Learning a Visually Grounded Memory Assistant
Paper and Code
Oct 07, 2022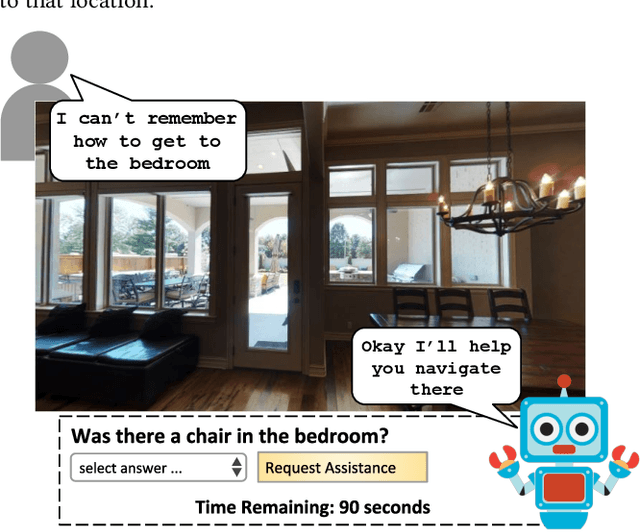

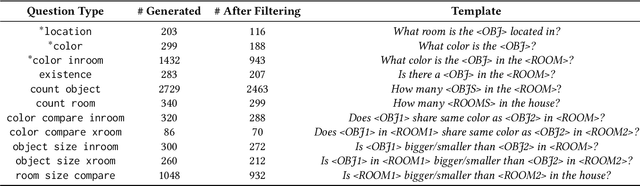
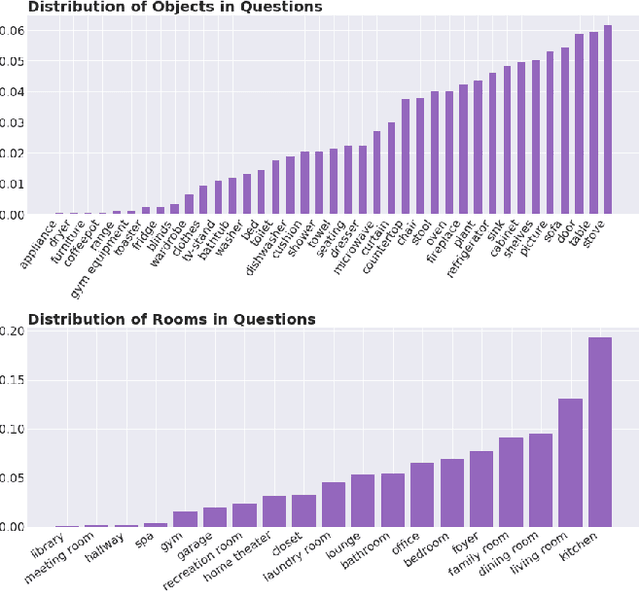
We introduce a novel interface for large scale collection of human memory and assistance. Using the 3D Matterport simulator we create a realistic indoor environments in which we have people perform specific embodied memory tasks that mimic household daily activities. This interface was then deployed on Amazon Mechanical Turk allowing us to test and record human memory, navigation and needs for assistance at a large scale that was previously impossible. Using the interface we collect the `The Visually Grounded Memory Assistant Dataset' which is aimed at developing our understanding of (1) the information people encode during navigation of 3D environments and (2) conditions under which people ask for memory assistance. Additionally we experiment with with predicting when people will ask for assistance using models trained on hand-selected visual and semantic features. This provides an opportunity to build stronger ties between the machine-learning and cognitive-science communities through learned models of human perception, memory, and cognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge