Muhammed Kocabas
FUSION: Full-Body Unified Motion Prior for Body and Hands via Diffusion
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Hands are central to interacting with our surroundings and conveying gestures, making their inclusion essential for full-body motion synthesis. Despite this, existing human motion synthesis methods fall short: some ignore hand motions entirely, while others generate full-body motions only for narrowly scoped tasks under highly constrained settings. A key obstacle is the lack of large-scale datasets that jointly capture diverse full-body motion with detailed hand articulation. While some datasets capture both, they are limited in scale and diversity. Conversely, large-scale datasets typically focus either on body motion without hands or on hand motions without the body. To overcome this, we curate and unify existing hand motion datasets with large-scale body motion data to generate full-body sequences that capture both hand and body. We then propose the first diffusion-based unconditional full-body motion prior, FUSION, which jointly models body and hand motion. Despite using a pose-based motion representation, FUSION surpasses state-of-the-art skeletal control models on the Keypoint Tracking task in the HumanML3D dataset and achieves superior motion naturalness. Beyond standard benchmarks, we demonstrate that FUSION can go beyond typical uses of motion priors through two applications: (1) generating detailed full-body motion including fingers during interaction given the motion of an object, and (2) generating Self-Interaction motions using an LLM to transform natural language cues into actionable motion constraints. For these applications, we develop an optimization pipeline that refines the latent space of our diffusion model to generate task-specific motions. Experiments on these tasks highlight precise control over hand motion while maintaining plausible full-body coordination. The code will be public.
BEDLAM2.0: Synthetic Humans and Cameras in Motion
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Inferring 3D human motion from video remains a challenging problem with many applications. While traditional methods estimate the human in image coordinates, many applications require human motion to be estimated in world coordinates. This is particularly challenging when there is both human and camera motion. Progress on this topic has been limited by the lack of rich video data with ground truth human and camera movement. We address this with BEDLAM2.0, a new dataset that goes beyond the popular BEDLAM dataset in important ways. In addition to introducing more diverse and realistic cameras and camera motions, BEDLAM2.0 increases diversity and realism of body shape, motions, clothing, hair, and 3D environments. Additionally, it adds shoes, which were missing in BEDLAM. BEDLAM has become a key resource for training 3D human pose and motion regressors today and we show that BEDLAM2.0 is significantly better, particularly for training methods that estimate humans in world coordinates. We compare state-of-the art methods trained on BEDLAM and BEDLAM2.0, and find that BEDLAM2.0 significantly improves accuracy over BEDLAM. For research purposes, we provide the rendered videos, ground truth body parameters, and camera motions. We also provide the 3D assets to which we have rights and links to those from third parties.
PromptHMR: Promptable Human Mesh Recovery
Apr 08, 2025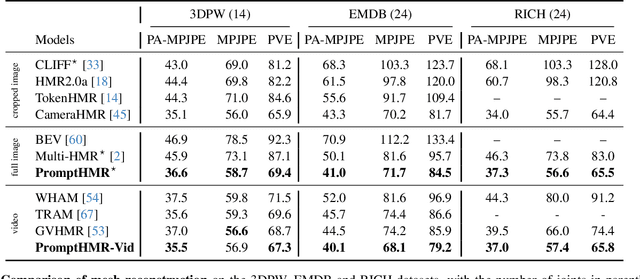
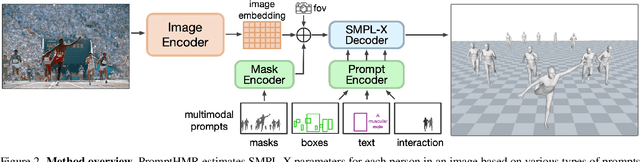
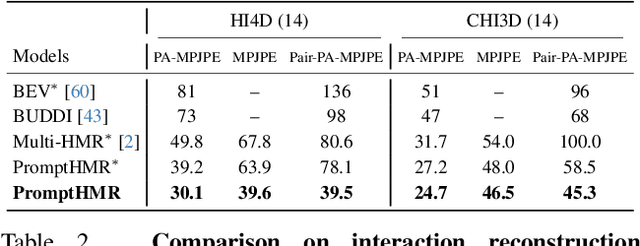
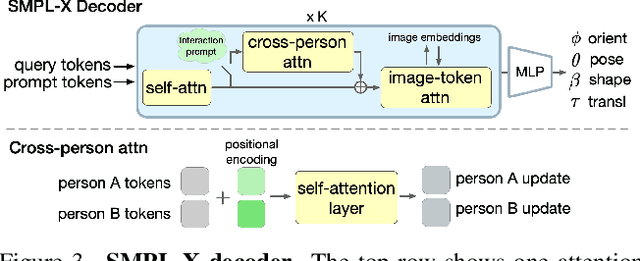
Abstract:Human pose and shape (HPS) estimation presents challenges in diverse scenarios such as crowded scenes, person-person interactions, and single-view reconstruction. Existing approaches lack mechanisms to incorporate auxiliary "side information" that could enhance reconstruction accuracy in such challenging scenarios. Furthermore, the most accurate methods rely on cropped person detections and cannot exploit scene context while methods that process the whole image often fail to detect people and are less accurate than methods that use crops. While recent language-based methods explore HPS reasoning through large language or vision-language models, their metric accuracy is well below the state of the art. In contrast, we present PromptHMR, a transformer-based promptable method that reformulates HPS estimation through spatial and semantic prompts. Our method processes full images to maintain scene context and accepts multiple input modalities: spatial prompts like bounding boxes and masks, and semantic prompts like language descriptions or interaction labels. PromptHMR demonstrates robust performance across challenging scenarios: estimating people from bounding boxes as small as faces in crowded scenes, improving body shape estimation through language descriptions, modeling person-person interactions, and producing temporally coherent motions in videos. Experiments on benchmarks show that PromptHMR achieves state-of-the-art performance while offering flexible prompt-based control over the HPS estimation process.
HMP: Hand Motion Priors for Pose and Shape Estimation from Video
Dec 27, 2023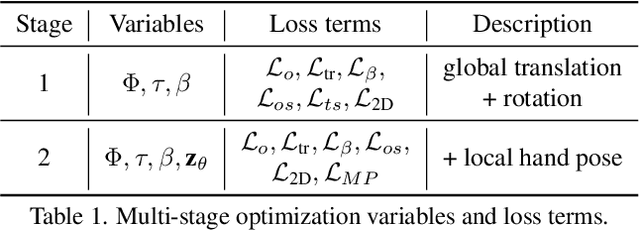
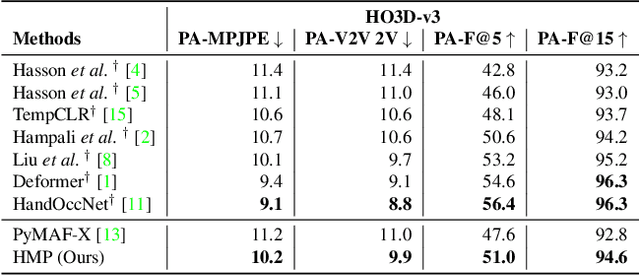


Abstract:Understanding how humans interact with the world necessitates accurate 3D hand pose estimation, a task complicated by the hand's high degree of articulation, frequent occlusions, self-occlusions, and rapid motions. While most existing methods rely on single-image inputs, videos have useful cues to address aforementioned issues. However, existing video-based 3D hand datasets are insufficient for training feedforward models to generalize to in-the-wild scenarios. On the other hand, we have access to large human motion capture datasets which also include hand motions, e.g. AMASS. Therefore, we develop a generative motion prior specific for hands, trained on the AMASS dataset which features diverse and high-quality hand motions. This motion prior is then employed for video-based 3D hand motion estimation following a latent optimization approach. Our integration of a robust motion prior significantly enhances performance, especially in occluded scenarios. It produces stable, temporally consistent results that surpass conventional single-frame methods. We demonstrate our method's efficacy via qualitative and quantitative evaluations on the HO3D and DexYCB datasets, with special emphasis on an occlusion-focused subset of HO3D. Code is available at https://hmp.is.tue.mpg.de
HOLD: Category-agnostic 3D Reconstruction of Interacting Hands and Objects from Video
Nov 30, 2023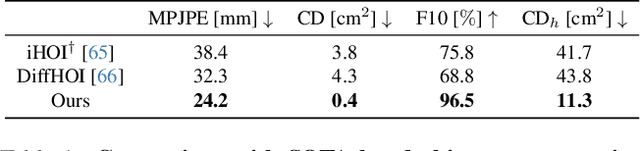
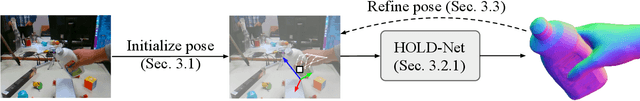
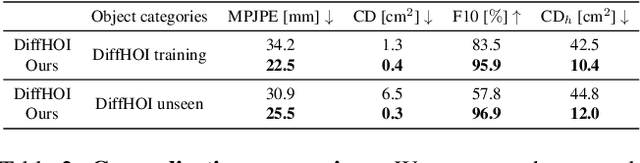
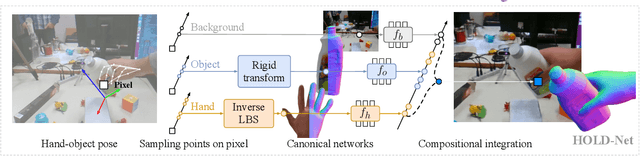
Abstract:Since humans interact with diverse objects every day, the holistic 3D capture of these interactions is important to understand and model human behaviour. However, most existing methods for hand-object reconstruction from RGB either assume pre-scanned object templates or heavily rely on limited 3D hand-object data, restricting their ability to scale and generalize to more unconstrained interaction settings. To this end, we introduce HOLD -- the first category-agnostic method that reconstructs an articulated hand and object jointly from a monocular interaction video. We develop a compositional articulated implicit model that can reconstruct disentangled 3D hand and object from 2D images. We also further incorporate hand-object constraints to improve hand-object poses and consequently the reconstruction quality. Our method does not rely on 3D hand-object annotations while outperforming fully-supervised baselines in both in-the-lab and challenging in-the-wild settings. Moreover, we qualitatively show its robustness in reconstructing from in-the-wild videos. Code: https://github.com/zc-alexfan/hold
HUGS: Human Gaussian Splats
Nov 29, 2023Abstract:Recent advances in neural rendering have improved both training and rendering times by orders of magnitude. While these methods demonstrate state-of-the-art quality and speed, they are designed for photogrammetry of static scenes and do not generalize well to freely moving humans in the environment. In this work, we introduce Human Gaussian Splats (HUGS) that represents an animatable human together with the scene using 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). Our method takes only a monocular video with a small number of (50-100) frames, and it automatically learns to disentangle the static scene and a fully animatable human avatar within 30 minutes. We utilize the SMPL body model to initialize the human Gaussians. To capture details that are not modeled by SMPL (e.g. cloth, hairs), we allow the 3D Gaussians to deviate from the human body model. Utilizing 3D Gaussians for animated humans brings new challenges, including the artifacts created when articulating the Gaussians. We propose to jointly optimize the linear blend skinning weights to coordinate the movements of individual Gaussians during animation. Our approach enables novel-pose synthesis of human and novel view synthesis of both the human and the scene. We achieve state-of-the-art rendering quality with a rendering speed of 60 FPS while being ~100x faster to train over previous work. Our code will be announced here: https://github.com/apple/ml-hugs
PACE: Human and Camera Motion Estimation from in-the-wild Videos
Oct 20, 2023Abstract:We present a method to estimate human motion in a global scene from moving cameras. This is a highly challenging task due to the coupling of human and camera motions in the video. To address this problem, we propose a joint optimization framework that disentangles human and camera motions using both foreground human motion priors and background scene features. Unlike existing methods that use SLAM as initialization, we propose to tightly integrate SLAM and human motion priors in an optimization that is inspired by bundle adjustment. Specifically, we optimize human and camera motions to match both the observed human pose and scene features. This design combines the strengths of SLAM and motion priors, which leads to significant improvements in human and camera motion estimation. We additionally introduce a motion prior that is suitable for batch optimization, making our approach significantly more efficient than existing approaches. Finally, we propose a novel synthetic dataset that enables evaluating camera motion in addition to human motion from dynamic videos. Experiments on the synthetic and real-world RICH datasets demonstrate that our approach substantially outperforms prior art in recovering both human and camera motions.
Physically Plausible Full-Body Hand-Object Interaction Synthesis
Sep 14, 2023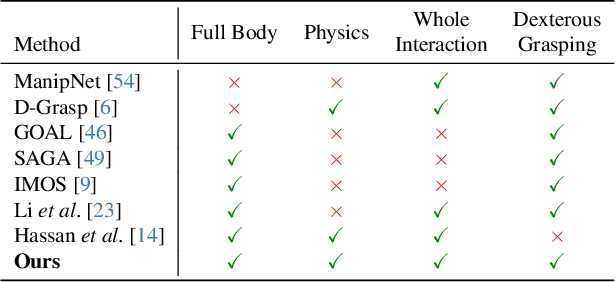
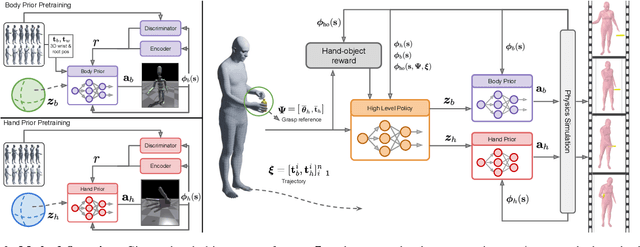
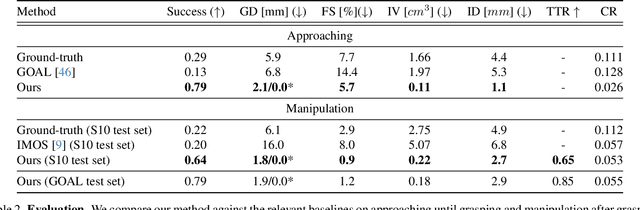
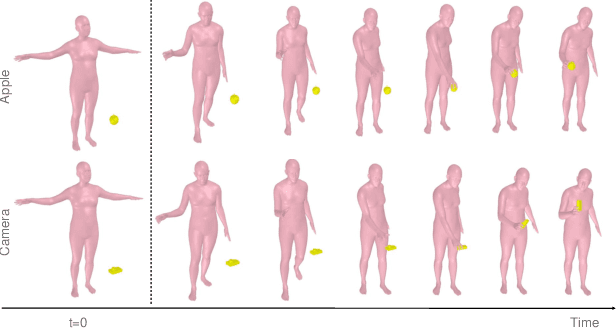
Abstract:We propose a physics-based method for synthesizing dexterous hand-object interactions in a full-body setting. While recent advancements have addressed specific facets of human-object interactions, a comprehensive physics-based approach remains a challenge. Existing methods often focus on isolated segments of the interaction process and rely on data-driven techniques that may result in artifacts. In contrast, our proposed method embraces reinforcement learning (RL) and physics simulation to mitigate the limitations of data-driven approaches. Through a hierarchical framework, we first learn skill priors for both body and hand movements in a decoupled setting. The generic skill priors learn to decode a latent skill embedding into the motion of the underlying part. A high-level policy then controls hand-object interactions in these pretrained latent spaces, guided by task objectives of grasping and 3D target trajectory following. It is trained using a novel reward function that combines an adversarial style term with a task reward, encouraging natural motions while fulfilling the task incentives. Our method successfully accomplishes the complete interaction task, from approaching an object to grasping and subsequent manipulation. We compare our approach against kinematics-based baselines and show that it leads to more physically plausible motions.
Reconstructing Action-Conditioned Human-Object Interactions Using Commonsense Knowledge Priors
Sep 06, 2022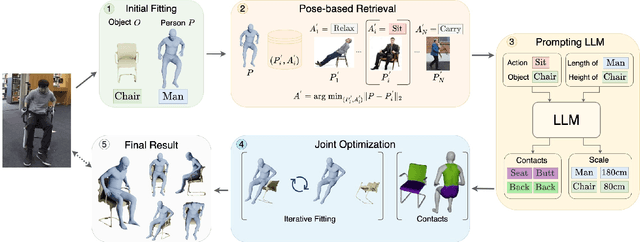
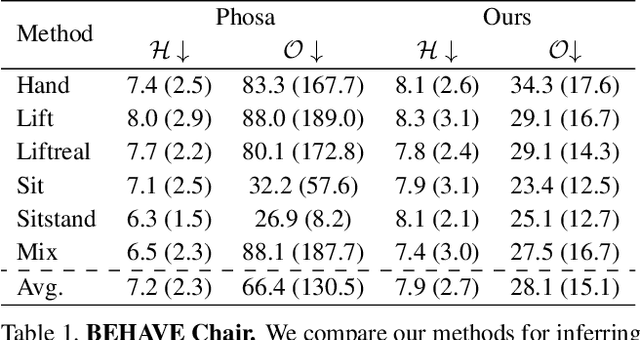
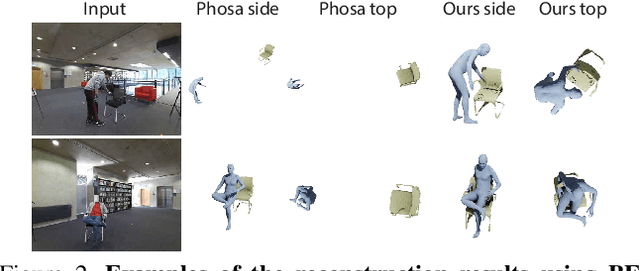
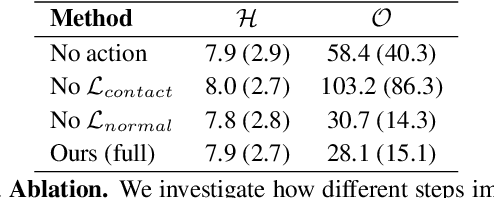
Abstract:We present a method for inferring diverse 3D models of human-object interactions from images. Reasoning about how humans interact with objects in complex scenes from a single 2D image is a challenging task given ambiguities arising from the loss of information through projection. In addition, modeling 3D interactions requires the generalization ability towards diverse object categories and interaction types. We propose an action-conditioned modeling of interactions that allows us to infer diverse 3D arrangements of humans and objects without supervision on contact regions or 3D scene geometry. Our method extracts high-level commonsense knowledge from large language models (such as GPT-3), and applies them to perform 3D reasoning of human-object interactions. Our key insight is priors extracted from large language models can help in reasoning about human-object contacts from textural prompts only. We quantitatively evaluate the inferred 3D models on a large human-object interaction dataset and show how our method leads to better 3D reconstructions. We further qualitatively evaluate the effectiveness of our method on real images and demonstrate its generalizability towards interaction types and object categories.
Articulated Objects in Free-form Hand Interaction
Apr 28, 2022



Abstract:We use our hands to interact with and to manipulate objects. Articulated objects are especially interesting since they often require the full dexterity of human hands to manipulate them. To understand, model, and synthesize such interactions, automatic and robust methods that reconstruct hands and articulated objects in 3D from a color image are needed. Existing methods for estimating 3D hand and object pose from images focus on rigid objects. In part, because such methods rely on training data and no dataset of articulated object manipulation exists. Consequently, we introduce ARCTIC - the first dataset of free-form interactions of hands and articulated objects. ARCTIC has 1.2M images paired with accurate 3D meshes for both hands and for objects that move and deform over time. The dataset also provides hand-object contact information. To show the value of our dataset, we perform two novel tasks on ARCTIC: (1) 3D reconstruction of two hands and an articulated object in interaction; (2) an estimation of dense hand-object relative distances, which we call interaction field estimation. For the first task, we present ArcticNet, a baseline method for the task of jointly reconstructing two hands and an articulated object from an RGB image. For interaction field estimation, we predict the relative distances from each hand vertex to the object surface, and vice versa. We introduce InterField, the first method that estimates such distances from a single RGB image. We provide qualitative and quantitative experiments for both tasks, and provide detailed analysis on the data. Code and data will be available at https://arctic.is.tue.mpg.de.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge