Matthew Brown
OmniNOCS: A unified NOCS dataset and model for 3D lifting of 2D objects
Jul 11, 2024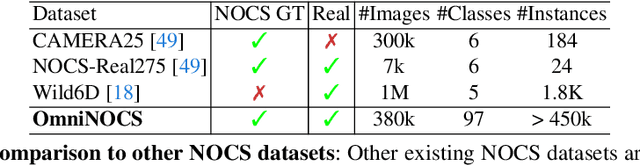
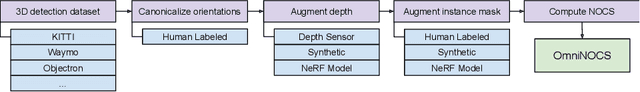
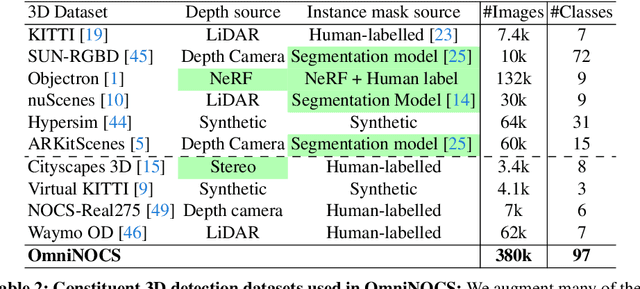
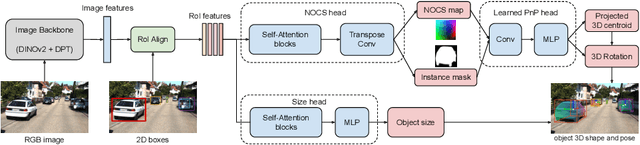
Abstract:We propose OmniNOCS, a large-scale monocular dataset with 3D Normalized Object Coordinate Space (NOCS) maps, object masks, and 3D bounding box annotations for indoor and outdoor scenes. OmniNOCS has 20 times more object classes and 200 times more instances than existing NOCS datasets (NOCS-Real275, Wild6D). We use OmniNOCS to train a novel, transformer-based monocular NOCS prediction model (NOCSformer) that can predict accurate NOCS, instance masks and poses from 2D object detections across diverse classes. It is the first NOCS model that can generalize to a broad range of classes when prompted with 2D boxes. We evaluate our model on the task of 3D oriented bounding box prediction, where it achieves comparable results to state-of-the-art 3D detection methods such as Cube R-CNN. Unlike other 3D detection methods, our model also provides detailed and accurate 3D object shape and segmentation. We propose a novel benchmark for the task of NOCS prediction based on OmniNOCS, which we hope will serve as a useful baseline for future work in this area. Our dataset and code will be at the project website: https://omninocs.github.io.
Module-wise Adaptive Distillation for Multimodality Foundation Models
Oct 06, 2023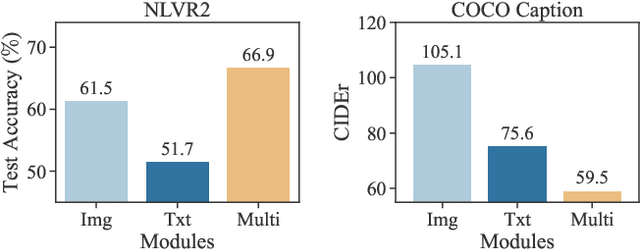
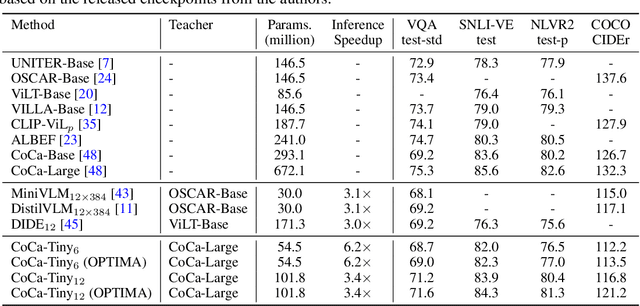
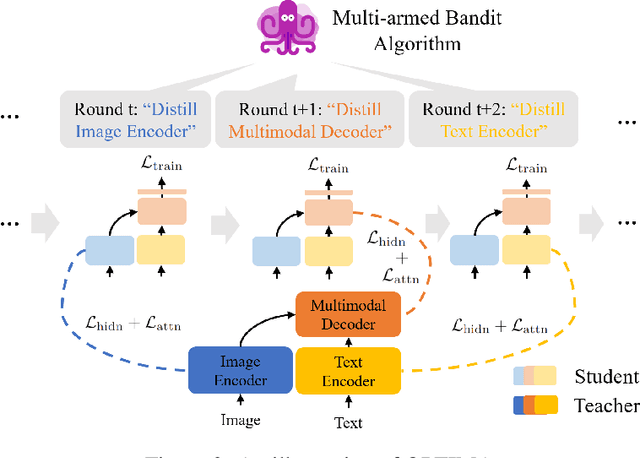
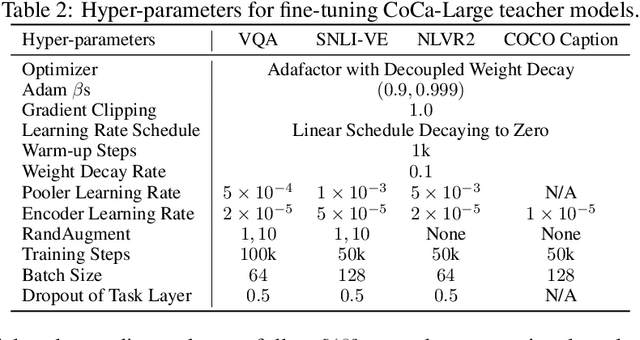
Abstract:Pre-trained multimodal foundation models have demonstrated remarkable generalizability but pose challenges for deployment due to their large sizes. One effective approach to reducing their sizes is layerwise distillation, wherein small student models are trained to match the hidden representations of large teacher models at each layer. Motivated by our observation that certain architecture components, referred to as modules, contribute more significantly to the student's performance than others, we propose to track the contributions of individual modules by recording the loss decrement after distillation each module and choose the module with a greater contribution to distill more frequently. Such an approach can be naturally formulated as a multi-armed bandit (MAB) problem, where modules and loss decrements are considered as arms and rewards, respectively. We then develop a modified-Thompson sampling algorithm named OPTIMA to address the nonstationarity of module contributions resulting from model updating. Specifically, we leverage the observed contributions in recent history to estimate the changing contribution of each module and select modules based on these estimations to maximize the cumulative contribution. We evaluate the effectiveness of OPTIMA through distillation experiments on various multimodal understanding and image captioning tasks, using the CoCa-Large model (Yu et al., 2022) as the teacher model.
Towards a Unified Foundation Model: Jointly Pre-Training Transformers on Unpaired Images and Text
Dec 14, 2021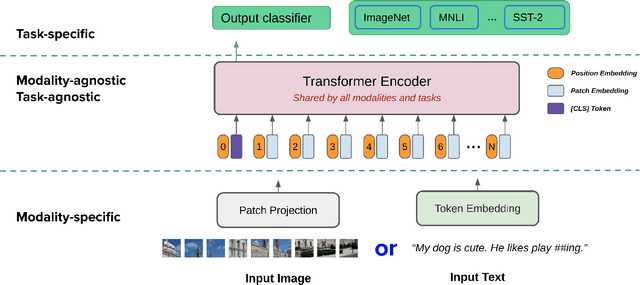


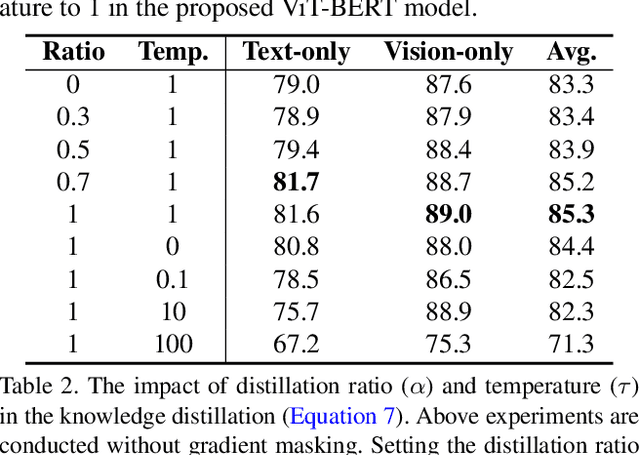
Abstract:In this paper, we explore the possibility of building a unified foundation model that can be adapted to both vision-only and text-only tasks. Starting from BERT and ViT, we design a unified transformer consisting of modality-specific tokenizers, a shared transformer encoder, and task-specific output heads. To efficiently pre-train the proposed model jointly on unpaired images and text, we propose two novel techniques: (i) We employ the separately-trained BERT and ViT models as teachers and apply knowledge distillation to provide additional, accurate supervision signals for the joint training; (ii) We propose a novel gradient masking strategy to balance the parameter updates from the image and text pre-training losses. We evaluate the jointly pre-trained transformer by fine-tuning it on image classification tasks and natural language understanding tasks, respectively. The experiments show that the resultant unified foundation transformer works surprisingly well on both the vision-only and text-only tasks, and the proposed knowledge distillation and gradient masking strategy can effectively lift the performance to approach the level of separately-trained models.
Exploring Temporal Granularity in Self-Supervised Video Representation Learning
Dec 08, 2021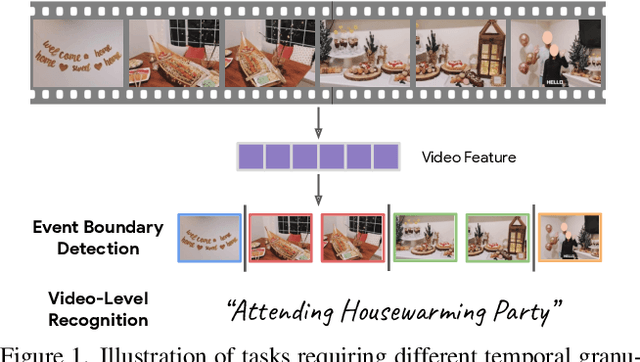
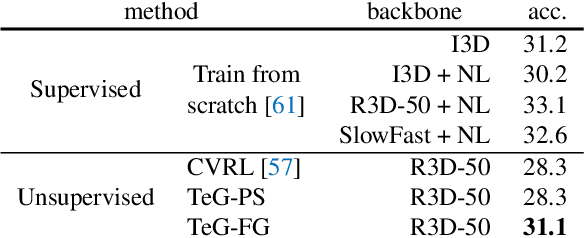
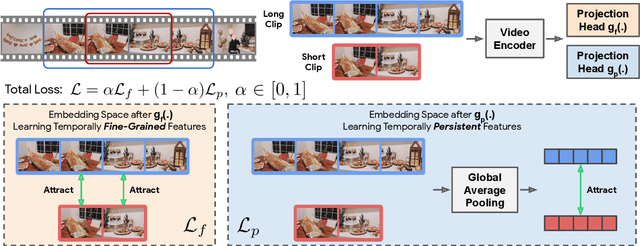
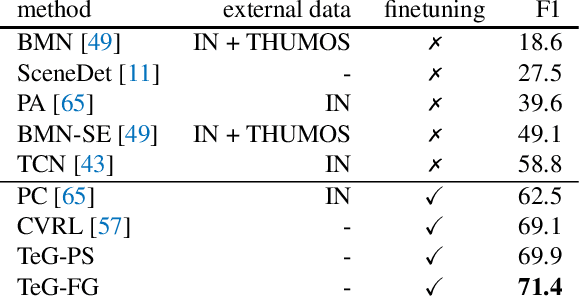
Abstract:This work presents a self-supervised learning framework named TeG to explore Temporal Granularity in learning video representations. In TeG, we sample a long clip from a video and a short clip that lies inside the long clip. We then extract their dense temporal embeddings. The training objective consists of two parts: a fine-grained temporal learning objective to maximize the similarity between corresponding temporal embeddings in the short clip and the long clip, and a persistent temporal learning objective to pull together global embeddings of the two clips. Our study reveals the impact of temporal granularity with three major findings. 1) Different video tasks may require features of different temporal granularities. 2) Intriguingly, some tasks that are widely considered to require temporal awareness can actually be well addressed by temporally persistent features. 3) The flexibility of TeG gives rise to state-of-the-art results on 8 video benchmarks, outperforming supervised pre-training in most cases.
2.5D Visual Relationship Detection
Apr 26, 2021
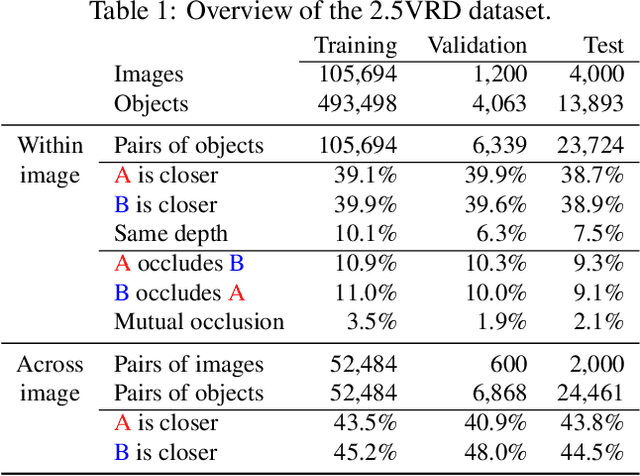
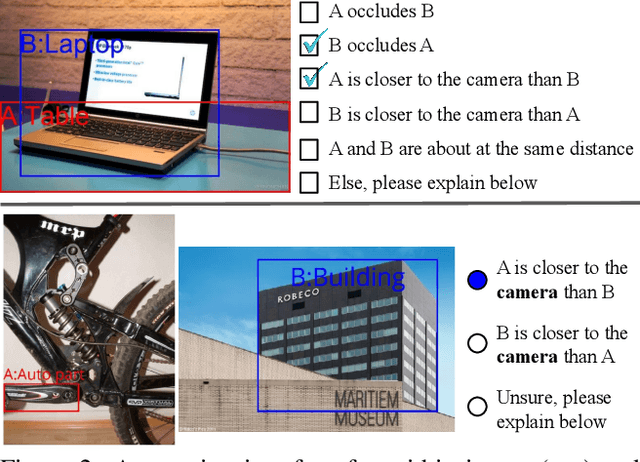

Abstract:Visual 2.5D perception involves understanding the semantics and geometry of a scene through reasoning about object relationships with respect to the viewer in an environment. However, existing works in visual recognition primarily focus on the semantics. To bridge this gap, we study 2.5D visual relationship detection (2.5VRD), in which the goal is to jointly detect objects and predict their relative depth and occlusion relationships. Unlike general VRD, 2.5VRD is egocentric, using the camera's viewpoint as a common reference for all 2.5D relationships. Unlike depth estimation, 2.5VRD is object-centric and not only focuses on depth. To enable progress on this task, we create a new dataset consisting of 220k human-annotated 2.5D relationships among 512K objects from 11K images. We analyze this dataset and conduct extensive experiments including benchmarking multiple state-of-the-art VRD models on this task. Our results show that existing models largely rely on semantic cues and simple heuristics to solve 2.5VRD, motivating further research on models for 2.5D perception. The new dataset is available at https://github.com/google-research-datasets/2.5vrd.
MoViNets: Mobile Video Networks for Efficient Video Recognition
Apr 18, 2021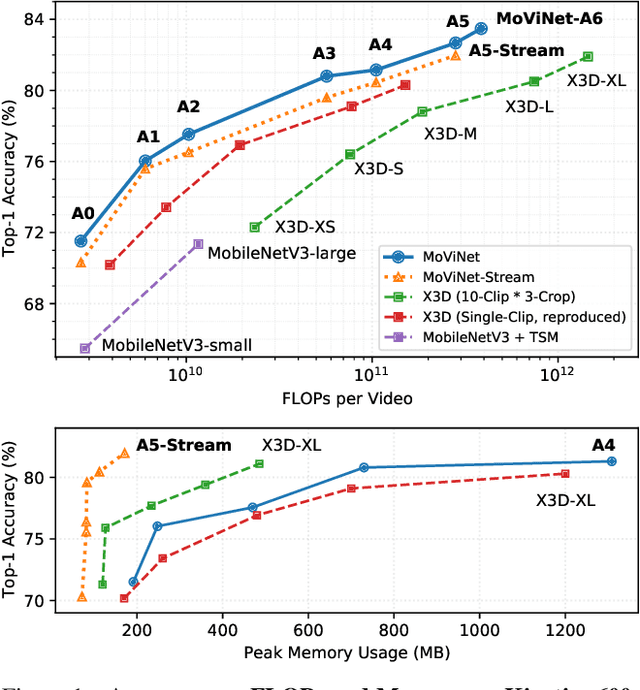

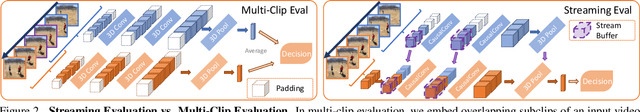
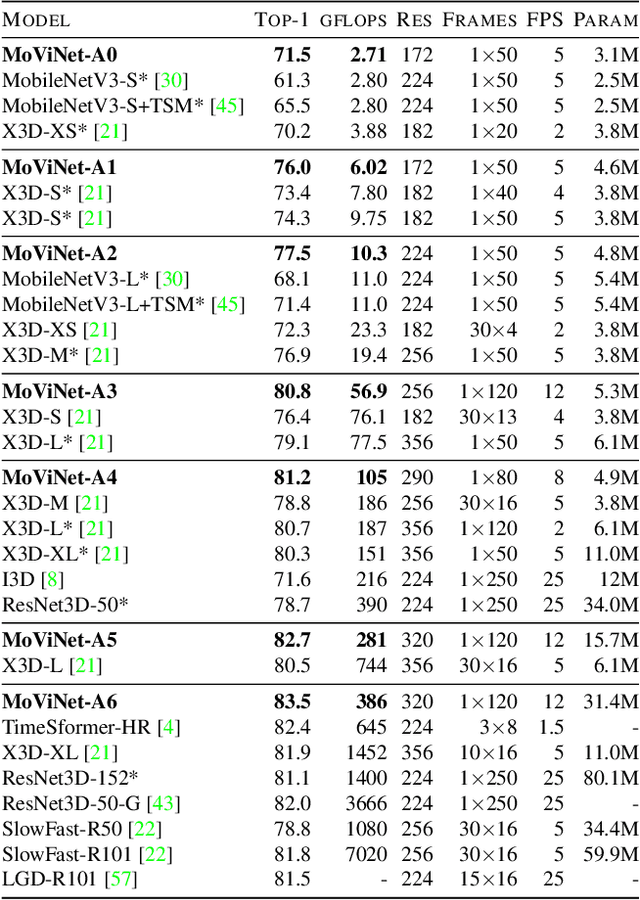
Abstract:We present Mobile Video Networks (MoViNets), a family of computation and memory efficient video networks that can operate on streaming video for online inference. 3D convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are accurate at video recognition but require large computation and memory budgets and do not support online inference, making them difficult to work on mobile devices. We propose a three-step approach to improve computational efficiency while substantially reducing the peak memory usage of 3D CNNs. First, we design a video network search space and employ neural architecture search to generate efficient and diverse 3D CNN architectures. Second, we introduce the Stream Buffer technique that decouples memory from video clip duration, allowing 3D CNNs to embed arbitrary-length streaming video sequences for both training and inference with a small constant memory footprint. Third, we propose a simple ensembling technique to improve accuracy further without sacrificing efficiency. These three progressive techniques allow MoViNets to achieve state-of-the-art accuracy and efficiency on the Kinetics, Moments in Time, and Charades video action recognition datasets. For instance, MoViNet-A5-Stream achieves the same accuracy as X3D-XL on Kinetics 600 while requiring 80% fewer FLOPs and 65% less memory. Code will be made available at https://github.com/tensorflow/models/tree/master/official/vision.
FiG-NeRF: Figure-Ground Neural Radiance Fields for 3D Object Category Modelling
Apr 17, 2021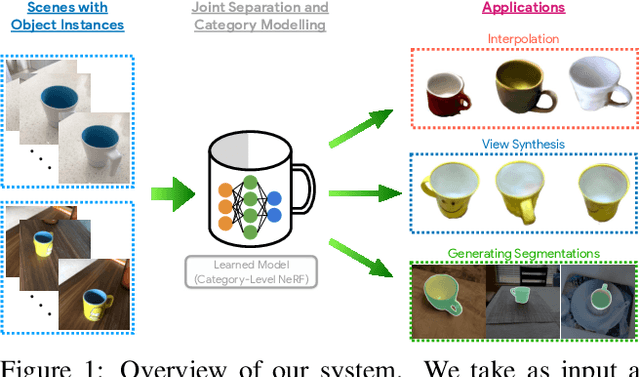
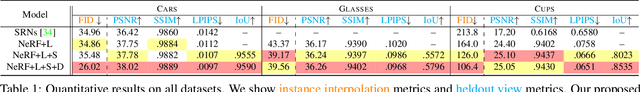
Abstract:We investigate the use of Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) to learn high quality 3D object category models from collections of input images. In contrast to previous work, we are able to do this whilst simultaneously separating foreground objects from their varying backgrounds. We achieve this via a 2-component NeRF model, FiG-NeRF, that prefers explanation of the scene as a geometrically constant background and a deformable foreground that represents the object category. We show that this method can learn accurate 3D object category models using only photometric supervision and casually captured images of the objects. Additionally, our 2-part decomposition allows the model to perform accurate and crisp amodal segmentation. We quantitatively evaluate our method with view synthesis and image fidelity metrics, using synthetic, lab-captured, and in-the-wild data. Our results demonstrate convincing 3D object category modelling that exceed the performance of existing methods.
GeLaTO: Generative Latent Textured Objects
Aug 11, 2020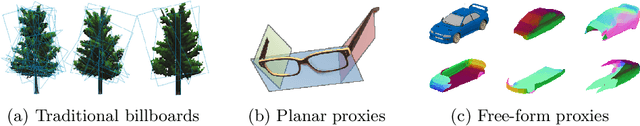
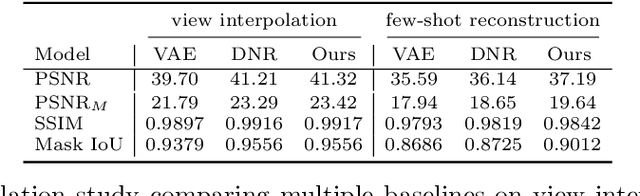
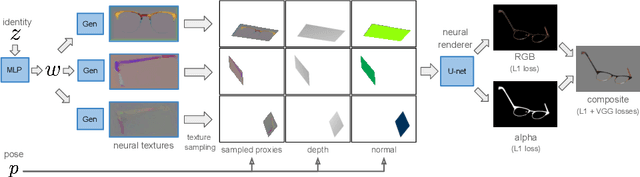
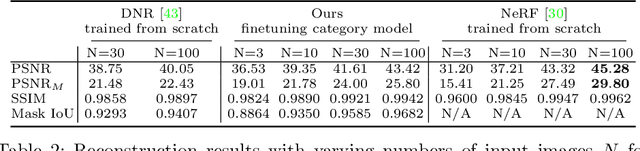
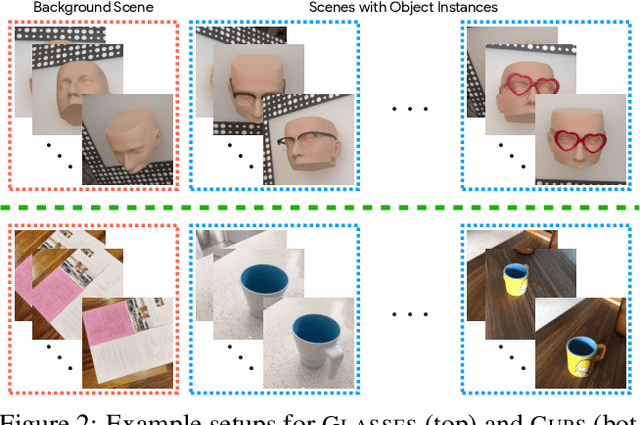
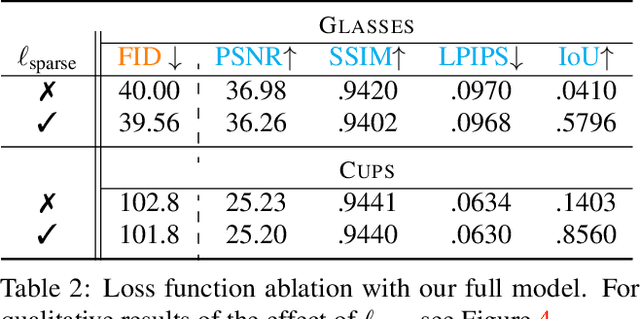
Abstract:Accurate modeling of 3D objects exhibiting transparency, reflections and thin structures is an extremely challenging problem. Inspired by billboards and geometric proxies used in computer graphics, this paper proposes Generative Latent Textured Objects (GeLaTO), a compact representation that combines a set of coarse shape proxies defining low frequency geometry with learned neural textures, to encode both medium and fine scale geometry as well as view-dependent appearance. To generate the proxies' textures, we learn a joint latent space allowing category-level appearance and geometry interpolation. The proxies are independently rasterized with their corresponding neural texture and composited using a U-Net, which generates an output photorealistic image including an alpha map. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach by reconstructing complex objects from a sparse set of views. We show results on a dataset of real images of eyeglasses frames, which are particularly challenging to reconstruct using classical methods. We also demonstrate that these coarse proxies can be handcrafted when the underlying object geometry is easy to model, like eyeglasses, or generated using a neural network for more complex categories, such as cars.
* ECCV 2020 Spotlight. Project website: https://gelato-paper.github.io
When Ensembling Smaller Models is More Efficient than Single Large Models
May 01, 2020


Abstract:Ensembling is a simple and popular technique for boosting evaluation performance by training multiple models (e.g., with different initializations) and aggregating their predictions. This approach is commonly reserved for the largest models, as it is commonly held that increasing the model size provides a more substantial reduction in error than ensembling smaller models. However, we show results from experiments on CIFAR-10 and ImageNet that ensembles can outperform single models with both higher accuracy and requiring fewer total FLOPs to compute, even when those individual models' weights and hyperparameters are highly optimized. Furthermore, this gap in improvement widens as models become large. This presents an interesting observation that output diversity in ensembling can often be more efficient than training larger models, especially when the models approach the size of what their dataset can foster. Instead of using the common practice of tuning a single large model, one can use ensembles as a more flexible trade-off between a model's inference speed and accuracy. This also potentially eases hardware design, e.g., an easier way to parallelize the model across multiple workers for real-time or distributed inference.
Rethinking Class-Balanced Methods for Long-Tailed Visual Recognition from a Domain Adaptation Perspective
Mar 24, 2020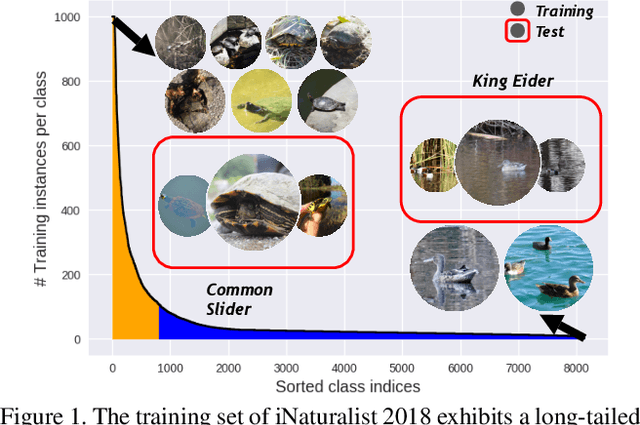
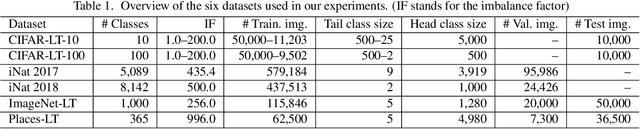
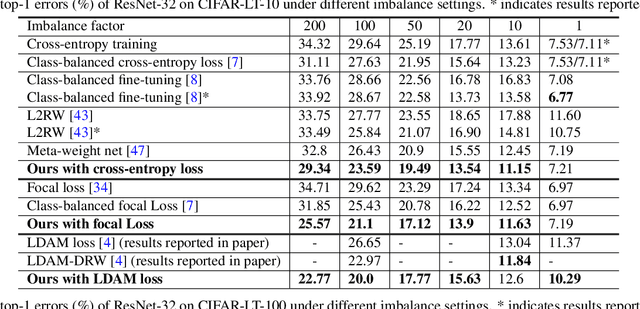
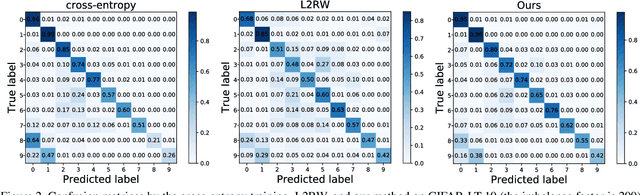
Abstract:Object frequency in the real world often follows a power law, leading to a mismatch between datasets with long-tailed class distributions seen by a machine learning model and our expectation of the model to perform well on all classes. We analyze this mismatch from a domain adaptation point of view. First of all, we connect existing class-balanced methods for long-tailed classification to target shift, a well-studied scenario in domain adaptation. The connection reveals that these methods implicitly assume that the training data and test data share the same class-conditioned distribution, which does not hold in general and especially for the tail classes. While a head class could contain abundant and diverse training examples that well represent the expected data at inference time, the tail classes are often short of representative training data. To this end, we propose to augment the classic class-balanced learning by explicitly estimating the differences between the class-conditioned distributions with a meta-learning approach. We validate our approach with six benchmark datasets and three loss functions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge