Wen Luo
ViTCoP: Accelerating Large Vision-Language Models via Visual and Textual Semantic Collaborative Pruning
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) incur high computational costs due to significant redundancy in their visual tokens. To effectively reduce this cost, researchers have proposed various visual token pruning methods. However, existing methods are generally limited, either losing critical visual information prematurely due to pruning in the vision encoder, or leading to information redundancy among the selected tokens due to pruning in the Large Language Models (LLMs). To address these challenges, we propose a Visual and Textual Semantic Collaborative Pruning framework (ViTCoP) that combines redundancy filtering in the vision encoder with step-wise co-pruning within the LLM based on its hierarchical characteristics, to efficiently preserve critical and informationally diverse visual tokens. Meanwhile, to ensure compatibility with acceleration techniques like FlashAttention, we introduce the L2 norm of K-vectors as the token saliency metric in the LLM. Extensive experiments on various Large Vision-Language Models demonstrate that ViTCoP not only achieves state-of-the-art performance surpassing existing methods on both image and video understanding tasks, but also significantly reduces model inference latency and GPU memory consumption. Notably, its performance advantage over other methods becomes even more pronounced under extreme pruning rates.
Two Pathways to Truthfulness: On the Intrinsic Encoding of LLM Hallucinations
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Despite their impressive capabilities, large language models (LLMs) frequently generate hallucinations. Previous work shows that their internal states encode rich signals of truthfulness, yet the origins and mechanisms of these signals remain unclear. In this paper, we demonstrate that truthfulness cues arise from two distinct information pathways: (1) a Question-Anchored pathway that depends on question-answer information flow, and (2) an Answer-Anchored pathway that derives self-contained evidence from the generated answer itself. First, we validate and disentangle these pathways through attention knockout and token patching. Afterwards, we uncover notable and intriguing properties of these two mechanisms. Further experiments reveal that (1) the two mechanisms are closely associated with LLM knowledge boundaries; and (2) internal representations are aware of their distinctions. Finally, building on these insightful findings, two applications are proposed to enhance hallucination detection performance. Overall, our work provides new insight into how LLMs internally encode truthfulness, offering directions for more reliable and self-aware generative systems.
Mitigating Overthinking through Reasoning Shaping
Oct 10, 2025Abstract:Large reasoning models (LRMs) boosted by Reinforcement Learning from Verifier Reward (RLVR) have shown great power in problem solving, yet they often cause overthinking: excessive, meandering reasoning that inflates computational cost. Prior designs of penalization in RLVR manage to reduce token consumption while often harming model performance, which arises from the oversimplicity of token-level supervision. In this paper, we argue that the granularity of supervision plays a crucial role in balancing efficiency and accuracy, and propose Group Relative Segment Penalization (GRSP), a step-level method to regularize reasoning. Since preliminary analyses show that reasoning segments are strongly correlated with token consumption and model performance, we design a length-aware weighting mechanism across segment clusters. Extensive experiments demonstrate that GRSP achieves superior token efficiency without heavily compromising accuracy, especially the advantages with harder problems. Moreover, GRSP stabilizes RL training and scales effectively across model sizes.
Well Begun is Half Done: Low-resource Preference Alignment by Weak-to-Strong Decoding
Jun 09, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) require alignment with human preferences to avoid generating offensive, false, or meaningless content. Recently, low-resource methods for LLM alignment have been popular, while still facing challenges in obtaining both high-quality and aligned content. Motivated by the observation that the difficulty of generating aligned responses is concentrated at the beginning of decoding, we propose a novel framework, Weak-to-Strong Decoding (WSD), to enhance the alignment ability of base models by the guidance of a small aligned model. The small model first drafts well-aligned beginnings, followed by the large base model to continue the rest, controlled by a well-designed auto-switch mechanism. We also collect a new dataset, GenerAlign, to fine-tune a small-sized Pilot-3B as the draft model, which effectively enhances different base models under the WSD framework to outperform all baseline methods, while avoiding degradation on downstream tasks, termed as the alignment tax. Extensive experiments are further conducted to examine the impact of different settings and time efficiency, as well as analyses on the intrinsic mechanisms of WSD in depth.
TIME: A Multi-level Benchmark for Temporal Reasoning of LLMs in Real-World Scenarios
May 19, 2025Abstract:Temporal reasoning is pivotal for Large Language Models (LLMs) to comprehend the real world. However, existing works neglect the real-world challenges for temporal reasoning: (1) intensive temporal information, (2) fast-changing event dynamics, and (3) complex temporal dependencies in social interactions. To bridge this gap, we propose a multi-level benchmark TIME, designed for temporal reasoning in real-world scenarios. TIME consists of 38,522 QA pairs, covering 3 levels with 11 fine-grained sub-tasks. This benchmark encompasses 3 sub-datasets reflecting different real-world challenges: TIME-Wiki, TIME-News, and TIME-Dial. We conduct extensive experiments on reasoning models and non-reasoning models. And we conducted an in-depth analysis of temporal reasoning performance across diverse real-world scenarios and tasks, and summarized the impact of test-time scaling on temporal reasoning capabilities. Additionally, we release TIME-Lite, a human-annotated subset to foster future research and standardized evaluation in temporal reasoning. The code is available at https://github.com/sylvain-wei/TIME , and the dataset is available at https://huggingface.co/datasets/SylvainWei/TIME .
GeoRAG: A Question-Answering Approach from a Geographical Perspective
Apr 03, 2025



Abstract:Geographic Question Answering (GeoQA) addresses natural language queries in geographic domains to fulfill complex user demands and improve information retrieval efficiency. Traditional QA systems, however, suffer from limited comprehension, low retrieval accuracy, weak interactivity, and inadequate handling of complex tasks, hindering precise information acquisition. This study presents GeoRAG, a knowledge-enhanced QA framework integrating domain-specific fine-tuning and prompt engineering with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technology to enhance geographic knowledge retrieval accuracy and user interaction. The methodology involves four components: (1) A structured geographic knowledge base constructed from 3267 corpora (research papers, monographs, and technical reports), categorized via a multi-agent approach into seven dimensions: semantic understanding, spatial location, geometric morphology, attribute characteristics, feature relationships, evolutionary processes, and operational mechanisms. This yielded 145234 classified entries and 875432 multi-dimensional QA pairs. (2) A multi-label text classifier based on BERT-Base-Chinese, trained to analyze query types through geographic dimension classification. (3) A retrieval evaluator leveraging QA pair data to assess query-document relevance, optimizing retrieval precision. (4) GeoPrompt templates engineered to dynamically integrate user queries with retrieved information, enhancing response quality through dimension-specific prompting. Comparative experiments demonstrate GeoRAG's superior performance over conventional RAG across multiple base models, validating its generalizability. This work advances geographic AI by proposing a novel paradigm for deploying large language models in domain-specific contexts, with implications for improving GeoQA systems scalability and accuracy in real-world applications.
Odysseus Navigates the Sirens' Song: Dynamic Focus Decoding for Factual and Diverse Open-Ended Text Generation
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly required to generate text that is both factually accurate and diverse across various open-ended applications. However, current stochastic decoding methods struggle to balance such objectives. We introduce Dynamic Focus Decoding (DFD), a novel plug-and-play stochastic approach that resolves this trade-off without requiring additional data, knowledge, or models. DFD adaptively adjusts the decoding focus based on distributional differences across layers, leveraging the modular and hierarchical nature of factual knowledge within LLMs. This dynamic adjustment improves factuality in knowledge-intensive decoding steps and promotes diversity in less knowledge-reliant steps. DFD can be easily integrated with existing decoding methods, enhancing both factuality and diversity with minimal computational overhead. Extensive experiments across seven datasets demonstrate that DFD significantly improves performance, providing a scalable and efficient solution for open-ended text generation.
FEA-Bench: A Benchmark for Evaluating Repository-Level Code Generation for Feature Implementation
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Implementing new features in repository-level codebases is a crucial application of code generation models. However, current benchmarks lack a dedicated evaluation framework for this capability. To fill this gap, we introduce FEA-Bench, a benchmark designed to assess the ability of large language models (LLMs) to perform incremental development within code repositories. We collect pull requests from 83 GitHub repositories and use rule-based and intent-based filtering to construct task instances focused on new feature development. Each task instance containing code changes is paired with relevant unit test files to ensure that the solution can be verified. The feature implementation requires LLMs to simultaneously possess code completion capabilities for new components and code editing abilities for other relevant parts in the code repository, providing a more comprehensive evaluation method of LLMs' automated software engineering capabilities. Experimental results show that LLMs perform significantly worse in the FEA-Bench, highlighting considerable challenges in such repository-level incremental code development.
Explanation based In-Context Demonstrations Retrieval for Multilingual Grammatical Error Correction
Feb 12, 2025



Abstract:Grammatical error correction (GEC) aims to correct grammatical, spelling, and semantic errors in natural language text. With the growing of large language models (LLMs), direct text generation has gradually become the focus of the GEC methods, and few-shot in-context learning presents a cost-effective solution. However, selecting effective in-context examples remains challenging, as the similarity between input texts does not necessarily correspond to similar grammatical error patterns. In this paper, we propose a novel retrieval method based on natural language grammatical error explanations (GEE) to address this issue. Our method retrieves suitable few-shot demonstrations by matching the GEE of the test input with that of pre-constructed database samples, where explanations for erroneous samples are generated by LLMs. We conducted multilingual GEC few-shot experiments on both major open-source and closed-source LLMs. Experiments across five languages show that our method outperforms existing semantic and BM25-based retrieval techniques, without requiring additional training or language adaptation. This also suggests that matching error patterns is key to selecting examples.
SiamSeg: Self-Training with Contrastive Learning for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation in Remote Sensing
Oct 17, 2024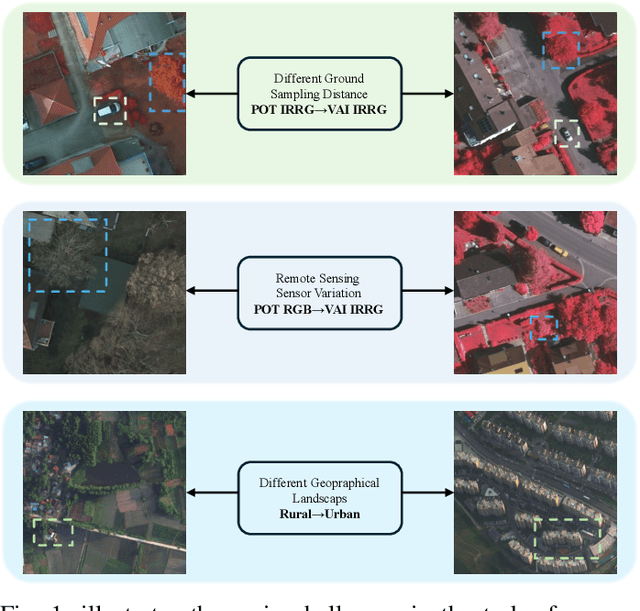
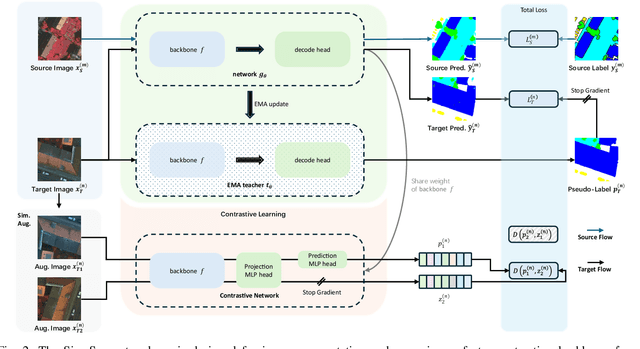
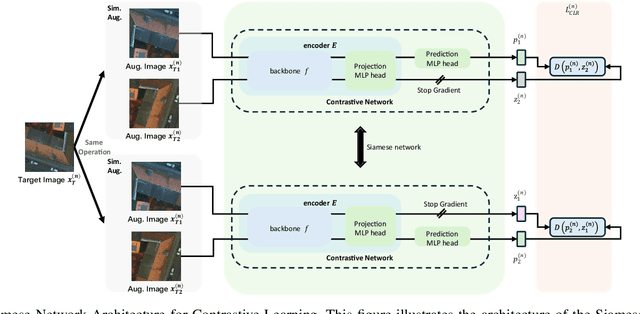
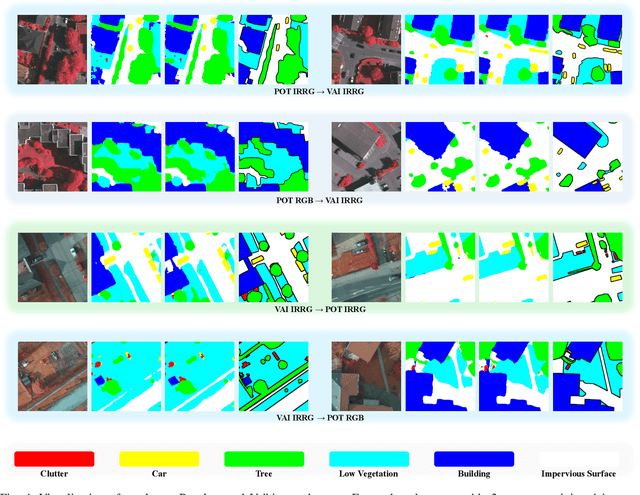
Abstract:Semantic segmentation of remote sensing (RS) images is a challenging task with significant potential across various applications. Deep learning, especially supervised learning with large-scale labeled datasets, has greatly advanced this field. However, acquiring high-quality labeled data is expensive and time-consuming. Moreover, variations in ground sampling distance (GSD), imaging equipment, and geographic diversity contribute to domain shifts between datasets, which pose significant challenges to models trained solely on source domain data, leading to poor cross-domain performance. Domain shift is well-known for undermining a model's generalization ability in the target domain. To address this, unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) has emerged as a promising solution, enabling models to learn from unlabeled target domain data while training on labeled source domain data. Recent advancements, particularly in self-supervised learning via pseudo-label generation, have shown potential in mitigating domain discrepancies. Strategies combining source and target domain images with their true and pseudo labels for self-supervised training have been effective in addressing domain bias. Despite progress in computer vision, the application of pseudo-labeling methods to RS image segmentation remains underexplored.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge