Meera Hahn
MALT Diffusion: Memory-Augmented Latent Transformers for Any-Length Video Generation
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models are successful for synthesizing high-quality videos but are limited to generating short clips (e.g., 2-10 seconds). Synthesizing sustained footage (e.g. over minutes) still remains an open research question. In this paper, we propose MALT Diffusion (using Memory-Augmented Latent Transformers), a new diffusion model specialized for long video generation. MALT Diffusion (or just MALT) handles long videos by subdividing them into short segments and doing segment-level autoregressive generation. To achieve this, we first propose recurrent attention layers that encode multiple segments into a compact memory latent vector; by maintaining this memory vector over time, MALT is able to condition on it and continuously generate new footage based on a long temporal context. We also present several training techniques that enable the model to generate frames over a long horizon with consistent quality and minimal degradation. We validate the effectiveness of MALT through experiments on long video benchmarks. We first perform extensive analysis of MALT in long-contextual understanding capability and stability using popular long video benchmarks. For example, MALT achieves an FVD score of 220.4 on 128-frame video generation on UCF-101, outperforming the previous state-of-the-art of 648.4. Finally, we explore MALT's capabilities in a text-to-video generation setting and show that it can produce long videos compared with recent techniques for long text-to-video generation.
Learning Complex Non-Rigid Image Edits from Multimodal Conditioning
Dec 13, 2024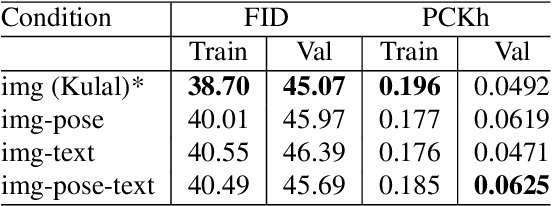
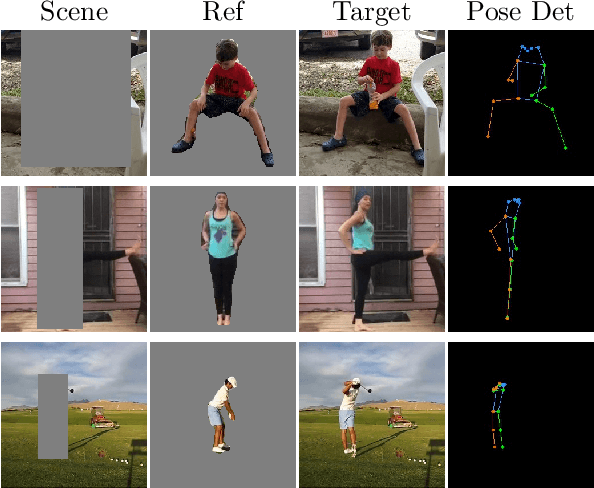
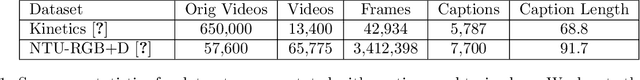
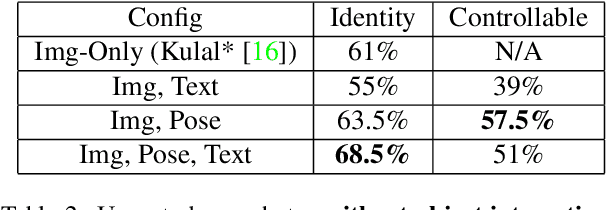
Abstract:In this paper we focus on inserting a given human (specifically, a single image of a person) into a novel scene. Our method, which builds on top of Stable Diffusion, yields natural looking images while being highly controllable with text and pose. To accomplish this we need to train on pairs of images, the first a reference image with the person, the second a "target image" showing the same person (with a different pose and possibly in a different background). Additionally we require a text caption describing the new pose relative to that in the reference image. In this paper we present a novel dataset following this criteria, which we create using pairs of frames from human-centric and action-rich videos and employing a multimodal LLM to automatically summarize the difference in human pose for the text captions. We demonstrate that identity preservation is a more challenging task in scenes "in-the-wild", and especially scenes where there is an interaction between persons and objects. Combining the weak supervision from noisy captions, with robust 2D pose improves the quality of person-object interactions.
Proactive Agents for Multi-Turn Text-to-Image Generation Under Uncertainty
Dec 09, 2024Abstract:User prompts for generative AI models are often underspecified, leading to sub-optimal responses. This problem is particularly evident in text-to-image (T2I) generation, where users commonly struggle to articulate their precise intent. This disconnect between the user's vision and the model's interpretation often forces users to painstakingly and repeatedly refine their prompts. To address this, we propose a design for proactive T2I agents equipped with an interface to (1) actively ask clarification questions when uncertain, and (2) present their understanding of user intent as an understandable belief graph that a user can edit. We build simple prototypes for such agents and verify their effectiveness through both human studies and automated evaluation. We observed that at least 90% of human subjects found these agents and their belief graphs helpful for their T2I workflow. Moreover, we develop a scalable automated evaluation approach using two agents, one with a ground truth image and the other tries to ask as few questions as possible to align with the ground truth. On DesignBench, a benchmark we created for artists and designers, the COCO dataset (Lin et al., 2014), and ImageInWords (Garg et al., 2024), we observed that these T2I agents were able to ask informative questions and elicit crucial information to achieve successful alignment with at least 2 times higher VQAScore (Lin et al., 2024) than the standard single-turn T2I generation. Demo: https://github.com/google-deepmind/proactive_t2i_agents.
VideoPoet: A Large Language Model for Zero-Shot Video Generation
Dec 21, 2023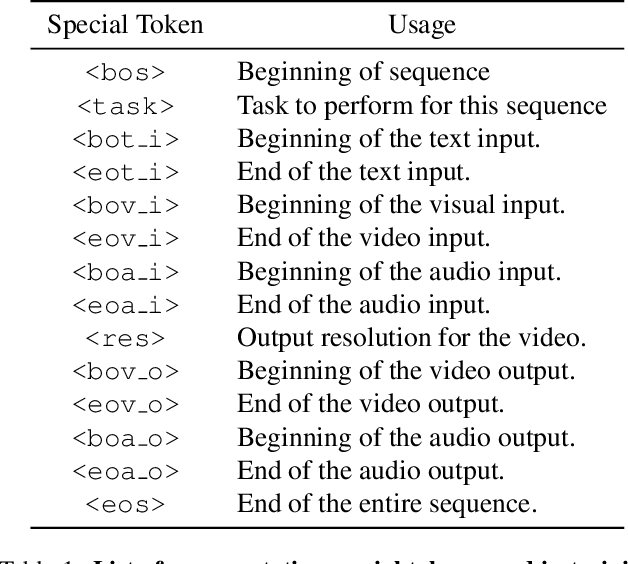



Abstract:We present VideoPoet, a language model capable of synthesizing high-quality video, with matching audio, from a large variety of conditioning signals. VideoPoet employs a decoder-only transformer architecture that processes multimodal inputs -- including images, videos, text, and audio. The training protocol follows that of Large Language Models (LLMs), consisting of two stages: pretraining and task-specific adaptation. During pretraining, VideoPoet incorporates a mixture of multimodal generative objectives within an autoregressive Transformer framework. The pretrained LLM serves as a foundation that can be adapted for a range of video generation tasks. We present empirical results demonstrating the model's state-of-the-art capabilities in zero-shot video generation, specifically highlighting VideoPoet's ability to generate high-fidelity motions. Project page: http://sites.research.google/videopoet/
Photorealistic Video Generation with Diffusion Models
Dec 11, 2023Abstract:We present W.A.L.T, a transformer-based approach for photorealistic video generation via diffusion modeling. Our approach has two key design decisions. First, we use a causal encoder to jointly compress images and videos within a unified latent space, enabling training and generation across modalities. Second, for memory and training efficiency, we use a window attention architecture tailored for joint spatial and spatiotemporal generative modeling. Taken together these design decisions enable us to achieve state-of-the-art performance on established video (UCF-101 and Kinetics-600) and image (ImageNet) generation benchmarks without using classifier free guidance. Finally, we also train a cascade of three models for the task of text-to-video generation consisting of a base latent video diffusion model, and two video super-resolution diffusion models to generate videos of $512 \times 896$ resolution at $8$ frames per second.
Which way is `right'?: Uncovering limitations of Vision-and-Language Navigation model
Nov 30, 2023
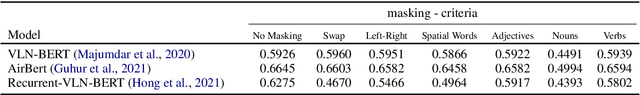
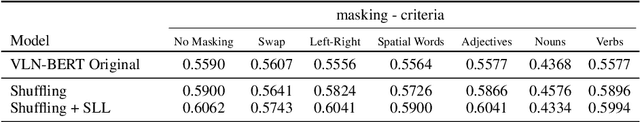
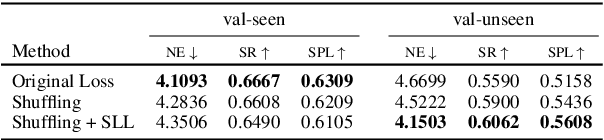
Abstract:The challenging task of Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) requires embodied agents to follow natural language instructions to reach a goal location or object (e.g. `walk down the hallway and turn left at the piano'). For agents to complete this task successfully, they must be able to ground objects referenced into the instruction (e.g.`piano') into the visual scene as well as ground directional phrases (e.g.`turn left') into actions. In this work we ask the following question -- to what degree are spatial and directional language cues informing the navigation model's decisions? We propose a series of simple masking experiments to inspect the model's reliance on different parts of the instruction. Surprisingly we uncover that certain top performing models rely only on the noun tokens of the instructions. We propose two training methods to alleviate this concerning limitation.
Text and Click inputs for unambiguous open vocabulary instance segmentation
Nov 24, 2023



Abstract:Segmentation localizes objects in an image on a fine-grained per-pixel scale. Segmentation benefits by humans-in-the-loop to provide additional input of objects to segment using a combination of foreground or background clicks. Tasks include photoediting or novel dataset annotation, where human annotators leverage an existing segmentation model instead of drawing raw pixel level annotations. We propose a new segmentation process, Text + Click segmentation, where a model takes as input an image, a text phrase describing a class to segment, and a single foreground click specifying the instance to segment. Compared to previous approaches, we leverage open-vocabulary image-text models to support a wide-range of text prompts. Conditioning segmentations on text prompts improves the accuracy of segmentations on novel or unseen classes. We demonstrate that the combination of a single user-specified foreground click and a text prompt allows a model to better disambiguate overlapping or co-occurring semantic categories, such as "tie", "suit", and "person". We study these results across common segmentation datasets such as refCOCO, COCO, VOC, and OpenImages. Source code available here.
Transformer-based Localization from Embodied Dialog with Large-scale Pre-training
Oct 10, 2022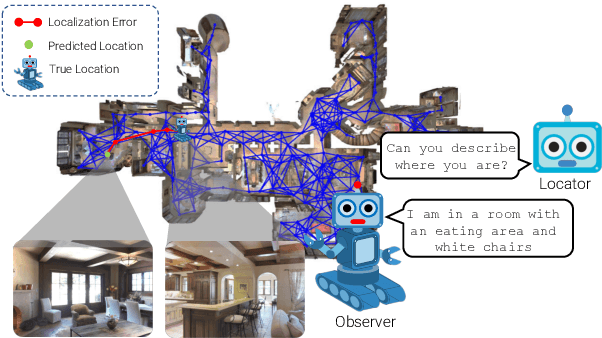
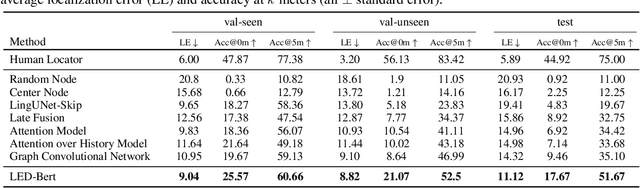
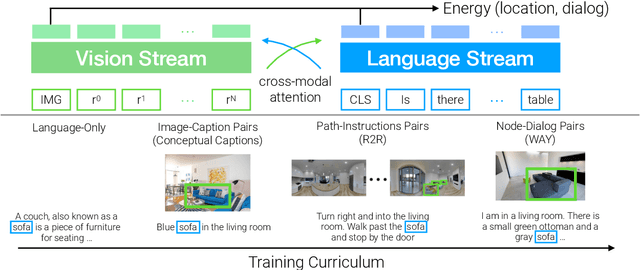
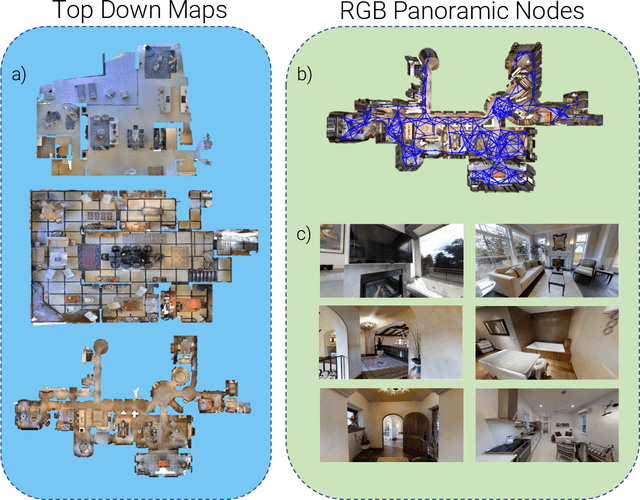
Abstract:We address the challenging task of Localization via Embodied Dialog (LED). Given a dialog from two agents, an Observer navigating through an unknown environment and a Locator who is attempting to identify the Observer's location, the goal is to predict the Observer's final location in a map. We develop a novel LED-Bert architecture and present an effective pretraining strategy. We show that a graph-based scene representation is more effective than the top-down 2D maps used in prior works. Our approach outperforms previous baselines.
Learning a Visually Grounded Memory Assistant
Oct 07, 2022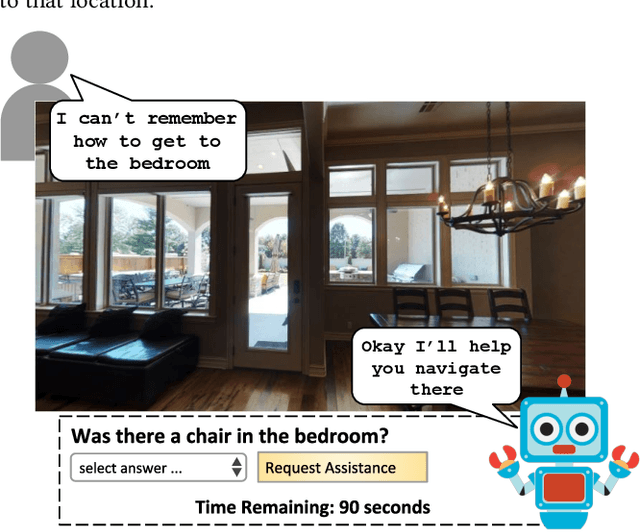

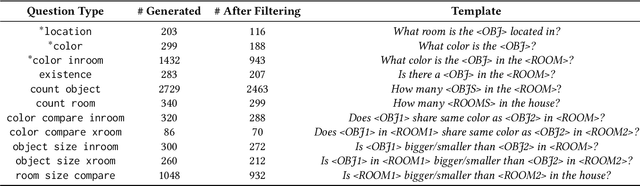
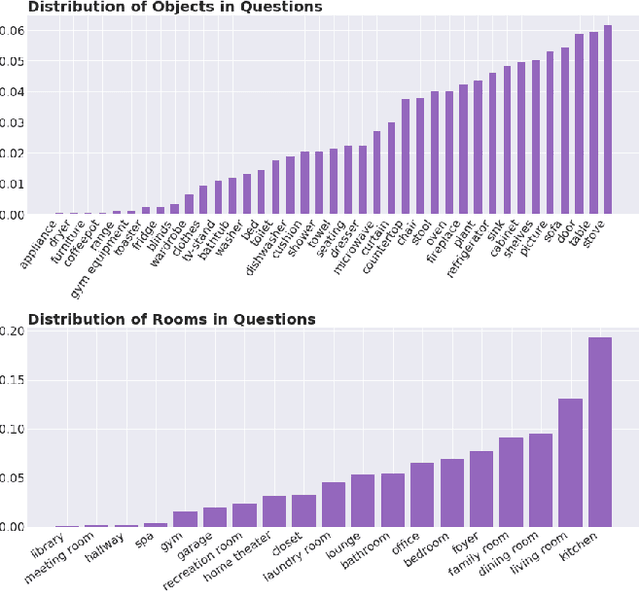
Abstract:We introduce a novel interface for large scale collection of human memory and assistance. Using the 3D Matterport simulator we create a realistic indoor environments in which we have people perform specific embodied memory tasks that mimic household daily activities. This interface was then deployed on Amazon Mechanical Turk allowing us to test and record human memory, navigation and needs for assistance at a large scale that was previously impossible. Using the interface we collect the `The Visually Grounded Memory Assistant Dataset' which is aimed at developing our understanding of (1) the information people encode during navigation of 3D environments and (2) conditions under which people ask for memory assistance. Additionally we experiment with with predicting when people will ask for assistance using models trained on hand-selected visual and semantic features. This provides an opportunity to build stronger ties between the machine-learning and cognitive-science communities through learned models of human perception, memory, and cognition.
No RL, No Simulation: Learning to Navigate without Navigating
Oct 22, 2021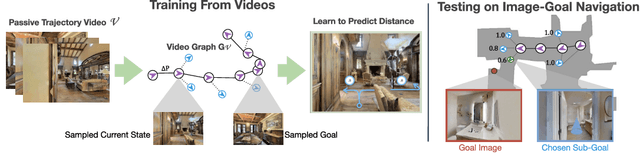
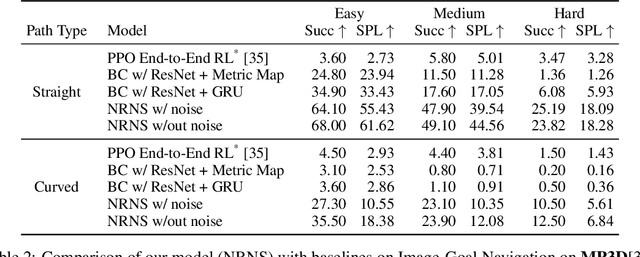
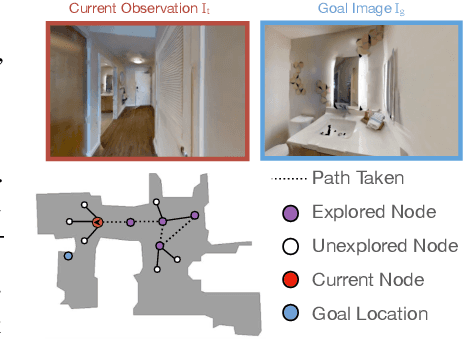
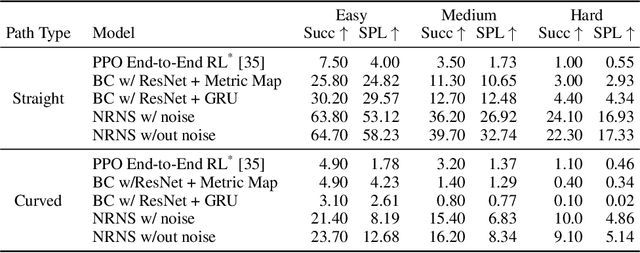
Abstract:Most prior methods for learning navigation policies require access to simulation environments, as they need online policy interaction and rely on ground-truth maps for rewards. However, building simulators is expensive (requires manual effort for each and every scene) and creates challenges in transferring learned policies to robotic platforms in the real-world, due to the sim-to-real domain gap. In this paper, we pose a simple question: Do we really need active interaction, ground-truth maps or even reinforcement-learning (RL) in order to solve the image-goal navigation task? We propose a self-supervised approach to learn to navigate from only passive videos of roaming. Our approach, No RL, No Simulator (NRNS), is simple and scalable, yet highly effective. NRNS outperforms RL-based formulations by a significant margin. We present NRNS as a strong baseline for any future image-based navigation tasks that use RL or Simulation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge