-Net generates reliable segmentation masks using image priors, refines object boundaries with an efficient graph-based method, and trains an image network with sperm head crops and a mask network with the corresponding masks. In the intermediate stages of the networks, image and mask features are fused with a fusion scheme to better learn morphological features. To handle noisy class labels and regularize training on small datasets, SHMC-Net applies Soft Mixup to combine mixup augmentation and a loss function. We achieve state-of-the-art results on SCIAN and HuSHeM datasets, outperforming methods that use additional pre-training or costly ensembling techniques.
FAIR: Frequency-aware Image Restoration for Industrial Visual Anomaly Detection
Sep 13, 2023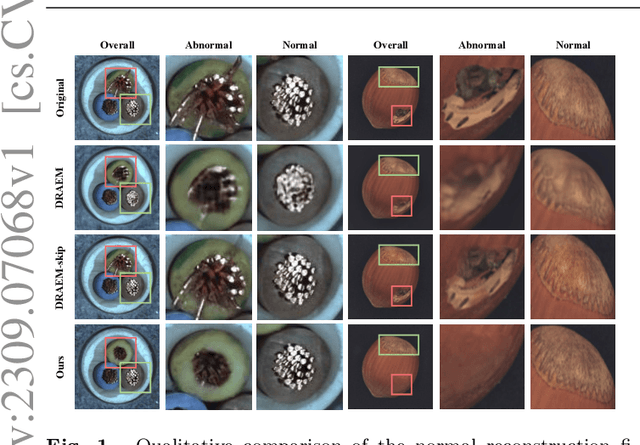
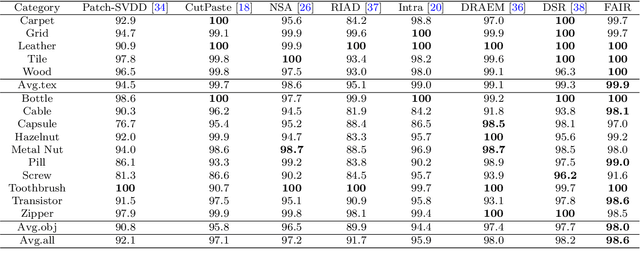
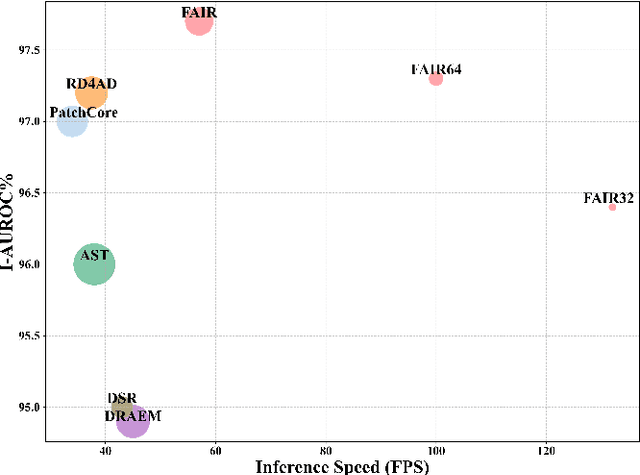
Abstract:Image reconstruction-based anomaly detection models are widely explored in industrial visual inspection. However, existing models usually suffer from the trade-off between normal reconstruction fidelity and abnormal reconstruction distinguishability, which damages the performance. In this paper, we find that the above trade-off can be better mitigated by leveraging the distinct frequency biases between normal and abnormal reconstruction errors. To this end, we propose Frequency-aware Image Restoration (FAIR), a novel self-supervised image restoration task that restores images from their high-frequency components. It enables precise reconstruction of normal patterns while mitigating unfavorable generalization to anomalies. Using only a simple vanilla UNet, FAIR achieves state-of-the-art performance with higher efficiency on various defect detection datasets. Code: https://github.com/liutongkun/FAIR.
Component-aware anomaly detection framework for adjustable and logical industrial visual inspection
May 15, 2023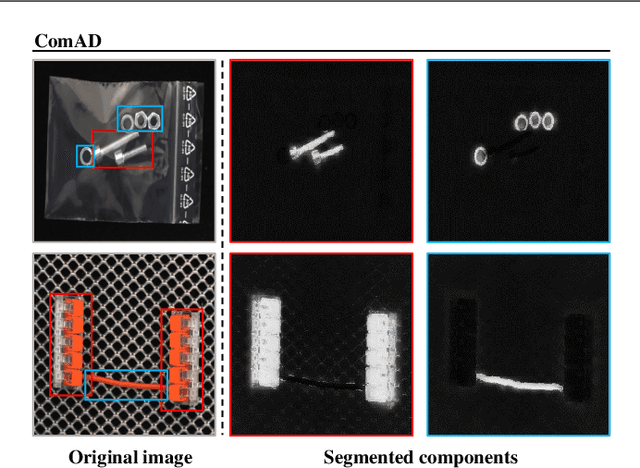
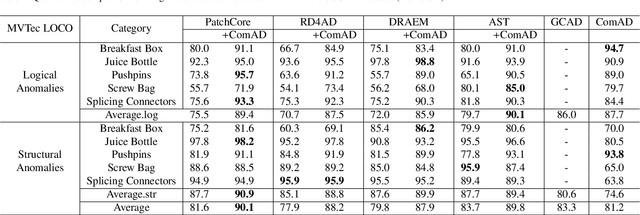
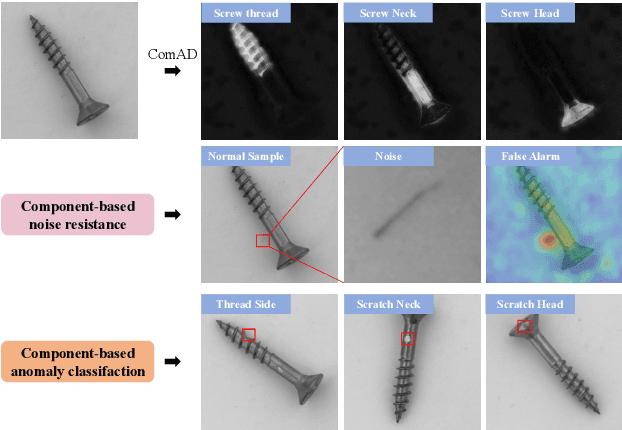
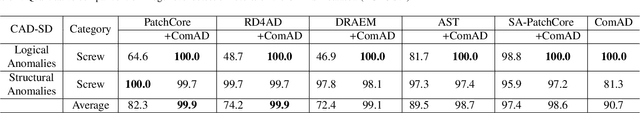
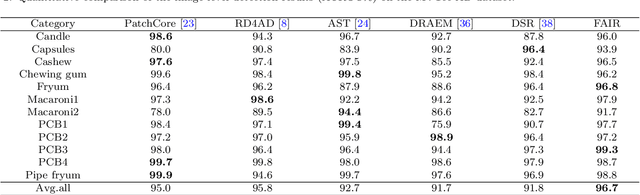
Abstract:Industrial visual inspection aims at detecting surface defects in products during the manufacturing process. Although existing anomaly detection models have shown great performance on many public benchmarks, their limited adjustability and ability to detect logical anomalies hinder their broader use in real-world settings. To this end, in this paper, we propose a novel component-aware anomaly detection framework (ComAD) which can simultaneously achieve adjustable and logical anomaly detection for industrial scenarios. Specifically, we propose to segment images into multiple components based on a lightweight and nearly training-free unsupervised semantic segmentation model. Then, we design an interpretable logical anomaly detection model through modeling the metrological features of each component and their relationships. Despite its simplicity, our framework achieves state-of-the-art performance on image-level logical anomaly detection. Meanwhile, segmenting a product image into multiple components provides a novel perspective for industrial visual inspection, demonstrating great potential in model customization, noise resistance, and anomaly classification. The code will be available at https://github.com/liutongkun/ComAD.
Fair Credit Scorer through Bayesian Approach
Jan 20, 2023



Abstract:Machine learning currently plays an increasingly important role in people's lives in areas such as credit scoring, auto-driving, disease diagnosing, and insurance quoting. However, in many of these areas, machine learning models have performed unfair behaviors against some sub-populations, such as some particular groups of race, sex, and age. These unfair behaviors can be on account of the pre-existing bias in the training dataset due to historical and social factors. In this paper, we focus on a real-world application of credit scoring and construct a fair prediction model by introducing latent variables to remove the correlation between protected attributes, such as sex and age, with the observable feature inputs, including house and job. For detailed implementation, we apply Bayesian approaches, including the Markov Chain Monte Carlo simulation, to estimate our proposed fair model.
Reconstruction from edge image combined with color and gradient difference for industrial surface anomaly detection
Oct 26, 2022

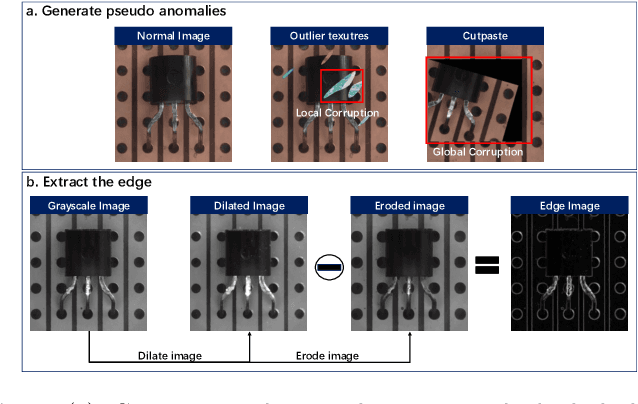
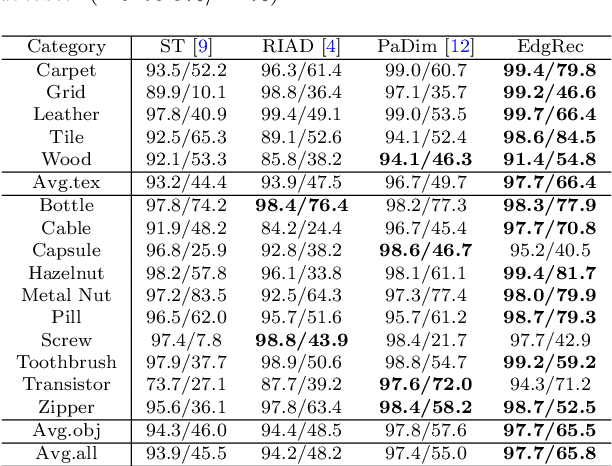
Abstract:Reconstruction-based methods are widely explored in industrial visual anomaly detection. Such methods commonly require the model to well reconstruct the normal patterns but fail in the anomalies, and thus the anomalies can be detected by evaluating the reconstruction errors. However, in practice, it's usually difficult to control the generalization boundary of the model. The model with an overly strong generalization capability can even well reconstruct the abnormal regions, making them less distinguishable, while the model with a poor generalization capability can not reconstruct those changeable high-frequency components in the normal regions, which ultimately leads to false positives. To tackle the above issue, we propose a new reconstruction network where we reconstruct the original RGB image from its gray value edges (EdgRec). Specifically, this is achieved by an UNet-type denoising autoencoder with skip connections. The input edge and skip connections can well preserve the high-frequency information in the original image. Meanwhile, the proposed restoration task can force the network to memorize the normal low-frequency and color information. Besides, the denoising design can prevent the model from directly copying the original high-frequent components. To evaluate the anomalies, we further propose a new interpretable hand-crafted evaluation function that considers both the color and gradient differences. Our method achieves competitive results on the challenging benchmark MVTec AD (97.8\% for detection and 97.7\% for localization, AUROC). In addition, we conduct experiments on the MVTec 3D-AD dataset and show convincing results using RGB images only. Our code will be available at https://github.com/liutongkun/EdgRec.
Hierarchical Self-Supervised Learning for Medical Image Segmentation Based on Multi-Domain Data Aggregation
Jul 10, 2021



Abstract:A large labeled dataset is a key to the success of supervised deep learning, but for medical image segmentation, it is highly challenging to obtain sufficient annotated images for model training. In many scenarios, unannotated images are abundant and easy to acquire. Self-supervised learning (SSL) has shown great potentials in exploiting raw data information and representation learning. In this paper, we propose Hierarchical Self-Supervised Learning (HSSL), a new self-supervised framework that boosts medical image segmentation by making good use of unannotated data. Unlike the current literature on task-specific self-supervised pretraining followed by supervised fine-tuning, we utilize SSL to learn task-agnostic knowledge from heterogeneous data for various medical image segmentation tasks. Specifically, we first aggregate a dataset from several medical challenges, then pre-train the network in a self-supervised manner, and finally fine-tune on labeled data. We develop a new loss function by combining contrastive loss and classification loss and pretrain an encoder-decoder architecture for segmentation tasks. Our extensive experiments show that multi-domain joint pre-training benefits downstream segmentation tasks and outperforms single-domain pre-training significantly. Compared to learning from scratch, our new method yields better performance on various tasks (e.g., +0.69% to +18.60% in Dice scores with 5% of annotated data). With limited amounts of training data, our method can substantially bridge the performance gap w.r.t. denser annotations (e.g., 10% vs.~100% of annotated data).
A New Ensemble Learning Framework for 3D Biomedical Image Segmentation
Dec 10, 2018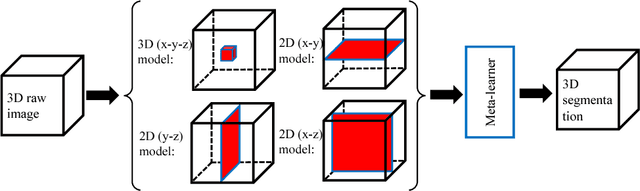
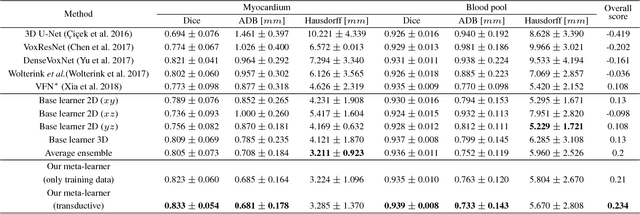
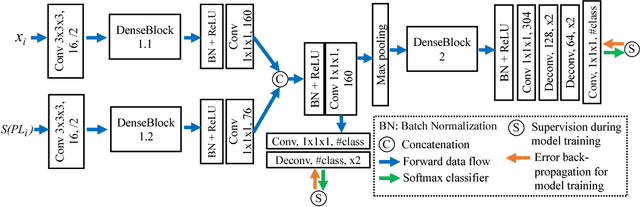
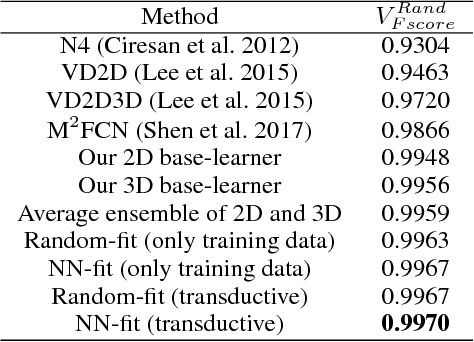
Abstract:3D image segmentation plays an important role in biomedical image analysis. Many 2D and 3D deep learning models have achieved state-of-the-art segmentation performance on 3D biomedical image datasets. Yet, 2D and 3D models have their own strengths and weaknesses, and by unifying them together, one may be able to achieve more accurate results. In this paper, we propose a new ensemble learning framework for 3D biomedical image segmentation that combines the merits of 2D and 3D models. First, we develop a fully convolutional network based meta-learner to learn how to improve the results from 2D and 3D models (base-learners). Then, to minimize over-fitting for our sophisticated meta-learner, we devise a new training method that uses the results of the base-learners as multiple versions of "ground truths". Furthermore, since our new meta-learner training scheme does not depend on manual annotation, it can utilize abundant unlabeled 3D image data to further improve the model. Extensive experiments on two public datasets (the HVSMR 2016 Challenge dataset and the mouse piriform cortex dataset) show that our approach is effective under fully-supervised, semi-supervised, and transductive settings, and attains superior performance over state-of-the-art image segmentation methods.
Deep Learning Based Instance Segmentation in 3D Biomedical Images Using Weak Annotation
Jun 28, 2018



Abstract:Instance segmentation in 3D images is a fundamental task in biomedical image analysis. While deep learning models often work well for 2D instance segmentation, 3D instance segmentation still faces critical challenges, such as insufficient training data due to various annotation difficulties in 3D biomedical images. Common 3D annotation methods (e.g., full voxel annotation) incur high workloads and costs for labeling enough instances for training deep learning 3D instance segmentation models. In this paper, we propose a new weak annotation approach for training a fast deep learning 3D instance segmentation model without using full voxel mask annotation. Our approach needs only 3D bounding boxes for all instances and full voxel annotation for a small fraction of the instances, and uses a novel two-stage 3D instance segmentation model utilizing these two kinds of annotation, respectively. We evaluate our approach on several biomedical image datasets, and the experimental results show that (1) with full annotated boxes and a small amount of masks, our approach can achieve similar performance as the best known methods using full annotation, and (2) with similar annotation time, our approach outperforms the best known methods that use full annotation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge