Abhinav Gupta
Words that make SENSE: Sensorimotor Norms in Learned Lexical Token Representations
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:While word embeddings derive meaning from co-occurrence patterns, human language understanding is grounded in sensory and motor experience. We present $\text{SENSE}$ $(\textbf{S}\text{ensorimotor }$ $\textbf{E}\text{mbedding }$ $\textbf{N}\text{orm }$ $\textbf{S}\text{coring }$ $\textbf{E}\text{ngine})$, a learned projection model that predicts Lancaster sensorimotor norms from word lexical embeddings. We also conducted a behavioral study where 281 participants selected which among candidate nonce words evoked specific sensorimotor associations, finding statistically significant correlations between human selection rates and $\text{SENSE}$ ratings across 6 of the 11 modalities. Sublexical analysis of these nonce words selection rates revealed systematic phonosthemic patterns for the interoceptive norm, suggesting a path towards computationally proposing candidate phonosthemes from text data.
Evolutionary Policy Optimization
Mar 24, 2025



Abstract:Despite its extreme sample inefficiency, on-policy reinforcement learning has become a fundamental tool in real-world applications. With recent advances in GPU-driven simulation, the ability to collect vast amounts of data for RL training has scaled exponentially. However, studies show that current on-policy methods, such as PPO, fail to fully leverage the benefits of parallelized environments, leading to performance saturation beyond a certain scale. In contrast, Evolutionary Algorithms (EAs) excel at increasing diversity through randomization, making them a natural complement to RL. However, existing EvoRL methods have struggled to gain widespread adoption due to their extreme sample inefficiency. To address these challenges, we introduce Evolutionary Policy Optimization (EPO), a novel policy gradient algorithm that combines the strengths of EA and policy gradients. We show that EPO significantly improves performance across diverse and challenging environments, demonstrating superior scalability with parallelized simulations.
HandsOnVLM: Vision-Language Models for Hand-Object Interaction Prediction
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:How can we predict future interaction trajectories of human hands in a scene given high-level colloquial task specifications in the form of natural language? In this paper, we extend the classic hand trajectory prediction task to two tasks involving explicit or implicit language queries. Our proposed tasks require extensive understanding of human daily activities and reasoning abilities about what should be happening next given cues from the current scene. We also develop new benchmarks to evaluate the proposed two tasks, Vanilla Hand Prediction (VHP) and Reasoning-Based Hand Prediction (RBHP). We enable solving these tasks by integrating high-level world knowledge and reasoning capabilities of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) with the auto-regressive nature of low-level ego-centric hand trajectories. Our model, HandsOnVLM is a novel VLM that can generate textual responses and produce future hand trajectories through natural-language conversations. Our experiments show that HandsOnVLM outperforms existing task-specific methods and other VLM baselines on proposed tasks, and demonstrates its ability to effectively utilize world knowledge for reasoning about low-level human hand trajectories based on the provided context. Our website contains code and detailed video results \url{https://www.chenbao.tech/handsonvlm/}
Gen2Act: Human Video Generation in Novel Scenarios enables Generalizable Robot Manipulation
Sep 24, 2024



Abstract:How can robot manipulation policies generalize to novel tasks involving unseen object types and new motions? In this paper, we provide a solution in terms of predicting motion information from web data through human video generation and conditioning a robot policy on the generated video. Instead of attempting to scale robot data collection which is expensive, we show how we can leverage video generation models trained on easily available web data, for enabling generalization. Our approach Gen2Act casts language-conditioned manipulation as zero-shot human video generation followed by execution with a single policy conditioned on the generated video. To train the policy, we use an order of magnitude less robot interaction data compared to what the video prediction model was trained on. Gen2Act doesn't require fine-tuning the video model at all and we directly use a pre-trained model for generating human videos. Our results on diverse real-world scenarios show how Gen2Act enables manipulating unseen object types and performing novel motions for tasks not present in the robot data. Videos are at https://homangab.github.io/gen2act/
1 Modular Parallel Manipulator for Long-Term Soft Robotic Data Collection
Sep 05, 2024



Abstract:Performing long-term experimentation or large-scale data collection for machine learning in the field of soft robotics is challenging, due to the hardware robustness and experimental flexibility required. In this work, we propose a modular parallel robotic manipulation platform suitable for such large-scale data collection and compatible with various soft-robotic fabrication methods. Considering the computational and theoretical difficulty of replicating the high-fidelity, faster-than-real-time simulations that enable large-scale data collection in rigid robotic systems, a robust soft-robotic hardware platform becomes a high priority development task for the field. The platform's modules consist of a pair of off-the-shelf electrical motors which actuate a customizable finger consisting of a compliant parallel structure. The parallel mechanism of the finger can be as simple as a single 3D-printed urethane or molded silicone bulk structure, due to the motors being able to fully actuate a passive structure. This design flexibility allows experimentation with soft mechanism varied geometries, bulk properties and surface properties. Additionally, while the parallel mechanism does not require separate electronics or additional parts, these can be included, and it can be constructed using multi-functional soft materials to study compatible soft sensors and actuators in the learning process. In this work, we validate the platform's ability to be used for policy gradient reinforcement learning directly on hardware in a benchmark 2D manipulation task. We additionally demonstrate compatibility with multiple fingers and characterize the design constraints for compatible extensions.
HRP: Human Affordances for Robotic Pre-Training
Jul 26, 2024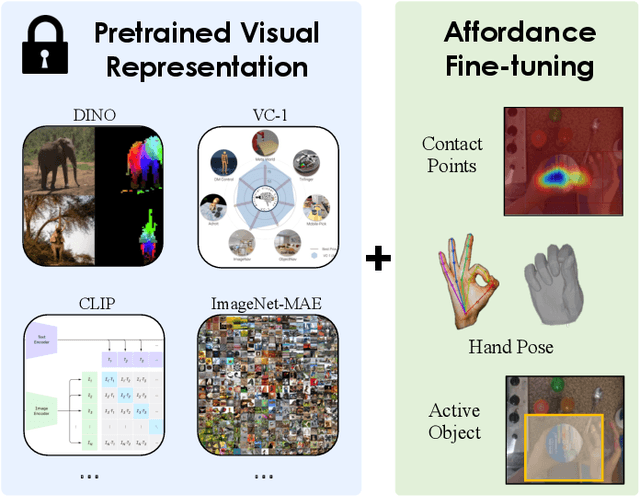
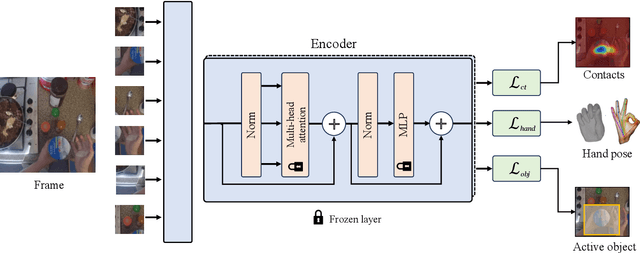
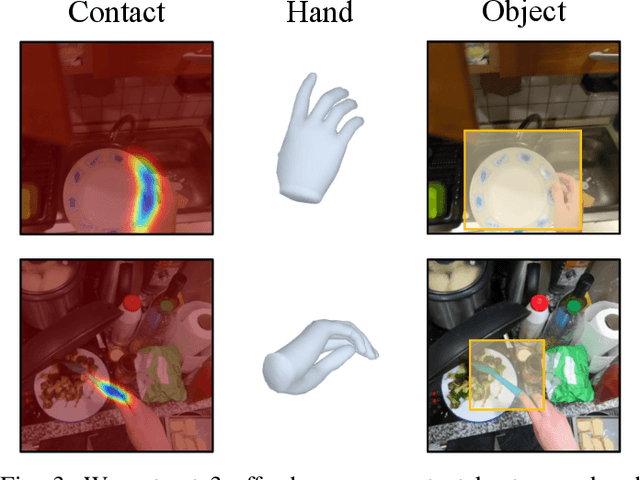
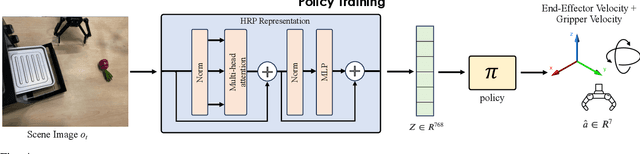
Abstract:In order to *generalize* to various tasks in the wild, robotic agents will need a suitable representation (i.e., vision network) that enables the robot to predict optimal actions given high dimensional vision inputs. However, learning such a representation requires an extreme amount of diverse training data, which is prohibitively expensive to collect on a real robot. How can we overcome this problem? Instead of collecting more robot data, this paper proposes using internet-scale, human videos to extract "affordances," both at the environment and agent level, and distill them into a pre-trained representation. We present a simple framework for pre-training representations on hand, object, and contact "affordance labels" that highlight relevant objects in images and how to interact with them. These affordances are automatically extracted from human video data (with the help of off-the-shelf computer vision modules) and used to fine-tune existing representations. Our approach can efficiently fine-tune *any* existing representation, and results in models with stronger downstream robotic performance across the board. We experimentally demonstrate (using 3000+ robot trials) that this affordance pre-training scheme boosts performance by a minimum of 15% on 5 real-world tasks, which consider three diverse robot morphologies (including a dexterous hand). Unlike prior works in the space, these representations improve performance across 3 different camera views. Quantitatively, we find that our approach leads to higher levels of generalization in out-of-distribution settings. For code, weights, and data check: https://hrp-robot.github.io
Towards Latent Masked Image Modeling for Self-Supervised Visual Representation Learning
Jul 22, 2024


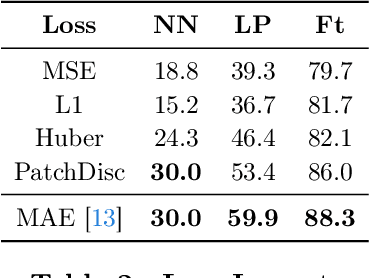
Abstract:Masked Image Modeling (MIM) has emerged as a promising method for deriving visual representations from unlabeled image data by predicting missing pixels from masked portions of images. It excels in region-aware learning and provides strong initializations for various tasks, but struggles to capture high-level semantics without further supervised fine-tuning, likely due to the low-level nature of its pixel reconstruction objective. A promising yet unrealized framework is learning representations through masked reconstruction in latent space, combining the locality of MIM with the high-level targets. However, this approach poses significant training challenges as the reconstruction targets are learned in conjunction with the model, potentially leading to trivial or suboptimal solutions.Our study is among the first to thoroughly analyze and address the challenges of such framework, which we refer to as Latent MIM. Through a series of carefully designed experiments and extensive analysis, we identify the source of these challenges, including representation collapsing for joint online/target optimization, learning objectives, the high region correlation in latent space and decoding conditioning. By sequentially addressing these issues, we demonstrate that Latent MIM can indeed learn high-level representations while retaining the benefits of MIM models.
Hearing Touch: Audio-Visual Pretraining for Contact-Rich Manipulation
May 14, 2024



Abstract:Although pre-training on a large amount of data is beneficial for robot learning, current paradigms only perform large-scale pretraining for visual representations, whereas representations for other modalities are trained from scratch. In contrast to the abundance of visual data, it is unclear what relevant internet-scale data may be used for pretraining other modalities such as tactile sensing. Such pretraining becomes increasingly crucial in the low-data regimes common in robotics applications. In this paper, we address this gap by using contact microphones as an alternative tactile sensor. Our key insight is that contact microphones capture inherently audio-based information, allowing us to leverage large-scale audio-visual pretraining to obtain representations that boost the performance of robotic manipulation. To the best of our knowledge, our method is the first approach leveraging large-scale multisensory pre-training for robotic manipulation. For supplementary information including videos of real robot experiments, please see https://sites.google.com/view/hearing-touch.
Track2Act: Predicting Point Tracks from Internet Videos enables Diverse Zero-shot Robot Manipulation
May 02, 2024



Abstract:We seek to learn a generalizable goal-conditioned policy that enables zero-shot robot manipulation: interacting with unseen objects in novel scenes without test-time adaptation. While typical approaches rely on a large amount of demonstration data for such generalization, we propose an approach that leverages web videos to predict plausible interaction plans and learns a task-agnostic transformation to obtain robot actions in the real world. Our framework,Track2Act predicts tracks of how points in an image should move in future time-steps based on a goal, and can be trained with diverse videos on the web including those of humans and robots manipulating everyday objects. We use these 2D track predictions to infer a sequence of rigid transforms of the object to be manipulated, and obtain robot end-effector poses that can be executed in an open-loop manner. We then refine this open-loop plan by predicting residual actions through a closed loop policy trained with a few embodiment-specific demonstrations. We show that this approach of combining scalably learned track prediction with a residual policy requiring minimal in-domain robot-specific data enables zero-shot robot manipulation, and present a wide array of real-world robot manipulation results across unseen tasks, objects, and scenes. https://homangab.github.io/track2act/
G-HOP: Generative Hand-Object Prior for Interaction Reconstruction and Grasp Synthesis
Apr 18, 2024Abstract:We propose G-HOP, a denoising diffusion based generative prior for hand-object interactions that allows modeling both the 3D object and a human hand, conditioned on the object category. To learn a 3D spatial diffusion model that can capture this joint distribution, we represent the human hand via a skeletal distance field to obtain a representation aligned with the (latent) signed distance field for the object. We show that this hand-object prior can then serve as generic guidance to facilitate other tasks like reconstruction from interaction clip and human grasp synthesis. We believe that our model, trained by aggregating seven diverse real-world interaction datasets spanning across 155 categories, represents a first approach that allows jointly generating both hand and object. Our empirical evaluations demonstrate the benefit of this joint prior in video-based reconstruction and human grasp synthesis, outperforming current task-specific baselines. Project website: https://judyye.github.io/ghop-www
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge